Business
Fast food operators rushing to use AI in the wake of minimum wage hikes

It didn’t take long for Harshraj Ghai to respond to the impact of California’s new $20 an hour minimum wage for his 3,700 fast-food employees.
Ghai and his family operate 180 Burger Kings, Taco Bells and Popeyes chicken restaurants across the state, and one of the first things they did after the law took effect April 1 was to start capping workers’ hours to avoid overtime pay. Also, they’re closing some outlets a little earlier, and opening others a bit later to avoid paying workers for less profitable periods.
But the biggest thing Ghai and his family are doing does not directly involve workers at all: They’ve speeded up and expanded their use of technology, especially AI.
Right now, they’ve moved up by several years their plans to install self-service kiosks at all of their locations, including 25 out of state.
But what has Ghai most hopeful about offsetting the higher labor costs is to have AI handle customers’ orders made at the drive-through. He’s testing the machine-learning system this month at a few locations and hopes to roll it out company-wide by this time next year.
Drive-throughs of course are quintessentially California, with its car culture and fast lifestyle. And now, with AI coming on to the scene in a big way, the state is emerging as ground zero for what many analysts see as the next big thing in the world of fast food and drinks.
Not that AI-led drive-through is quite ready for prime time. As it is today, the system can have trouble with people’s accents and ambient noise, making it hard to recognize speech and translate it into text. Pilot programs run by McDonald’s and others thus far often have backed up the AI technology with an employee, like the Wizard of Oz man behind the curtain. The unseen worker from as far away as the Philippines monitors and sometimes intervenes to complete an order if AI falters.
Even so, Ghai thinks that once the kinks are worked out, it’ll be a godsend for fast-food operators like him.
“It has the potential of being the most impactful,” says Ghai, 39, whose Indian immigrant father, Sunny, started the family business in 1998 by buying a failing Burger King in San Jose, where he was an assistant manager.
What pushed the envelope for businesses like the Ghais’ was California’s sudden 25% hike in the minimum wage for the fast-food industry’s half-million or so workers in the state.
To deal with the big increase in labor costs — which average about one-third of a fast-food store’s sales — many of the affected business owners immediately jacked up menu prices.
Ghai said he’s raised prices overall this year by just 2%. But that’s not been the norm. By the middle of last month, at many franchises across the state — from Jack in the Box to Chipotle to Starbucks — consumers on average were paying a mid- to high-single-digit percentage more than just a month or two earlier, according to a survey by BTIG, the investment banking and research firm.
Relatively few appear to have resorted to layoffs, in part because many were already staffed at bare-bones levels. So to hold the line on further price increases, a growing number of fast-food operators are now racing to install as much automation as they can afford.
Perhaps the most visible and soon to be widely adopted are all kinds of kiosks for ordering food. The self-service machines have been around for more than a decade, but franchise owners such as Michaela Mendelsohn resisted the move for many years.
“We just didn’t want to force our customers to use technology. We thought the personal contact was important,” said Mendelsohn, who has six El Pollo Loco restaurants in Los Angeles and Ventura counties.
But when the industry’s basic pay rose to $20 an hour, she said, that amounted to $180,000 in additional labor costs a year per store. Within a month of the wage hike, Mendelsohn bought two standing kiosks for each of her six restaurants. That set her back $25,000 per store, for two screens, installation, software and other related costs. One of the two machines accepts cash, which she said was needed for her blue-collar customers.
An L.A. Carl’s Jr. restaurant. In California, CKE Restaurants, the owner and franchisor of Carl’s Jr. and Hardee’s, appears to be ahead of the pack on the use of AI technology.
(Los Angeles Times)
Mendelsohn figures that the kiosks might save five hours of labor a day. By that estimate, the machines would pay for themselves within a year and shave about 20% of the increased cost from the latest minimum wage increase. “We’re chipping away at it,” she said.
