Science
Mosquito season is upon us. So why are Southern California officials releasing more of them?
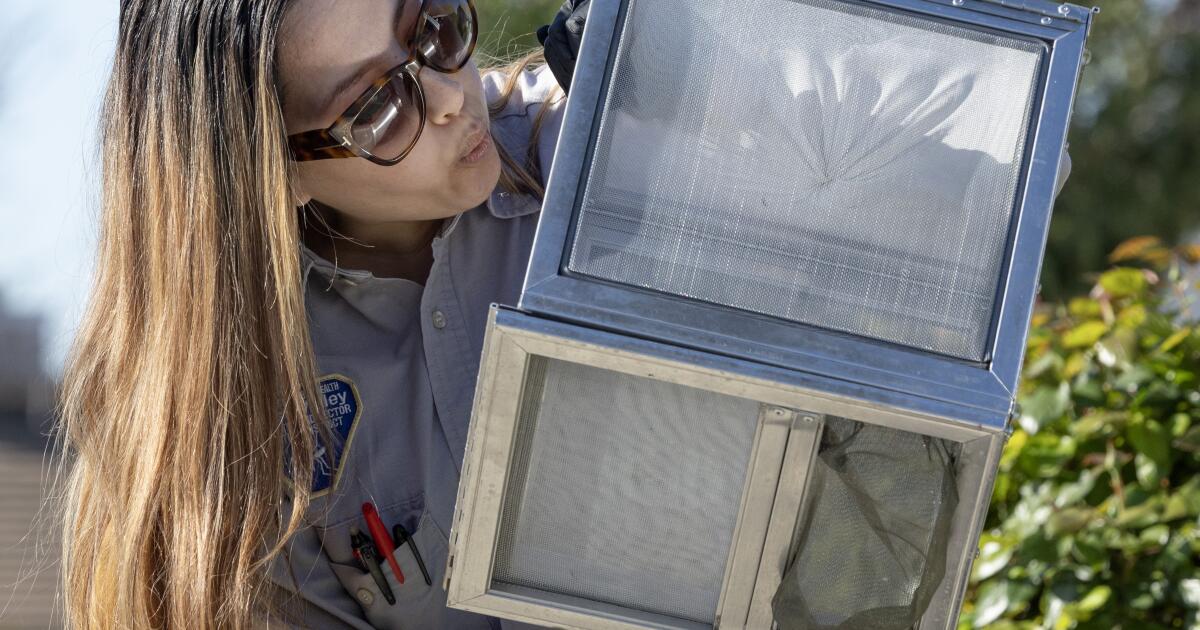

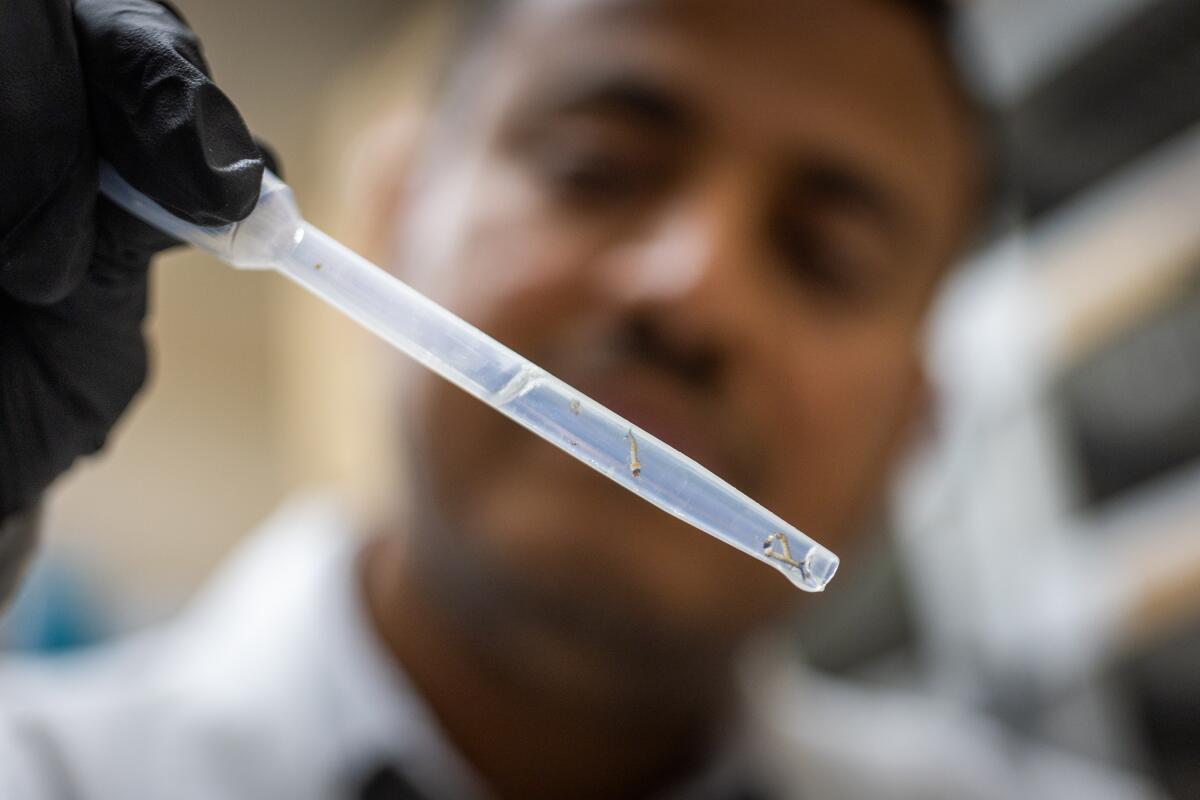
Jennifer Castellon shook, tapped and blew on a box to shoo out more than 1,000 mosquitoes in a quiet, upscale Inland Empire neighborhood.
The insects had a job to do, and the pest scientist wanted every last one out.
Aggressive and impactful reporting on climate change, the environment, health and science.
Their task? Find lady mosquitoes and mate.
But these were no ordinary mosquitoes. Technicians had zapped the insects, all males, with radiation in a nearby lab to make them sterile. If they achieve their amorous quest, there will be fewer baby mosquitoes than there would be if nature ran its course. That means fewer mouths to feed — mouths that thirst for human blood.
“I believe, fingers crossed, that we can drop the population size,” said Solomon Birhanie, scientific director for the West Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District, which released the mosquitoes in several San Bernardino County neighborhoods this month.
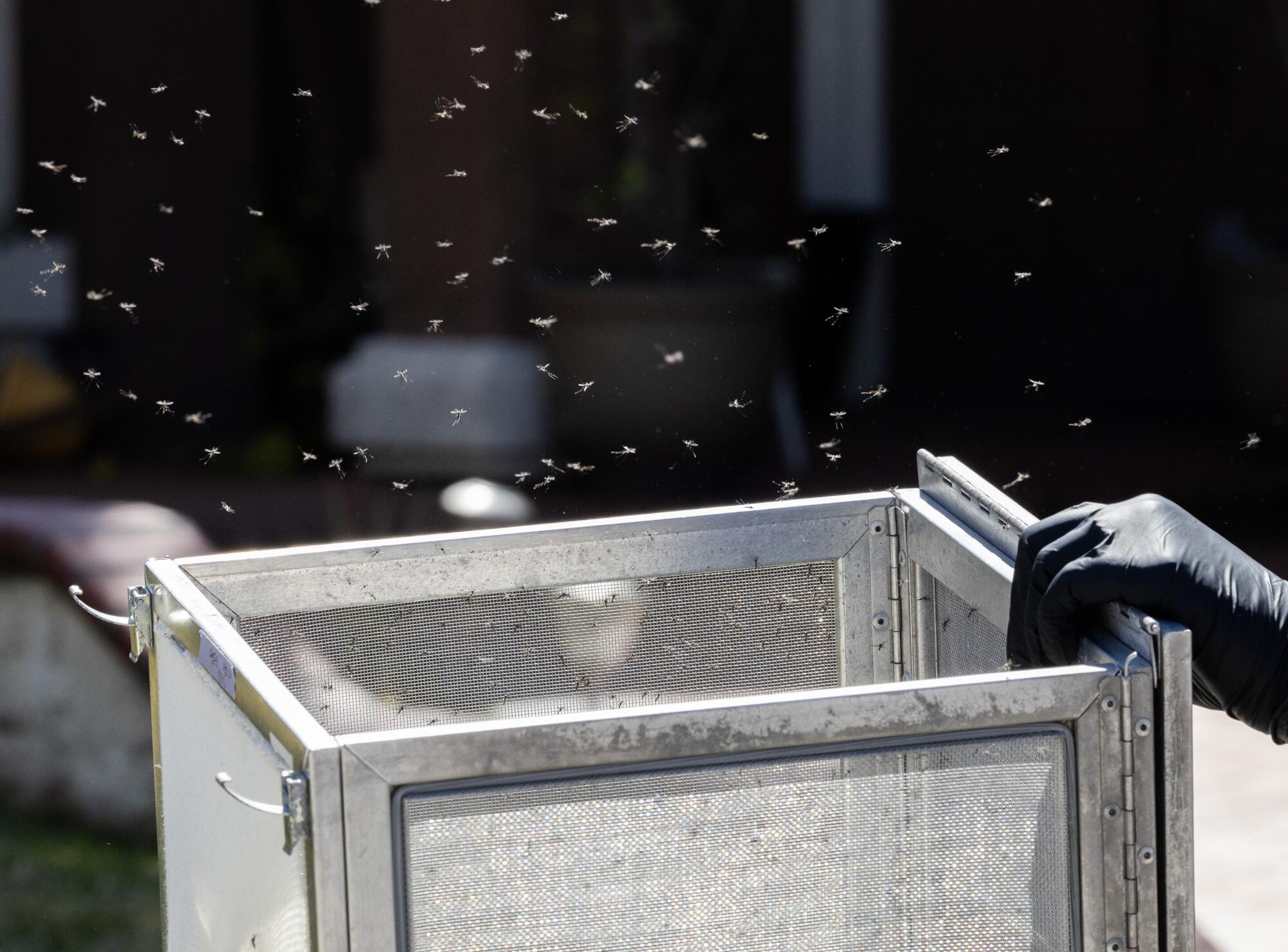

