Health
Expert Panel Votes for Stricter Rules on Risky Virus Research

An knowledgeable panel on Friday endorsed a sweeping set of proposed modifications to the federal authorities’s program for regulating experiments that contain tinkering with dangerous viruses and different pathogens. The transfer units the stage for a intently watched determination by the Biden administration about its method to defending towards lab disasters that might kick off a pandemic.
The consultants unanimously accepted draft suggestions that, amongst different issues, ask well being officers to increase their oversight to much less harmful pathogens, together with ones just like the coronavirus. In addition they really useful an finish to exemptions for analysis associated to vaccine improvement and surveillance of rising viruses.
“Now we have quite a lot of oversight on paper, however not likely quite a lot of oversight,” mentioned Dr. Kenneth Bernard, a retired rear admiral and a member of the knowledgeable panel, making the case for the proposed modifications, which can nonetheless obtain some slight modifications.
The proposals have added to the momentum in Washington for tightening authorities oversight of research of harmful pathogens.
Two inside federal watchdogs not too long ago issued stories that criticized the monitoring of such research. Congressional Republicans are making ready to hunt testimony from Dr. Anthony S. Fauci, who till not too long ago directed the institute chargeable for funding a lot of the nation’s pathogen analysis. And the Biden administration has signaled a willingness to behave, describing organic threats as among the many most critical risks going through the USA.
The knowledgeable panel, the Nationwide Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity, is charged with advising the federal government on biosecurity points. Its proposals emerged out of a decade of debate over so-called achieve of perform research, through which pathogens are endowed with new talents. Members of the board started discussing their newest reforms in January 2020, solely to place the method on maintain so they may deal with pandemic-related analysis.
The pandemic, although, bolstered what some critics of dangerous pathogen analysis noticed as a necessity for oversight of a broader set of viruses: Regardless of killing solely a tiny fraction of these it contaminated, the coronavirus created a worldwide disaster.
Extra on the Coronavirus Pandemic
Now, the query is whether or not the advisory board’s proposals sweep up too broad a spread of pathogens or fail to succeed in far sufficient.
Proponents of stronger oversight have largely been heartened by the suggestions and applauded their deal with any experiments that might be anticipated to provide a pathogen with pandemic potential.
“If the federal government implements the spirit of what they’ve written, this is able to be a significant overhaul of dual-use analysis oversight in the USA,” mentioned Gregory Koblentz, a biodefense specialist at George Mason College, referring to analysis that is also used to do hurt.
Nonetheless, he mentioned, the White Home ought to transcend the board’s suggestions in creating an unbiased company to carry out that oversight, streamlining a system he thought-about too fragmentary.
Different consultants have warned that even the prevailing proposals go too far. Some have mentioned that the suggestions would create an oversight system so expansive and complicated that it might discourage minimally dangerous experiments with large potential public well being advantages.
“There’s quite a bit that might doubtlessly fall into this as a result of it’s so vaguely written,” mentioned Gigi Gronvall, a biosafety specialist on the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg College of Public Well being. She advised that the kind of analysis used to make the Ebola vaccine might fall below the brand new coverage. “You would doubtlessly be creating an enormous oversight burden,” she mentioned, “which the federal government doesn’t have the technical capability to implement.”
These considerations had been echoed by 150 virologists, who in a commentary revealed on Thursday cautioned towards hampering researchers with unnecessary burdens. They warned that cumbersome rules “will result in unwarranted constraints on pandemic preparation and response and will depart humanity extra weak to future illness outbreaks.”
Seema Lakdawala, a virologist at Emory College, instructed the advisory board on Friday that extra rules might, for instance, intervene with efforts to trace the hen flu epidemic that has killed tens of millions of chickens and pushed up egg costs. Influenza strains that infect folks evolve from hen flu viruses that achieve new mutations.
The advisory board’s last report can be despatched to the White Home’s Workplace of Science and Expertise Coverage, which may have additional discussions with totally different authorities businesses earlier than issuing a brand new coverage.
“I’d be hesitant to even guess what the time-frame is, however I’m positive that will probably be longer than one month,” Dr. Lawrence Tabak, who’s performing the duties of director on the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, mentioned in a information convention after the assembly.
Proponents of stronger oversight have been lobbying in latest days for extra aggressive controls. For instance, the board really useful that the federal government be extra clear about its critiques of potential pathogens. A gaggle of scientists together with Dr. Tom Inglesby, the director of the Johns Hopkins Heart for Well being Safety on the Bloomberg College of Public Well being, have argued that the general public ought to be allowed to see the ensuing risk-benefit assessments earlier than any analysis begins.
One board member, Mark Denison, a virologist at Vanderbilt College, who voted for the suggestions, mentioned he nonetheless had reservations about their potential to constrain testing of recent monoclonal antibody remedies for viral infections.
Even when the White Home embraces the core of the advisory board’s suggestions, it’s unclear whether or not it can undertake among the consultants’ extra bold proposals. For instance, the board advised evaluating analysis for its impression on not solely people, but additionally animals and even crops.
The board proposed that experiments be topic to oversight whether or not or not they obtain authorities funding. At the moment, solely government-funded analysis is topic to monitoring.
That loophole drew consideration not too long ago when Boston College got here below hearth for an experiment through which researchers tinkered with the Omicron variant to study its severity. The experiment was not vetted by a authorities harmful pathogen committee partially as a result of it was carried out with out federal funds, the college mentioned, though federal cash went to develop the instruments used within the analysis.
Board members mentioned closing that loophole would most definitely require federal laws. “This can be a tough one to unravel,” Gerald Parker, an affiliate dean at Texas A&M College and chairman of the board, mentioned on the information convention.
A lot of the controversy over the board’s proposals has turned on whether or not biosecurity oversight ought to be restricted to particular pathogens and varieties of experiments or ought to as an alternative apply broadly to any analysis that might plausibly lead to a harmful outbreak.
The proposals, for instance, counsel a high-level overview of any analysis that’s “fairly anticipated” to create a extra harmful pathogen. Dr. Inglesby applauded that language.
“The end result is what issues,” he mentioned. “If that may be a cheap potential consequence of your work, then it ought to be ruled in the identical manner as one thing that we all know already has pandemic potential.”
Some virologists mentioned that the menace posed by an experiment might solely be decided by evaluating the main points of its methodology, like whether or not a virus was being modified to develop higher in a petri dish or in a mosquito.
“Who decides what’s cheap, and who decides what’s anticipated?” mentioned Angela Rasmussen, a virologist on the Vaccine and Infectious Illness Group on the College of Saskatchewan in Canada. “Is it going to have an effect on just some extra research or mainly each virology research?”

Health
New Jersey woman recovering after receiving successful pig kidney transplant
- Lisa Pisano faced heart and kidney failure, rendering her ineligible for traditional transplants, but a pioneering procedure at NYU Langone Health offered hope.
- Doctors implanted a mechanical heart pump to stabilize Pisano’s failing heart, followed by a kidney transplant from a genetically modified pig.
- Pisano’s recovery is progressing well, marking a significant advancement in animal-to-human transplantation.
