Business
Column: Disneyland just promised electric cars at Autopia. Gas will be gone by 2026

When the Walt Disney Co. announced earlier this month that it would at long last ditch the smog-spewing gasoline engines at its beloved Autopia attraction in Anaheim, the company left a few key details to the imagination.
Would the new ride vehicles be purely electric? Or would they be hybrids that still burned some climate-wrecking, oil-based fuel? And how long would it take for Walt Disney’s creative and engineering heirs to make the long-overdue switch?
After I wrote a story breaking the news about the company’s plans, a coalition of electric vehicle activists launched a campaign to pressure Disney to commit to electric vehicles — not hybrids — and to phase out gasoline within two years.
On Thursday, those activists won.
In a written statement, Disneyland spokesperson Jessica Good confirmed to The Times that electrification “means fully electric — it does not mean hybrid or any other version of a gasoline combustion engine.” She added that the theme park “will no longer be using the current engines within the next 30 months.”
That means by fall 2026, Disneyland guests will no longer have to worry about breathing lung-damaging exhaust as they wait in line for Autopia — and park employees won’t have spend hours-long shifts inhaling those fumes as they work the ride.
It’s not yet clear when the newly electrified Autopia will reopen.
“Reimagining an attraction does take time, so we don’t have a reopening date at this time,” Good said.
Zan Dubin, the electric vehicle advocate leading the pressure campaign, was thrilled when she heard Thursday’s news. She called it a “huge victory” and a powerful reminder that climate activism works.
“All it takes for bad stuff to keep happening is for good people to do nothing,” she said, paraphrasing Abraham Lincoln. “And we refuse to stand by and do nothing.”
Dubin had been planning to lead a rally outside Walt Disney Studios in Burbank on Sunday, to urge the company to do better on Autopia. She’s told me she’s moving forward with the event, although she said it will now be more of a celebration.
“We are thrilled,” she said.
The stories that Disney tells at its theme parks — and on its streaming services, cruise ships and other platforms — are far more than entertainment. They play a powerful role in shaping how we understand our world and ourselves. That’s why the company’s decision to close Disneyland’s Splash Mountain ride — which was based on a racist film — and its increasing embrace of LGBTQ+ characters in its films have become such political flash points. The opponents of progress know that these choices matter.
If you care about climate progress, you should care about Autopia.
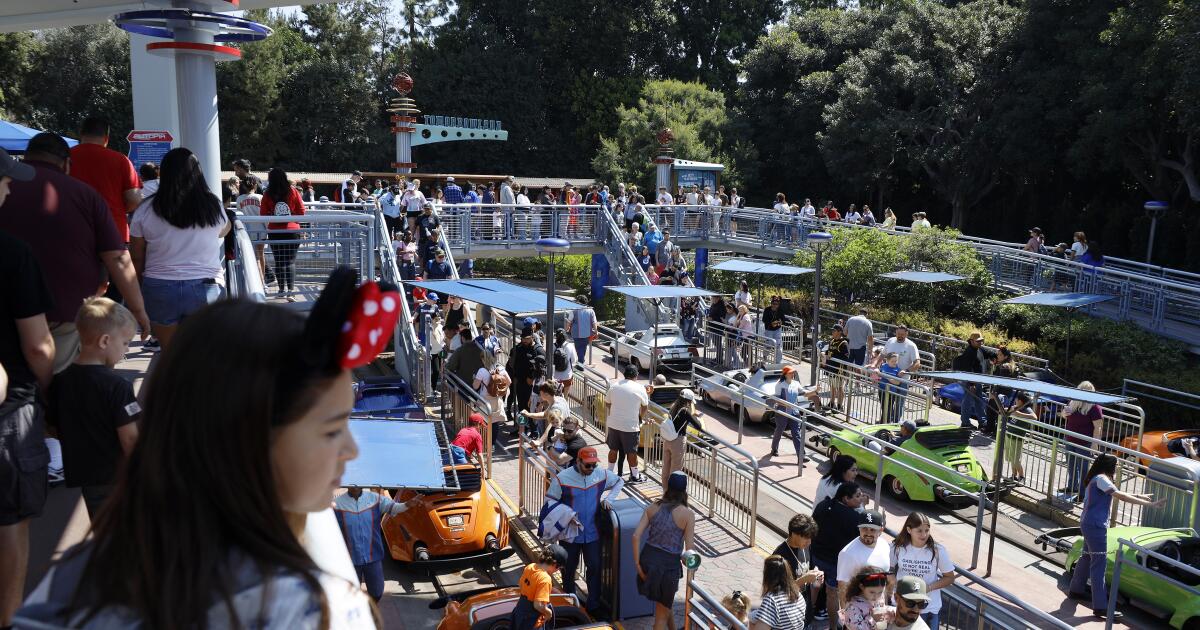
Disneyland visitors wait to exit the Autopia attraction in March.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
When the ride opened in 1955 as a centerpiece of Walt Disney’s Tomorrowland, it helped cement in the American consciousness the idea that gas-guzzling cars — and sprawling freeways — were the promise of the future. Within a year, President Eisenhower had signed the bill that would create the Interstate Highway System as we know it today.
