World
Sea changes: How NATO’s expansion could stabilise the Baltic region

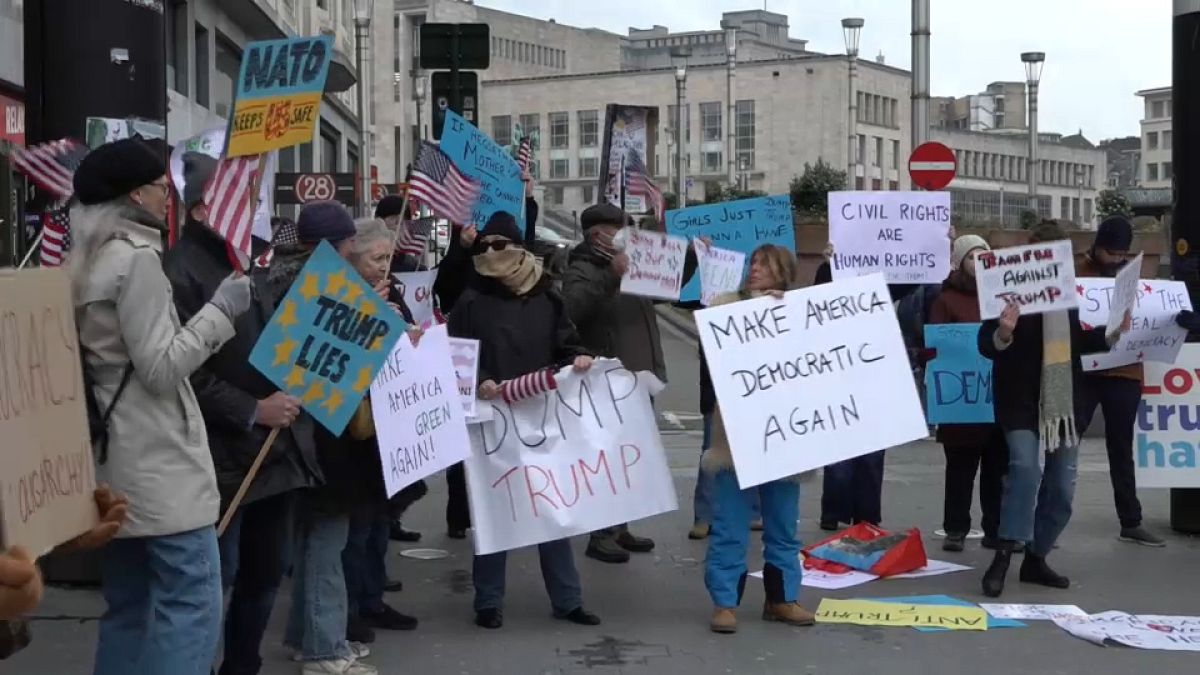
Train Hedgehog might need been deliberate lengthy earlier than Russian troops invaded Ukraine, however the big struggle video games going down this month in Estonia are a prickly reminder of NATO readiness simply 64km from the closest Russian base.
“Each prick counts, as all the time,” one Estonian reserve soldier who’s at present collaborating in Train Hedgehog, informed Euronews.
Some 15,000 NATO army personnel from 14 nations are concerned within the train, one of many largest of its variety since Estonia gained independence for the second time, in 1991.