Self-service kiosks are ubiquitous in Western Europe, but they’re in fewer than 20% of fast-food establishments in the U.S., says Perse Faily, chief executive at Los Angeles-based Tillster, one of earliest providers of kiosks and other digital platforms for restaurants.
The COVID-19 pandemic pushed the trend in the U.S., she said, and now in California, “We’re seeing this complete sea change in thinking, ‘How do I address my labor costs?’”
Kiosks may be appealing in that they can not only save on labor, but also drive higher sales. Unlike people, the programmed machines are always trying to “upsell,” never forgetting to ask customers whether they want a drink with their meal or something else to go along with their entree.
Faily, Tillster’s CEO since late 2007, wouldn’t disclose the company’s sales increase, but said its new customers include Burger King and Popeyes, and that employment at the firm is up 75 from a year ago, to 340 currently. “The minimum wage increase has completely changed the landscape,” she said.
Other computer-guided upgrades are also aimed at cutting labor costs, from automatic avocado peelers and dishwashers to robotic arms that flip burgers and turn over fryer baskets.
But return on investments, while helpful for the bottom line, don’t do enough to offset burgeoning payroll expenses. So relatively few fast-food operators, for now, are making major investments in robotics and similar mechanical devices.
AI, on the other hand, looks like it could be a game-changer.
The pandemic boosted drive-through traffic at fast-food places to about 80% of sales from two-thirds pre-COVID, said Peter Selah, a restaurant industry analyst at BTIG. And AI order-taking opens the possibility of speeding up the drive-through process, increasing sales and reducing significant labor overhead.
But analysts say it’s likely to be at least a year or two, maybe longer, before AI-led drive-through reaches a consistent and high enough level of accuracy where companies are comfortable with it. Tests have often left frustrated customers demanding to talk to a live person rather than a bot, according to various accounts.
Major fast-food brands were reluctant to discuss their AI drive-through efforts. Nationally, McDonald’s has been out in front, using an IBM-developed system. A spokesperson would only say that McDonald’s “continues to gather learnings from the roughly 100 pilot restaurants testing automated order taking technology in the U.S. We expect to share more later this year.”
In California, CKE Restaurants, the owner and franchisor of Carl’s Jr. and Hardee’s, appears to be ahead of the pack on the technology, but like other chains, including Taco Bell, Burger King and El Pollo Loco, CKE declined to comment.
Analysts, however, say none of the AI platforms have reached more than 85% success in which human intervention isn’t needed.
“The hardest part is when you have people with accents, from different states and immigrants. It’s challenging,” said Danilo Gargiulo, senior analyst covering restaurants for Bernstein, an investment and research firm.
Still, Gargiulo sees the day when AI will speed up the drive-through line, boosting sales and consumer satisfaction. “Right now the drive-through time is slowed by repeated orders,” he said. With accurate AI speech recognition and faster, clearer communication to the kitchen staff, he said, you can cut as much as 90 seconds off what typically takes 5½ minutes for a customer to complete a drive-through purchase.
That’s what Ghai is betting on.
He says his initial investment for the AI drive-through technology, purchased from San Carlos-based Presto, is about $10,000 per store. Ghai estimates that if he can get it to perform at 90%, a store employee might have to step in to take over an order just three times every hour, freeing up the worker to do other tasks.
The AI system is getting better as it gathers more data, he said, and it’ll soon be able to communicate in Spanish. Add in mobile apps and loyalty programs, and AI has the potential to give fast-food customers a faster and more personalized service. And of course there’s the labor saving part: Ghai thinks the AI drive-through could reduce 10 to 15 hours of wages a day, and double that where he has two human order takers.
“Our goal isn’t to get rid of people. We’re in the people business at the end of the day,” he said. At the same time, Ghai added, over the long haul, “we’ll have fewer people.”

Business
Sony warns tech companies: Don't use our music to train your AI

Sony Music Group is sending letters to 700 artificial intelligence developers and music streaming services warning them to not use its artists’ music to train generative AI tools without its permission.
