Business
Column: How did America get addicted to a policy that fails everyone but the rich?

Right here’s the central riddle of U.S. politics for the reason that Nice Despair:
Social Democratic insurance policies crafted within the Thirties succeeded in creating an extended period of widespread prosperity, then abruptly misplaced its credibility within the mid-Seventies. It was changed by the neoliberalism of Ronald Reagan, which didn’t assist anybody however the wealthy, but nonetheless governs American financial coverage.
The ascent of neoliberalism and its endurance “is a puzzle,” J. Bradford DeLong writes in his magisterial new financial historical past of the twentieth century, “Slouching In the direction of Utopia.” It’s the central puzzle that DeLong, a professor of economics at UC Berkeley, a broadly adopted economics blogger and one in all our main critics of financial inequality, goals to look at.
‘It was simply unhealthy luck that landed us with Reagan and Thatcher, … who wound up doing nothing constructive besides drastically rising revenue and wealth inequality after which entrenching the flexibility of inequality to place its thumb on the size of elections.’
— J. Bradford DeLong, UC Berkeley
Delong takes because the canvas what he calls the “lengthy twentieth century,” which he defines because the interval from 1870 to 2010 and argues was “probably the most consequential years of all humanity’s centuries.”
The “watershed-crossing occasions” of 1870, in his view, embody the emergence of globalization, the economic analysis lab and the fashionable company. The period ends in 2010 with the developed world — particularly the international locations of the North Atlantic — nonetheless coming to grips with the Nice Recession of 2008.
The story DeLong tells doesn’t actually finish there, for its reverberations nonetheless are felt at this time. In that context, crucial portion of his e-book covers the shifting method to market forces. That portion begins with the Despair.
By bringing to the center class and dealing class the popularity of their shared curiosity in a extra inclusive economic system, the Despair produced a drive for social insurance coverage and social justice. Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal acknowledged these pursuits by creating packages comparable to Social Safety and pro-labor insurance policies via the Nationwide Labor Relations Act.
This was the period of social democracy, reflecting the views of Hungarian economist Karl Polanyi, who rejected the conservative view that the market needed to be permitted to perform with out interference, even when it produced unjust outcomes.
“Polanyi’s counter was that whether or not saying the market can do all of it or that it’s all we will have, folks is not going to stand for it,” DeLong informed me throughout a prolonged dialog about his e-book. “You’ll get a big group of individuals eager to elect somebody who will do one thing in regards to the system.”
Within the post-Despair period, it grew to become understood that “not solely shouldn’t the market be left to do all of it,” DeLong says, “it could actually’t do all of it or very a lot except it’s correctly primed and aided and guided.”
“So that you want issues just like the GI Invoice to supply a cash circulation into training, and issues like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac [the government-sponsored housing finance agencies], as a result of in any other case funding homeownership growth on the size that America wanted can be all however unattainable.”
Social democracy, in DeLong’s telling, encompassed an enormous array of packages not usually considered core financial ventures — airport development, the Nationwide Park Service, government-funded analysis in well being, Head Begin in training.
Nonetheless one defines it, social democracy labored, ushering in what DeLong calls “thirty superb years” of prosperity (truly 1938-1973 — the phrase was coined by a French economist, referring to the postwar French economic system of 1939-1979). The developed economies grew by an annual common of three% throughout these years.
The very breadth of financial growth made the general public extremely receptive to all these packages, together with the social security internet. As president, Dwight Eisenhower warned that tampering with, a lot much less abolishing, Social Safety, unemployment insurance coverage and different social packages would imply the extinction of the Republican Celebration.
However then all of it got here aside. It might have been exhausting to maintain annual progress of three% underneath any circumstances, however the Seventies introduced the oil shocks, which tripled the value of oil, produced excessive inflation and provoked a pointy financial slowdown.
Opinion soured on redistribution of revenue to maintain the poor, and on environmental rules. “The fading reminiscence of the Nice Despair,” DeLong writes, “led to the fading of the center class’s perception … that they, in addition to the working class, wanted social insurance coverage.”
The stage was set for what DeLong calls “the neoliberal flip.” In fact, “neoliberal” is a misnomer; the idea is extra correctly described as a return to conservative market economics. The appropriate wing yoked financial conservatism to a cultural critique geared toward discontent with the motion for racial justice.
Certainly, one perception that DeLong’s method leads us to is how little the correct’s assault on social justice initiatives has developed in practically a half-century. In 1980, conservative economist Martin Feldstein inveighed towards unemployment insurance coverage as a result of it will produce inflation, well being and security rules as a result of they would scale back productiveness, and welfare as a result of it will “weaken household buildings,” Medicare and Medicaid as a result of they might drive up healthcare prices.