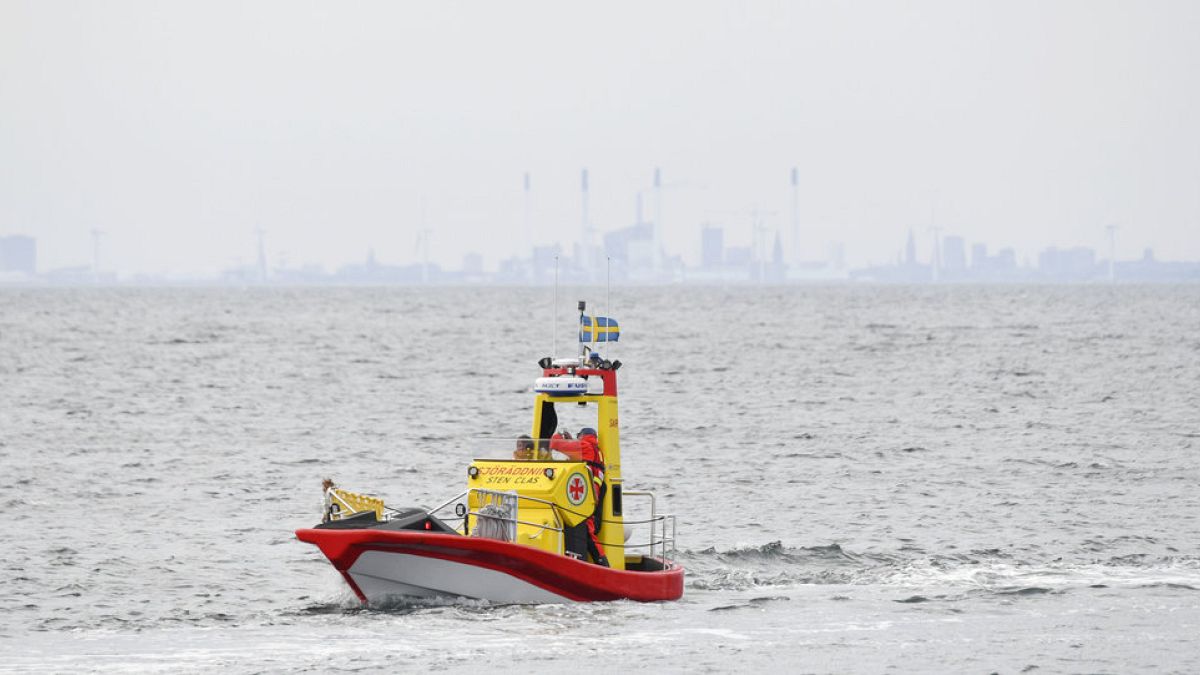
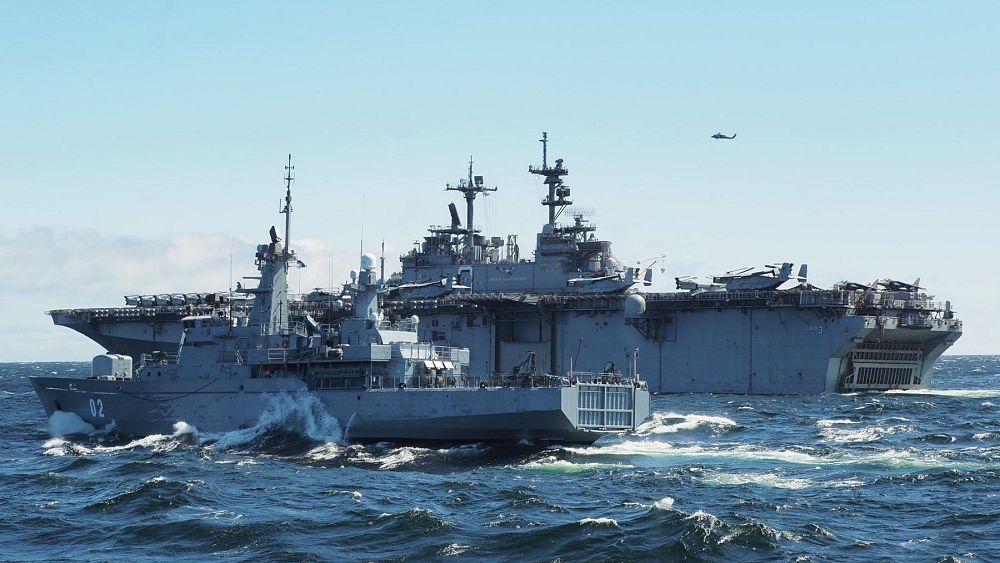
Offshore, there is a sturdy naval presence as properly, with a US Navy Wasp-class amphibious assault vessel, a guided missile destroyer, and a touchdown ship.
Importantly, the Finnish and Swedish navies are additionally collaborating — an image of what the modified safety paradigm may seem like within the Baltic Sea if and when each nations are admitted to NATO. The Finns are even throwing in some anti-ship missile reside firing coaching from the south coast, in case anybody did not get the message.
