World
Can Biden afford to lose the Arab and Muslim vote?

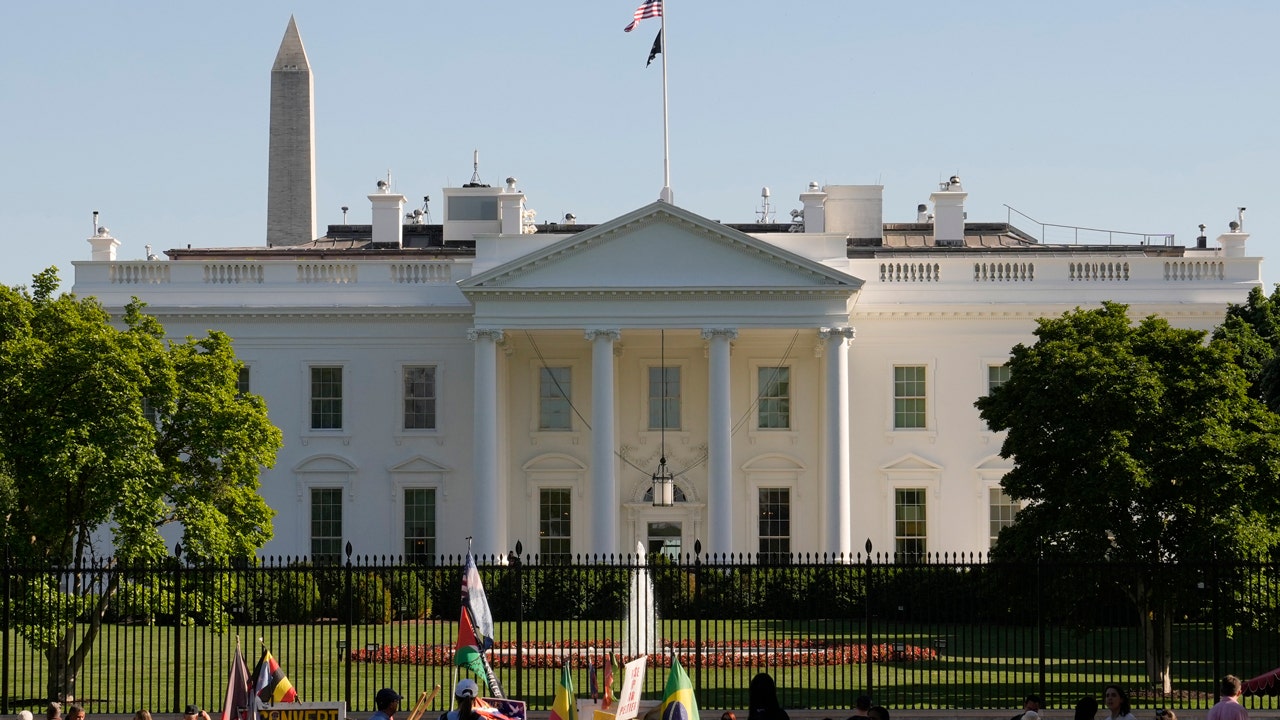
In 2020, Joe Biden won the state of Michigan by a much closer margin over then-incumbent President Donald Trump than the polls and pundits had predicted: just more than 150,000 votes.
Two partly overlapping sets of voters helped tip Biden over the line in Michigan and other vital swing states, including Pennsylvania and Wisconsin: Muslim Americans and Arab Americans.
Now, four years later, as Biden and Trump head towards a rematch in November, the current Democratic Party incumbent faces the mounting prospects of a backlash from those very same voters, many of whom are seeking to bleed his re-election bid.
Growing outrage over Washington’s support for Israel in its unprecedented bombardment of Gaza is many prompting Arab-American and Muslim voters to declare that they intend to stay away from the polls. As the US continues military funding for Tel Aviv, the number of Palestinians killed in the war on Gaza has risen to nearly 30,000 since October 7, many of them children.
In Michigan, where early primaries begin this week, one-time Biden voters have promised to send his administration a strong message by sabotaging the elections, even as the president’s aides have scrambled to meet and mend broken ties with community leaders.