Sterilized male Aedes mosquitoes are released from a box in Rancho Cucamonga.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
Controlling mosquitoes with mosquitoes
Mosquito control agencies in Southern California are desperate to tamp down an invasive mosquito — called Aedes aegypti — that has exploded in recent years. Itchy, unhappy residents are demanding it. And the mosquitoes known for fierce ankle biting aren’t just putting a damper on outdoor hangouts — they also spread disease.
The low-flying, day-biting mosquitoes can lay eggs in tiny water sources. A bottle cap is fair game. And they might lay a few, say, in a plant tray and others, perhaps, in a drain. Tackling the invaders isn’t easy when it can be hard to even locate all the reproduction spots. So public health agencies increasingly are trying to use the insects’ own biology against them by releasing sterilized males.
The West Valley district, which covers six cities in San Bernardino County, rolled out the first program of this kind in California last year. Now they’re expanding it. Next month, a vector district covering a large swath of Los Angeles County will launch its own pilot, followed by Orange County in the near future. Other districts are considering using the sterile insect technique, as the method is known, or watching early adopters closely.
On the plus side, it’s an approach that doesn’t rely on pesticides, which mosquitoes become resistant to, but it requires significant resources and triggers conspiracy theories.
“People are complaining that they can’t go into their backyard or barbecue in the summer,” Birhanie said at his Ontario lab. “So we needed something to strengthen our Aedes control.” Of particular concern is the Aedes aegypti, which love to bite people — often multiple times in rapid succession.
Releasing sterilized male insects to combat pests is a proven scientific technique, but using it to control invasive mosquitoes is relatively new.
Vector control experts often point to the success of a decades-long effort in California to fight Mediterranean fruit flies by dropping enormous quantities of sterile males from small planes. That program, run by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the California Department of Food and Agriculture, costs about $16 million a year. That’s nearly four times West Valley’s annual budget.
So rather than try to tackle every nook and cranny of the district, encompassing roughly 650,000 residents, West Valley decided to use a more targeted approach. If a problem area reaches a certain threshold — over 50 mosquitoes counted in an overnight trap — it becomes a candidate.
1
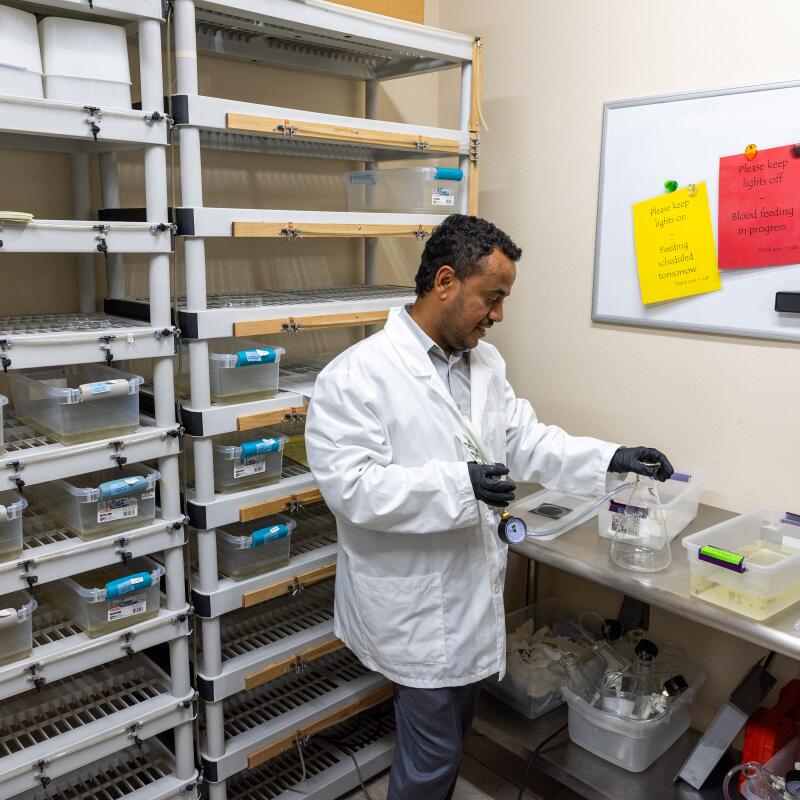