There is not any doubt that the governments of the three Baltic States see the intrinsic of getting Finland and Sweden as members of NATO.
“Once we see that in our neighbourhood additionally different democratic nations belong to NATO, it might imply that we may have broader joint workout routines and likewise … extra defence cooperation,” Estonia’s Overseas Minister Eva-Maria Liimets informed reporters not too long ago.
Liimets mentioned that Estonia appreciates NATO imposing its presence within the Baltic area, however would love the allies to maneuver from enhancing their presence to enhancing their defence.
“It could imply that we’d have extra sturdy presence of land forces, but additionally air and maritime defence,” she added.
Turning into a NATO sea
The Baltic Sea will quickly grow to be a NATO sea, says Glen Grant, a defence knowledgeable on the Baltic Safety Basis in Riga.
“I see the Baltic Sea space as a typical operational area, however I see the Baltic States cooperation, Nordic defence cooperation, NATO reinforcement within the Baltic States, US agreements with Finland and Sweden, all as components of a jigsaw however lacking a single operational image and focus.”
Finland and Sweden turning into a part of NATO will put a number of extra items of the jigsaw puzzle in place however there additionally must be extra operational coherence within the area, and the important thing gamers should additionally take the Baltic extra critically, Grant provides.
“NATO thinks about deterrence with additional troops and about reinforcement or regaining floor – after the occasion. While the EU has no seen regional coverage in any respect. Thoughts, I counsel that it has no correct army coverage for wherever. Who pulls the regional strings to reply coherently within the early levels of a disaster is in no way clear,” says Grant, a former British army officer and Defence Attaché on the British Embassies in Helsinki and Riga.
Trying on the complete Baltic area safety image
Martin Harm on the Worldwide Centre for Defence and Safety ICDS in Tallinn explains that Moscow has definitely seen Sweden and Finland as being a part of the West for the reason that mid-90s and that in any struggle, they have been prone to help NATO.
He additionally sees NATO membership for the Nordic neighbours as serving to to finish the general safety image of the area — on land, at sea and within the air — enhancing safety within the spherical, an improve from the present state of affairs.
“Right this moment if we take a look at NATO’s operation planning, we can not depend on Sweden and Finland. In our planning, they don’t exist as a result of we can not depend on them, on utilizing their airspace, water and land. Now we have to plan with what we are able to belief, which is our personal allies,” he tells Euronews.
“It could make a huge effect if particularly Sweden, but additionally Finland, would be a part of.”
One of many key drive multipliers the 2 applicant nations convey to the desk is their naval capabilities.
Though Finland is prohibited by treaty from having submarines, Sweden does preserve its personal submarine fleet. The Finns have intensive expertise in minesweeper actions, and each nations have in-shore patrol boats with experience working within the shallow archipelago waters, strewn with 1000’s of tiny islands and rocky outcrops.
“Within the Baltic states, the navies are comparatively weak and specializing in minor countermeasures. It is not a major struggle preventing functionality after all. The Finnish and Swedish navies are stronger. They’ve extraordinarily good high quality, not good amount, however nonetheless way more than Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania mixed,” explains Hurst.
That target Baltic naval capabilities is vital as a result of the opposite regional naval powers Germany, Norway and Denmark are wanting in the direction of the North Atlantic, to maintain key traces of communication open fairly than being accessible for Baltic Sea defence.
And whereas Poland does have a navy, the federal government has targeted extra on land and air capabilities.
“For Poland, the maritime area has not been precedence primary,” says Martin Hurst.
Working with the Russians
So if the Baltic Sea turns into a de facto NATO sea, as Glen Grant says, does that squeeze the Russians with their fleets in St. Petersburg and the Kaliningrad exclave?
In army phrases, there may not be a lot — or any — cooperation, however there’s nonetheless common contact within the area with Russia in terms of maritime safety and security too.
“In fact, we’ve to have the ability to contact our neighbours in case of emergency and thus far after all they’re keen to make the cooperation primarily based on maritime agreements,” says Commander Mikko Simola, Head of Maritime Security on the Finnish Border Guard.