Here’s what American Arab and Muslim communities want, why the two voting blocs are important for Biden, and the parts of the US where they are most influential:
What are Arab Americans demanding?
Arab and Muslim communities say they’ve called on the Biden administration to speak up and halt the killings in Gaza with no results. Some are Palestinians with families and friends in the besieged strip.
These communities have diverse demands, the main ones being that:
- The US support an immediate ceasefire in Gaza and work to see Palestinian political prisoners, as well as Israeli captives, freed.
- Washington stops military funding to Israel.
- The US pushes for sufficient aid to Palestinians and resumes paused humanitarian funding to UNRWA, the UN aid agency under investigation amid accusations its staff members took part in Hamas’s October 7 attacks when 1,200 Israelis were killed.
- The US government do more to fight rising anti-Arab and anti-Palestinian hate.
However, many say they’re not being heard and that Washington’s stance is particularly painful because of how they’ve supported Biden in the past. Communities in Dearborn, Detroit, and other major cities with significant Arab-American populations have successfully lobbied their local council leaders to pass unilateral resolutions for a ceasefire in Gaza.
While the local laws do not weigh on US foreign policy, Mai El-Sadany, director of the DC-based Tahrir Institute for Middle East Policy (TIMEP) told Al Jazeera that local resolutions are symbolic and are pointers to the concerns and priorities of American citizens.
“These spaces provide a platform for citizens to explain why this issue matters and how it affects them and their families,” El-Sadany said.
“[Local councils] have the potential to be mobilising spaces to bring like-minded individuals together, to create a larger sense of urgency and pressure on policymakers who do have foreign policy influence to reconsider their approach.”
What’s the ‘uncommitted’ option some voters want to go with?
Some Arab-American voters are choosing to pull a no-show in state primaries, and – if Biden does not call for a ceasefire – at the November polls. Community leaders in Minnesota launched the #AbandonBiden campaign in October.
Others say they plan to write “Free Palestine” on their unticked ballot papers.
Still others, particularly in Michigan, are planning to turn out for the Democratic primaries — not to tick Biden’s name, but rather to choose the “uncommitted” option on ballots.
The option signifies that voters support the party but are not attached to any of the listed candidates. An uncommitted vote will not count for Biden. At the same time, since Trump is not on the Democratic Party ballot, it will not count for him either. While there won’t be an uncommitted option in November in the general ballots, no-show votes and ballot papers not properly ticked from former Democratic Party supporters could reduce the vote count for Biden.
Lexis Zeidan of Listen to Michigan, a group that has organised call-a-thons to get thousands of “uncommitted” Michigan voters on board, told Al Jazeera the effort was “to put President Biden on notice” after protests had failed to change the White House’s stance on Gaza.
“You can’t weaponise this whole notion that because you’re not Republican, you’re the better party especially when you’re aiding a genocide and even more when you’re taking our taxes that could be reinvested in the communities that are suffering and you claim to care about,” said Zeidan, a Palestinian Christian who promises not to vote for Biden in November. The group is aiming for at least 10,000 people to vote uncommitted in the primaries, the same number of votes that helped Trump win Michigan in the 2016 elections, over Hillary Clinton.
“For us, at the minimum, that’s the margin of votes that we can showcase that we are able to swing Michigan in any direction,” she said.
Some 30 elected state leaders in Michigan have joined the movement, including Rashida Tlaib, the only Palestinian American in the US Congress.
Dearborn city mayor Abdullah Hammoud in a New York Times opinion confirmed that he’d vote ‘uncommitted’ in the primaries, saying that in doing so, he was choosing “hope that Mr. Biden will listen”.
Which states are Arab-American voting strongholds?
There are approximately 3.5 million Arab Americans according to the Arab American Institute, making up around 1 percent of the US population. About 65 percent are Christians, approximately 30 percent are Muslim, and a small number practise Judaism.
While these groups tend to vote based on varying interests, “there’s almost unanimous consensus on the need for a Gaza ceasefire,” said Youssef Chouhoud, a race and religion researcher with Virginia’s Christopher Newmark University (CNU).