The company — one of the three largest recorded music firms — said it is explicitly opting out of the use of its music for training or developing AI models through text or data mining or web scraping as it relates to lyrics, audio recordings, artwork, musical compositions and images. Sony Music Group artists include Celine Dion, Doja Cat and Harry Styles.
“We support artists and songwriters taking the lead in embracing new technologies in support of their art,” Sony Music Group said in a statement on its website Thursday. “Evolutions in technology have frequently shifted the course of creative industries. … However, that innovation must ensure that songwriters’ and recording artists’ rights, including copyrights, are respected.”
The letters were sent to companies including San Francisco-based ChatGPT creator OpenAI and Mountain View-based search giant Google, according to a person familiar with the matter who was not authorized to speak publicly. OpenAI and Google did not immediately respond to requests for comment.
The move comes as the entertainment industry is grappling with rapid innovations in artificial intelligence technology. Writers and actors raised concerns last summer about whether leaving AI unchecked could threaten their livelihoods. Meanwhile, some creatives have marveled at the advancements that could allow them to pursue bold ideas with tight budgets.
This year, OpenAI unveiled its text-to-video tool Sora, which was used to create a four-minute music video for music artist Washed Out. The director of the video told The Times that Sora helped him depict multiple locations and visual effects that he otherwise couldn’t have.
But AI can also create chaos. Celebrities have dealt with “deep fakes” — false videos or audio depicting a celebrity endorsing certain brands or activities. To help protect their clients against unauthorized use of their voice and likeness, Century City-based Creative Artists Agency is helping talent create their own digital doubles.
On Thursday, two New York voice-over actors sued Berkeley-based AI voice generator business Lovo for unauthorized use of their voices. Lovo did not immediately return a request for comment. The lawsuit was filed in U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York.
Some people in the entertainment industry have said they would like the AI companies to be more transparent about how they are training their tools and whether they have the appropriate copyright permissions.
OpenAI has said its large language models, including those that power ChatGPT, are developed through information available publicly on the internet, material acquired through licenses with third parties and information its users and “human trainers” provide.
The company said in a blog post that it believes training AI models on publicly available materials on the internet is “fair use.”
But some media outlets, including the New York Times, have sued OpenAI. The newspaper raised alarms about how its stories are being used by the tech company.
In Sony Music Group’s letters to AI businesses, the company said it has reason to believe its content may have been used to train, develop or commercialize artificial intelligence systems without its permission, according to a copy obtained by the Times. Sony Music Group asked the tech companies to provide information regarding that use and why it was necessary.
Sony Music Group, owned by Tokyo-based electronics giant Sony Corp., also wants music streaming providers to add language in its terms of service saying that third parties are not allowed to mine and train using Sony Music Group content, the person familiar with the matter said.