Previously, there have been common workout routines involving the Russians — the newest was in November 2021 — to follow coordinated rescue efforts in case a passenger ship will get in misery within the Baltic Sea; or to cooperate in containment and clean-up operations within the occasion of a spill from a cargo ship.
“The connection in follow takes place between the Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre in St. Petersburg, and Helsinki on our facet main the security operations within the Gulf of Finland,” Simola tells Euronews.
So may Russia lower off the sort of important Baltic Sea contacts in the event that they really feel threatened by NATO’s elevated presence within the Baltic Sea? Commander Simola says he thinks that is unlikely, particularly since Russia is a celebration to worldwide agreements on maritime search and rescue, in addition to bilateral Finnish-Russian agreements.
“I do not personally see a direct reference to becoming a member of NATO for that, ” says Simola.
“The neighbouring areas must cooperate if there’s a want to save lots of lives.”

World
Kelsey Grammer Slams Paramount+ for Frasier Cancellation: ‘They Didn’t Really Promote It’

ad
World
Pope Francis in stable but 'guarded' condition, according to Vatican

Pope Francis’ condition remained stable and “guarded” Thursday, a day when the pontiff did not have difficulty breathing and remained fever-free.
The pope had a “good night” and continued physical therapy at Rome’s Gemelli hospital for his third week of treatment for double pneumonia, the Vatican said Thursday.
“Today, the Holy Father dedicated himself to some work activities during the morning and afternoon, alternating rest and prayer,” the Vatican said. “Before lunch, he received the Eucharist.”
The next update will come Saturday, the Vatican said, because of his stable condition.
CHRISTIANS USE HALLOW APP’S PRAY40 CHALLENGE AMONG OTHER TRADITIONAL WAYS TO GROW CLOSER TO GOD AS LENT BEGINS
Pope Francis waves from the central loggia of St. Peter’s basilica during the Easter ‘Urbi et Orbi’ message and blessing to the City and the World as part of the Holy Week celebrations, in the Vatican on March 31, 2024. (Tiziana Fabi/Pool/AFP/Getty)
“The night passed quietly; the Pope is still resting,” the Holy See press office said earlier Thursday, adding that the Pope’s “clinical condition has remained stable for the last couple of days, and his doctors say he has not had more episodes of respiratory insufficiency.”
The 88-year-old pope, who has chronic lung disease and had part of one lung removed as a young man, has been stable for two days after suffering a pair of respiratory crises on Monday. Doctors underlined that his prognosis remained guarded due to the complex picture.
In recent days, he has been sleeping with a non-invasive mechanical mask to guarantee that his lungs expand properly overnight and help his recovery. He has been transitioning to receiving oxygen with a nasal tube during the day.
The pope on Wednesday marked the start of Lent by receiving ashes on his forehead and by calling the parish priest in Gaza, the Vatican said. He also added physical therapy to his hospital routine of respiratory therapy.
The Catholic Church opened the solemn Lenten season without the pope’s participation. A cardinal took his place leading a short penitential procession between two churches on the Aventine Hill and opened an Ash Wednesday sermon prepared for the pontiff with words of solidarity and thanks.