Dearborn, Michigan, is home to the largest Arab-American community in the US — more than 40 percent of the city’s population. Georgia, Pennsylvania, Florida, and Virginia are also home to large Arab communities.
At least three of those states – Georgia, Michigan and Pennsylvania — are going to be battleground swing states in November, where the difference in support for Democrats and Republicans is marginal, and small shifts could swing outcomes.
Arab votes made the difference in the tight 2020 race. Biden pushed ahead of Trump by 154,000 votes in Michigan – credited majorly to the Arab-American community, which accounted for 5 percent of the vote. Michigan is home to an estimated 240,000 Arab Americans.
In Georgia, Biden won by fewer than 12,000 votes. The state is home to more than 57,000 Arab Americans.
However, soaring discontent in those communities means for the first time in 26 years, the Democratic Party is no longer a choice for many Arab voters, whether Christian or Muslim. Biden’s approval ratings among American Arabs went from 59 percent in 2020 to 17 percent in 2023.
How might non-Arab Muslims vote?
There are about 4.5 million American Muslims, and a majority — almost 3.5 million — of them are not of Arab ethnicity. Most are of Pakistani and Indian descent.
But non-Arab Muslim communities who’ve traditionally voted Democrat are losing faith in Biden, too.
In all, about one million Muslims voted in 2020, and 80 percent of them voted for Biden. According to the Council on American-Islamic Relations (CAIR), some two million Muslims are already registered to vote in the 2024 elections.
This time, though, only 5 percent of Muslim Americans say they’ll vote for Biden in November, according to a poll by Emgage, a Muslim civic engagement group.
American Muslims are concentrated in New York, California, Illinois, New Jersey, Texas, Florida, Ohio, Virginia, Georgia and Michigan.
What effects will no-show voting have?
Some analysts say that, whether they withhold their vote or go for Trump, the Muslim and Arab-American vote is not going to make a huge dent in Biden’s campaign as they only make up about 2 to 3 percent of the total voting population.
But no-shows or damaged votes, from those who will write on the ballot, for example, could put Biden at risk of losing tiny margins in swing states and could clear the ground for another Trump White House, Chouhoud of CNU said.
“It is well within the realm of reason that he will lose over 50 percent of the votes that he got in 2020 from Arabs and Muslims collectively, and that’s equivalent to the margin of victory that he got just from those two groups alone,” Chouhoud said. “He cannot count on their votes.”
Such a scenario, Chohoud added, would make it likelier for Trump to get elected. The former president has signalled he’d bring back a controversial ban on travel to the US from several Muslim-majority countries.
“That’s not to say that we should, quote-unquote, blame the Muslims,” Chouhoud said. “They’ve been telling you what they were going to do for months now. If the Democratic establishment really cared about a second Trump presidency as much as they say they do, they would have done something different. So, it’s really not on Arabs and Muslims, right?”
Other communities, too, might hurt Biden at the ballot box. Polls by the Pew Research Center show that 40 percent of Americans across party lines do not approve of Biden’s response to the war, particularly young people.
How well is Biden’s damage control working?
Biden’s campaign has tried to paint the president as frustrated with the situation in Gaza to appeal to Arab and Muslim communities, as well as other Americans across religious affiliations who support a ceasefire in Gaza.
According to an NBC news exclusive this month, Biden privately vented his frustrations with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s unwillingness to agree to a ceasefire, and called the prime minister an “a******”. The president also told reporters at a February 8 news conference in the White House that the Israeli response in Gaza “has been over the top”.
But in moves contradicting the president’s alleged private stance, Washington has so far continued to back Israel’s war. In mid-February, UN Ambassador Linda Thomas-Greenfield was the sole hand to oppose, and veto, a resolution proposed by Algeria calling for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza. Thomas-Greenfield said that could jeopardise continuing negotiations aimed at freeing Israeli captives still held by Hamas and that an immediate ceasefire would derail US attempts to build a “lasting peace” in the region. It was one of several such vetoes blocking an end to the war since October 7.
In January, the US Senate also approved an additional $14bn package to fund Israel’s war on Gaza. Already, Israel receives the largest chunk of US aid, according to the Council on Foreign Relations – about $3.3bn a year. Nearly all of that funding goes to military operations.
