North Carolina
Meet the volunteers trying to 'Flip' North Carolina's courts

It all started with Donald Trump’s win in 2016. After the election, a group of shellshocked progressive Durham Democrats met at a bar to commiserate over their loss.
“We just were obviously horrified post-2016 election,” said Andrea Cash. “And that was the real moment of, ‘What are we going to do?’”
What they did was create FLIP NC, an all-volunteer grassroots organization co-founded by Amy Cox and Briana Brough. For the next year they knocked on 20,000 doors and sent 250,000 text messages to prospective voters in legislative districts that were competitive in the 2018 elections. Two years later, they worked even harder, making 400,000 calls and sending 1.4 million text messages to prospective voters.
FLIP’s focus in its first few elections was winning competitive seats up for grabs in the legislature. Volunteers wanted to end gerrymandering, and put legislators in office who were not going to draw districts skewed toward a specific political party.
“We want to be able to fight on a fair playing field for our progressive values, and it doesn’t feel like we can do that in North Carolina without fair maps,” Cox said.
But after the North Carolina Supreme Court upheld Republican lawmakers’ gerrymandered maps last year — the high court’s Republican majority reversed a ruling issued by a Democratic majority just months earlier — it became clear to FLIP NC volunteers that they’d need to focus on different races in the 2024 election: those for seats in the state Supreme Court and Court of Appeals.
“We can’t get fair maps,” Cox said. “Now we have to flip the court, then the legislature, so that we can get fair maps in 2030.”
Democrats cannot retake control of the state Supreme Court this year. Only one seat is up for election, the one currently occupied by Justice Allison Riggs, a Democrat. Even if Riggs wins, Democrats will still be outnumbered by the Republicans 5-2.
But if organizers like FLIP NC protect Riggs’ seat, protect Justice Anita Earls’ in 2026, and then flip two of the three seats up for election in 2028, Democrats will regain control of North Carolina’s high court — just in time for redistricting in 2030, when the maps will be redrawn once again.
“We need judges who are fair and who are not motivated by these extreme partisan aims, which I think is what we have now,” Brough said. “We focus on the courts because if we don’t have judges who are going to protect the rights of citizens, then we are not going to ever be able to stop the gerrymandering.”
FLIP NC’s efforts are aligned with the state Democratic Party’s. Earlier this year, Anderson Clayton, the party chair, vowed to put more attention and resources on the judicial races this November. After getting swept in recent statewide judicial races, Clayton said in January the party would hire a judicial coordinating campaign director, a specialist she said the Republicans have had for years.
FLIP’s ethos also echoes public comments made by Riggs, the Supreme Court justice and candidate herself. In a virtual forum in January, Riggs said she wasn’t just running to keep her seat. She was campaigning for the long game, talking to voters about Democratic judges’ values in an attempt to build “the pipeline to ensure that when we have the chance, we win back our courts in 2028.”
‘These races matter’
FLIP NC volunteers practice a “deep canvassing” style, prioritizing conversational flow over strict adherence to a script. They still hit the highlights, the stakes of the judicial races, but they ask voters what issues matter to them and talk about how judges’ decisions impact their everyday lives.
“It’s not transactional. It’s going to the door and asking, ‘What issues matter to you?’” said Cash, FLIP NC’s director of communications.
“Ideally, we want the voter to talk more than we’re talking,” Cox said. “It’s not just delivering information at them. It’s listening.”
They pass along an information sheet that gives general details about the political makeup of the state Supreme Court, and another that details how the Republican judges have ruled on key issues, inviting prospective voters to learn about how GOP Supreme Court justices blocked almost $700 million in public school funding and restored a voter ID law that a Democratic majority on the high court had deemed unconstitutional just months earlier. Their website makes note of Republican justices’ cozy relationship with corporations and the threat they can pose to reproductive rights.
“This court feels very corrupt, and people don’t know about it,” said Cox.