2
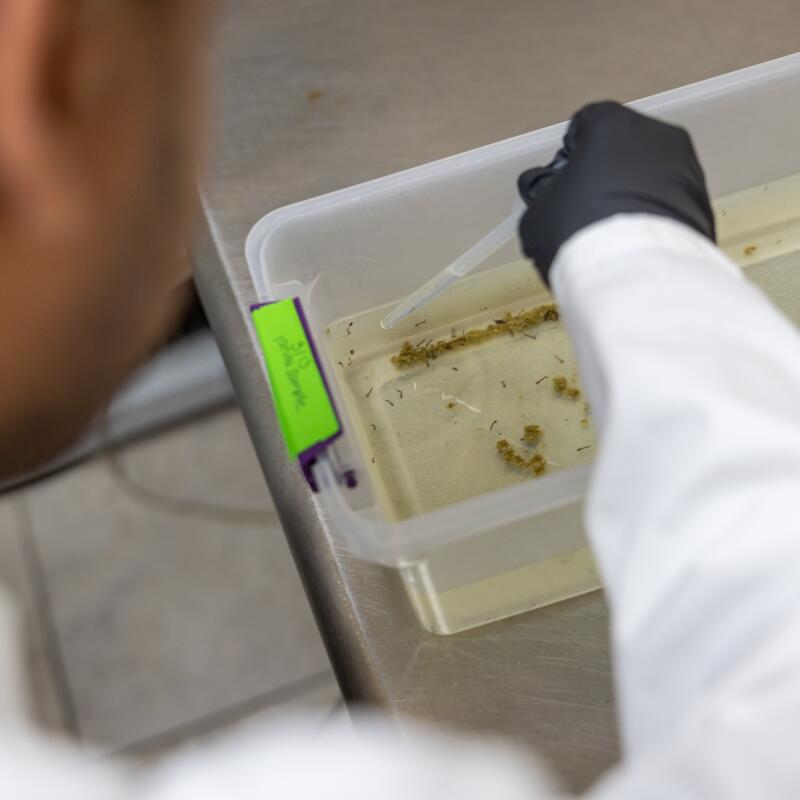

3
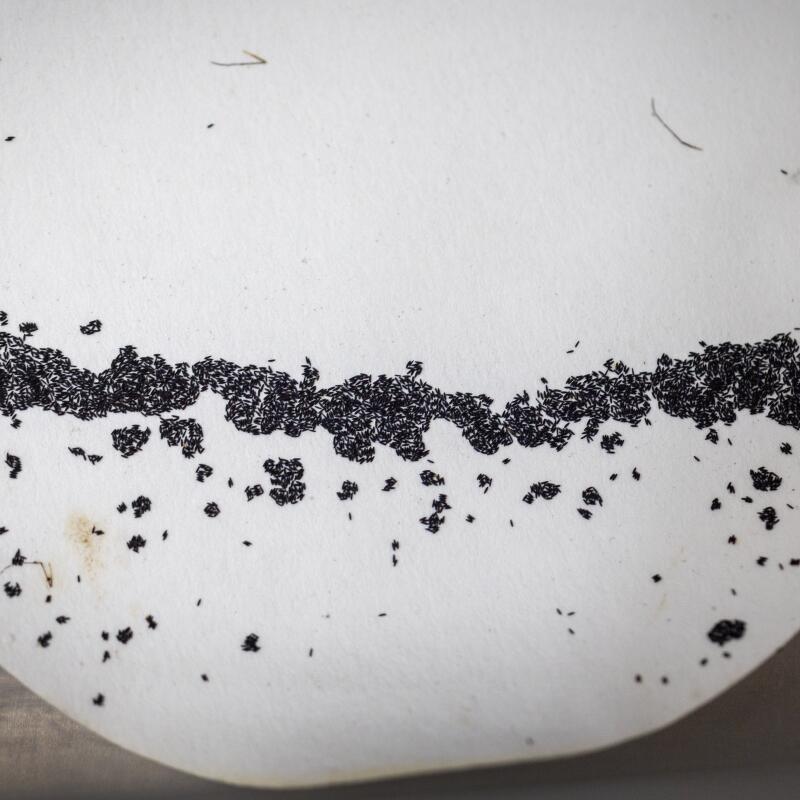

4
5
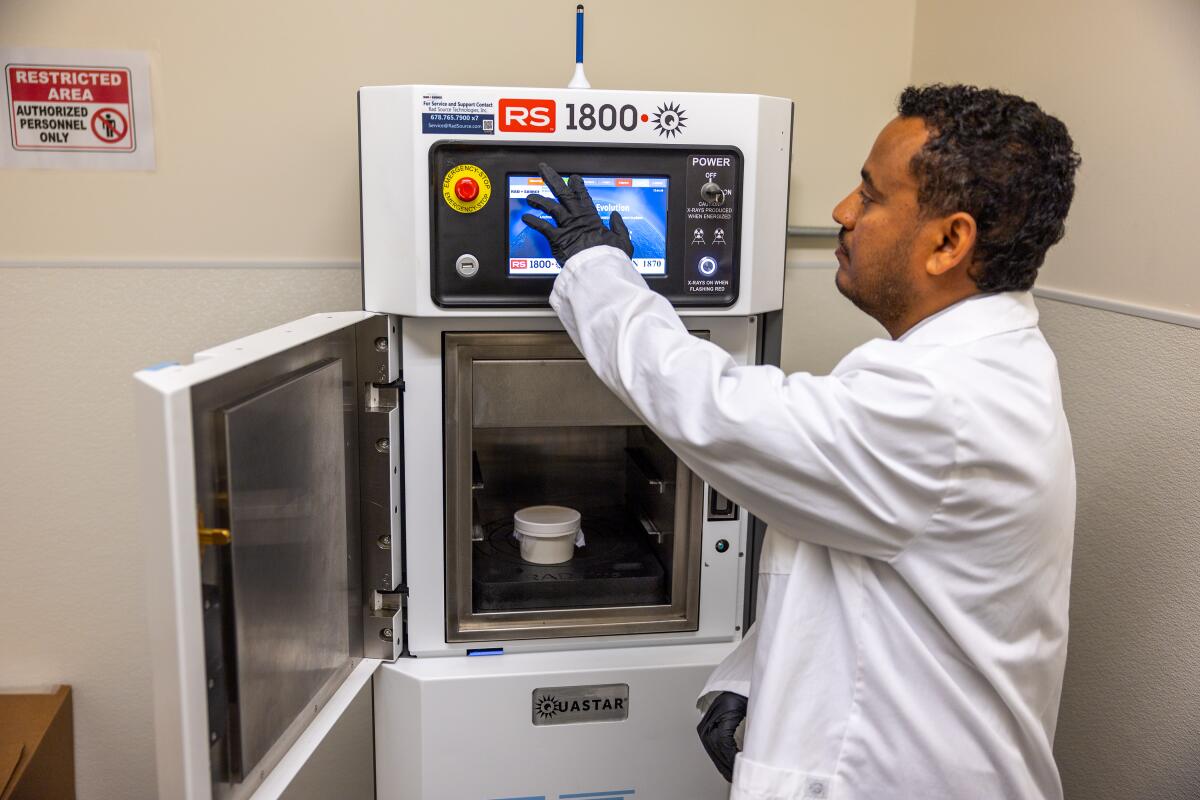

1. Solomon Birhanie inspects a container of mosquito larvae in the lab at the West Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District in Ontario. 2. Birhanie and his team raise mosquitoes in the lab, separating them by sex, because only the males, which don’t bite humans, will eventually be released. 3. Mosquito eggs in the West Valley lab. 4. The lab can grow about 10,000 mosquitoes at a time. 5. Before the male mosquitoes are released, an X-ray machine sterilizes them. If the zapped males mate with a female, her eggs won’t hatch. (Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
And it’s still a big lift. About 10,000 mosquitoes are reared at a time at West Valley’s facility, about half of which will be males. The males are separated out, packed into cups and placed into an X-ray machine that looks like a small refrigerator. The sterilizing process isn’t that different from microwaving a frozen dinner. Zap them on a particular setting for four to five minutes and they’re good to go.
Equipment purchased for the program costs roughly $200,000, said Brian Reisinger, spokesperson for the district. He said it was too early to pin down a cost estimate for the program, which is expanding.
Some districts serving more people are going bigger.
The Greater Los Angeles County Vector Control District plans to unleash up to 60,000 mosquitoes a week in two neighborhoods in Sunland-Tujunga from mid-May through November.
With the sterile-insect program, “the biggest hurdle we’re up against really is scalability,” said Susanne Kluh, general manager of the L.A. County district, which is responsible for nearly 6 million residents across 36 cities.
In part to save money, Kluh’s district has partnered with the Orange County Mosquito and Vector Control District. They’re sharing equipment and collaborating on studies, but L.A. County’s releases will move forward first, said Brian Brannon, spokesperson for the O.C. district. Orange County expects to release its “ankle biter fighters,” as Brannon called them, in Mission Viejo this fall or next spring.
So far, the L.A. County district has shelled out about $255,000 for its pilot, while O.C. has spent around $160,000. It’s a relatively small portion of their annual budgets: L.A. at nearly $25 million and O.C. at $17 million. But the area they’re targeting is modest.
Mosquito control experts tout sterilization for being environmentally friendly because it doesn’t involve spraying chemicals, and it may have a longer-lasting effectiveness than pesticides. It can also be done now. Other methods involving genetically modified mosquitoes and ones infected with bacteria are stuck in an approval process that spans federal and state agencies. One technique, involving the bacteria Wolbachia was recently approved by the Environmental Protection Agency and is now heading to the California Department of Pesticide Regulation to review, said Jeremy Wittie, general manager for the Coachella Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District.