In a flurry of activity in recent weeks, Biden representatives have attempted to soothe Arab leaders in meetings, with limited success. Dearborn officials were set to meet Biden campaign manager Julie Chavez Rodriguez in a sit-down but cancelled at the last minute after pressure mounted from community members who were against any talks regarding the elections. At another meeting with Biden’s senior advisors in February, Dearborn Mayor Hammoud said the community was not shifting from its demands for a ceasefire.

World
Blinken says US cannot support Rafah assault without humanitarian plan

World
The unexpected announcement of a prime minister divides Haiti's newly created transitional council
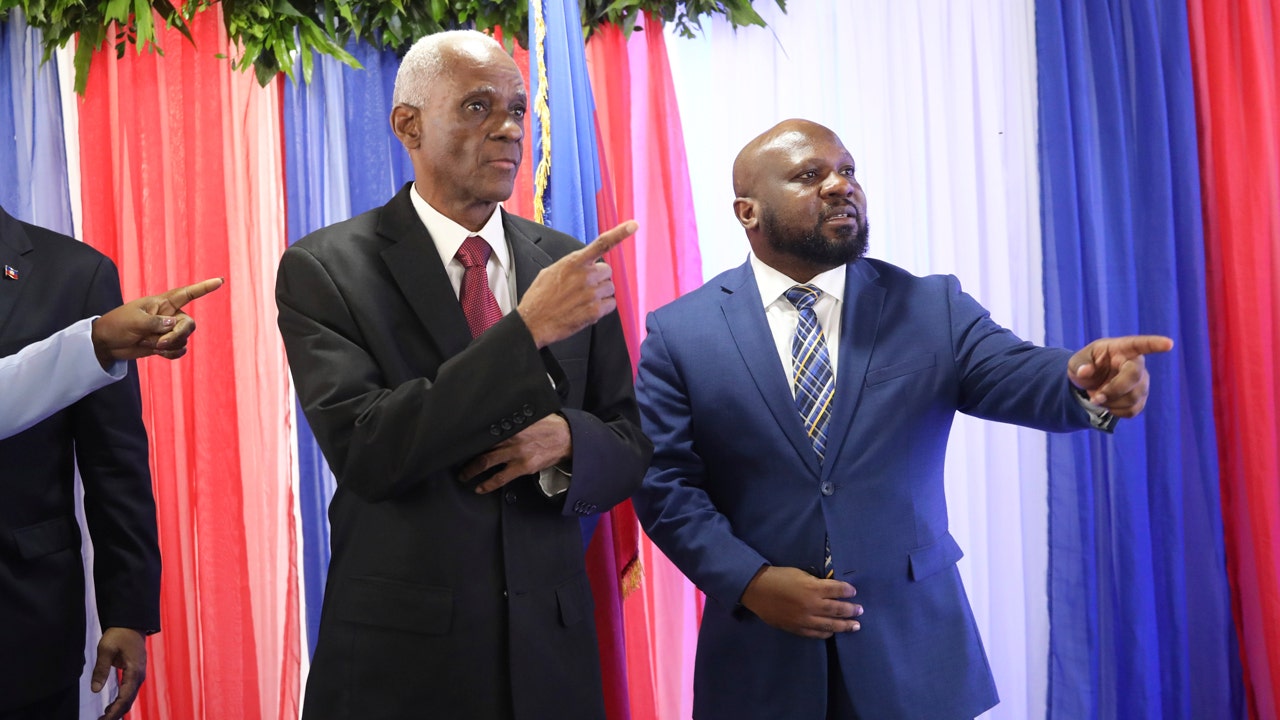

A surprise announcement that revealed Haiti’s new prime minister is threatening to fracture a recently installed transitional council tasked with choosing new leaders for the gang-riddled Caribbean country.
Four of seven council members with voting powers said Tuesday that they had chosen Fritz Bélizaire as prime minister, taking many Haitians aback with their declaration and unexpected political alliance.