Even earlier, in 1962, Nobel economics laureate George Stigler lamented the “insolence” of civil rights demonstrators. Complaints in regards to the “permissiveness” of liberal mother and father was a characteristic of Republican critiques.
Evaluate that to at this time’s GOP shibboleths. Republican governors competed to see which ones may rescind pandemic-related unemployment advantages sooner; deregulation has turn out to be a everlasting plank within the GOP platform; Medicaid continues to be a goal of right-wing “reformers”; Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) depicts President Biden’s scholar mortgage aid program as one directed at “the man that studied queer pet literature,” and Rep. Lauren Boebert (R-Colo.) says it’s going to rob hardworking People to pay for a scholar’s “diploma in lesbian dance principle.”
Concentrating on ethnic and Black communities nonetheless exists on the correct, although the GOP at this time additionally targets LGBTQ rights.
The social democracy motion “ran aground within the Seventies,” DeLong informed me.
To some extent, social democracy foundered on an outbreak of unhealthy luck.
“With no Iranian revolution, no tripling of world oil costs, Jimmy Carter wins reelection and also you get a reconfiguration of social democracy with extra respect for the function of a market economic system with the correct changes and the correct distribution of revenue,” DeLong says.
“So it was simply unhealthy luck that landed us with Reagan and Thatcher, who had little or no concept about tips on how to truly speed up progress, and who wound up doing nothing constructive besides drastically rising revenue and wealth inequality after which entrenching the flexibility of inequality to place its thumb on the size of elections.”
As DeLong writes, “The wealthy had the most important megaphones, they usually trumpeted the truth that their incomes have been rising quickly. And people decrease down … have been informed that if solely they have been sufficiently worthy, the unleashed market would give to them too, they usually greater than half believed it.”
It’s correct to acknowledge, as DeLong does, that even amid rising inequality the typical American’s dwelling requirements have improved markedly, partially because of the autumn in costs of know-how: Households with dwelling air-conditioning have risen from 55% in 1979 to 90% in 2010; microwave ovens from 5% to 92% of households; computer systems from 0% to 70%.
But Delong factors out that the options of a middle-class life that was once inside attain have receded, comparable to a indifferent home in a superb neighborhood, the flexibility to pay for a superb faculty with out borrowing, medical health insurance that doesn’t depart one bankrupt after a coronary heart assault.
Regardless of its apparent shortcomings, neoliberalism has wriggled its method into political orthodoxy. It was embraced by Invoice Clinton who, as DeLong writes, declared in a State of the Union deal with that “the age of huge authorities is over” and pledged to “finish welfare as we all know it” (by way of a reform program that has had a disastrous impact on poor households). Barack Obama, DeLong notes, referred to as for presidency austerity when the unemployment fee rose above 9%.
Delong posits that the neoliberal flip has survived as a result of the top of the Chilly Conflict gave Reagan a halo that persists, and for some purpose has infused his financial insurance policies regardless of their failure to supply financial justice.
So the place does that depart us at this time?
“Resurrecting social democracy is just not within the playing cards, as a result of it rested on applied sciences of manufacturing and social group as they existed within the Nineteen Fifties,” DeLong informed me. “Neither is resurrecting Reaganism. But when there is no such thing as a left-wing different to neoliberalism, the right-wing options are far more disagreeable — a politics of ‘you’ve enemies and you have to give me near plenary energy so I can defend you.’ That’s a harmful scenario, and one which we appear to be drifting in direction of.”
Whether or not the palms on America’s financial tiller are able to guiding us to a good future stays in query. DeLong concludes his e-book with that query: “A brand new story,” he writes, “which wants a brand new grand narrative that we don’t but know, has begun.”

Business
Column: After a years-long pause, the FCC resurrects 'network neutrality,' a boon for consumers

In the midst of its battle to extinguish the Mendocino Complex wildfire in 2018, the Santa Clara County Fire Department discovered that its internet connection provider, Verizon, had throttled their data flow virtually down to zero, cutting off communications for firefighters in the field. One firefighter died in the blaze and four were injured.
Verizon refused to restore service until the fire department signed up for a new account that more than doubled its bill.
That episode has long been Exhibit A in favor of restoring the Federal Communications Commission’s authority to regulate broadband internet service, which the FCC abdicated in 2017, during the Trump administration.
This is an industry that requires a lot of scrutiny.
— Craig Aaron, Free Press, on the internet service industry
Now that era is over. On Thursday, the FCC — now operating with a Democratic majority — reclaimed its regulatory oversight of broadband via an order that passed on party lines, 3-2.
The commission’s action could scarcely be more timely.