Nearly 70 years later, cars, trucks and other modes of transportation are the nation’s largest source of heat-trapping emissions — emissions that have fueled record global temperatures for 10 straight months, resulting in deadlier heat waves, fires and storms. Fossil fuel combustion also produces regular old air pollution that researchers say kills millions of people each year.
Switching from gasoline engines to electric cars alone won’t solve all of our environmental and public health problems.
Mining to supply lithium for lithium-ion electric car batteries can be environmentally destructive in some places. Freeways have historically been built through low-income communities of color, tearing apart vibrant neighborhoods. The more we can rebuild our cities around public transit, electric bikes and green space — and less around cars — the happier and healthier we’ll be.
Beyond Autopia, Disney has an opportunity to promote that kind of future in Tomorrowland.
As I wrote earlier this month, Disneyland fans agree that the once-futuristic land hasn’t been especially forward-thinking for a long time. To my mind, clean energy and sustainability would make the perfect theme for a new and improved Tomorrowland. There’s already a major public transit element in the Monorail. Throw in some gas-free induction stoves at the main restaurant, some solar panels, some environmental films at the currently empty movie theater — it could be pretty awesome.
But even short of all that, we’re going to need a lot of electric vehicles, fast, to get the climate crisis under control. And for Disney to start telling the story of those EVs at Autopia is a big deal. The company deserves credit for getting it right.
“I’m glad they’re stepping up and doing the right hitting,” said Joel Levin, executive director of Plug In America, a national electric vehicle advocacy group that’s sponsoring this Sunday’s rally. “It’s a great way for the public to experience electrification, to turn it into a teachable moment, rather than the experience of standing next to a gas lawnmower, which is what it feels like now.”

Business
Fast food operators rushing to use AI in the wake of minimum wage hikes
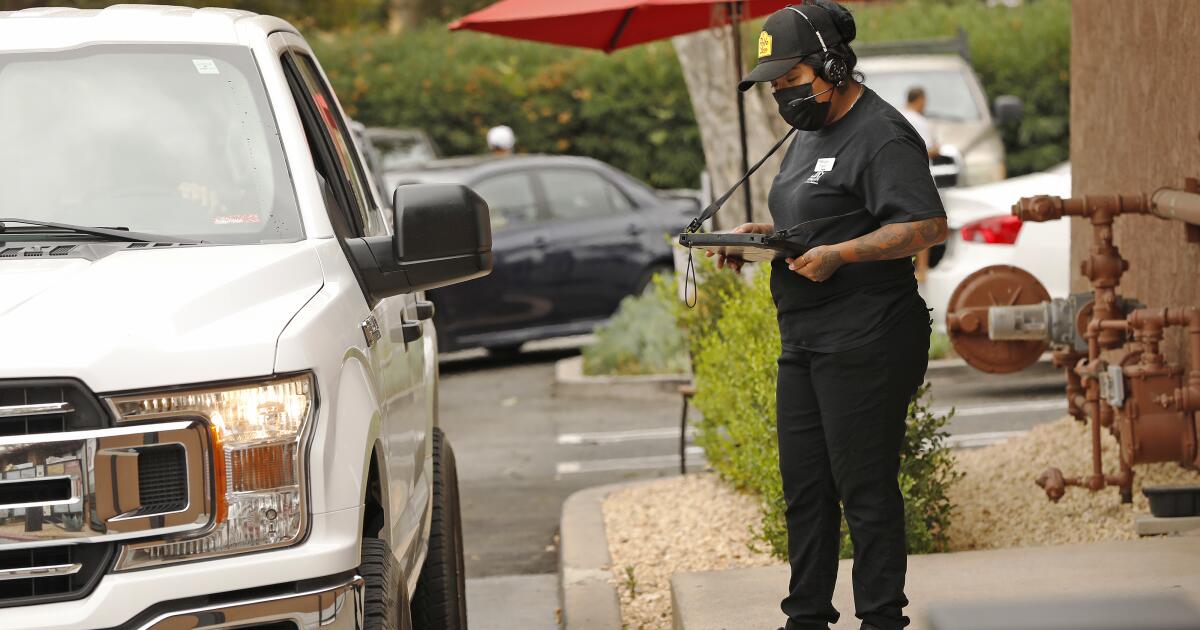

It didn’t take long for Harshraj Ghai to respond to the impact of California’s new $20 an hour minimum wage for his 3,700 fast-food employees.