“Using pesticides or insecticides, resistance crops up very quickly,” said Nathan Grubaugh, associate professor of epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health.
Vector control experts hope the fact that the sterilization technique doesn’t involve genetic modification will tamp down conspiracy theories that have cropped up around mosquito releases. One erroneous claim is that a Bill Gates-backed effort to release mosquitoes was tied to malaria cases in Florida and Texas. Reputable outlets debunked the conspiracy theory, pointing out that Gates’ foundation didn’t fund the Florida project and that the type of mosquito released (Aedes) does not transmit malaria.
To get ahead of concerns, districts carrying out the releases say they’ve engaged in extensive outreach and education campaigns. Residents’ desire to rid themselves of a scourge may overcome any anxieties.
“I think if you have the choice of getting eaten alive by ankle biters or having a DayGlo male X-rayed mosquito come by looking for a female to not have babies with, you’d probably go for the latter,” Brannon said. (“DayGlo” is a riff on the fluorescent pigment product of the same name — the sterilized mosquitoes were dusted with bright colors to help identify them.)
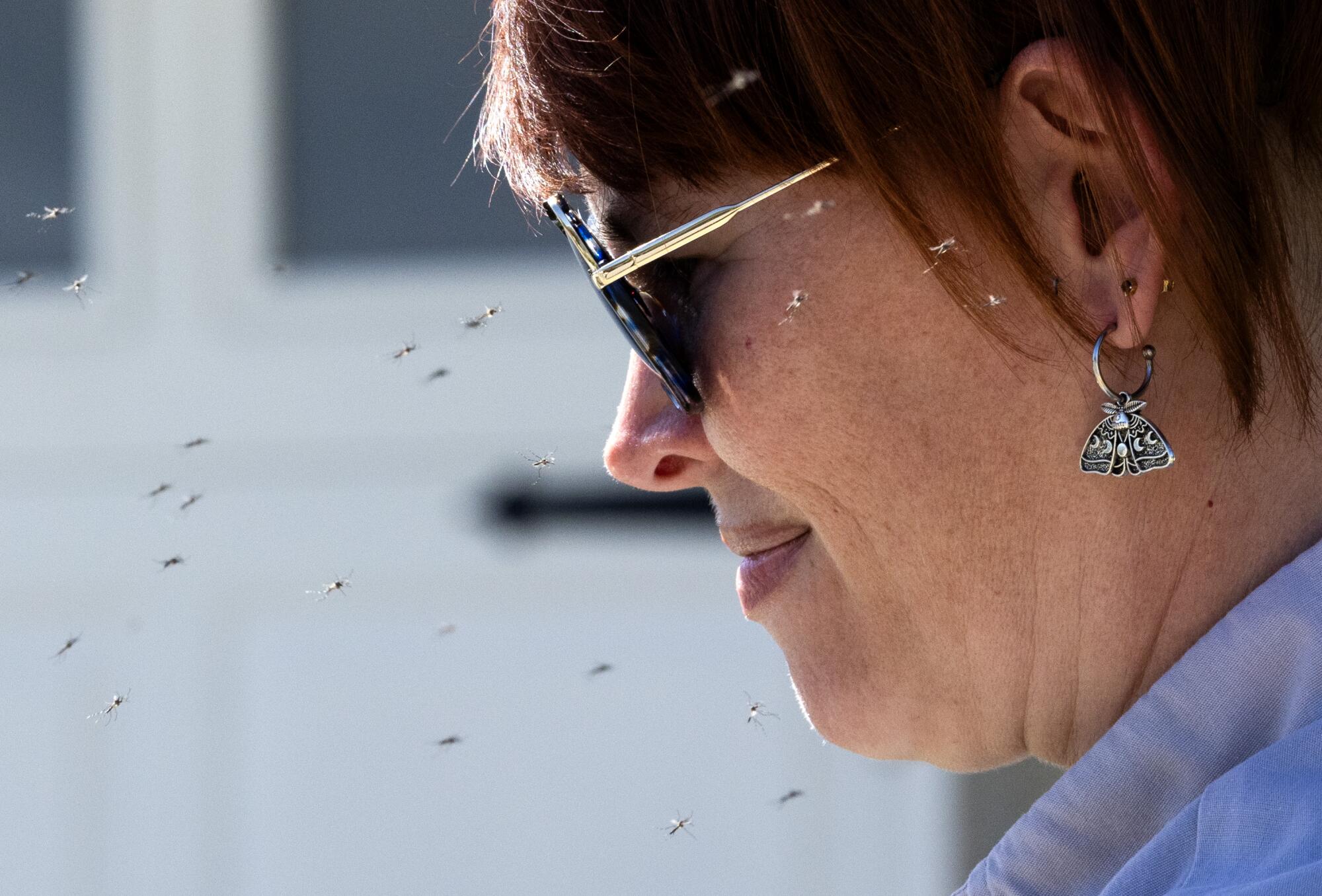

Sterilized male mosquitoes buzz around vector ecologist Jennifer Castellon as they are released in Rancho Cucamonga earlier this month.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
Disease at our doorstep
As the climate warms and some regions become wetter, dengue is expanding to areas it’s never been seen before — and surging in areas where it’s established. Florida has seen alarming spikes in the viral infection in recent years, and Brazil and Puerto Rico are currently battling severe outbreaks. While most people infected with dengue have no symptoms, it can cause severe body aches and fever and, in rare cases, death. Its alias, “breakbone fever,” provides a grim glimpse into what it can feel like.
In October of last year, the city of Pasadena announced the Golden State’s first documented locally transmitted case of dengue, describing it as “extremely rare” in a news release. That same month, a second case was confirmed in Long Beach. Local transmission means the patient hadn’t traveled to a region where dengue is common; they may have been bitten by a mosquito carrying the disease in their own neighborhood.
Surging dengue abroad means there’s more opportunity for travelers to bring it home. However, Grubaugh said it doesn’t seem that California is imminently poised for a “Florida-like situation,” where there were nearly 1,000 cases in 2022, including 60 that were locally acquired. Southern California in particular lacks heavy rainfall that mosquitoes like, he said. But some vector experts believe more locally acquired cases are inevitable.
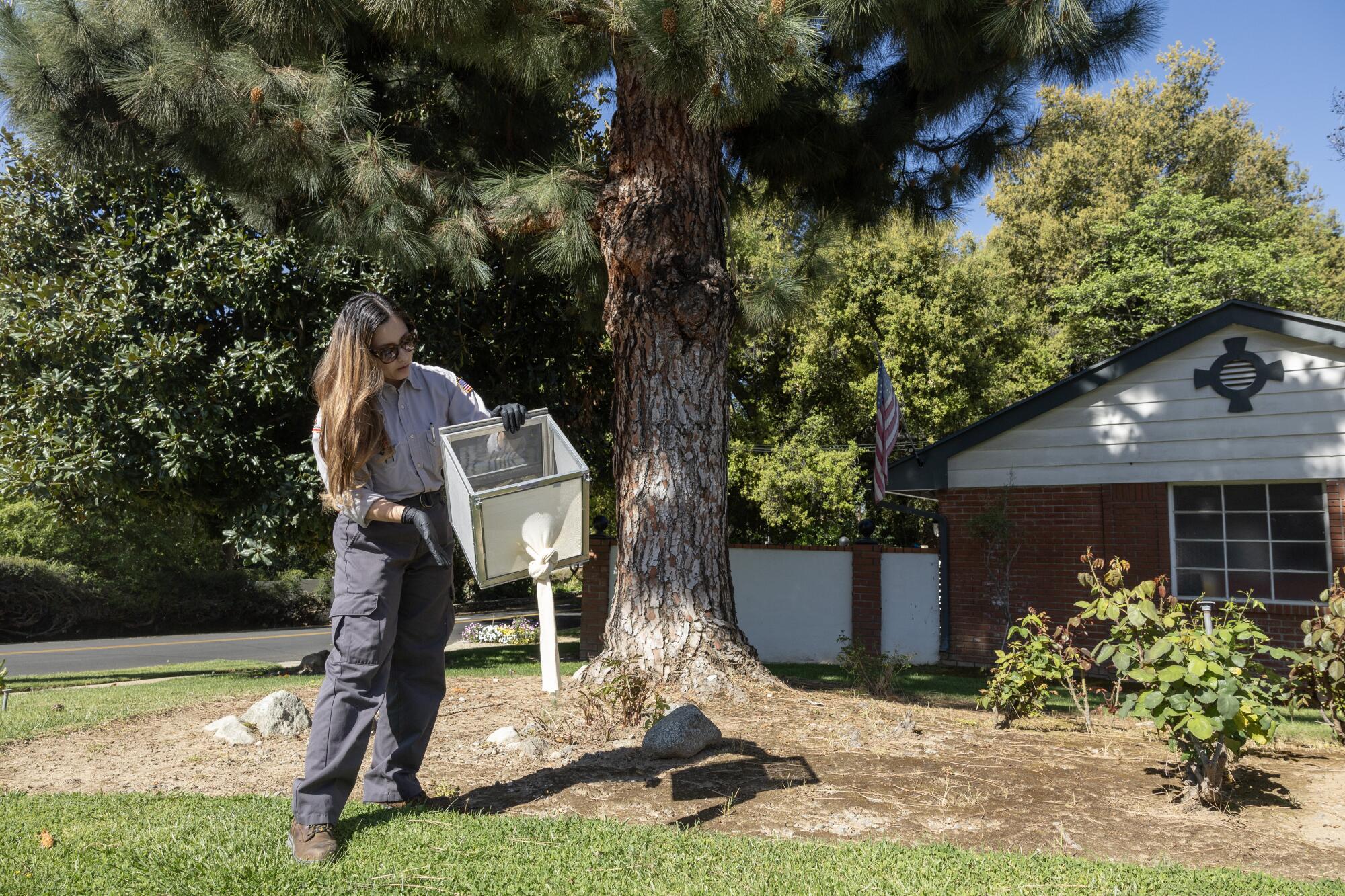