“Four years ago,” FCC Chair Jessica Rosenworcel observed Thursday as the commission prepared to vote, “the pandemic changed life as we know it. … Much of work, school and healthcare migrated to the internet. … It became clear that no matter who you are or where you live, you need broadband to have a fair shot at digital age success. It went from ‘nice to have’ to ‘need to have.’ ”
Yet the commission in 2017 had thrown away its own ability to supervise this essential service. By categorizing broadband services as “information services,” it relinquished its right to address consumer complaints about crummy service, or even collect data on outages. It couldn’t prevent big internet service providers such as Comcast from favoring their own content or websites over competitors by degrading the rivals’ signals when they reached their subscribers’ homes.
“We fixed that today,” Rosenworcel said.
The issue the FCC addressed Thursday is most often viewed in the context of “network neutrality.” This core principle of the open internet means simply that internet service providers can’t discriminate among content providers trying to reach your home or business online — they can’t block websites or services, or degrade their signal, slow their traffic or, conversely, provide a better traffic lane for some rather than others.
The principle is important because their control of the information highways and byways gives ISPs tremendous power, especially if they control the last mile of access to end users, as do cable operators such as Comcast and telecommunications firms such as Verizon. If they use that power to favor their own content or content providers that pay them for a fast lane, it’s consumers who suffer.
Net neutrality has been a partisan football for more than two decades, or ever since high-speed broadband connections began to supplant dial-up modems.
In legal terms, the battle has been over the classification of broadband under the Communications Act of 1934 — as Title I “information services” or Title II “telecommunications.” The FCC has no jurisdiction over Title I services, but great authority over those classified by Title II as common carriers.
The key inflection point came in 2002, when a GOP-majority FCC under George W. Bush classified cable internet services as Title I. In effect, the commission stripped itself of its authority to regulate the nascent industry. (Then-FCC Chair Michael Powell subsequently became the chief Washington lobbyist for the cable industry, big surprise.)
Not until 2015 was the error rectified, at the urging of President Obama. Broadband was reclassified under Title II; then-FCC Chair Tom Wheeler was explicit about using the restored authority to enforce network neutrality.
But that regulatory regime lasted only until 2017, when a reconstituted FCC, chaired by a former Verizon executive Ajit Pai, reclassified broadband again as Title I in deference to President Trump’s deregulatory campaign. The big ISPs would have geared up to take advantage of the new regime, had not California and other states stepped into the void by enacting their own net neutrality laws.
A federal appeals court upheld California’s law, the most far-reaching of the state statutes, in 2022. And although the FCC’s action could theoretically preempt the state law, “what the FCC is doing is perfectly in line with what California did,” says Craig Aaron, co-CEO of the consumer advocacy organization Free Press.
The key distinction, Aaron told me, is that the FCC’s initiative goes well beyond the issue of net neutrality — it establishes a single federal standard for broadband and reclaims its authority over the technology more generally, in ways that “safeguard national security, advance public safety, protect consumers and facilitate broadband deployment,” in the commission’s own words.
Although Verizon’s actions in the 2018 wildfire case did not violate the net neutrality principle, for instance, the FCC’s restored regulatory authority might have enabled it to set forth rules governing the provision of services when public safety is at stake that might have prevented Verizon from throttling the Santa Clara Fire Department’s connection in the first place.
Until Thursday, the state laws functioned as bulwarks against net neutrality abuses by ISPs. “California helped discourage companies from trying things,” Aaron says. Indeed, provisions of the California law are explicit enough that state regulators haven’t had to bring a single enforcement case. “It’s been mostly prophylactic,” he says — “telling the industry what it can and can’t do. But it’s important to have set down the rules of the road.”
None of this means that the partisan battle over broadband regulation is over. Both Republican FCC commissioners voted against the initiative Thursday. A recrudescence of Trumpism after the November election could bring a deregulation-minded GOP majority back into power at the FCC.
Indeed, in a lengthy dissenting statement, Brendan Carr, one of the commission’s Republican members, repeated all the conventional conservative arguments presented to justify the repeal of network neutrality in 2017. Carr painted the 2015 restoration of net neutrality as a liberal plot — “a matter of civic religion for activists on the left.”
He asserted that the FCC was then goaded into action by President Obama, who was outspoken on the need for reclassification and browbeat Wheeler into going along. Leftists, he said, “demand that the FCC go full-Title II whenever a Democrat is president.”
Carr also depicted network neutrality as a drag on profits and innovation in the broadband sector. “Broadband investment slowed down after the FCC imposed Title II in 2015,” he said, “and it picked up again after we restored Title 1 in 2017.”
Carr chose his time frame very carefully. Examine the longer period in which net neutrality has been debated at the FCC, and one finds that broadband investment crashed after a Republican-led FCC reclassified broadband as an information service in 2002, falling to $57 billion in 2003 from $111.5 billion in 2001.