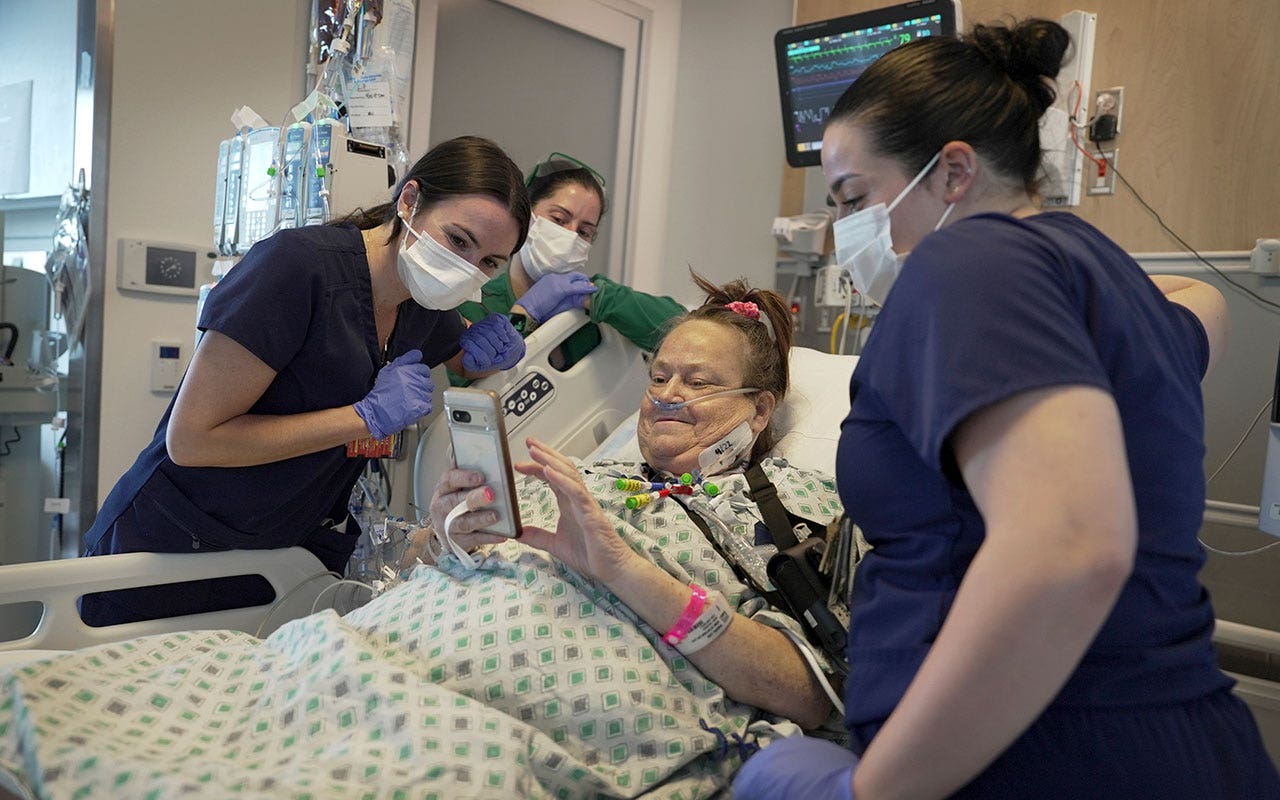
Doctors have transplanted a pig kidney into a New Jersey woman who was near death, part of a dramatic pair of surgeries that also stabilized her failing heart.
Lisa Pisano’s combination of heart and kidney failure left her too sick to qualify for a traditional transplant, and out of options. Then doctors at NYU Langone Health devised a novel one-two punch: Implant a mechanical pump to keep her heart beating and days later transplant a kidney from a genetically modified pig.
Pisano is recovering well, the NYU team announced Wednesday. She’s only the second patient ever to receive a pig kidney — following a landmark transplant last month at Massachusetts General Hospital – and the latest in a string of attempts to make animal-to-human transplantation a reality.
MASSACHUSETTS MAN, RECIPIENT OF FIRST SUCCESSFUL PIG KIDNEY TRANSPLANT, IS DISCHARGED FROM HOSPITAL
This week, the 54-year-old grasped a walker and took her first few steps.
Lisa Pisano looks at photos of her dog after her surgeries at NYU Langone Health in New York on April 22, 2024. Doctors transplanted a pig kidney into Pisano, who was near death, part of a dramatic pair of surgeries that also included a fix for her failing heart. (AP Photo/Shelby Lum)
“I was at the end of my rope,” Pisano told The Associated Press. “I just took a chance. And you know, worst case scenario, if it didn’t work for me, it might have worked for someone else and it could have helped the next person.”
Dr. Robert Montgomery, director of NYU Langone Transplant Institute, recounted cheers in the operating room as the organ immediately started making urine.
“It’s been transformative,” Montgomery said of the experiment’s early results.
But “we’re not off the hook yet,” cautioned Dr. Nader Moazami, the NYU cardiac surgeon who implanted the heart pump.
“With this surgery I get to see my wife smile again,” Pisano’s husband Todd said Wednesday.
FEDS INVESTIGATE TEXAS SURGEON ACCUSED OF DENYING PATIENTS LIFE-SAVING LIVER TRANSPLANTS
Other transplant experts are closely watching how the patient fares.
“I have to congratulate them,” said Dr. Tatsuo Kawai of Mass General, who noted that his own pig kidney patient was healthier overall going into his operation than NYU’s patient. “When the heart function is bad, it’s really difficult to do a kidney transplant.”
THE PIG ORGAN QUEST
More than 100,000 people are on the U.S. transplant waiting list, most who need a kidney, and thousands die waiting. In hopes of filling the shortage of donated organs, several biotech companies are genetically modifying pigs so their organs are more humanlike, less likely to be destroyed by people’s immune system.
NYU and other research teams have temporarily transplanted pig kidneys and hearts into brain-dead bodies, with promising results. Then the University of Maryland transplanted pig hearts into two men who were out of other options, and both died within months.
Mass General’s pig kidney transplant last month raised new hopes. Kawai said Richard “Rick” Slayman experienced an early rejection scare but bounced back enough to go home earlier this month and still is faring well five weeks post-transplant. A recent biopsy showed no further problems.
A COMPLEX CASE AT NYU
Pisano is the first woman to receive a pig organ — and unlike with prior xenotransplant experiments, both her heart and kidneys had failed. She went into cardiac arrest and had to be resuscitated before the experimental surgeries. She’d gotten too weak to even play with her grandchildren. “I was miserable,” the Cookstown, New Jersey, woman said.
A failed heart made her ineligible for a traditional kidney transplant. But while on dialysis, she didn’t qualify for a heart pump, called a left ventricular assist device or LVAD, either.
“It’s like being in a maze and you can’t find a way out,” Montgomery explained — until the surgeons decided to pair a heart pump with a pig kidney.
TWO SURGERIES IN EIGHT DAYS
With emergency permission from the Food and Drug Administration, Montgomery chose an organ from a pig genetically engineered by United Therapeutics Corp. so its cells don’t produce a particular sugar that’s foreign to the human body and triggers immediate organ rejection.
Plus a tweak: The donor pig’s thymus gland, which trains the immune system, was attached to the donated kidney in hopes that it would help Pisano’s body tolerate the new organ.
Surgeons implanted the LVAD to power Pisano’s heart on April 4, and transplanted the pig kidney on April 12. There’s no way to predict her long-term outcome but she’s shown no sign of organ rejection so far, Montgomery said. And in adjusting the LVAD to work with her new kidney, Moazami said doctors already have learned lessons that could help future care of heart-and-kidney patients.
Special “compassionate use” experiments teach doctors a lot but it will take rigorous studies to prove if xenotransplants really work. What happens with Pisano and Mass General’s kidney recipient will undoubtedly influence FDA’s decision to allow such trials. United Therapeutics said it hopes to begin one next year.