Ghai and his family operate 180 Burger Kings, Taco Bells and Popeyes chicken restaurants across the state, and one of the first things they did after the law took effect April 1 was to start capping workers’ hours to avoid overtime pay. Also, they’re closing some outlets a little earlier, and opening others a bit later to avoid paying workers for less profitable periods.
But the biggest thing Ghai and his family are doing does not directly involve workers at all: They’ve speeded up and expanded their use of technology, especially AI.
Right now, they’ve moved up by several years their plans to install self-service kiosks at all of their locations, including 25 out of state.
But what has Ghai most hopeful about offsetting the higher labor costs is to have AI handle customers’ orders made at the drive-through. He’s testing the machine-learning system this month at a few locations and hopes to roll it out company-wide by this time next year.
Drive-throughs of course are quintessentially California, with its car culture and fast lifestyle. And now, with AI coming on to the scene in a big way, the state is emerging as ground zero for what many analysts see as the next big thing in the world of fast food and drinks.
Not that AI-led drive-through is quite ready for prime time. As it is today, the system can have trouble with people’s accents and ambient noise, making it hard to recognize speech and translate it into text. Pilot programs run by McDonald’s and others thus far often have backed up the AI technology with an employee, like the Wizard of Oz man behind the curtain. The unseen worker from as far away as the Philippines monitors and sometimes intervenes to complete an order if AI falters.
Even so, Ghai thinks that once the kinks are worked out, it’ll be a godsend for fast-food operators like him.
“It has the potential of being the most impactful,” says Ghai, 39, whose Indian immigrant father, Sunny, started the family business in 1998 by buying a failing Burger King in San Jose, where he was an assistant manager.
What pushed the envelope for businesses like the Ghais’ was California’s sudden 25% hike in the minimum wage for the fast-food industry’s half-million or so workers in the state.
To deal with the big increase in labor costs — which average about one-third of a fast-food store’s sales — many of the affected business owners immediately jacked up menu prices.
Ghai said he’s raised prices overall this year by just 2%. But that’s not been the norm. By the middle of last month, at many franchises across the state — from Jack in the Box to Chipotle to Starbucks — consumers on average were paying a mid- to high-single-digit percentage more than just a month or two earlier, according to a survey by BTIG, the investment banking and research firm.
Relatively few appear to have resorted to layoffs, in part because many were already staffed at bare-bones levels. So to hold the line on further price increases, a growing number of fast-food operators are now racing to install as much automation as they can afford.
Perhaps the most visible and soon to be widely adopted are all kinds of kiosks for ordering food. The self-service machines have been around for more than a decade, but franchise owners such as Michaela Mendelsohn resisted the move for many years.
“We just didn’t want to force our customers to use technology. We thought the personal contact was important,” said Mendelsohn, who has six El Pollo Loco restaurants in Los Angeles and Ventura counties.
But when the industry’s basic pay rose to $20 an hour, she said, that amounted to $180,000 in additional labor costs a year per store. Within a month of the wage hike, Mendelsohn bought two standing kiosks for each of her six restaurants. That set her back $25,000 per store, for two screens, installation, software and other related costs. One of the two machines accepts cash, which she said was needed for her blue-collar customers.