HAITI COUNCIL APPOINTS NEW PRIME MINISTER AS COUNTRY CONTINUES TO FACE DEADLY GANG VIOLENCE
The council members who oppose Bélizaire, who served as Haiti’s sports minister during the second presidency of René Préval from 2006 to 2011, are now weighing options including fighting the decision or resigning from the council.
A person with direct knowledge of the situation who did not want to be identified because negotiations are ongoing said the council’s political accord had been violated by the unexpected move and that some council members are considering other choices as potential prime minister.
Edgard Leblanc Fils, left, and Smith Augustin prepare to pose for a group photo with the transitional council after it named Fils as its president in Port-au-Prince, Haiti, Tuesday, April 30, 2024. The transitional council will act as the country’s presidency until it can arrange presidential elections sometime before it disbands, which must be by February 2026. (AP Photo/Odelyn Joseph)
The council on Tuesday was scheduled to hold an election and choose its president. But two hours and a profuse apology later, one council member said that not only a council president had been chosen, but a prime minister as well. Murmurs rippled through the room.
The Montana Accord, a civil society group represented by a council member with voting powers, denounced in a statement late Tuesday what it called a “complot” hatched by four council members against the Haitian people “in the middle of the night.”
“The political and economic mafia forces have decided to take control of the presidential council and the government so that they can continue to control the state,” the Montana Accord said.
Haitian politics have long been characterized by secretive dealings, but many worry the country cannot afford further political instability as gangs lay siege to the capital of Port-au-Prince and beyond.
“People change parties (like) they’re changing their shirts,” said François Pierre-Louis, a professor of political science at Queens College in New York and former Haitian politician.
He spoke during an online webinar on Tuesday evening.
Like others, he said he believed that Jean-Charles Moïse, a powerful politician who was a former senator and presidential candidate, was behind Bélizaire’s nomination.
“Interestingly, Moïse, of all the politicians there, is the one calling the shots,” Pierre-Louis said.
Moïse, however, does not sit on the council. His party, Pitit Desalin, is represented by Emmanuel Vertilaire, who is among the four council members who support Bélizaire.
The others are Louis Gérald Gilles, Smith Augustin and Edgard Leblanc Fils, the council’s new president.
They could not be immediately reached for comment.
A document shared with The Associated Press and signed by the four council members who chose the new prime minister state they have agreed to make decisions by consensus. The document is titled, “Constitution of an Indissoluble Majority Bloc within the Presidential Council.”
The move prompted the Fanmi Lavalas party to issue a statement Wednesday calling it a “masquerade” and “conspiracy” to guarantee that PHTK “thugs and their allies retain power…and continue the tradition of corruption.”
“The Lavalas Family strongly rejects the betrayal scandal that occurred on April 30,” the party said.
Fils represents the January 30 political group, which is made up of parties including PHTK, whose members include former President Michel Martelly and slain President Jovenel Moïse. Meanwhile, Augustin represents the EDE/RED political party, founded by former Prime Minister Claude Joseph, and Gilles represents the Dec. 21 agreement, which is associated with former Prime Minister Ariel Henry, who recently resigned.
Henry was on an official visit to Kenya to push for the U.N.-backed deployment of a police force from the East African country when gangs in Haiti launched coordinated attacks starting Feb. 29.
They have burned police stations, opened fire on the main international airport that remains closed since early March and stormed Haiti’s two biggest prisons, releasing more than 4,000 inmates. The violence continues unabated in certain part of Port-au-Prince, including the area around the National Palace.
Haitians are demanding that security be a top priority for the council, which is tasked with selecting a new prime minister and Cabinet, as well as prepare for eventual general elections.
But some Haitians are wary of the council and the decisions it’s taking.
Jean Selcé, a 57-year-old electrician, noted that most of the council members are longtime politicians: “Their past is not really positive.”
“I hope their mentality can change, but I don’t believe it will,” he said. “They don’t really love the country. Who’s dying right now? It’s Haitians like me.”
Robert Fatton, a Haitian politics expert at the University of Virginia, noted that some of the parties represented on the council are responsible for the current chaos in Haiti.
“It’s a contradiction,” he said. “Every time we seem to be in a crisis, we reappoint the same people and hope that they change their ways, but they do not.”