Health
‘Sleep disorder drove my son to suicide,’ New York mother says: ‘Broke my heart’
This story discusses suicide. If you or someone you know is having thoughts of suicide, please contact the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or 1-800-273-TALK (8255).
Chronic lack of sleep can cause a long list of physical and mental issues — and for one young man, his mother believes it led to his death.
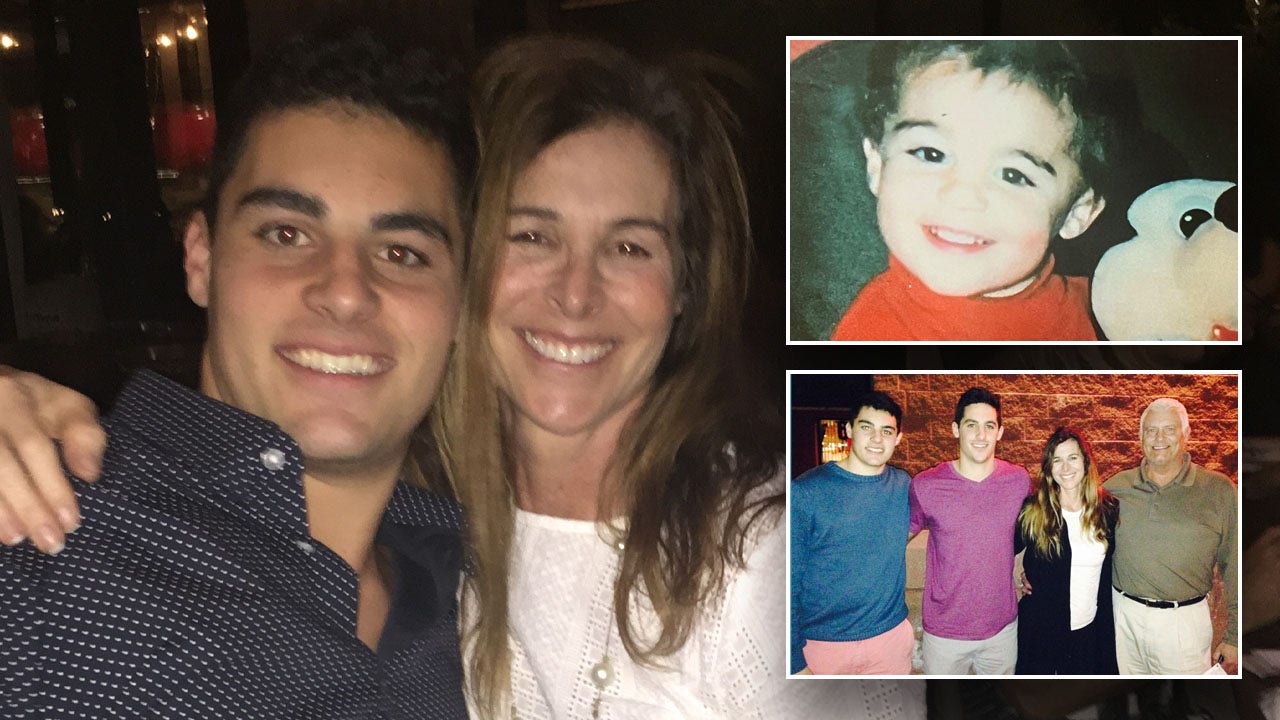
Derek McFadden was just 23 when he took his own life on Aug. 17, 2018, in Tucson, Arizona.
His mother, Robin McFadden, who lives in Tuxedo Park, New York, said she believes her son’s insomnia was the “only driver” of his suicide.
SLEEP DISORDERS AND SUICIDE: A MENTAL HEALTH EXPERT REVEALS THE CONCERNING LINK
Derek McFadden was an “extremely funny kid” who loved swimming, snow-skiing and cuddling, his mother said — but for most of his life, he struggled with debilitating insomnia.
At around 8 years old, he started taking small doses of sleeping medication, which helped for several years.
Derek McFadden, pictured at left with his mom Robin McFadden, was 23 when he took his own life on Aug, 17, 2018, in Tucson, Arizona. (Robin McFadden)
Around the time he turned 18, during his senior year of high school, the medication stopped working, McFadden said.
“He never got a good night’s sleep, but he soldiered through his school day and then would come home and lie down on his bed, exhausted, but couldn’t fall asleep,” she told Fox News Digital in an interview.
SUICIDE WARNING SIGNS ARE MISSED BY MOST AMERICANS, NEW SURVEY FINDS: IT’S ‘ALARMING’
McFadden took her son to multiple doctors and they tried different medications — none of which worked, she said.
“Derek would just lie there at night, and he was so tired, but he couldn’t fall sleep,” she said.
Amid the sleep struggles, her son managed to graduate from high school — but things got even worse when he left for college at the University of Arizona.
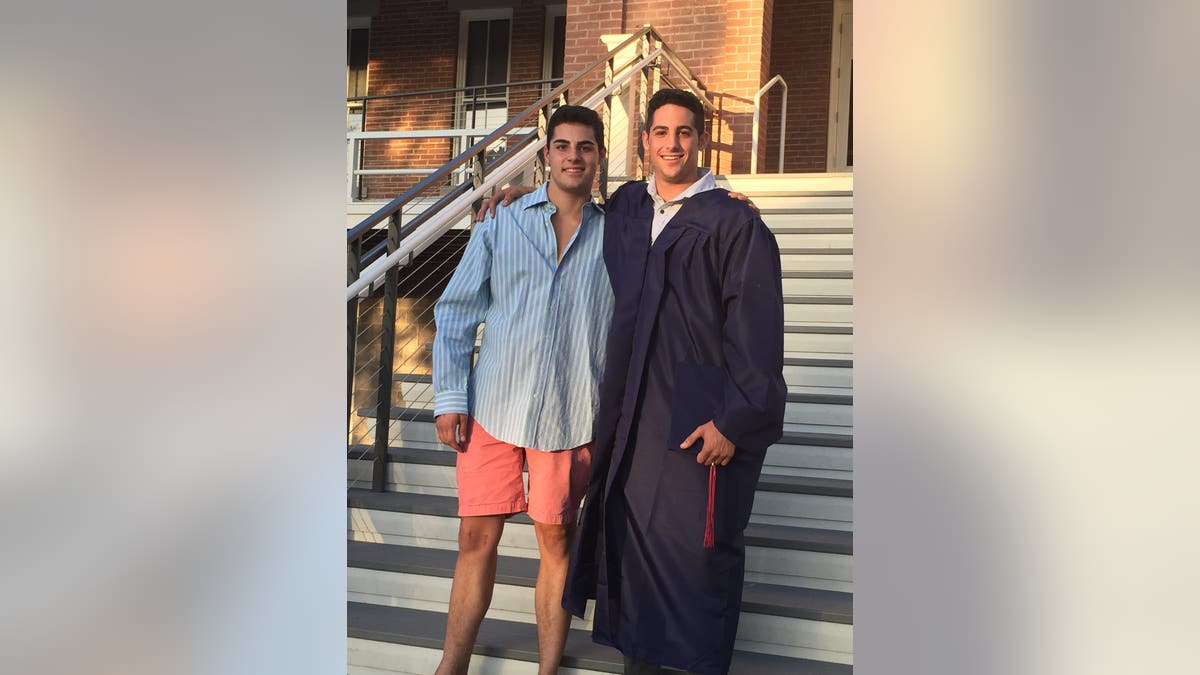

Derek McFadden, left, is pictured with his older brother Jake McFadden. (Robin McFadden)
He’d chosen Arizona because he was an “avid outdoorsman” who loved fly-fishing, going off-roading in his Jeep and spending time with his dog, which he’d adopted for emotional support.