Business
A woman was dragged by a self-driving Cruise taxi in San Francisco. The company is paying her millions
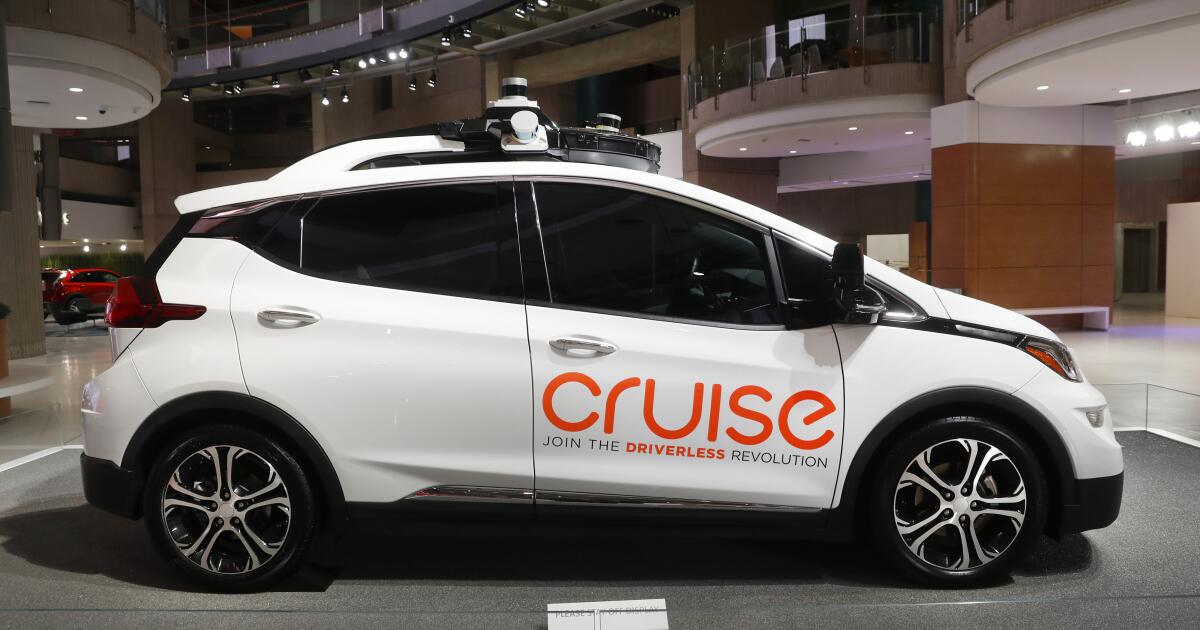

General Motors’ autonomous car company, Cruise, has reportedly agreed to pay an $8-million to $12-million settlement to a woman who was hospitalized after getting dragged along the pavement by a self-driving taxi in San Francisco last year.
The woman, a pedestrian, was struck by a hit-and-run vehicle at 5th and Market streets and thrown into the path of Cruise’s self-driving car, which pinned her underneath, according to Cruise and authorities. The car dragged her about 20 feet as it tried to pull out of the roadway before coming to a stop.
She sustained “multiple traumatic injuries” and was treated at the scene before being hospitalized.
It’s unclear when the settlement was reached or the exact amount, sources familiar with the situation told Fortune and Bloomberg. The condition of the woman, whose name was not released by authorities, is unknown, but a representative of Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital told Fortune that she had been discharged.
Cruise initially said that its self-driving car “braked aggressively to minimize impact” but later said the vehicle’s software made a mistake in registering where it hit the woman. The car tried to pull over but continued driving 7 mph for 20 feet with the woman still under the vehicle.
“The hearts of all Cruise employees continue to be with the pedestrian, and we hope for her continued recovery,” Cruise said in a statement.
Cruise halted its driverless operations after its autonomous taxi license was suspended by California’s Department of Motor Vehicles. The company was also accused of lying to investigators and withholding footage of the car crash.
Cruise said this week that it would start testing robotaxis in Arizona with a “safety driver” behind the wheel in case a human needs to take control of the vehicle, according to a company news release.
“Safety is the defining principle for everything we do and continues to guide our progress towards resuming driverless operations,” according to the release.