An L.A. Carl’s Jr. restaurant. In California, CKE Restaurants, the owner and franchisor of Carl’s Jr. and Hardee’s, appears to be ahead of the pack on the use of AI technology.
(Los Angeles Times)
Mendelsohn figures that the kiosks might save five hours of labor a day. By that estimate, the machines would pay for themselves within a year and shave about 20% of the increased cost from the latest minimum wage increase. “We’re chipping away at it,” she said.
Self-service kiosks are ubiquitous in Western Europe, but they’re in fewer than 20% of fast-food establishments in the U.S., says Perse Faily, chief executive at Los Angeles-based Tillster, one of earliest providers of kiosks and other digital platforms for restaurants.
The COVID-19 pandemic pushed the trend in the U.S., she said, and now in California, “We’re seeing this complete sea change in thinking, ‘How do I address my labor costs?’”
Kiosks may be appealing in that they can not only save on labor, but also drive higher sales. Unlike people, the programmed machines are always trying to “upsell,” never forgetting to ask customers whether they want a drink with their meal or something else to go along with their entree.
Faily, Tillster’s CEO since late 2007, wouldn’t disclose the company’s sales increase, but said its new customers include Burger King and Popeyes, and that employment at the firm is up 75 from a year ago, to 340 currently. “The minimum wage increase has completely changed the landscape,” she said.
Other computer-guided upgrades are also aimed at cutting labor costs, from automatic avocado peelers and dishwashers to robotic arms that flip burgers and turn over fryer baskets.
But return on investments, while helpful for the bottom line, don’t do enough to offset burgeoning payroll expenses. So relatively few fast-food operators, for now, are making major investments in robotics and similar mechanical devices.
AI, on the other hand, looks like it could be a game-changer.
The pandemic boosted drive-through traffic at fast-food places to about 80% of sales from two-thirds pre-COVID, said Peter Selah, a restaurant industry analyst at BTIG. And AI order-taking opens the possibility of speeding up the drive-through process, increasing sales and reducing significant labor overhead.
But analysts say it’s likely to be at least a year or two, maybe longer, before AI-led drive-through reaches a consistent and high enough level of accuracy where companies are comfortable with it. Tests have often left frustrated customers demanding to talk to a live person rather than a bot, according to various accounts.
Major fast-food brands were reluctant to discuss their AI drive-through efforts. Nationally, McDonald’s has been out in front, using an IBM-developed system. A spokesperson would only say that McDonald’s “continues to gather learnings from the roughly 100 pilot restaurants testing automated order taking technology in the U.S. We expect to share more later this year.”
In California, CKE Restaurants, the owner and franchisor of Carl’s Jr. and Hardee’s, appears to be ahead of the pack on the technology, but like other chains, including Taco Bell, Burger King and El Pollo Loco, CKE declined to comment.
Analysts, however, say none of the AI platforms have reached more than 85% success in which human intervention isn’t needed.
“The hardest part is when you have people with accents, from different states and immigrants. It’s challenging,” said Danilo Gargiulo, senior analyst covering restaurants for Bernstein, an investment and research firm.
Still, Gargiulo sees the day when AI will speed up the drive-through line, boosting sales and consumer satisfaction. “Right now the drive-through time is slowed by repeated orders,” he said. With accurate AI speech recognition and faster, clearer communication to the kitchen staff, he said, you can cut as much as 90 seconds off what typically takes 5½ minutes for a customer to complete a drive-through purchase.
That’s what Ghai is betting on.
He says his initial investment for the AI drive-through technology, purchased from San Carlos-based Presto, is about $10,000 per store. Ghai estimates that if he can get it to perform at 90%, a store employee might have to step in to take over an order just three times every hour, freeing up the worker to do other tasks.
The AI system is getting better as it gathers more data, he said, and it’ll soon be able to communicate in Spanish. Add in mobile apps and loyalty programs, and AI has the potential to give fast-food customers a faster and more personalized service. And of course there’s the labor saving part: Ghai thinks the AI drive-through could reduce 10 to 15 hours of wages a day, and double that where he has two human order takers.
“Our goal isn’t to get rid of people. We’re in the people business at the end of the day,” he said. At the same time, Ghai added, over the long haul, “we’ll have fewer people.”