“Our hope was that with Derek being in Arizona, the sunshine during the day would stimulate his brain to wake up so he could go to sleep at night, but it just didn’t work,” McFadden said.
The doctor’s visits continued, but none of the experts could figure out what was causing the insomnia.
“There was something wrong in his brain that was preventing him from sleeping.”
“Every doctor would assume it was sleep hygiene, and that he was doing something wrong,” McFadden said.
AMERICANS NEED MORE SLEEP, LESS STRESS, EXPERTS SAY, AS GALLUP POLL REVEALS TROUBLING FINDINGS
“They assumed that because he was 18, 19 or 20 years old that he was playing video games all night.”
She added, “But Derek knew sleep hygiene. He had done so much research on his own. There was something wrong in his brain that was preventing him from sleeping.”
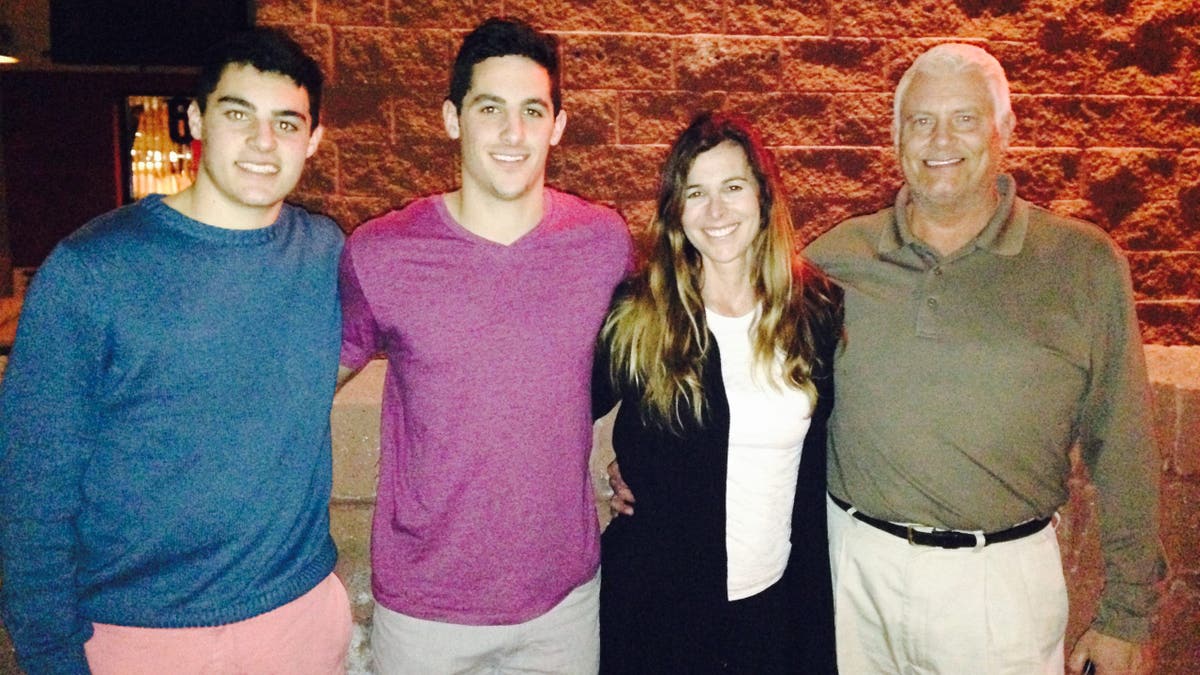

Derek McFadden, far left, is pictured with his brother, mother and father. (Robin McFadden)
The family looked into holistic approaches, including hypnosis, acupuncture and “brain training,” but “nothing seemed to work,” McFadden said.
Many nights, he would go the entire night without sleeping — sometimes up to three days in a row, she said.
“It was really, really bad,” McFadden said.
Physical and mental toll
As the months went by and sleep continued to elude her son, McFadden said it began to take a toll on his immune system.
After consecutive nights without sleeping, he developed bruises all around his eyes.
SUICIDE RATES REACH ALL-TIME HIGH IN US, PER CDC DATA
“Derek was constantly getting sick, and that made him feel like he was not a normal kid,” she said. “He just couldn’t fight anything off. He was always at Urgent Care.”
Her son developed severe acid reflux and stomach pain, to the point where it became difficult for him to eat.
“Sometimes his insomnia got so severe that he couldn’t keep any food or fluids down at all,” McFadden said.
Multiple times, he ended up in the emergency room with dehydration and severe cramping, she said.

Derek was an “avid outdoorsman” who loved fly-fishing, going off-roading in his Jeep and spending time with his dog, which he’d adopted for emotional support, his mother said. (Robin McFadden)
The lack of sleep also changed her son’s demeanor and personality, McFadden said.
“Derek had tremendous mood swings — he became anxiety-ridden and depressed,” she recalled.
“He would have hallucinations, and was constantly losing things. He couldn’t think clearly.”
On the rare occasion that her son had a good night’s sleep, McFadden said, he was “a completely different person, as happy as could be.”
IMPROVE YOUR SLEEP BY OPTIMIZING 6 BIOMARKERS: ‘INTEGRAL TO HEALTH’
“It broke my heart, because he was such a happy, funny, huge-hearted person, and it was really sad to watch his decline.”
Unable to keep up with his studies, her son had to drop out of college.
“He couldn’t even hold a job because he couldn’t sleep at night,” McFadden said.
“He saw there was no cure, no future, and he just didn’t see a point in going on.”
In July 2018, when her son came home from Tucson for the summer, McFadden knew something had shifted.
“We were sitting on the sofa and he said to me, ‘Mom, I’m gonna die young,’” she recalled.
“And I said, ‘Derek, why do you say that?’ And he said, ‘Because my mind and body can’t take the sleep deprivation.’”
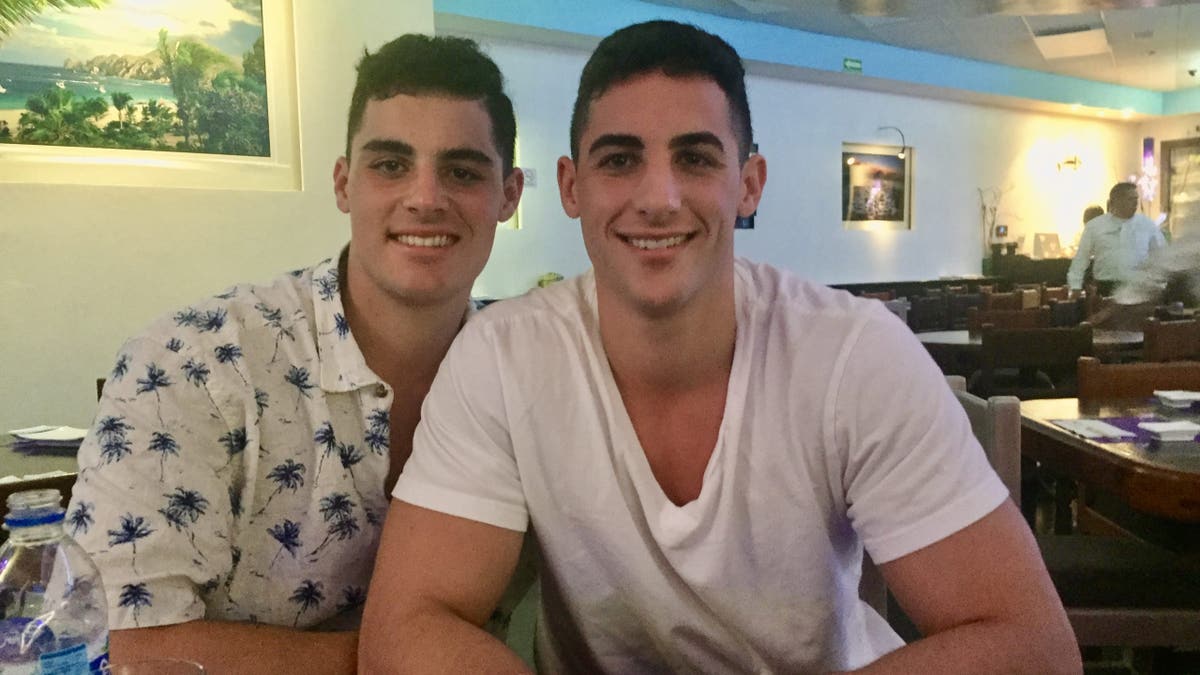

Derek McFadden, left, is pictured with his older brother. After the tragedy, his mother said she realized her son had likely been planning his suicide in recent weeks. (Robin McFadden)
Her son had also expressed that he didn’t want to have children because he didn’t want to pass on the disorder, McFadden said.