FLIP NC hosts a monthly canvas in Durham. Their next one is May 19. They are planning on hosting others in Asheville, Raleigh and Wendell in the coming months. And they are open to doing more throughout the state, should they find volunteers interested in helping spread the word throughout, or outside of, The Triangle.
“We hope to host more canvasses if we have other volunteers who can bring them to other areas,” said Cox.
For this year’s election, volunteers have knocked on 1,500 doors in Durham over two canvass sessions. Three issues they keep hearing about from voters: abortion, housing and education.
“We train volunteers to have the information about how the judges are ruling on all of these things,” Cox said.”[But] delivering that is not the most important thing. We want people to feel heard and we want them to come away with, ‘These races matter.’”
Turnout tends to be higher in presidential election years than in the midterms, but FLIP NC is trying to convince North Carolinians to fill out the entire ballot, not just tick the box for who they want to be president.
“We even saw that in the Democratic primary in March, people who voted in the presidential and then dropped off and didn’t vote in the governor’s [race,] didn’t vote in the Supreme Court [race,]” Cash said. “It’s just not a given that everyone who goes to the polls will fill out the full ballot.”
Despite the challenge, Cash, Cox and Brough are optimistic, if cautious. They are excited about the direction of the Democratic Party’s leadership and its candidates. But that doesn’t mean they’ve forgotten their despair after Trump’s victory in 2016, the election that led to FLIP NC’s genesis.
“I will never again be flagrantly optimistic about elections,” Brough said. “I just think you need to fight for every inch, because you don’t know what’s going to happen.”

North Carolina
The question of master’s pay for North Carolina teachers

 |
When Diana Chapman was applying to UNC-Chapel Hill’s Master of Arts in Teaching (MAT) program earlier this year, she knew she eventually wanted to teach in the Wake County Public School System — or leave North Carolina entirely.
The convenience of being close to her family in Raleigh was one factor, but a more important one was pay. Last year, Wake County Schools re-implemented a master’s pay program for teachers in the district: a 10% pay bump for teachers with a master’s degree.
This pay raise was an initiative funded statewide in North Carolina until 2013. Teachers who already had a master’s degree retained their raises, as did any teachers who had already started a master’s program in education or a related field before August 1, 2013 — but anyone who began their program after that date did not receive the higher pay.
The program was discontinued at the state level that year because of studies demonstrating that teachers with master’s degrees aren’t more effective at raising student test scores than teachers without them.
But to future teachers like Chapman, test scores aren’t the only way she sees herself measuring student success — and her own skills in the classroom — after she graduates with her MAT.
“I think there’s a lot more merit to be said about getting a master’s degree than teacher effectiveness via student test scores in the classroom,” Chapman said.
Education funding in North Carolina
Last March, Wake County’s school board voted to reinstate the 10% pay bump for teachers with master’s degrees using local recurring funds.
Elena Ashburn, the central area superintendent at Wake County Schools, didn’t work directly on the proposal, but fully supports it. She said master’s pay compensates qualified teachers for an increased level of professionalism they bring to the classroom.
“We have a lot of staff who have committed to this work that have their master’s degree — that are, quite frankly, going to do this work, even if they didn’t get this 10% raise,” Ashburn said. “So on the one hand, it rewards, it helps retain, it helps professionalize the people that we already have that are doing such incredible work in our schools.”
The other reason for the salary bump was to help recruit new teachers, Ashburn said.
For teachers in Wake County already grandfathered into the program, there weren’t any salary changes. But with the pay bump, a new teacher with a master’s degree would be making almost $400 a month more, according to North Carolina’s 2023-2024 State Salary Schedules.
In North Carolina, public school teachers are paid a base salary from the state dependent on years of experience. In the 2023-2024 school year, a first-year teacher earned $39,000 annually, while a teacher with 15 years of classroom experience earned $52,060 as their base pay.
That number can increase based on bonuses for classroom achievement and local supplements that range widely between districts. The average supplement is just over $5,000, but some counties don’t have a local supplement at all.