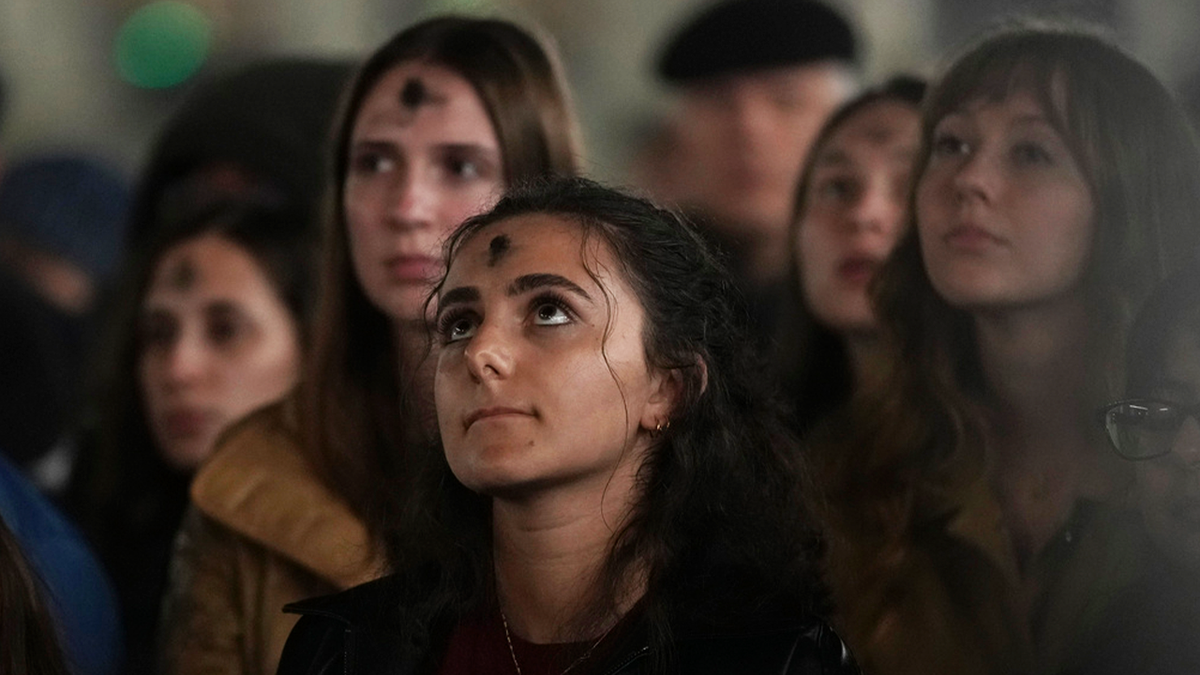

Girls, with ashes on their foreheads, pray during a rosary prayer for Pope Francis’ health in St. Peter’s Square at the Vatican, Wednesday, March 5, 2025. (AP Photo/Alessandra Tarantino)
On Ash Wednesday, observant Catholics receive a sign of the cross in ashes on their foreheads, a gesture that underscores human mortality. It is an obligatory day of fasting and abstinence that signals the start of Christianity’s most penitent season, leading to Easter on April 20.
The pope was supposed to attend a spiritual retreat this weekend with the rest of the Holy See hierarchy. On Tuesday, the Vatican said the