“He saw there was no cure, no future, and he just didn’t see a point in going on,” she said. “Physically, he was starting to fall apart, and mentally, his cognitive ability was going.”
“Physically, he was starting to fall apart.”
Four weeks later, McFadden got an early-morning call from the Tucson Police Department notifying her that her son had taken his life.
After the tragedy, McFadden realized that her son had likely been planning his suicide in recent weeks.
FOR QUALITY SLEEP, TIMING IS EVERYTHING, EXPERTS SAY: HERE’S THE SECRET OF SUCCESSFUL SLUMBER
“He had contacted some old friends, and in his text messages and phone calls, he sounded very serene, relieved and calm,” she recalled. “I truly believe Derek had made the decision. He just saw no future for himself.”
The sleep-suicide link
Studies have suggested a likely connection between sleep and suicide.
Research published in the journal Current Psychiatry Reports found that treating insomnia and nightmares, or addressing the source of those issues, could help prevent “the rising threat of suicide.”
“Sleep is crucial for emotional and psychological balance.”
Dr. Brett Osborn, a Florida neurologist and longevity expert with the firm Senolytix, said there is a “significant body of research” suggesting a link between sleep deprivation and an increased risk of suicide.
“Sleep is crucial for emotional and psychological balance,” he told Fox News Digital in an interview.
“Lack of sleep can lead to mood disturbances, irritability and decreased stress tolerance, all of which can worsen feelings of despair or depression — potentially leading to suicidal thoughts.”
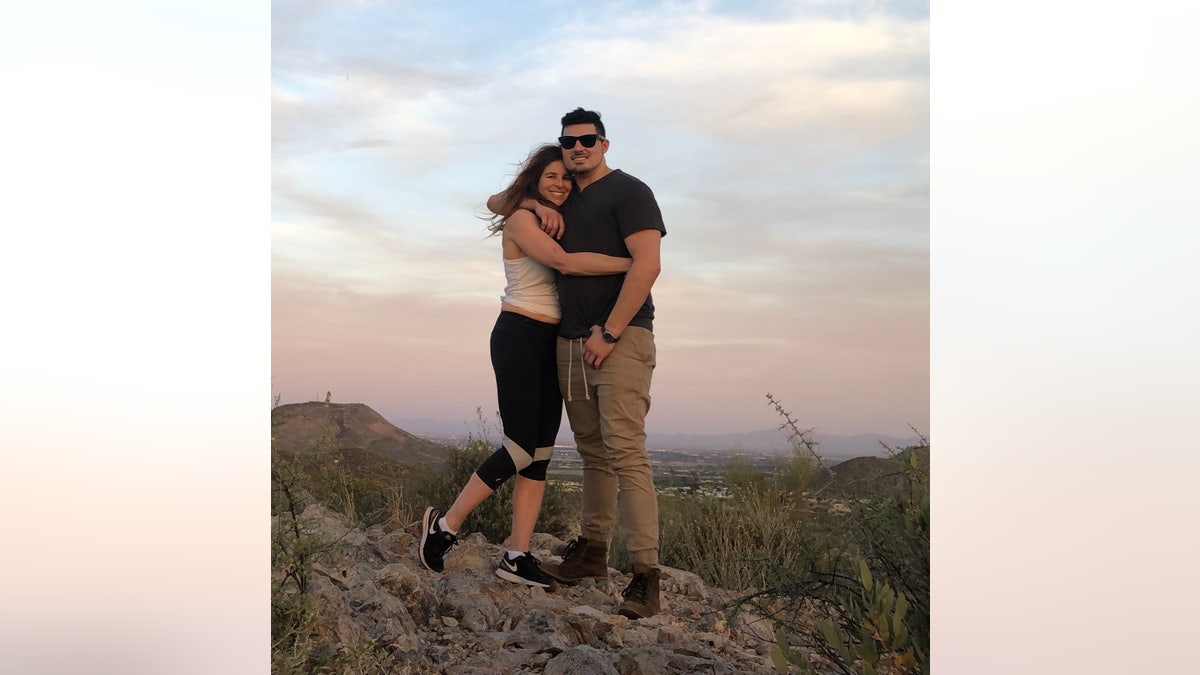

On the rare occasion that her son had a good night’s sleep, McFadden said, he was “a completely different person, as happy as could be.” Derek McFadden is pictured here with his mother, Robin McFadden. (Robin McFadden)
Sleep deprivation can also affect cognitive functions, the doctor continued.
“This impairment can make it harder for individuals to see alternative solutions to problems or seek help, potentially increasing the risk of suicidal behavior,” he said.
LACK OF SLEEP COULD BE A FACTOR IN A ‘SILENT EPIDEMIC,’ EXPERTS WARN
Sleep problems are also commonly associated with psychiatric disorders, such as depression and anxiety, which are themselves significant risk factors for suicide, according to Osborn.
“Sleep pathology is extremely complex and challenging, because sleep itself is poorly understood.”
“Insomnia and disrupted sleep patterns are particularly prevalent in these conditions,” he warned. “This can be a source of diagnostic confusion and resultant treatment errors.”
Sleep also affects various biological processes, Osborn noted — “including the regulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin (which is involved in mood regulation) and stress hormones like cortisol.”