Before reintroducing the master’s pay program, Wake County’s average teacher supplement was $8,670 — the second-highest in the state in 2021-22, according to a BEST NC report on teacher pay.
Because these extra funds come from local dollars, lower-wealth counties typically aren’t able to offer as high of a supplement. The state legislature created the Teacher Supplement Assistance allotment in 2021 to try to address this problem.
If other districts wanted to re-implement a master’s pay program, they wouldn’t necessarily have the money to, unless the funds came from the state.
“Our rural counties can’t do that kind of supplemental pay program that our urban counties are doing,” said Susan Book, one of the co-founders of Save Our Schools NC. “And so we see great inequities in teacher pay across the state, which I find concerning.”
Paths to teaching with a master’s
The master’s degree in history Katie Bollinger received from American Military University in 2010 meant she was eligible for North Carolina’s master’s pay program when she started teaching middle school in Wake County in 2011.
She taught primarily social studies and science classes, and also a few in language arts, during her 12 years in Wake County. But because her degree was in history — and not a master’s in education or a master’s in teaching — she was more constrained in how that pay was applied.
“I actually had to teach my subject matter to get that pay,” Bollinger, who now teaches in Onslow County Schools, said. “Because if I were to teach anything less than 50% social studies, I would not get that master’s pay.”
Master’s pay programs offering raises to teachers with advanced degrees are popular throughout the rest of the country — North Carolina was the first state to eliminate the program in 2013. About 90% of the largest districts in the country have some kind of incentive for teachers with master’s degrees, according to the National Council on Teacher Quality’s Teacher Contract Database.
Critics of master’s pay programs claim that master’s pay only incentivizes getting a degree, not being a better teacher.
When the statewide program was in place, the master’s degree received had to be content-specific to a teacher’s subject area — like Bollinger’s — or in education.
That meant a teacher could get an advanced degree in School Administration, for example, for the sake of the master’s pay bump, but then go straight back to the classroom — where the skills they built during the graduate degree weren’t necessarily being applied to make them more effective educators.
In other cases, a master’s degree is how a future teacher gets their teaching license after an undergraduate degree in another subject — like Chapman, the future MAT student, who will graduate from UNC-CH in May with a degree in English and a minor in education.
UNC-CH does not have an undergraduate education major where students graduate with a teaching license. For UNC-CH students, a master’s degree — or an external program like Teach for America — is a natural next step toward a career in teaching.
While Chapman has both content-specific and teaching knowledge from her minor going into the MAT, Frank Forcino — the director of the science education program at Western Carolina University — said that’s not always the case.
“Folks that are trying to get in [Western’s] MAT program don’t have that content knowledge as often as they used to,” Forcino said. “And that is typically not as good for the students because in order to, you know, explain content, teach content, you really do need to have a deep understanding of it.”
Students who come into the MAT from other disciplines or careers don’t always have the opportunity to develop a pedagogical background — and because so much of the MAT structure is in the classroom, it can feel like they’re just being thrown in the deep end, Forcino said.
“They are learning how to be a teacher by being a teacher,” Forcino said. “They don’t have any training when they start and they’re getting this training as they go, while they’re being overwhelmed with being a first-time teacher.”
He said it’s hard to generalize which route leads to “better” teachers because there are so many factors affecting teacher effectiveness and student success in the classroom.
Forcino, though, almost always recommends a four-year education degree over just a MAT to the students he advises at Western. Even if it takes an extra semester of a student’s undergraduate career, there is much more time for a future teacher to develop both content-specific knowledge and learn teaching methods, he said.
But that’s the route that wouldn’t get a teacher a pay bump with a master’s pay system in place.
Read more about teacher pay
Beyond master’s pay
Since accepting admission to UNC-CH’s MAT program, Chapman has changed her mind about Wake County Schools. As someone who eventually wants to teach future teachers in a higher education setting, she thinks the experience of teaching in different districts in North Carolina will be valuable for her future career.
And the scholarships she’s gotten from UNC-CH mean she now knows she won’t have to worry about student loans going into her teaching career.