Investment did decline between 2015, when net neutrality rules were reinstated, and 2017, when they were rescinded — by a minuscule 0.8%. It hasn’t been especially robust since then — as of 2002 it was still running at only about 92% of what it had been two decades earlier.
As the FCC observed in Thursday’s order, “regulation is but one of several factors that drive investment and innovation in the telecommunications and digital media markets.”
The commission cited consumer demand and the arrival of new technologies, among others. Strong, consistent regulation, moreover, opens the path for new competitors with new ideas and innovations — and can bring prices down for users in the process.
The truth is that network neutrality has been heavily favored by the public, in part because examples of ISPs abusing their power were not hard to find. In 2007, Comcast was caught degrading traffic from the file-sharing service BitTorrent, which held contracts to distribute licensed content from Hollywood studios and other sources in direct competition with Comcast’s pay-TV business.
In 2010, Santa Monica-based Tennis Channel complained to the FCC that Comcast kept it isolated on a little-watched sports tier while giving much better placement to the Golf Channel and Versus, two channels that compete with it for advertising, and which Comcast happened to own. The FCC sided with the Tennis Channel but was overruled by federal court.
Even barring a change at the White House, the need for vigilant enforcement will never go away; ISPs will always be looking for business models and manipulative practices that could challenge the FCC’s oversight capabilities, especially as cable and telecommunications companies consolidate into bigger and richer enterprises and combine content providers with their internet delivery services.
“This is an industry,” Aaron says, “that requires a lot of scrutiny.”
Business
How athletes and entertainers like Shohei Ohtani get financially duped by those they trust

R. Allen Stanford is among the most brazen white-collar criminals — and he’s paying dearly for it. The former financier is in the 14th year of a 110-year prison sentence after being convicted in 2012 for selling $7 billion in fraudulent certificates of deposits in the Caribbean island of Antigua.
He also was required to pay a judgment of $5.9 billion, much of which was intended to go to victims of his crimes. Among those affected by his elaborate Ponzi scheme were seven Major League Baseball stars: Greg Maddux, Johnny Damon, Bernie Williams, J.D. Drew, Andruw Jones, Jay Bell and Carlos Peña.
The players invested in certificates of deposit offered by Stanford’s company, and it was that easy to have their bank accounts frozen in 2009 by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission while authorities investigated the case despite putting their trust in advisors with stellar reputations and a wealth of experience.
Damon complained during spring training that year that he couldn’t pay bills and told a personal trainer that he’d pay him when “all this stuff gets resolved.”
The questions lingered for months: How long would the accounts be frozen and would funds be confiscated?
“This certainly shakes up every athlete out there,” Robert Boland, professor of sports business at New York University, said at the time. “They’re all thinking: ‘Who’s guarding my money?’ ”
The Stanford episode might have prompted a reckoning inside MLB clubhouses, but the lesson didn’t stick with the entire next generation of players.
Shohei Ohtani has so far been cleared of wrongdoing in the recent illegal gambling probe that resulted in his interpreter, Ippei Mizuhara, being charged with bank fraud for stealing $16 million from Ohtani’s bank account to pay gambling debts. But the Dodgers and former Angels superstar was unaware of the theft until investigators uncovered wire transfers from his account to a bookie and Mizuhara admitted to Ohtani after a Dodgers team meeting March 20 in Seoul that he’d stole the money.
Ohtani was repeatedly described by authorities as a “victim,” but the extent to which the Japanese player was seemingly oblivious about his personal finances and blindly trusting Mizuhara is jarring at first glance. The federal complaint also says that Ohtani’s high-powered agent and financial advisors from Creative Artists Agency allowed Mizuhara to dissuade them from overseeing the account from which he stole.
“In this particular situation, it’s somebody who’s relying on someone to interpret an entire language to them, so they could be taking advantage of documents, wire transfers, all kinds of things that the other person doesn’t understand but is trusting that they have their best interests at heart,” said Kristin Lee, owner of the athletic and entertainment business management firm KLBM. “That’s rather predatory, and blatantly taking advantage of a very vulnerable person.”
Wealth management experts say athletes and entertainers who squander enormous sums fall into three interconnected buckets: They are naive about or inattentive to their finances; they make risky investments; they overspend on family, friends and expensive toys.
An eye-opening Sports Illustrated study in 2009 that included interviews with athletes, agents and financial advisors found that 78% of former NFL players had gone bankrupt or were under financial stress within two years of retirement and 60% of NBA players were broke within five years of retirement.
“Only those you trust completely can rip you off completely.”
— Diana B. Henriques, financial journalist
Wealthy athletes in nearly every sport as well as famous entertainment figures have experienced the same misfortune. NFL quarterback Mark Sanchez and MLB pitcher Jake Peavy were fleeced of millions of dollars by financial advisor Ash Narayan, who was sentenced in 2020 to 37 months in federal prison. Narayan gained the players’ trust because he was active in the Fellowship of Christian Athletes.