Business
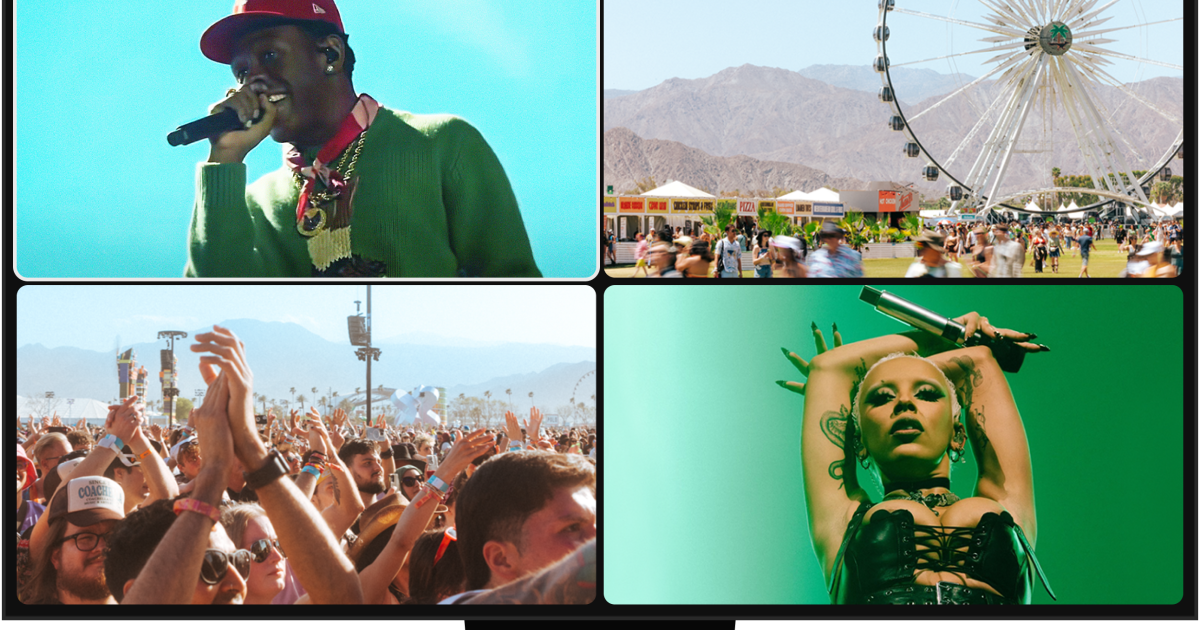
How YouTube became must-see TV: Shorts, sports and Coachella livestreams

When YouTube launched nearly two decades ago, its first clip was a grainy video of co-founder Jawed Karim speaking to the camera while standing in front of the elephants at the San Diego Zoo.
Not exactly must-see TV.
Since, then the online video giant has increasingly been the entertainment of choice for billions of people. And while the Google-owned service is still often thought of as being the destination for people watching funny short videos on their smartphones, the way that Americans watch it has changed in a big way.
People are increasingly choosing to watch YouTube on their connected TVs rather than on laptops and mobile devices, treating it more and more like a regular television destination.
The San Bruno, Calif.-based video giant said more than 150 million people in the U.S. are watching YouTube on connected TV screens every month, citing December 2022 data. That’s up 11% from 2021. YouTube is consistently the most watched streaming service in the U.S. on a TV in the U.S. every month, even beating Netflix and Amazon’s Prime Video since February 2023, according to Nielsen. The service accounts for nearly 10% of television viewing, the data firm said.
According to research firm Emarketer, U.S. adults spend 36 minutes each day watching YouTube, with 17 of those minutes on a connected TV, four minutes on a desktop or laptop computer and 15 minutes on a mobile device.
A variety of content is driving the company’s evolution. YouTube said TVs accounted for more than 50% of the watch time for its Coachella livestream this year, which is higher than ever before. Views of Shorts, clips that are 60 seconds or less, on connected TVs more than doubled last year, YouTube said.
“We’ve invested in making sure that YouTube really captures the totality of the experience that people want,” said Christian Oestlien, YouTube’s vice president of product management for connected TV. “What we hear from our users is they want to be able to watch their favorite creators but also highlights from their favorite sporting events, listen to their favorite artist and watch their favorite podcast and do it all in this one contained experience.”
At a time when consumers are choosing between multiple streaming services, YouTube has an advantage of having a wide variety of options, from live sports to user-generated videos. The company said the increase in TV watch time comes as connected TVs are becoming more widely available.
TV screen time can be helpful to streamers wishing to court more advertising dollars. This week, television networks and streaming services Amazon and Netflix made gala presentations to advertisers, showing off the programming they have coming up.
YouTube on Wednesday presented to advertisers new features such as branded QR codes and non-skippable assets on connected TVs.