“But I think that for a while, I was definitely looking around, like, ‘Where can I live comfortably, and not have to eat ramen every day?’” Chapman said.
Bollinger now teaches at a middle school in Onslow County. She makes less there than she did during her years in the Wake County Public School System, but the rapidly rising cost of living in the Triangle area was too much for her to sustain on a teacher’s salary, she said.
The base pay for a new teacher will increase to $41,000 for 2024-2025 school year, due to raises approved in the North Carolina General Assembly’s most recent budget.
But, according to Forbes, the average two-year master’s program in the United States costs almost $40,000. UNC-CH’s MAT costs roughly $13,000 in tuition for the yearlong program, with Duke University’s MAT running closer to $50,000 — more than the starting teacher base salary.
Tara Wojciechowski, a chemistry teacher at Wake County High School, has reached the top of the North Carolina teacher pay scale — which caps at 25 years — with her 27 years in Wake County classrooms. Even so, for her, it’s never been about the dollar figure she brings home.
“It’s not about the pay, necessarily — I mean, if you have a partner that makes a decent amount of money, anyway,” Wojciechowski said. “I feel bad for all the single teachers out there.”
Wojciechowski said she has never felt the need to get her master’s degree — partially because of her financial situation, but also because she has her National Board Certification — which comes with a 12% pay bump paid out at the state level.
To be National Board-certified, teachers who have been in the classroom for at least three years to “demonstrate standards-based evidence of the positive effect they have on student learning,” according to the National Board website.
Research has demonstrated National Board certification is correlated with student achievement, but high-poverty districts have a much lower percentage of certified teachers.
According to a 2023 BEST NC report on teacher pay, just 5% of teachers at the highest-poverty schools are National Board-certified, compared with nearly triple that in the most well-off districts — presumably, at least in part, because of temptingly higher salaries in those districts.
Forcino said in his eight years teaching at Western, there have been only a few students who have stayed in the area to teach after graduating. Most of them, he said, have headed back to where they’re from, or to Raleigh and Charlotte for those more competitive salaries. Others have left to go to Georgia, South Carolina or even further away.