Former heavyweight champion Mike Tyson, once worth about $400 million, declared bankruptcy in 2003 when he was still boxing. Prominent entertainment figures have been fleeced by business managers (Judy Garland, Leonard Cohen, Alanis Morissette) or fallen prey to questionable investment opportunities (Robert De Niro, Ben Stiller, Jack Nicholson).
“It’s a heartbreaking tale that’s played out time and time and time again,” said Diana B. Henriques, financial journalist and author of “The Wizard of Lies: Bernie Madoff and the Death of Trust.” “Regardless of the industry, a person’s lucrative talent, lack of financial expertise and sudden access to wealth primes them as a candidate for a scam.
“Whether you’re an athlete, artist, surgeon or even a Silicon Valley entrepreneur, a con artist’s ideal victim is someone who knows very little about money but has a great deal of it,” she added. “You have a brilliant career that’s taken off and you’re making a ton of money from something you love to do, but you’ve never had to deal with this amount of wealth before.
“So it’s tempting when someone says, ‘Let me make it simple for you. Let me handle this messy, complex, confusing stuff so you can focus all your creative energy on being great and getting greater.’ ”
This strategic positioning of finances as a distraction to a star’s performance in their chosen field makes them particularly susceptible. Ohtani acknowledged as much in his only public comments since Mizuhara was charged with bank fraud: “I’m very grateful for the Department of Justice’s investigation,” he said. “For me personally, this marks a break from this, and I’d like to focus on baseball.”
Dodgers designated hitter Shohei Ohtani walks to the dugout after being stranded at second base in the eighth inning against the Washington Nationals on Wednesday.
(Robert Gauthier / Los Angeles Times)
In fact, it isn’t uncommon for the rich and famous to be blissfully unaware of their money’s movements. Take the musician Sting, who was notified by an anonymous tip that his former accountant, Keith Moore, had stolen more than $9 million from the British rock star over four years in order to invest in global schemes and stave off personal bankruptcy.
“He’d created something like 70 different bank accounts in different countries,” Sting said in a 2002 interview with the Independent. “And the money was coming in different denominations — Deutschemarks, Japanese yen — from different sources … touring, recording, publishing, merchandising, TV appearances. So for that kind of money to be siphoned away is not that surprising. And since it took forensic accountants about two years to sort through the complexities, how could a bass player figure it out?”
In cases like Sting’s, “It’s a fractional deceit that happens over the years, where somebody skims off a little bit here and there from a bunch of different types of accounts with different assets in them, and it adds up to a lot of stolen money,” Lee said.
Such complex financial structures often are entrusted to a family member or close friend. Comedian and actor Dane Cook had millions stolen by his half-brother Darryl McCauley, who was convicted of larceny, embezzlement and forgery. Singer-songwriter Jewel said last year on “The Verywell Mind” podcast that her mother and former manager, Nedra Carroll, stole $100 million from her.
“Only those you trust completely can rip you off completely,” Henriques said.
Billy Joel sued his ex-brother-in-law and former manager Frank Weber for unauthorized loans to Weber’s companies, secret investments in speculative ventures and mortgages on the copyrights for his songs — losses that initially went unnoticed and totaled $30 million.
“It was much more of an emotional betrayal for me than financial, because this was somebody I trusted so much,” Joel said in a 2013 interview with the New York Times Magazine. “I always had this sense that OK, I’m an artist and I shouldn’t have to be concerned about something as banal as money, which is baloney. It’s my job. It’s what I do. I didn’t pay any attention to it, and I trusted other people, and I got screwed.”

Billy Joel performs at the 66th Grammy Awards at Crypto.com Arena on Feb. 4.
(Robert Gauthier / Los Angeles Times)
Athletes started signing contracts worth millions in the 1980s. It’s no coincidence that financial predators began to gravitate toward them around that time. One of the earliest instances involved Lakers great Kareem Abdul-Jabbar and several other NBA stars, including Ralph Sampson and Alex English.
Dubious investments initiated by the players’ former business manager, Thomas M. Collins, included Arabian horses and oil wells in addition to hotel and restaurant ventures.
The prize acquisition was the venerable Balboa Inn in Newport Beach, where Errol Flynn, Humphrey Bogart, Gary Cooper and other Hollywood stars once gathered. But the partnership that owned that hotel and others went bankrupt.
Abdul-Jabbar sued Collins, his sole representative for six years, and others for $59 million, charging negligence, fraud and breach of trust, triggering a flurry of legal action.