retreat would go ahead without Francis but in “spiritual communion” with him. The theme, selected before Francis got sick, was “Hope in eternal life.”
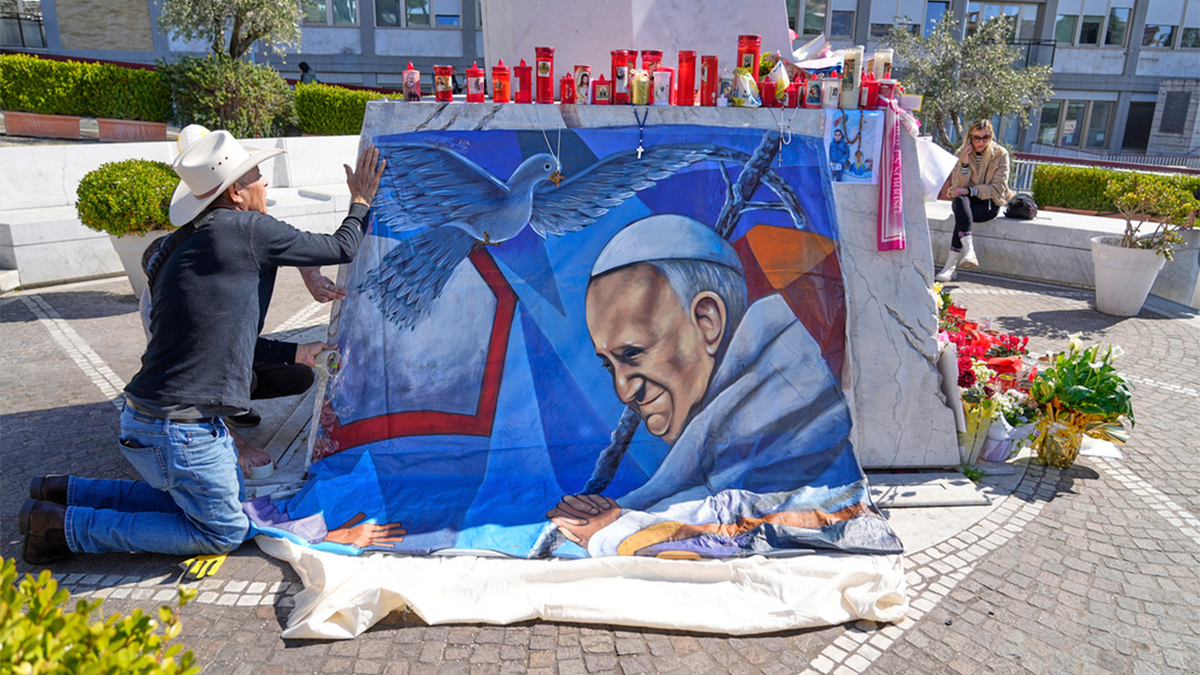

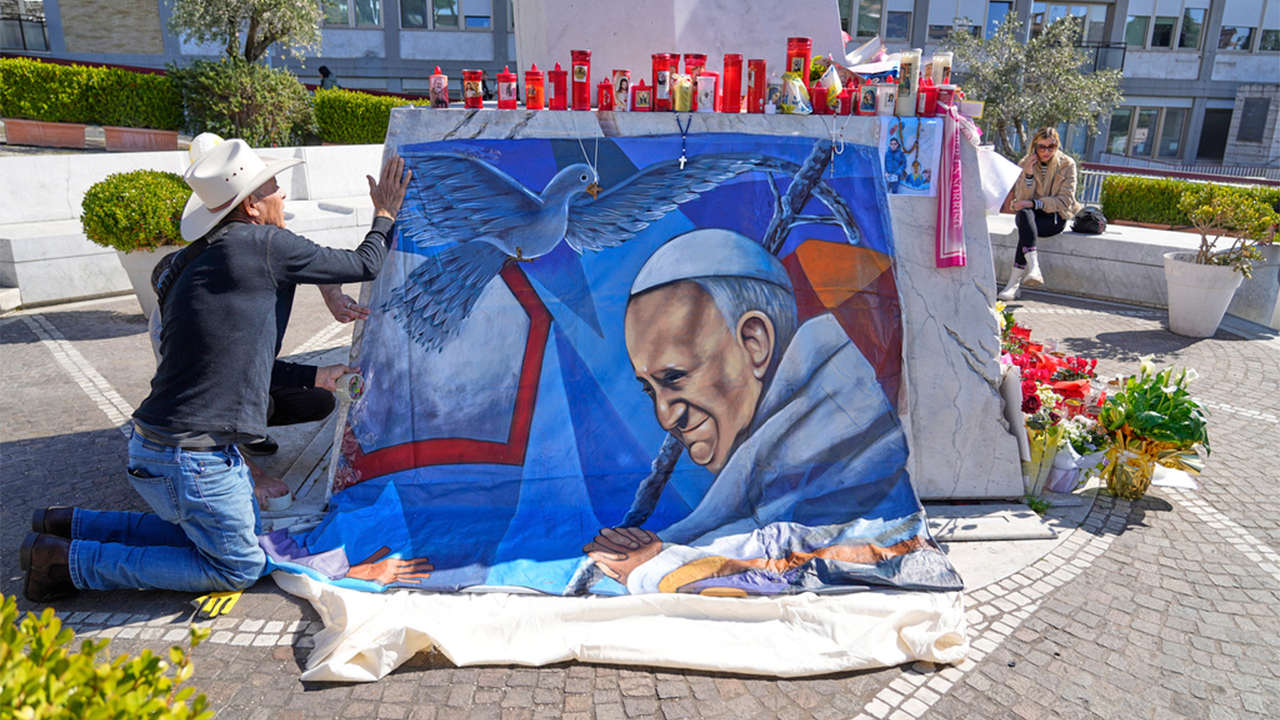
Mexican painter Roberto Marquez places a painting of Pope Francis he made outside the Agostino Gemelli hospital in Rome on Ash Wednesday. (AP Photo/Gregorio Borgia)
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
World
Trump again spreads baseless claims about Trudeau, Canada’s election

US president accuses outgoing Canadian prime minister of seeking to use issue of tariffs to extend his time in office.