Keeping salaries competitive, by whatever means, is essential for ensuring there are qualified teachers in North Carolina classrooms, he said, but there’s more to it. Forcino said if parents and administrators are making teachers’ lives more difficult, that hardly incentivizes them to remain in a classroom, much less advance their professionalism with a degree.
“We need to pay teachers more — that’s the definitive fact. We need to pay them a competitive salary,” Forcino said. “But aside from that, the other key factor that goes into ensuring teachers stay in the field is giving them support, making them feel valued in their career.”
North Carolina
Why are flags flying at half-staff in North Carolina?

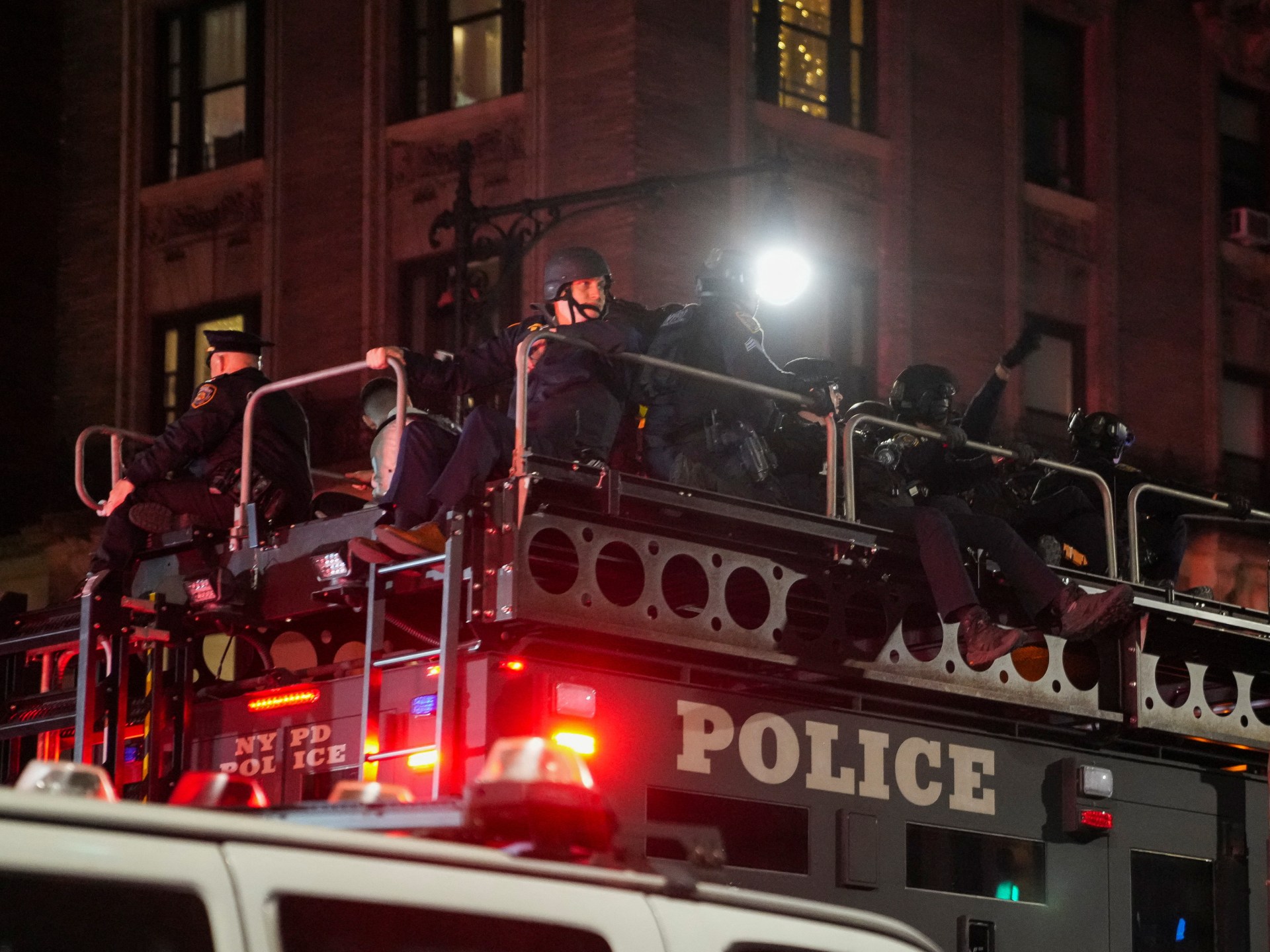
Four law enforcement officers killed in North Carolina shooting
Charlotte police say U.S. Marshals were killed while trying to serve a warrant when suspects started shooting at them
United States and North Carolina flags at state facilities are flying at half-staff in North Carolina to honor the lives of four officers slain in a shootout on Monday, April 29.
Gov. Roy Cooper made a statement on the lowering of flags in an April 30 news release.
“Yesterday, North Carolina and our country lost four heroes who made the ultimate sacrifice in the line of duty working to protect our communities,” Cooper said. “Our prayers are with their friends and families as they navigate this difficult time and we remember and honor the lives of these law enforcement officers.”
Why are the flags at half-staff in North Carolina?
Cooper ordered flags to be lowered to half-staff to honor four officers who were shot to death in a standoff in Charlotte, N.C., on Monday.
The news release named Samuel “Sam” Poloche and William “Alden” Elliott, both 14-year veterans of the N.C. Department of Adult Corrections who served in the Special Operations and Intelligence Unit. Poloche joined the unit in 2013, Elliott in 2016 after each served several years as probation/parole officers. Officer Joshua Eyer was a six-year veteran of the Charlotte Mecklenburg Police Department. A Deputy U.S. Marshal, who has not yet been publicly named, was the fourth officer killed.
4 Charlotte, NC officers killed: Suspect named, two people being questioned after 4 officers killed serving warrant in NC
How long will flags be at half-staff?