Raising the same criticism is Michael Deibert, author of “Notes From the Last Testament: The Struggle for Haiti,” and “Haiti Will Not Perish: A Recent History.”
He noted in a recent essay that the council is “dominated by the same political currents who have spent the last 25 years driving Haiti over a cliff, taking advantage of impoverished young men in the slums to be used as political bludgeons before – bloated on the proceeds from kidnapping, extortion, drug trafficking and other criminal enterprises – these groups outgrew the necessity of their patrons.”
More than 2,500 people have been killed or injured across Haiti from January to March, according to the U.N.
In addition, more than 90,000 people have fled Port-au-Prince in just one month given the relentless gang violence.
World
Arizona Senate repeals near-total 1864 abortion ban in divisive vote
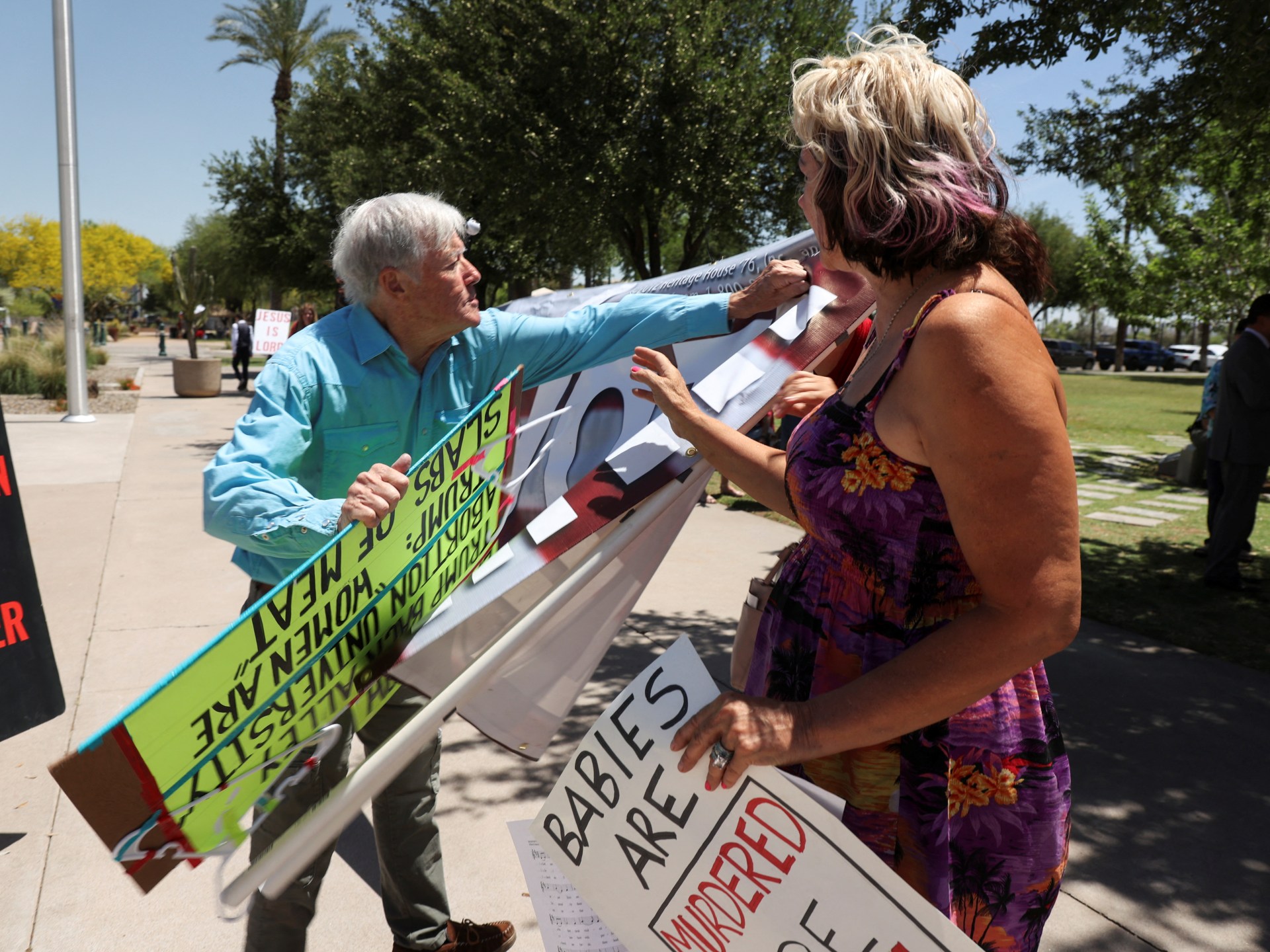
The repeal of abortion ban was passed 16 to 14 and is expected to be signed into law by Governor Katie Hobbs.