United States President Donald Trump has reiterated baseless claims that outgoing Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau is seeking to use US tariffs against Canada to extend his time in office, as a rift widens between the two countries.
In a social media post on Thursday, Trump said he believed Trudeau “is using the Tariff problem, which he has largely caused, in order to run again for Prime Minister”.
“So much fun to watch!” the US president wrote.
The remark follows a similar post Trump shared on his Truth Social website on Wednesday, accusing Trudeau of using trade tensions as a way “to stay in power”.
“He was unable to tell me when the Canadian Election is taking place, which made me curious, like, what’s going on here? I then realized he is trying to use this issue to stay in power. Good luck Justin!” Trump wrote.
Tensions have soared between the two leaders since Trump first threatened late last year to impose steep tariffs on Canadian goods if Trudeau’s government did not do more to stem irregular migration and drug trafficking over its border with the US.
This week, the Trump administration followed through on its plans and imposed 25-percent tariffs on most Canadian imports, as well as 10-percent levies on oil and gas.
Canada responded by announcing it would be implementing 25-percent tariffs against $106bn (155 billion Canadian) worth of US goods. Tariffs on $21bn (30 billion Canadian) came into immediate effect on Tuesday.
“This is a very dumb thing to do,” Trudeau told reporters on Tuesday of the US measures, which he described as an unjustified “trade war against Canada”.
Trudeau, who has been Canada’s prime minister since 2015, is set to step down as leader of the governing Liberal Party after it chooses its next leader on Sunday.
The new leader is expected to assume the duties of prime minister after a short transition period.
Asked during a news conference on Thursday whether he would consider staying on as prime minister in a caretaker role to help manage the uncertainty surrounding US tariffs, Trudeau said: “No. I will not be.”
He added, “I look forward to a transition to my duly elected successor in the coming days or week.”
Meanwhile, some experts in Canada have said Trump’s attack on Trudeau underscores his ignorance of the country’s political system.
Stewart Prest, a political science professor at the University of British Columbia, said on social media that the US president’s remarks represent “a reckless disregard for the Canadian democratic system”.
“To be clear, Trudeau will step aside after the Liberal leadership race,” Prest wrote on the social media platform Bluesky on Wednesday.
Under Canadian electoral rules, the next federal election must be held by October 20.
But the Liberals, as the party in government, can choose to trigger a vote before then.
An election could also be called earlier if opposition parties pass a vote of no confidence in Canada’s Parliament, which is set to resume on March 24.
As it currently stands, no election date has been formally set.
“Parliamentary democracy is by design more flexible than the American presidential system, with its fixed election dates,” Prest explained.
“That’s deliberate, as it makes it much easier to get rid of a leader who is either unfit or unpopular – or both.”
Many experts have speculated that the Liberals may choose to call a vote shortly after their next leader is chosen in an effort to capitalise on a recent upswing in public support.
At the beginning of the year, the Liberals had been trailing the opposition Conservatives by as many as 26 percentage points.
But Trudeau’s decision to resign – coupled with the race to select his replacement as Liberal leader and Trump’s threats against Canada – have helped the party bounce back in the polls.
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoNHL trade board 7.0: The 4 Nations break is over, and things are about to get real
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoJustice Dept. Takes Broad View of Trump’s Jan. 6 Pardons
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHamas says deal reached with Israel to release more than 600 Palestinians
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoKilling 166 million birds hasn’t helped poultry farmers stop H5N1. Is there a better way?
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoChristianity’s Decline in U.S. Appears to Have Halted, Major Study Shows
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoGermany's Merz ‘resolute and determined,' former EU chief Barroso says
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMicrosoft makes Copilot Voice and Think Deeper free with unlimited use
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoTimberwolves erase 25-point deficit to defeat Thunder 131-128 in overtime