The U.S. and N.C. flags will be flown at half-staff beginning immediately and will remain at half-staff until sunset on Friday, May 3.
Why do flags fly at half-staff?
Usa.gov states that the American flag flies at half-staff when the country or a state is mourning. The president, a state governor or the mayor of the District of Columbia can order flags to fly at half-staff.
An American flag flying at half-staff generally indicates one of these three things:
- The death of a government official, military member or emergency first responder.
- A national tragedy.
- Memorial Day or another national day of remembrance.
Where will flags be flown at half-staff?
Cooper ordered all state facilities in N.C. to fly flags at half-staff.
While only state facilities are ordered to lower flags, the news release encouraged individuals, businesses, schools, municipalities, counties and other government subdivisions to fly flags at half-staff for the duration of time indicated to honor the fallen officers.
Is it half-mast or half-staff?
Previous reporting from Memphis Commercial Appeal explained that flags are flown at half-mast on ships and at naval stations ashore, and at half-staff elsewhere.
Iris Seaton is the trending news reporter for the Asheville Citizen Times, part of the USA TODAY Network. Reach her at iseaton@citizentimes.com.
North Carolina
Boviet Solar Invests $294 Million in North Carolina: First Manufacturing Facility in North America Signals Growth in U.S. Solar Industry

Boviet Solar Technology Co. Ltd., a leading Vietnamese solar energy technology company specializing in monocrystalline PV cells, announces its decision to establish its inaugural production facility in North America, specifically in Greenville, Pitt County, North Carolina. The facility, representing a $294 million investment, is set to create approximately 908 skilled local jobs and bolster the region’s economy.

The company’s move signifies its commitment to the U.S. solar market and aims to meet the growing demand for renewable energy solutions. Boviet Solar’s expansion into North Carolina follows its successful track record of PV cell and module production in Vietnam.

The manufacturing facility will initially focus on producing Boviet Solar’s TOPCon N-Type cell-based Monofacial and Bifacial PV modules for various applications, including residential, commercial, industrial, and utility-scale projects. Phase one of the project will utilize existing infrastructure, while phase two involves constructing a state-of-the-art factory on 34 acres to manufacture PV cells.

Scheduled for completion in Q1 2025, the facility is expected to output 2 GW of solar panels and 2 GW of PV cells annually, significantly contributing to the local clean energy sector.
North Carolina Governor Roy Cooper expressed his enthusiasm for welcoming Boviet Solar to the state, highlighting North Carolina’s reputation as a hub for clean energy and its supportive business environment.
Representative Don Davis of North Carolina’s 1st District emphasized the positive impact of Boviet Solar’s investment in the region, noting its contribution to innovation and sustainability efforts.
Greenville Mayor P.J. Connelly echoed the sentiment, underscoring the collaborative efforts that led to attracting Boviet Solar to the community and the significant economic benefits it brings.
Boviet Solar’s decision to establish a manufacturing facility in North Carolina underscores its dedication to providing high-quality, locally-made PV modules and its commitment to sustainability and innovation in the U.S. solar industry.
Related
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Dozens of Yale Students Arrested as Campus Protests Spread
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoEU sanctions extremist Israeli settlers over violence in the West Bank
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoShipping firms plead for UN help amid escalating Middle East conflict
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago'Nothing more backwards' than US funding Ukraine border security but not our own, conservatives say
-
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDemocrats hold major 2024 advantage as House Republicans face further chaos, division
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFetterman hammers 'a–hole' anti-Israel protesters, slams own party for response to Iranian attack: 'Crazy'
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPeriod poverty still a problem within the EU despite tax breaks
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoA battle over 100 words: Judge tentatively siding with California AG over students' gender identification



:focal(0x0:3000x2000)/static.texastribune.org/media/files/7f2ab0eaa2e932a5836ae87d24b97af6/1107%20Election%20Day%20Houston%20AM%20TT%2013.jpg)