Ale Macias releases sterilized male mosquitoes in Upland this month.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
Set them free
In mid-April, a caravan of staffers from the West Valley district traveled to five mosquito “hot spots” in Chino, Upland and Rancho Cucamonga — where data showed mosquito levels were particularly high — to release their first batches of sterilized male mosquitoes for the year. Peak Aedes season is months away, typically August to October in the district, and Birhanie said that’s the point. The goal is to force down the numbers to prevent an itchy tsunami later.
Males don’t bite, so the releases won’t lead to more inflamed welts. But residents might notice more insects in the air. Sterilized males released by West Valley will outnumber females in the wild by at least 100 to 1 to increase their chances of beating out unaltered males, spokeperson Reisinger said.
“They’re not going to be contributing to the biting pressure; they’re just going to be looking for love,” as Reisinger put it.
Eggs produced by a female after a romp with a sterile male don’t hatch. And female mosquitoes typically mate only once, meaning all her eggs are spoiled, so to speak. Vector experts say the process drives down the population over time.
Interestingly, the hot spots were fairly spread out across the district, indicative of the bloodsuckers’ widespread presence and adaptive nature. A picturesque foothills community in Upland was “especially interesting” because of its relatively high elevation, Birhanie said.
It was once inhabited primarily by another invasive mosquito that prefers colder, mountainous climates. Construction and deforestation in the area has literally paved the way for its humidity- and heat-loving brethren to move in.
Another neighborhood, in Rancho Cucamonga, posed a mystery. For the last two years, mosquito levels were consistently high. Door-to-door inspections, confoundingly, didn’t reveal the source.
“That’s one of the things about invasive Aedes mosquitoes — you can’t find them,” he said.
Next steps
Some vector control experts want to see a regional approach to sterile mosquito releases, similar to the state Medfly program.
Jason Farned, district manager for the San Gabriel Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District, believes a widespread effort “would be much more effective” and thinks that will come in time.
There are no talks underway to make it happen, and it’s not yet clear how it would work. Vector control agencies are set up to serve their local communities.
Fears of a bad mosquito year ahead are bubbling as the weather warms. Rain — which there was plenty of this spring — can quickly transform into real estate for mosquito reproduction.
When the swarms come, mosquito haters can take typical precautions: dump standing water and wear repellent. And they can root for the sterile males to get lucky.

Science
A champion of psychedelics who includes a dose of skepticism
Book Review
Trippy: The Peril and Promise of Medicinal Psychedelics
By Ernesto Londoño
Celadon Books: 320 pages, $29.99
If you buy books linked on our site, The Times may earn a commission from Bookshop.org, whose fees support independent bookstores.
Ernesto Londoño’s engrossing and unsettling new book, “Trippy: The Peril and Promise of Medicinal Psychedelics,” is part memoir, part work of journalism. It tells of how Londoño sought relief from depression with mind-altering drugs. It also investigates the current fad of “medicinal” psychedelics as a treatment for those struggling with depression, trauma, suicidality and other conditions.
Like other psychedelic enthusiasts, Londoño — a journalist who reported in conflict zones such as Iraq and Afghanistan and served as the New York Times’ Brazil bureau chief — wants us to like psychedelics. They relieve him of depression and suicidality. He then continues to “trip” to engage in self-exploration: escape reality, journey into himself and return with an expanded view of the world.
Calling street drugs and hallucinogenics such as psilocybin, MDMA/ecstasy, LSD and ayahuasca “medicine” is problematic. Psychedelic psychiatry has had a resurgence in the past decade, though only among a minority of medical professionals. Mainstream psychiatry largely abandoned psychedelics by the 1970s, for a variety of reasons.
The renewed interest in psychedelics as a treatment seems to arise more from hope than science — a wish that medicinal psychedelics will be effective because our current treatments are inadequate. Antidepressants known as SSRIs and other approaches are often ineffectual, but that doesn’t mean psychedelics, which can be damaging to many in acute distress, should be tried.
Londoño is more balanced in discussing the benefits and dangers than Michael Pollan and others. Pollan’s bestselling book-turned-Netflix-series “How to Change Your Mind” proselytizes medicinal psychedelics in a way that “Trippy” thankfully doesn’t.
Londoño brings a healthy dose of skepticism. Psychedelics aren’t romanticized with examples of the counterculture movement of the 1960s or hyped by listing celebrities currently using them. The author often questions how much of what he’s part of is “a cult” and if what he’s taking is “voodoo,” not medicine.