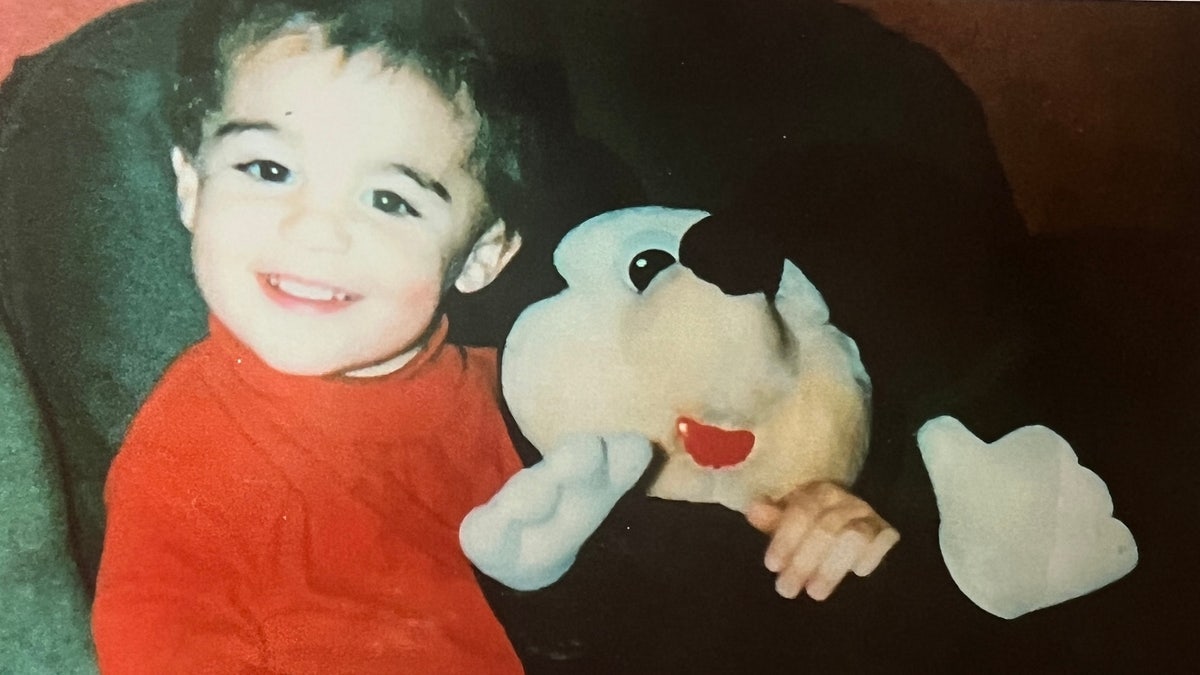

Derek McFadden was an “extremely funny kid” who loved swimming, snow-skiing and cuddling, his mother said. (Robin McFadden)
“Chronic sleep deprivation may lead to dysregulation in these systems, which could contribute to depressive symptoms and suicidal ideation.”
While the majority of insomnia patients respond to lifestyle changes and/or medications, Osborn noted, there is a subset of patients who are “more difficult to manage.”
“Often, there are underlying medical problems, like reflux, that fly under the radar and predispose the individual to insomnia,” he told Fox News Digital.
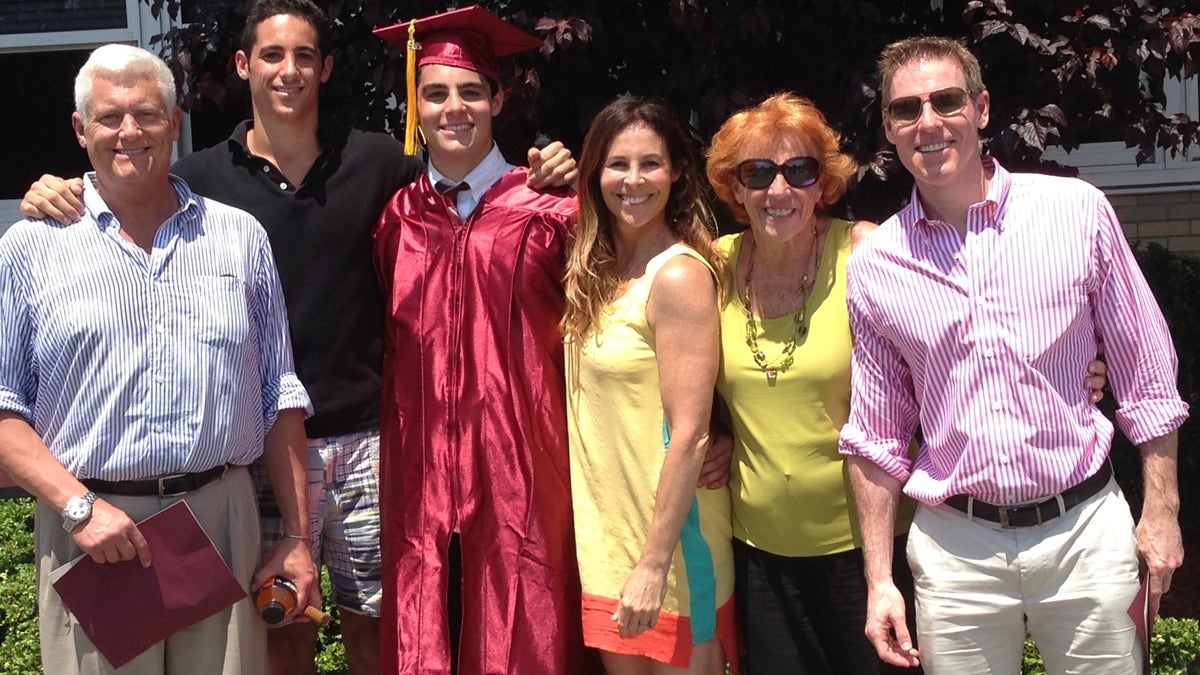

Derek McFadden, center, in cap and gown, is pictured with his family at his high-school graduation. (Robin McFadden)
“Another issue is the potentially reciprocal relationship between depression and anxiety,” Osborn said.
“Sleep pathology is extremely complex and challenging, because sleep itself is poorly understood,” he continued. “A multimodal, interdisciplinary approach — involving a psychiatrist and a sleep specialist — is always best.”
SURPRISING SLEEP TRENDS REVEALED IN NEW SURVEY, INCLUDING THE RISE OF ‘SCANDINAVIAN SLEEPING’
Dr. Marc Siegel, clinical professor of medicine at NYU Langone Medical Center and a Fox News medical contributor, agreed that there is a proven link between insomnia, stress, anxiety and depression.
“Since suicide is a manifestation of severe depression, I think there is a link there, too, though insomnia wouldn’t be the entire cause,” he told Fox News Digital.
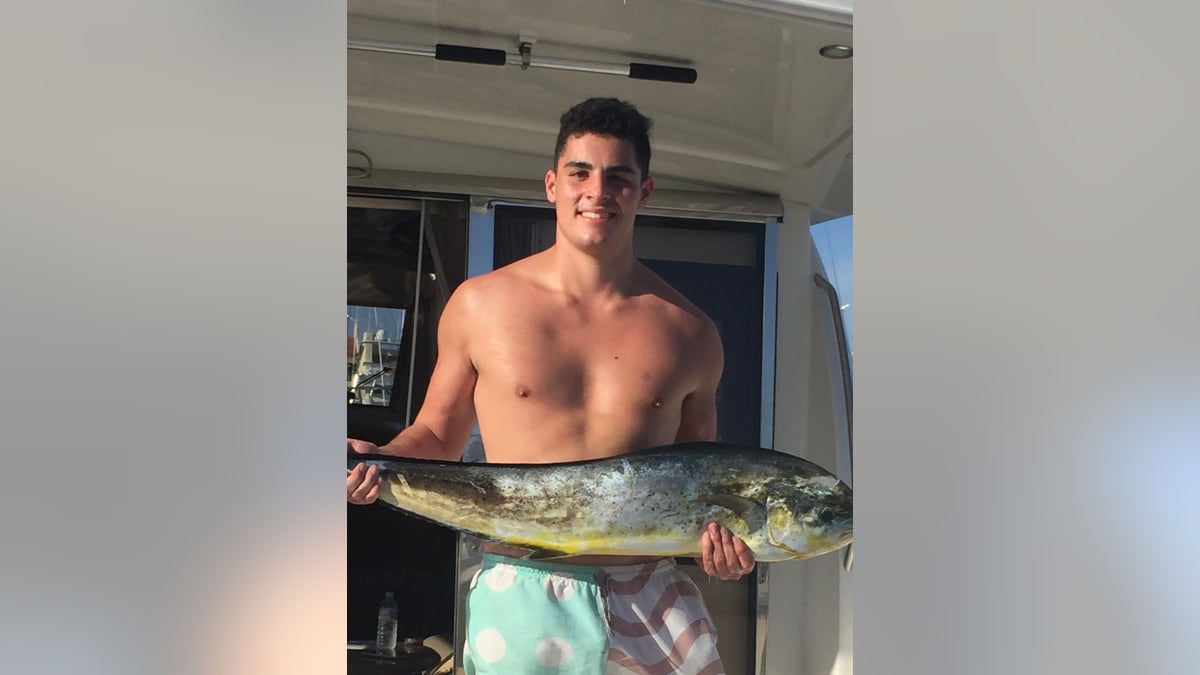

Fly-fishing was one of Derek McFadden’s favorite hobbies. (Robin McFadden)
Siegel refers to it as a “cycle of worry.”