“YouTube is wanting to position themselves not just as a digital advertising option, they want advertisers to see them on the same advertising footing as any other streaming service,” said Brett Sappington, founder of Dallas-based media and insights firm Sappington Media.
YouTube has introduced features to improve the television viewing experience, including the option to watch Coachella performances through a four-way split screen. The company also has shopping options.
“This isn’t my dad’s TV or my grandma’s TV,” Oestlien said. “This is TV rethought for a new generation.”
YouTube video creators have also embraced TV viewing, Oestlien said. In the last three years, the number of top YouTube creators who receive most of their watch time from TV screens has quintupled, YouTube said.
YouTube has also gotten a boost from its deal to become the home of pro football’s “NFL Sunday Ticket” game package. Fans will watch live games on YouTube on Sunday, then come back and watch clips through its video library or commentary from its creators, Oestlien said.
“It really becomes this surround-sound experience where, as a football fan, you can come to YouTube any day of the week,” he said.
YouTube and other streaming services have been competing for sports league rights in order to increase viewership. Amazon has the NFL’s “Thursday Night Football” games and has bid for a package of NBA matches. On Wednesday, Netflix announced it had secured two Christmas NFL games for 2024.
-
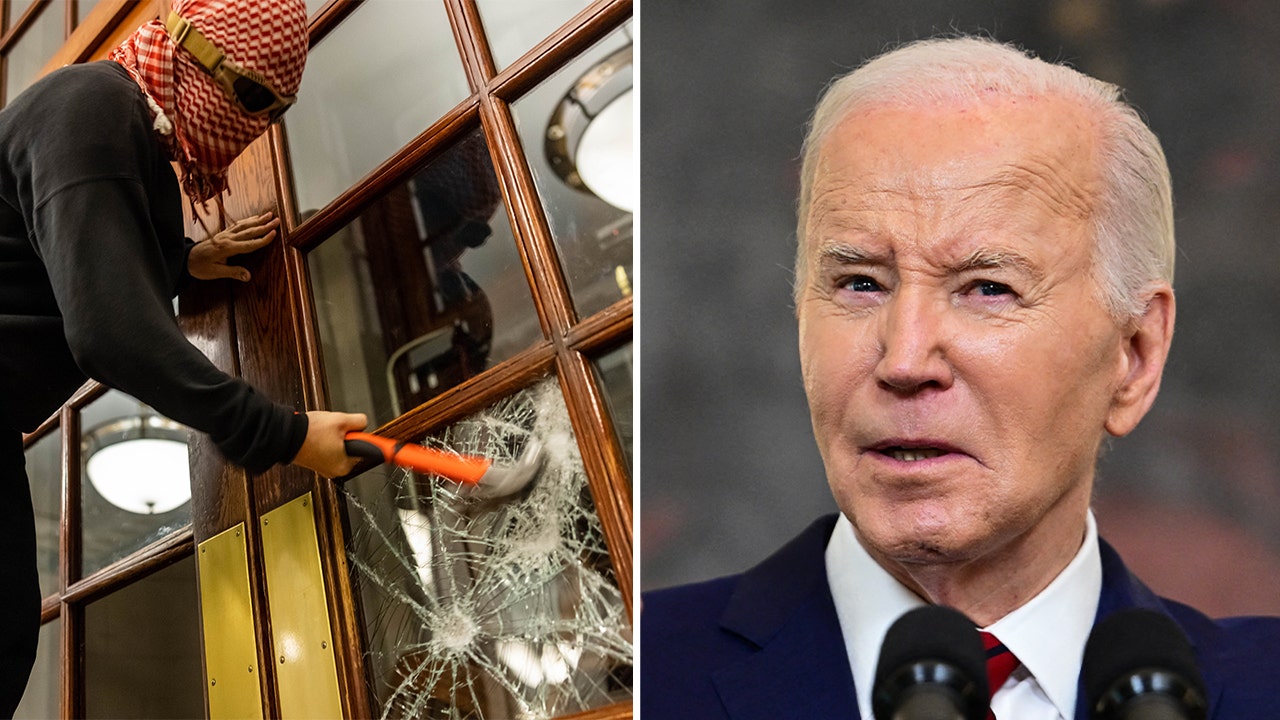

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoBiden takes role as bystander on border and campus protests, surrenders the bully pulpit
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago'You need to stop': Gov. Noem lashes out during heated interview over book anecdote about killing dog
-
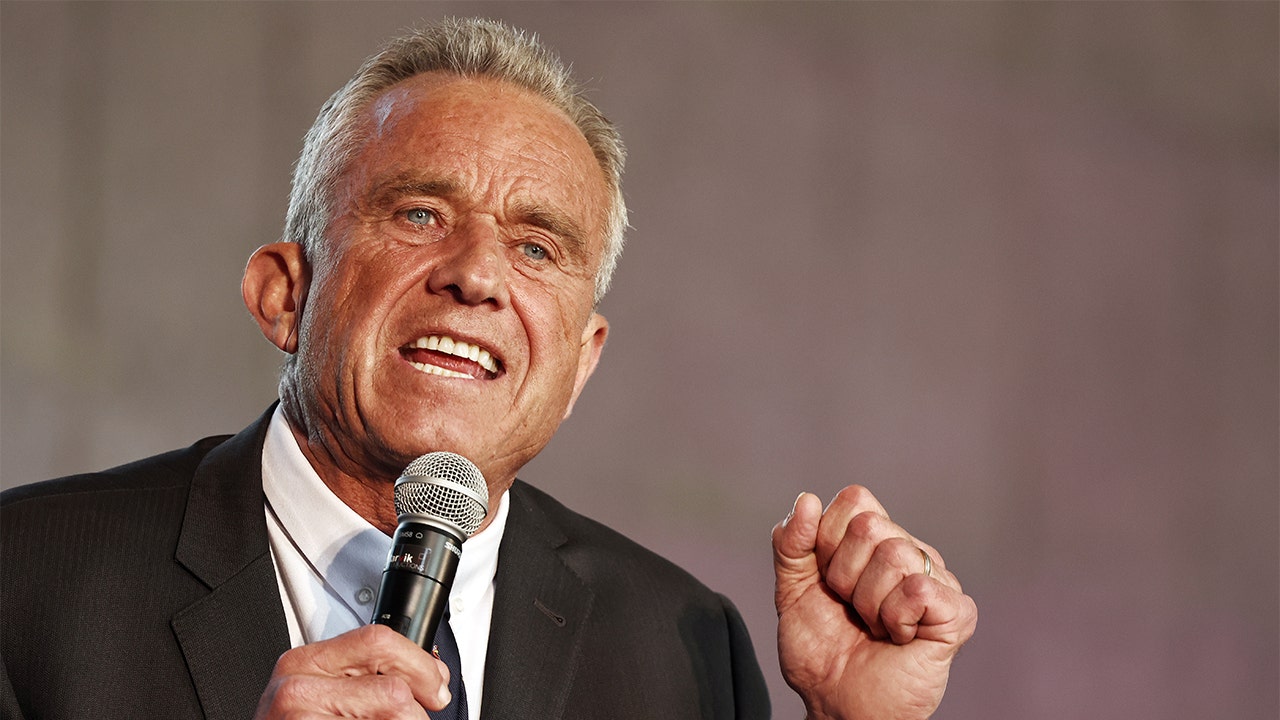

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRFK Jr said a worm ate part of his brain and died in his head
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoMan, 75, confesses to killing wife in hospital because he couldn’t afford her care, court documents say
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPentagon chief confirms US pause on weapons shipment to Israel
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoHere's what GOP rebels want from Johnson amid threats to oust him from speakership
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPro-Palestine protests: How some universities reached deals with students
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoConvicted MEP's expense claims must be published: EU court