Collins countersued, claiming that Abdul-Jabbar owed him $382,050 in unpaid commissions and fees. English sued Abdul-Jabbar, and had him served with papers in the Lakers’ locker room. Abdul-Jabbar added English to his suit against Collins and had those papers served while English sat on the bench during a game.
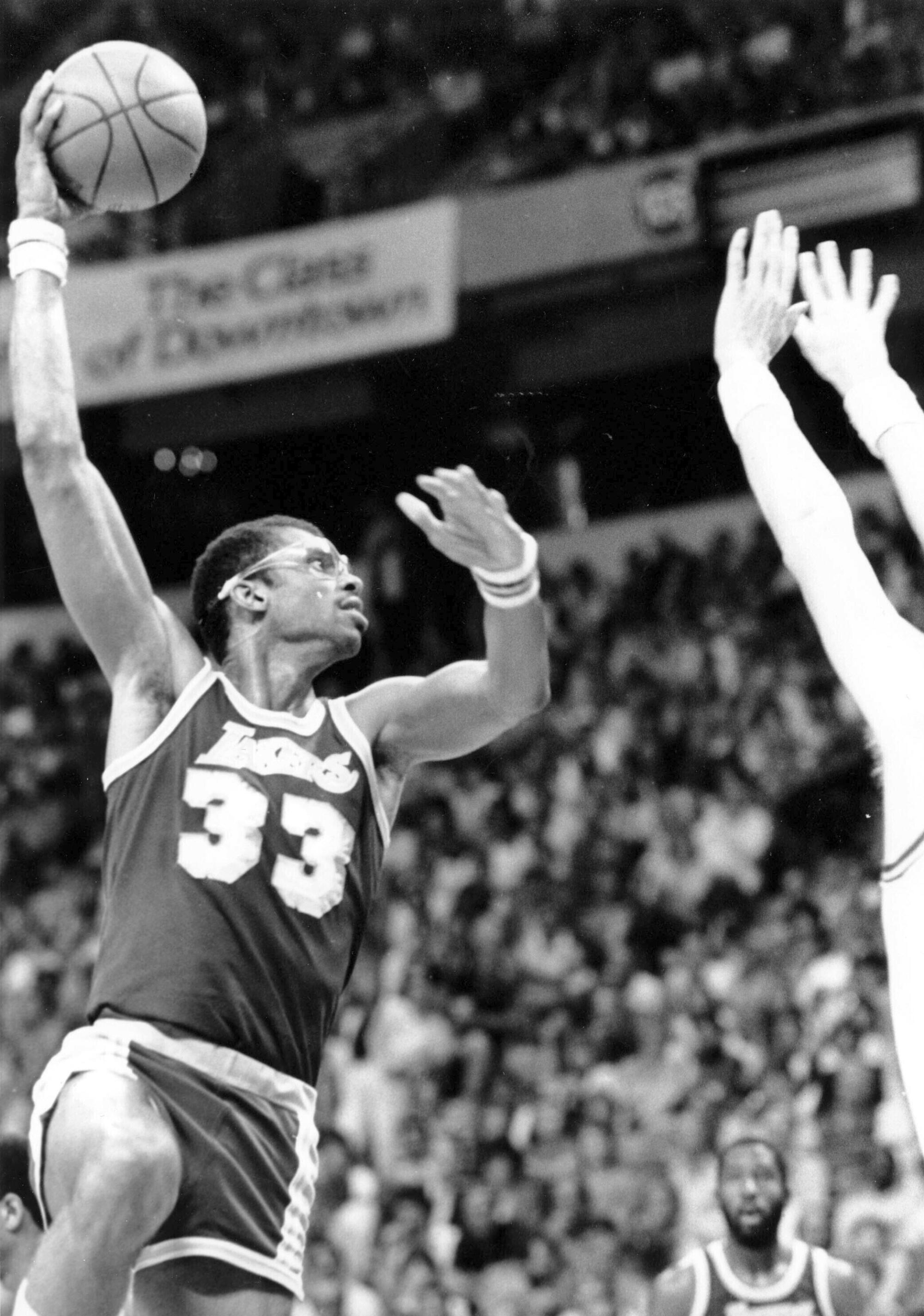

Lakers center Kareem Abdul-Jabbar shoots a sky hook in a game against the Utah Jazz in Las Vegas on April 5, 1984.
(Lennox McLendon / Associated Press)
The players had given Collins power of attorney in administering their financial affairs even though his only background in finance was an entry-level position at an investment information service. Ed Butowsky, managing partner of wealth management advisory firm Chapwood Investments, said giving power of attorney to anybody is usually foolish.
“The responsibility lies with these athletes, they should not parcel out that responsibility,” he said. “They should know where their money is, how much they have, where the account statements go and so on. If they don’t, it’s their own fault.”