“Anxiety interferes with sleep, which then makes you more anxious and more sleepless, especially if you add caffeine to combat the grogginess,” he said.
During sleep, the brain relaxes and “cleanses” itself, Siegel said.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“Waking up refreshed can improve mood, especially when accompanied by exercise,” he noted.
For those with severe insomnia, Siegel recommends undergoing a full sleep study/evaluation — typically with an EEG or video monitoring — to help determine the causes.
“Severe, resistant cases require evaluations by sleep specialists, neurologists and psychiatrists,” he added.
Call for awareness
The most “disheartening” part of her son’s tragedy, according to McFadden, was a lack of support from the health community, in her view.
“Other than sleep apnea and bad sleep hygiene, the medical community does not seem to believe that severe insomnia really exists,” she told Fox News Digital.
“And that just infuriates me.”
Today, McFadden’s goal is to raise awareness of chronic insomnia — “because there are so many people in this world who are suffering from this.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
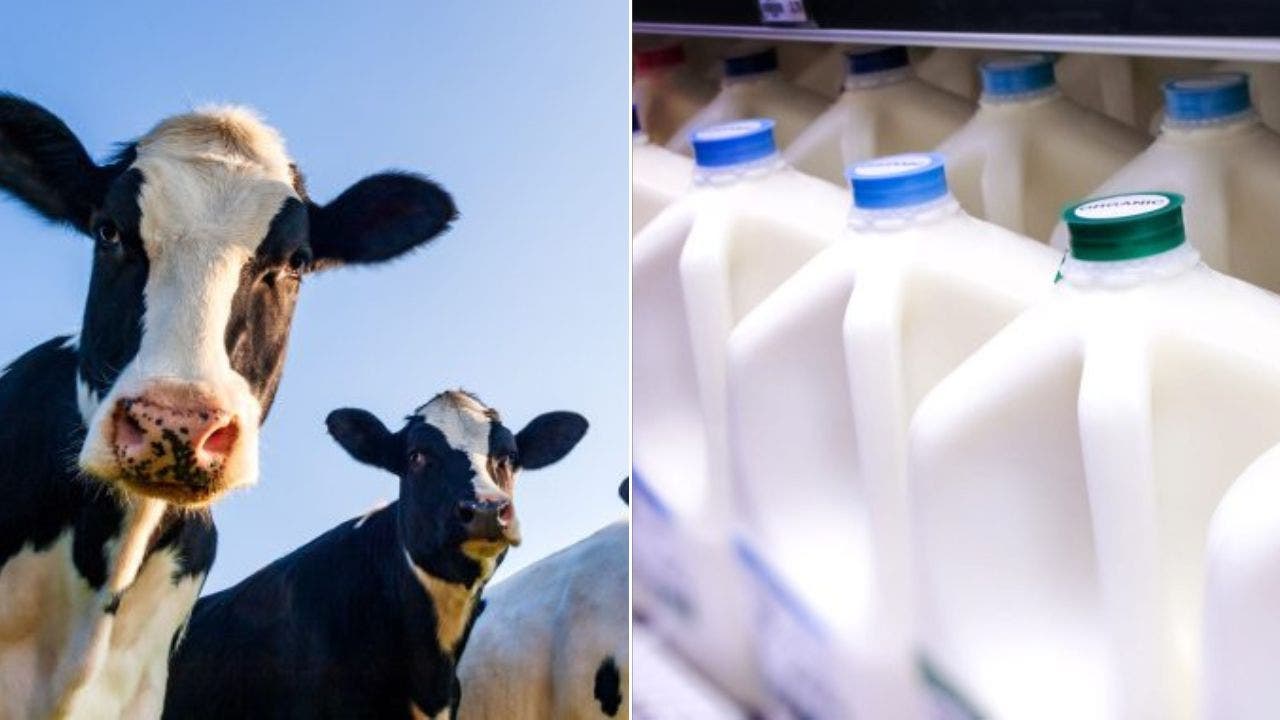
Bird flu virus found in grocery store milk, but no risk to customers, FDA says

CDC issues alert over bird flu case
Fox News medical contributor Dr. Marc Siegel on what to know about bird flu and why it is important to not look directly at the solar eclipse without proper glasses
Samples of pasteurized milk on grocery store shelves have tested positive for remnants of the bird flu virus that has already infected herds of dairy cows, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) said Tuesday.
The FDA stressed that the material is inactivated and that the findings “do not represent [an] actual virus that may be a risk to consumers.” Officials added that they’re continuing to study the issue.
Bird flu virus, known as Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) or H5N1, is a disease that is highly contagious and often deadly in poultry.
Infection with the virus causes decreased lactation, low appetite and other symptoms in affected cattle, the FDA says.
CDC ISSUES BIRD FLU HEALTH ALERT TO CLINICIANS, STATE HEALTH DEPARTMENTS, PUBLIC AFTER TEXAS FARMER INFECTED
The FDA says pasteurized milk on grocery store shelves has tested positive for remnants of the bird flu virus, but there is no risk to customers’ safety. (iStock)
The FDA and U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) said that commercial milk supply is safe because of the pasteurization process.
The pasteurization process involves killing harmful bacteria and viruses by heating milk to a specific temperature for a set period of time to make milk safer. Federal regulations require milk that enters interstate commerce to be pasteurized.
“The pasteurization process has served public health well for more than 100 years,” the FDA said. “Even if [the] virus is detected in raw milk, pasteurization is generally expected to eliminate pathogens to a level that does not pose a risk to consumer health.”
“To date, we have seen nothing that would change our assessment that the commercial milk supply is safe.”
Pasteurization is different from complete sterilization, which extends shelf life but is not required to ensure milk safety, the agency said.
Officials with the FDA and the USDA had previously said milk from affected cattle did not enter the commercial supply. Milk from sick animals is supposed to be diverted and destroyed.
FDA officials did not indicate how many samples they tested or where they were obtained. The agency has been evaluating milk during processing and from grocery stores, officials said. Results of additional tests are expected in “the next few days to weeks.”
The PCR lab test the FDA used would have detected viral genetic material even after a live virus was killed by pasteurization or heat treatment, Lee-Ann Jaykus, an emeritus food microbiologist and virologist at North Carolina State University told the Associated Press.