Ernesto Londoño, author of “Trippy.”
(Jenn Ackerman)
“Trippy” is a fascinating account of the world of medicinal psychedelics. We attend psychedelic retreats in the Amazon and Latin America. We drink ayahuasca, a syrupy, foul-tasting psychoactive tea that induces vomiting and hallucinations. Ayahuasca calls back “memories” — some real, others false — that participants take as the cause of their emotional ill health.
We visit a ketamine clinic, where Londoño feels a “blissful withdrawal,” retaining “strong powers of perception” but losing “any sense of being a body with limbs that can move at will.”
We watch MDMA (a German pharmaceutical from 1912 now best known as the street drug called ecstasy or molly) being administered at a veterans hospital to treat post-traumatic stress disorder. At a “treatment center”/church/spiritual refuge in Austin, Texas, we witness tobacco being blown into a man’s nostrils, extract from an Amazonian plant squirted into his eyes, and toad venom burned into his forearms under the guise of spiritual salvation.
Unlike the unbridled enthusiasts, Londoño exposes the predatory nature of the psychedelic industry and how it exoticizes the use of hallucinogens as Indigenous medicines. We’re privy to some scandals in this field, specifically sexual abuse and harassment and taking advantage of vulnerable people looking for help.
It’s an engaging memoir of one man’s experiences with psychedelics. Londoño’s little asides, like when he’s talking about meeting the man who would become his husband, endear him to us: “I saw the profile of a handsome man visiting from Minnesota for the weekend. He was a vegetarian and veterinarian. Swoon!”
But as a work of mental health journalism, “Trippy” isn’t, as the book jacket suggests, “the definitive book on psychedelics and mental health today.”
Much is overlooked and left out. Londoño fails to stress that these treatments best serve the “worried well,” those struggling with relatively mild complaints, but can be extremely unsafe for those with serious mental illness, meaning severe dysfunction. Such a person has typically been diagnosed with bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder with suicidality, post-traumatic stress or schizophrenia. They can’t hold a job or live independently, often for years.
Most people Londoño interviews in “Trippy” seek “bliss,” not lifesaving measures to give them a chance at basic functioning. The retreats are less mental health centers than gatherings of spiritual seekers.
Full disclosure: I read “Trippy” with an open mind and as someone who spent 25 years in the American mental health system with serious mental illness. Those years passed the way they do for so many: a string of hospitalizations endured, countless therapeutic modalities tried, numerous mental health professionals seen and myriad psychiatric medications taken (yes, in the double digits).
“Medicinal” psychedelics never came up as a potential treatment. I recovered before fringe psychiatry’s renewed interest in psychedelics became a fad in the past decade.
It’s unsettling that Londoño doesn’t mention the recovery movement and what we know can lead to mental health recovery. He doesn’t mention the five Ps, which are based on the four Ps that Thomas Insel, former head of the National Institute of Mental Health, writes about in “Healing: Our Path from Mental Illness to Mental Health.” To heal, we need people (social support), place (a safe home), purpose (meaning in life), payment (access to mental health care) and physical health (a clean diet and, ironically, no drugs or alcohol).
In this, Londoño fails to explore whether his recovery had as much to do with the changes he made as a result of his first treatment/trip as with psychedelics themselves: changes in diet, renewed purpose, finding love, moving into a new home, leaving his stressful job. If two centuries of psychiatric research has taught us one thing, it’s that there is no magic bullet for mental health recovery.
The book’s most compelling explorations into psychedelics as mental health treatments come when Londoño discusses their use in treating trauma, particularly that which war journalists and veterans experience.
He also explores the pervasiveness of mental health issues and the particular challenges LGBTQ+ people can face.
“Trippy” raises seminal questions we need to be asking as the psychedelic industry reaches further into mental health treatment:
What is “medicine” and what is an illicit drug?
Are we trying to treat those in crisis or simply help anyone escape the suffering that’s part of the human experience?
Should we continue to try more and more extreme treatments?
Or should we finally pay attention to and change systemic issues that are the root cause of so much mental and emotional distress?
Sarah Fay is the author of the bestselling memoirs “Pathological: The True Story of Six Misdiagnoses” and “Cured.”
Science
Maps of Two Cicada Broods, Reunited After 221 Years

This spring, two broods of cicadas will emerge in the Midwest and the Southeast, in their first dual appearance since 1803.
A cicada lays eggs in an apple twig.
“Insects: Their Ways and Means of Living,” by Robert E. Snodgrass, 1930, via the Biodiversity Heritage Library
Brood XIII, the Northern Illinois Brood, hatched and burrowed into the ground 17 years ago, in 2007.
Brood XIX, the Great Southern Brood, hatched in 2011 and has spent 13 years underground, sipping sap from tree roots.
The entomologist Charles L. Marlatt published a detailed map of Brood XIX, the largest of the 13-year cicada broods, in 1907.
Historic map of cicada emergence.
He also mapped the expected emergence of Brood XIII in 1922.
Historic map of cicada emergence.
This spring the two broods will surface together, and are expected to cover a similar range.
Modern map of cicada emergence.
Up to a trillion cicadas will rise from the warming ground to molt, sing, mate, lay eggs and die.
A Name and a Number
Charles L. Marlatt proposed using Roman numerals to identify the regional groups of 13- and 17-year periodical cicadas, beginning with Brood I in 1893.
A brood can include up to three or four cicada species, all emerging at the same time and singing different songs. Long cicada lifespans of 13 or 17 years spent underground have spawned many theories, and may have evolved to reduce the likelihood of different broods surfacing at the same time.
Large broods might sprawl across a dozen or more states, while a small brood might only span a few counties. Brood VII is the smallest, limited to a small part of New York State and at risk of disappearing.
At least two named broods are thought to have vanished: Brood XXI was last seen in 1870, and Brood XI in 1954.
Not Since the Louisiana Purchase
Brood XIII and Brood XIX will emerge together this year, for the first time in more than two centuries. But only in small patches of Illinois are they likely to come out of the ground in the same place.
In 1786 and 1790, the two broods burrowed into Native lands, divided by the Mississippi River into nominally Spanish territory and the new nation of the United States.
An historic map of the United States from 1783.
Brood XIII entered the ground in 1786, and Brood XIX in 1790. (Expected 2024 ranges are overlaid on the map.)
An historic map of the United States from 1783.
As the ground was warming in April 1803, France sold the rights to the territory of Louisiana, which it acquired from Spain in 1800, to the United States for $15 million.
An historic map of the United States from 1801. That spring, Brood XIII and Brood XIX emerged together into a newly enlarged United States.
An historic map of the United States from 1803.
Their descendants — 13 and 17 generations later — are now poised to return, and will not sing together again until 2245. An historic map of the United States from 1868.
A ‘Great Visitation’
After an emergence of Brood X cicadas in 1919, the naturalist Harry A. Allard wrote:
Although the incessant concerts of the periodical cicadas persisting from morning until night became almost disquieting at times, I felt a positive sadness when I realized that the great visitation was over, and there was silence in the world again, and all were dead that had so recently lived and filled the world with noise and movement.
It was almost a painful silence, and I could not but feel that I had lived to witness one of the great events of existence, comparable to the occurrence of a notable eclipse or the invasion of a great comet.
Then again the event marked a definite period in my life, and I could not but wonder how changed would be my surroundings, my experiences, my attitude toward life, should I live to see them occur again seventeen years later.
The transformation of a cicada nymph (1), into an adult (10).
“The Periodical Cicada,” by Charles L. Marlatt, 1907, via the Biodiversity Heritage Library
Science
What are the blue blobs washing up on SoCal beaches? Welcome to Velella velella Valhalla
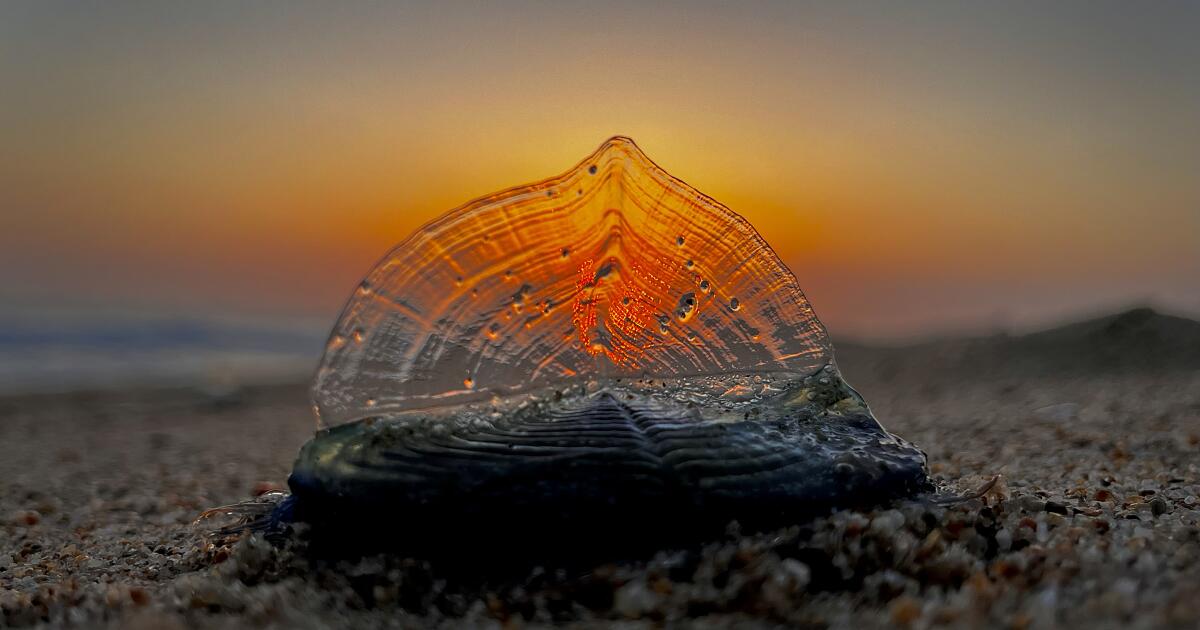