Business
Video: ‘Lack of Further Progress’ on Inflation Keeps Interest Rates High

new video loaded: ‘Lack of Further Progress’ on Inflation Keeps Interest Rates High
transcript
transcript
‘Lack of Further Progress’ on Inflation Keeps Interest Rates High
Jerome H. Powell, the Fed chair, said that the central bank needed “greater confidence” that inflation was coming down before it decided to cut interest rates, which are at a two-decade high.
-
Today, the F.O.M.C. decided to leave our policy interest rate unchanged and to continue to reduce our securities holdings, though, at a slower pace. Our restrictive stance of monetary policy has been putting downward pressure on economic activity and inflation, and the risks to achieving our employment and inflation goals have moved toward better balance over the past year. However, in recent months, inflation has shown a lack of further progress toward our 2 percent objective, and we remain highly attentive to inflation risks. We’ve stated that we do not expect that it will be appropriate to reduce the target range for the federal funds rate until we have gained greater confidence that inflation is moving sustainably toward 2 percent. So far this year, the data have not given us that greater confidence. In particular, and as I noted earlier, readings on inflation have come in above expectations. It is likely that gaining such greater confidence will take longer than previously expected.
Recent episodes in Business
Business
Global film and TV production down 7% this year following Hollywood strikes, report says

Global film and TV production was down 7% during the first quarter of 2024 compared with the previous year, according to a Wednesday report by film and TV tracking company ProdPro that illustrates Hollywood’s slow return to work in the wake of the writers’ and actors’ strikes.
ProdPro, a relatively new firm that follows film and TV production around the world, also found that production volume and spending levels were 50% lower over the last 12 months compared with the same period a year ago.
In the aftermath of the dual strikes — which largely halted film and TV shoots for about six months straight — entertainment workers and companies alike seemed eager to get back to business and resume filming immediately. But production has not rebounded as quickly or strongly as many had hoped, particularly in the Los Angeles area.
The recent decline in production continues a larger downward trend dating back to late 2022, when the entertainment industry began to feel the consequences of studios’ overspending during the streaming wars of the early 2020s. Since then, companies have been cutting back on staff and content in an effort to make up for their financial losses.
During the first week of 2024, 73 English-language scripted film and TV projects were actively shooting in the United States, compared with 136 in the first week of 2022, per ProdPro. By late March 2024, that number had risen to 135 — still lagging behind 2022’s total of 157.
Globally, 148 scripted TV productions began filming in the first quarter of 2024, compared with 140 during the same stretch in 2023; while only 165 feature films began shooting in the first quarter of 2024 compared with 216 in 2023, according to ProdPro.
While production for the big and small screen has been sluggish this year so far, ProdPro reported that “a significant number” of TV series and feature films are currently in development and on track to start shooting in the third and fourth quarters of 2024.
The ProdPro study notes that “studios are presumed to be holding back in part because of the uncertainty around the ongoing” contract campaigns by the International Alliance of Theatrical Stage Employees and Teamsters Local 399 — two labor unions advocating for Hollywood crew members.
On Monday, IATSE entered general contract negotiations with the Alliance of Motion Picture and Television Producers, which represents the major studios such as Disney, Warner Bros. and Netflix. This is the most critical phase of negotiations that could result, depending on how talks go, in a tentative deal or another work stoppage.
General negotiations are expected to cover issues related to pay, pension and health benefits, work-life balance, job security, streaming residuals and artificial intelligence.
“It’s civil,” Matthew Loeb, IATSE’s international president, previously told The Times about the current stage of bargaining. “Everybody wants to avoid a strike. But that’s not to say that it’s a foregone conclusion that they’ll meet our demands.”
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Dozens of Yale Students Arrested as Campus Protests Spread
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoLarry Webb’s deathbed confession solves 2000 cold case murder of Susan and Natasha Carter, 10, whose remains were found hours after he died
-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoHaiti Prime Minister Ariel Henry resigns, transitional council takes power
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoFirst cargo ship passes through new channel since Baltimore bridge collapse
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUS secretly sent long-range ATACMS weapons to Ukraine
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTurkey’s Erdogan meets Iraq PM for talks on water, security and trade
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSpanish PM Pedro Sanchez suspends public duties to 'reflect'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAmerican Airlines passenger alleges discrimination over use of first-class restroom