NBA stars Antoine Walker, Latrell Sprewell, Vin Baker and Shawn Kemp each spent close to $100 million not long after retiring in the 2000s, much of it from excessive partying and showering family and friends with cash. And let’s not forget Allen Iverson, who went broke despite earning nearly $200 million in salary and endorsements and is hanging on to reach his 55th birthday seven years from now when he will receive $32 million from Reebok, thanks to a lifetime contract he signed with the shoe company in 2001.
Those cautionary tales have made an impact, Butowsky said. Fewer athletes and entertainment figures are spending ungodly amounts on jewelry, cars and handouts to friends.
“You have some one-off situations, but because of the publicity, people have become a lot more careful about wild expenditures,” Butkowsky said. “But they are still trusting the wrong people to make financial decisions.”
Financial planners often suggest that wealthy clients create a diverse portfolio. Athletes and entertainers often make the mistake of putting too much money into one venture. Butowsky calls it the “front row” mistake.
“A lot of them see some entrepreneur sitting in the front row at a basketball game and want to know what they did to make it,” he said. “But the idea that they are going to replicate that? It’s not going to happen. The very same thing that got a few people rich gets 20 to 30 times that many people broke.”
Though technological advancements have made it arguably harder for scammers to get away with thefts — “People probably used to be able to shuffle papers around, white things out and make photocopies, but now, everything is maintained in some sort of online system with a solid trail around it,” Lee said — athletes and entertainers still need to stay vigilant to prevent themselves from becoming the next headline-making victim.
“These dubious schemes are absolutely not going away,” Henriques said. “Part of it is that we devote so little attention to basic financial literacy in this country. We don’t train young people to have even the most basic knowledge about how finance works. … No one wants to hear that with great wealth comes great responsibility, but it’s true.”
Sometimes investors are fortunate. The seven MLB players who unwittingly invested $10 million in Stanford’s phony certificates of deposit in 2008 sold their shares before the Ponzi scheme collapsed, according to Kevin Sadler, lead counsel for the receivership appointed by the court to recover as much of Stanford’s ill-gotten gains as possible.
Maddux, a Hall of Fame pitcher who earned $153.8 million during a 23-year career, made the largest profit: $169,000 in 10 months on an investment of $3.5 million. Damon made the least, $70 in two months on an investment of $400,000.
However, the players were among hundreds of investors who had bank accounts frozen until they agreed to return their profits to the receivership. All seven players gave back their profits in December 2009, Sadler said, a small amount of the $2.7 billion that will have been recovered by this summer. About 45% of the principal investments stolen by Stanford will have been returned to the approximately 18,000 fraud victims.
“Starting at zero, to be able to return this much, I really do think it is remarkable,” Sadler said. “It’s taken 15 years, so I don’t think saying the recovery is monumental is overkill or hype.”
In most cases involving fraudulent investments, little if anything is recovered, he said. And when it comes to athletes and entertainers with immense earnings, the money lost is often well into the millions.
“How does a person blow that much money?” Sadler said. “You can do it. It’s possible. You don’t even have to try that hard. You can actually blow it quite easily.”
Business
TikTok to crack down on content that promotes disordered eating and dangerous weight-loss habits

Saying it does not want to promote negative body comparisons, TikTok is cracking down on posts about disordered eating, dangerous weight loss habits and potentially harmful weight management products.
The wildly popular social media app updated its community guidelines last week, introducing a slate of rules that it hopes will make the platform a safer place for its roughly 1 billion users worldwide.
The initiative comes at a time when TikTok, which is owned by Beijing technology firm ByteDance, is facing increased scrutiny over its operations and content as it fights a potential ban in the U.S.
Weight loss videos make up a huge category on TikTok, with influencers extensively detailing and demonstrating how they slimmed down. Such videos have proliferated in the last few years with the rise of injectable prescription drugs such as Ozempic, Wegovy and Mounjaro, which many people are using to shed weight quickly.
Critics say the skyrocketing demand for the drugs has exposed the cracks in the body positivity movement, showing that there is still immense pressure to look thin at whatever cost. They say TikTok and Instagram, anti-aging filters, selfie culture and relentless celebrity and influencer self-promotion have all contributed to the problem.
TikTok already had policies around body image and disordered eating, but the updated guidelines explicitly break down such content into four categories: allowed; not allowed; restricted to users 18 and older; and ineligible for the “For You Feed,” TikTok’s personalized recommendation algorithm. They go into effect May 17.
The guidelines are intended to “improve understanding and bring greater transparency about our rules and how we enforce them,” Adam Presser, TikTok’s head of operations as well as the company’s trust and safety unit, said in a statement.
In the past, TikTok creators said they would sometimes see posts restricted or removed without understanding why they were flagged.