The corpses are washing up by the thousands on Southern California’s beaches: a transparent ringed oval like a giant thumbprint 2 to 3 inches long, with a sail-like fin running diagonally down the length of the body.
Those only recently stranded from the sea still have their rich, cobalt-blue color, a pigment that provides both camouflage and protection from the sun’s UV rays during their life on the open ocean.
Aggressive and impactful reporting on climate change, the environment, health and science.
These intriguing creatures are Velella velella, known also as by-the-wind sailors or, in marine biology circles, “the zooplankton so nice they named it twice,” said Anya Stajner, a biological oceanography PhD student at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
A jellyfish relative that spends the vast majority of its life on the surface of the open sea, velella move at the mercy of the wind, drifting over the ocean with no means of locomotion other than the sails atop their bodies. They tend to wash up on the U.S. West Coast in the spring, when wind conditions beach them onshore.
Springtime velella sightings documented on community science platforms like iNaturalist spiked both this year and last, though scientists say it’s too early to know if this indicates a rise in the animal’s actual numbers.
Velella are an elusive species whose vast habitat and unusual life cycle make them difficult to study. Though they were documented for the first time in 1758, we still don’t know exactly what their range is or how long they live.
These beaching events confront us with a little-understood but essential facet of marine ecology — and may become more common as the oceans warm.
“Zooplankton” — the tiny creatures at the base of the marine food chain — “are sort of this invisible group of animals in the ocean,” Stajner said. “Nobody really knows anything about them. No one really cares about them. But then during these mass Velella velella strandings, all of a sudden there’s this link to this hidden part of the ocean that most of us don’t get to experience.”
What looks like an individual Velella velella is actually a colony of teeny multicellular animals, or zooids, each with their own function, that come together to make a single organism. They’re carnivorous creatures that use stinging tentacles hanging below the surface to catch prey such as copepods, fish eggs, larval fish and smaller plankton.
Unlike their fellow hydrozoa, the Portuguese man o’ war, the toxin in their tentacles isn’t strong enough to injure humans. Nevertheless, “I wouldn’t encourage anyone to touch their mouth or their eyes after they pick one up on the beach,” said Nate Jaros, senior director of fishes and invertebrates at the Aquarium of the Pacific in Long Beach.
Velella that end their lives on California beaches typically have sails that run diagonally from left to right along the length of their bodies, an orientation that catches the onshore winds heading in this direction. As the organism’s carcass dries in the sun and the soft tissues decay, the blue color disappears, leaving the transparent chitinous float behind.
“The wind really just brings them to our doorstep in the right conditions,” Jaros said. “But they’re designed as open ocean animals. They’re not designed to interact with the shoreline, which is usually why they meet their demise when they come into contact with the shore.”
1
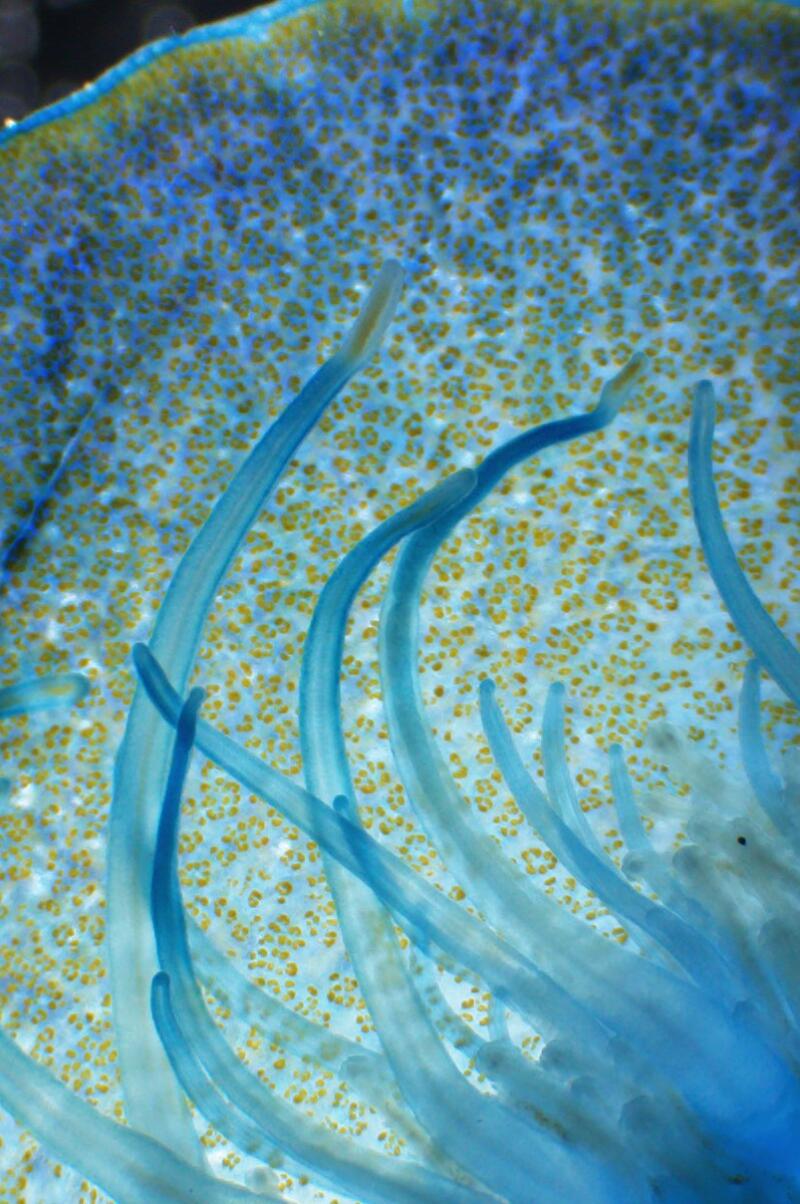

2
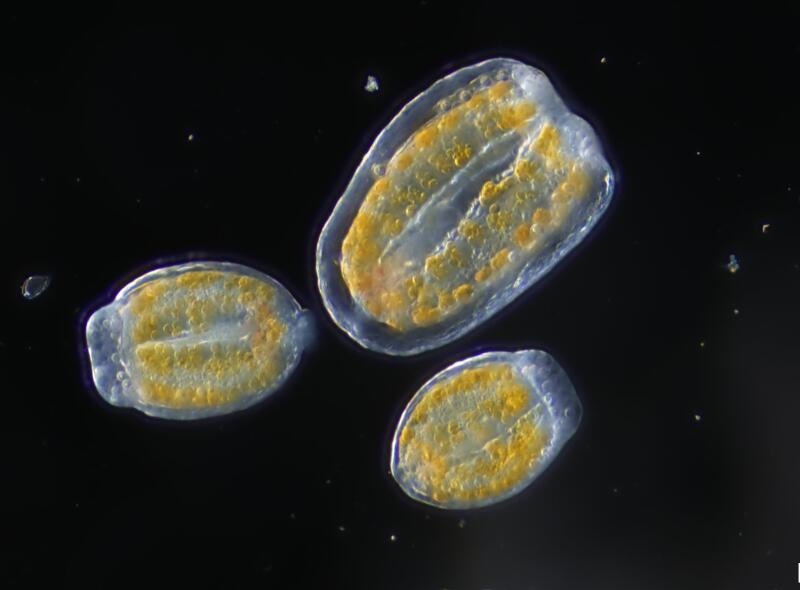
3
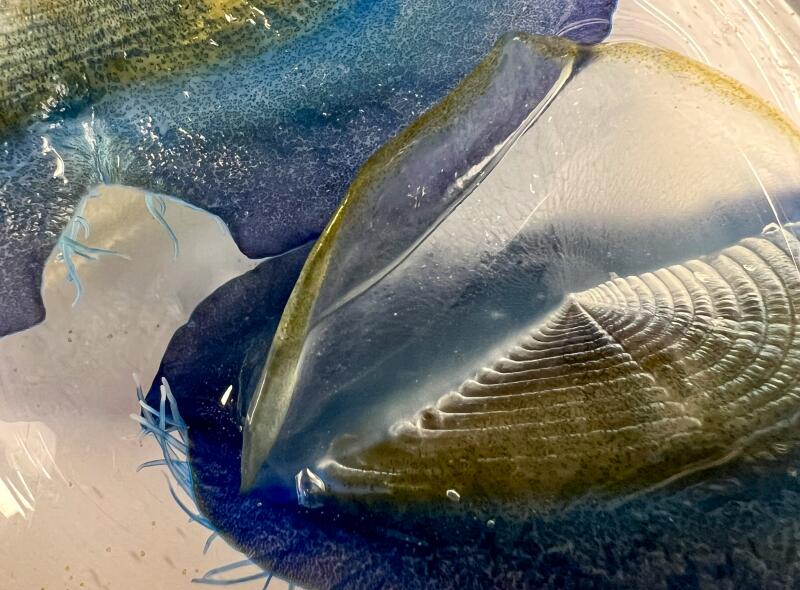