AVIAN INFLUENZA: SYMPTOMS OF THE DISEASE AND HOW IT AFFECTS BIRDS AND HUMANS
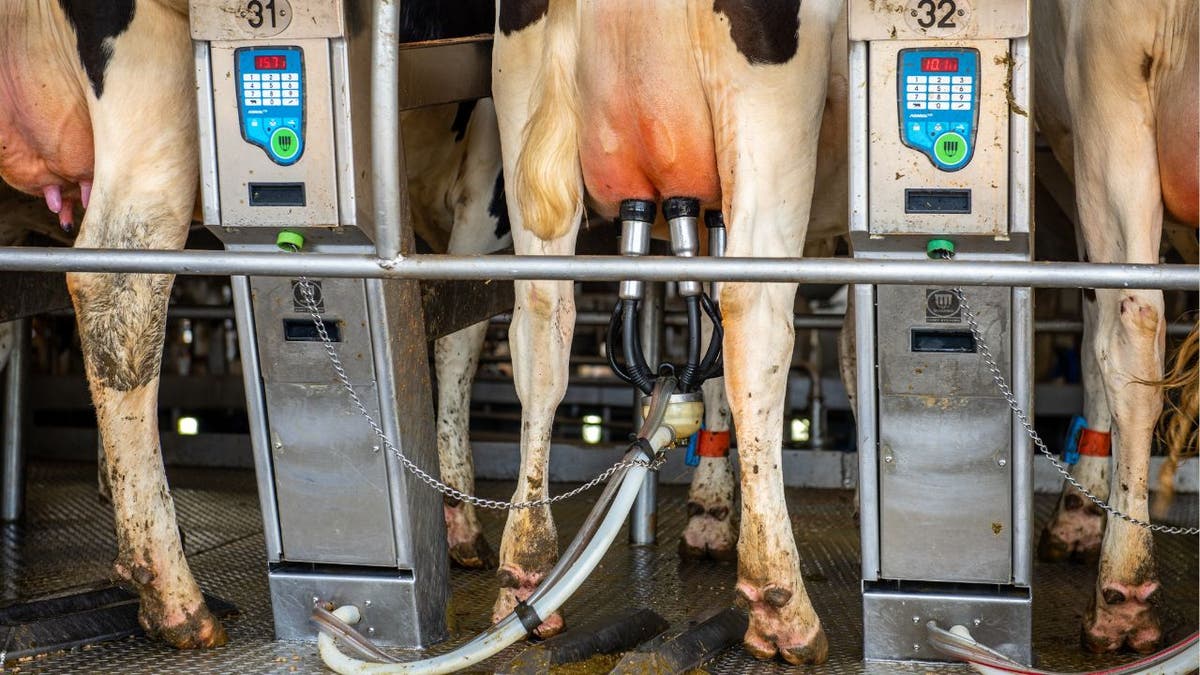

Cows being milked while riding a slowly-moving carousel. (Edwin Remsberg/VW Pics/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
“There is no evidence to date that this is [an] infectious virus and the FDA is following up on that,” Jaykus said.
Scientists confirmed the H5N1 virus in dairy cows in March after weeks of reports that cows in Texas were suffering from a mysterious malady.
The FDA says HPAI has now been confirmed in domestic livestock in 33 herds across eight states: Idaho, New Mexico, Texas, South Dakota, Kansas, Michigan, Ohio, and North Carolina.
While the virus is lethal to commercial poultry, most infected cattle seem to recover within two weeks, experts say.
The National Milk Producers Federation (NMPF) echoed the FDA’s assertions that pasteurization is effective against HPAI and that commercial milk supply is safe.
“Viral fragments detected after pasteurization are nothing more than evidence that the virus is dead; they have zero impact on human health,” the NMPF said in a statement.
“Further, the federal PMO prohibits milk from sick cows from entering the food supply chain. Milk and milk products produced and processed in the United States are among the safest in the world.”
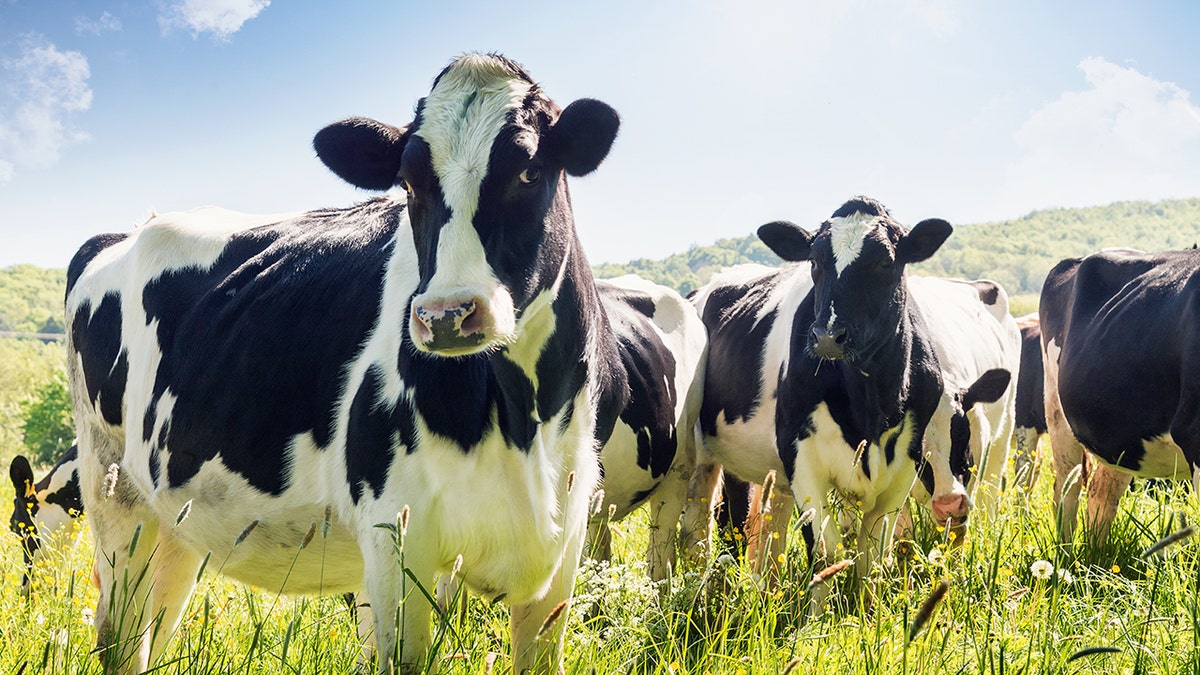

Bird flu virus has been found in samples of pasteurized milk on grocery store shelves but there is no risk to customers, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) said Tuesday. (iStock)
The news comes after a goat in Minnesota tested positive HPAI in February, which marked the first U.S. case of bird flu in domestic cattle, sheep, goats or their relatives.
CLICK HERE FOR THE FOX NEWS APP
The positive juvenile goat was residing on a Stevens County farm that already had bird flu infected poultry, according to the Minnesota Board of Animal Health.
To date, two people in the U.S. have been infected with bird flu. A Texas dairy worker who was in close contact with an infected cow earlier this year developed “eye redness” and has recovered, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
In 2022, a prison inmate in a work program caught it while killing infected birds at a Colorado poultry farm. His only symptom was fatigue and he also recovered.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job
-
 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: The American Society of Magical Negroes
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoGOP senators demand full trial in Mayorkas impeachment
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoFilm Review: Season of Terror (1969) by Koji Wakamatsu
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCroatians vote in election pitting the PM against the country’s president
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago'You are a criminal!' Heckler blasts von der Leyen's stance on Israel
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump trial: Jury selection to resume in New York City for 3rd day in former president's trial
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoPon Ondru Kanden Movie Review: This vanilla rom-com wastes a good premise with hasty execution

:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/adn/UJL6GONUKFFJ5PYB6FO5EUVHMY.jpg)