The Arizona Senate has voted to repeal the state’s 1864 ban on abortion, which would otherwise have taken effect within weeks.
The repeal was passed by the Senate in a 16-14 vote on Wednesday and is expected to be signed swiftly by Governor Katie Hobbs, a Democrat. Two Republican senators crossed party lines to vote in favour of repealing the ban.
The Arizona House last week passed the measure after a handful of Republicans broke party ranks and voted with Democrats to send it to the Senate.
“We’re here to repeal a bad law,” Senator Eva Burch, a Democrat, said from the floor. “I don’t want us honouring laws about women, written during a time when women were forbidden from voting.”
Republican Senator Wendy Rogers said in casting her vote to maintain the 1864 ban that repealing the law went against the conservative values of Arizona.
“Life starts at conception. They got it right in 1864. We need to continue to get it right in 2024,” Rogers said.
The fight over the Civil War-era abortion ban in Arizona, a state sharply split between Democrats and Republicans, is the latest flashpoint on women’s reproductive rights in the United States. In 2022, the country’s Supreme Court ended the constitutional right to abortion, leaving it up to states to decide the issue. Conservative-led states quickly invoked strict bans on the procedure within their borders.
Democrats across the US, confident that public opinion is on their side in supporting abortion rights, have sought to elevate the issue ahead of November’s presidential election. Arizona is a key battleground state.
Heather Williams, president of the Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee that works to elect Democrats to state legislatures, said her party would capitalise on the “extreme nature of MAGA Arizona Republicans” who voted to maintain the 1864 law as Democrats try to flip the state’s House and Senate in November’s elections.
Rogers, the Republican state senator, acknowledged the political risks.
“Some colleagues would say it’s politically pragmatic for us to find middle ground,” she said. “We might lose the legislature, we might lose the presidential election. But it’s more important to do what’s right.”
Near-total ban on abortions
The 1864 law was revived by a state Supreme Court ruling on April 9, and unless the legislature intervened, it would have taken effect within 60 days of that ruling, according to state Attorney General Kris Mayes, a Democrat.
If the repeal bill is signed, a 2022 statute banning the procedure after 15 weeks of pregnancy would become Arizona’s prevailing abortion law. Still, there would probably be a period when nearly all abortions would be outlawed because the repeal would not take effect until 90 days after the end of the legislative session, which is expected to be in June or July.
Planned Parenthood Arizona, a sexual health organisation in the state, announced it filed a motion on Wednesday afternoon asking the state Supreme Court to prevent a pause in abortion services until the repeal takes effect.
The near-total ban on abortions predates Arizona becoming a state.
Under the 1864 law, “every person” who participates in conducting an abortion can be held criminally liable and face a minimum sentence of two years in prison.
There are no exceptions for cases of rape or incest, although there is an exception when the pregnancy puts a woman’s life at risk.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Dozens of Yale Students Arrested as Campus Protests Spread
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoLarry Webb’s deathbed confession solves 2000 cold case murder of Susan and Natasha Carter, 10, whose remains were found hours after he died
-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoHaiti Prime Minister Ariel Henry resigns, transitional council takes power
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUS secretly sent long-range ATACMS weapons to Ukraine
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoFirst cargo ship passes through new channel since Baltimore bridge collapse
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTurkey’s Erdogan meets Iraq PM for talks on water, security and trade
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSpanish PM Pedro Sanchez suspends public duties to 'reflect'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAmerican Airlines passenger alleges discrimination over use of first-class restroom