1. Anya Stajner put Velella velella under a microscope. 2. Magnified, you can see more than blue in the organism. “That green and brown coloration comes from their algae symbionts,” Stajner said. 3. Notice the tentacles too. (Anya Stajner)
Velella show up en masse when two key factors coincide, Stajner said: an upwelling of food-rich, colder water from deeper in the ocean, followed by shoreward winds and currents that direct the colonies to beaches.
A 2021 paper from researchers at the University of Washington found a third variable that appears to correlate with more velella sightings: unusually high sea surface temperatures.
After looking at data over a 20-year period, the researchers found that warmer-than-average winter sea surface temperatures followed by onshore winds tended to correlate with higher numbers of velella strandings the following spring, from Washington to Northern California.
“The spring transition toward slightly more onshore winds happens every year, but the warmer winter conditions are episodic,” said co-author Julia K. Parrish, a University of Washington biologist who runs the Coastal Observation and Seabird Survey Team community science project.
Given that sea surface temperatures have been consistently above the historical average every day since March 2023, the current velella bloom is consistent with those findings.
Previous research has found that gelatinous zooplankton like velella and their fellow jellyfish thrive in warmer waters, portending an era some scientists have referred to as the “rise of slime.”
Other winners of a slimy new epoch would be ocean sunfish, a giant bony fish whose individuals can clock in at more than 2,000 pounds and consume jellyfish — and velella — in mass quantities. Ocean sunfish sightings tend to rise when velella observations do, Jaros said.
“The ocean sunfish will actually kind of put their heads out of the water as they eat these. It resembles Pac-Man eating pellets,” he said. (KTLA-TV published a picture of just that this week.)
Though velella blooms are ephemeral, we don’t yet know how long any individual colony lives. The blue seafaring colonies are themselves asexual, though they bud off tiny transparent medusas that are thought to go to the deep sea and reproduce sexually there, Stajner said. The fertilized egg then evolves into a float that returns to the surface and forms another colony.
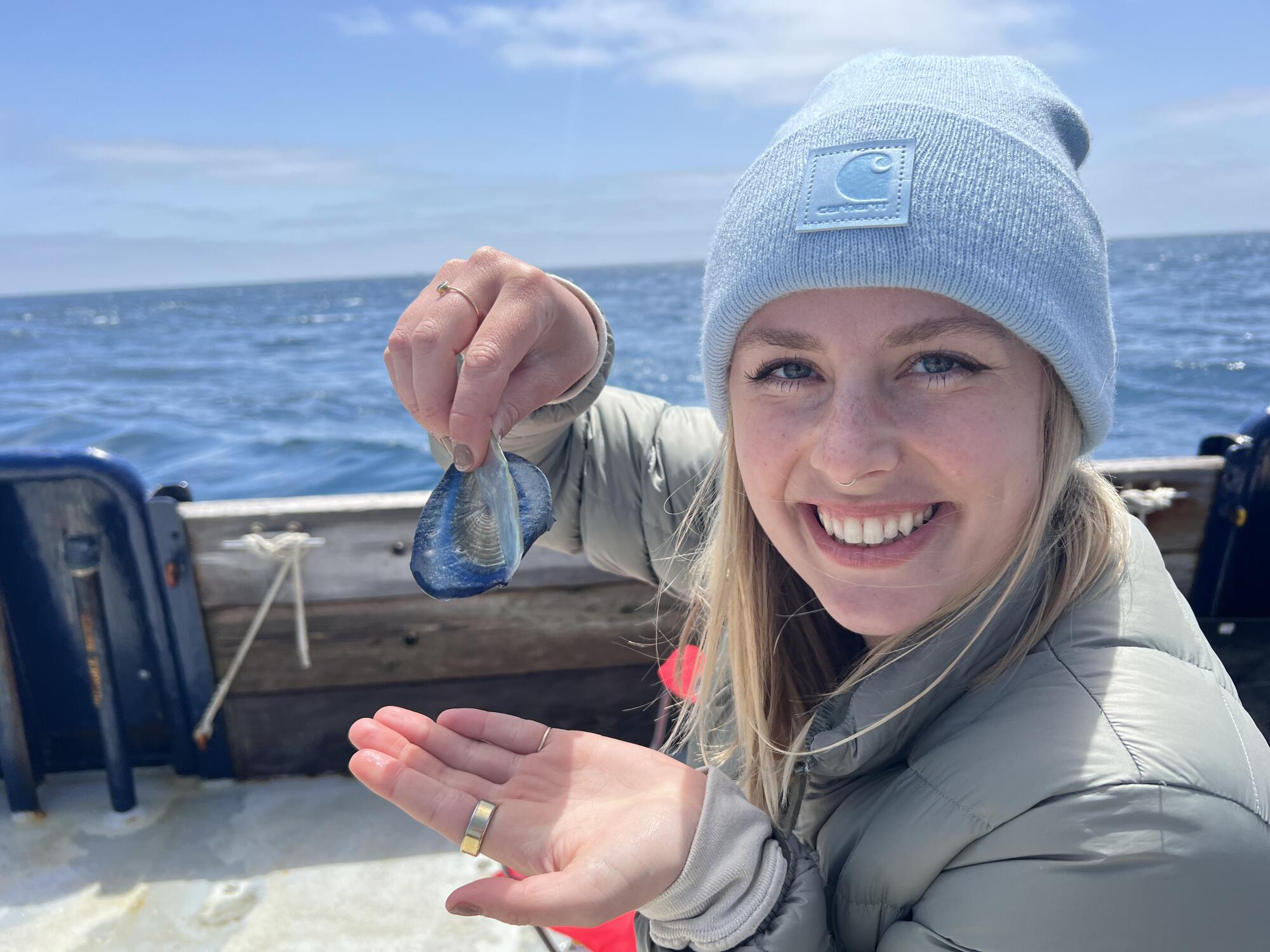

Anya Stajner, a PhD student at Scripps, collected by-the-wind sailors but was unable to keep them alive in a lab. “Rearing gelatinous organisms is pretty difficult,” she said.
“I was able to actually collect some of those medusae last year during the bloom, but rearing gelatinous organisms is pretty difficult,” Stajner said. The organisms died in the lab.
Stajner left May 1 on an eight-day expedition to sample velella at multiple points along the Santa Lucia Bank and Escarpment in the Channel Islands, with the goal of getting “a better idea of their role in the local ecosystem and trying to understand what these big blooms mean,” she said.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoLarry Webb’s deathbed confession solves 2000 cold case murder of Susan and Natasha Carter, 10, whose remains were found hours after he died
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoFirst cargo ship passes through new channel since Baltimore bridge collapse
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHaiti Prime Minister Ariel Henry resigns, transitional council takes power
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSpanish PM Pedro Sanchez suspends public duties to 'reflect'
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUS secretly sent long-range ATACMS weapons to Ukraine
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAmerican Airlines passenger alleges discrimination over use of first-class restroom
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Johnson Condemns Pro-Palestinian Protests at Columbia University
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoAbigail Movie Review: When pirouettes turn perilous




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(745x234:747x236)/ryder-harold-dean-lilly-050424-8effe989494f4c7391a21e1b3db77f33.jpg)