TikTok now clearly states that it bans videos “showing, describing, promoting, or offering or requesting coaching for disordered eating or dangerous weight-loss behaviors.”
The company defines those behaviors as extreme low-calorie diets, binging and intentional vomiting, misusing medication or supplements for weight loss and exercising through serious injuries or illness.
TikTok specifically called out content that shows or promotes unhealthy body measurements and “body checking” trends, such as comparing the size of body parts to household objects, as not allowed. Facilitating the trade or marketing of weight loss or muscle gain products is also on its way out.
Content that will be restricted to users 18 and older — and which will also be ineligible for the For You Feed — includes showing or promoting “potentially harmful weight-management behaviors” such as restrictive low-calorie diets; using medication or supplements for weight loss or muscle gain; and exercises designed for rapid and significant weight loss, such as “cardio routines that promise to help you lose a waist size in a week,” the company said.
TikTok also said it would restrict before-and-after transformation photos promoting weight loss and muscle gain products, as well as videos that promote body types as “ideal or perfect” when associated with potentially harmful weight management behaviors.
“We want TikTok to be a place that encourages self-esteem,” the company said.
Creators who have documented their weight loss journeys using the new class of trendy medications said they were disappointed by the crackdown. TikTok, they said, has become an important resource and close-knit community for people who have struggled for years to shed pounds and get healthy.
You’re just shutting down and secluding a group of people that is already so used to being shamed and put in a corner.
— Kelsey Martinez, 32, a content creator who has chronicled her weight-loss journey on TikTok
“I think countless amounts of lives have been saved by the ability to communicate about these medications,” said Kelsey Martinez, 32, who began posting about using Mounjaro, a medication intended to treat Type 2 diabetes, to lose weight in September 2022. She weighed 232 pounds when she started using the weekly injectable; by last fall, she was down to 153.
“It’s giving people who are obese access and that’s something we don’t always have,” said Martinez, who lives in Los Angeles and has 296,000 TikTok followers. “So I think it’s going to be very harmful. You’re just shutting down and secluding a group of people that is already so used to being shamed and put in a corner.”
A spokesperson for TikTok said content about medically necessary health interventions under the guidance of a medical or health professional is allowed, including discussions about glucagon-like peptide 1 medications, which includes the diabetes drug Ozempic. The spokesperson added that content about using GLP-1 medications for weight loss could still be discovered in other ways, such as through search tools or by following an account, even if it is ineligible for the For You Feed.
Showing or describing competitive eating contests; fitness routines, sports and nutrition that are not primarily focused on extreme weight loss, marathon training or bodybuilding competitions; and religious diet behavior and fasting will still be allowed.
TikTok users will be permitted to condemn disordered eating, dangerous weight loss behaviors or potentially harmful weight management “as long as it does not show or describe a diet or behavior,” the company said.
Michelle York, a full-time content creator from Moorpark, said she understood that the app is in a “really tough spot” right now as it faces a divest-or-ban bill in the U.S., where it has 170 million users.
“TikTok is under a big microscope, and they need to go out of their way to make sure it’s a safe space,” York, 40, said. But “I think they’re overcompensating by making these new guidelines.”
Even though she believes her content is beneficial and far from promoting “get-thin-quick supplements,” and despite her follower base of 203,000 people imploring her to keep the weight loss content coming, she has already turned some of her old Mounjaro videos private and will focus even more on lifestyle and beauty content going forward.
“It’s really disheartening to be told I can’t share that here anymore, and now it’s at risk of my platform, which I worked so hard to build,” York said. “The problem is, this is now my job — I rely on this as my income and I can’t post things to jeopardize that.”
TikTok’s latest community guidelines also include new and updated definitions on the company’s policies around hate speech and health misinformation.
In announcing the updated rules, TikTok said it would introduce a “warning strike” when a creator violates the platform’s community guidelines for the first time.
“The warning strike does not count toward an account’s strike tally, but any future violations will,” Presser said. “We notify creators about which rule they’ve broken and how they can appeal if they believe a mistake has been made. Zero-tolerance policies (for example, incitement to violence) aren’t eligible for these reminders; accounts will immediately be banned.”
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job
-
 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: The American Society of Magical Negroes
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoGOP senators demand full trial in Mayorkas impeachment
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoFilm Review: Season of Terror (1969) by Koji Wakamatsu
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCroatians vote in election pitting the PM against the country’s president
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago'You are a criminal!' Heckler blasts von der Leyen's stance on Israel
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoAnd the LUX Audience Award goes to… 'The Teachers' Lounge'
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump trial: Jury selection to resume in New York City for 3rd day in former president's trial
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(727x249:729x251)/lindsay-candy-and-family-42624-ca1fcb0742b248e8b99c4e17aa558586.jpg)