Health
Marburg virus: CDC warns US public health officials of Ebola-like disease
The U.S. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention (CDC) printed a warning in regards to the uncommon Ebola-like Marburg virus Thursday, advising American public well being officers and docs to be looking out.
There are two confirmed outbreaks of Marburg virus illness (MVD) in Tanzania and Equatorial Guinea. The CDC says the pathogen possible spilled over from wild animals to people.
There have been no reported Marburg diagnoses within the U.S., however the CDC seeks to “enhance consciousness of the danger of imported circumstances in america.”
The illness is normally unfold by means of contact with contaminated blood or different bodily fluids relatively than airborne transmission.
PRIOR COVID INFECTION PROVIDES JUST AS MUCH PROTECTION AS VACCINES, NEW STUDY FINDS
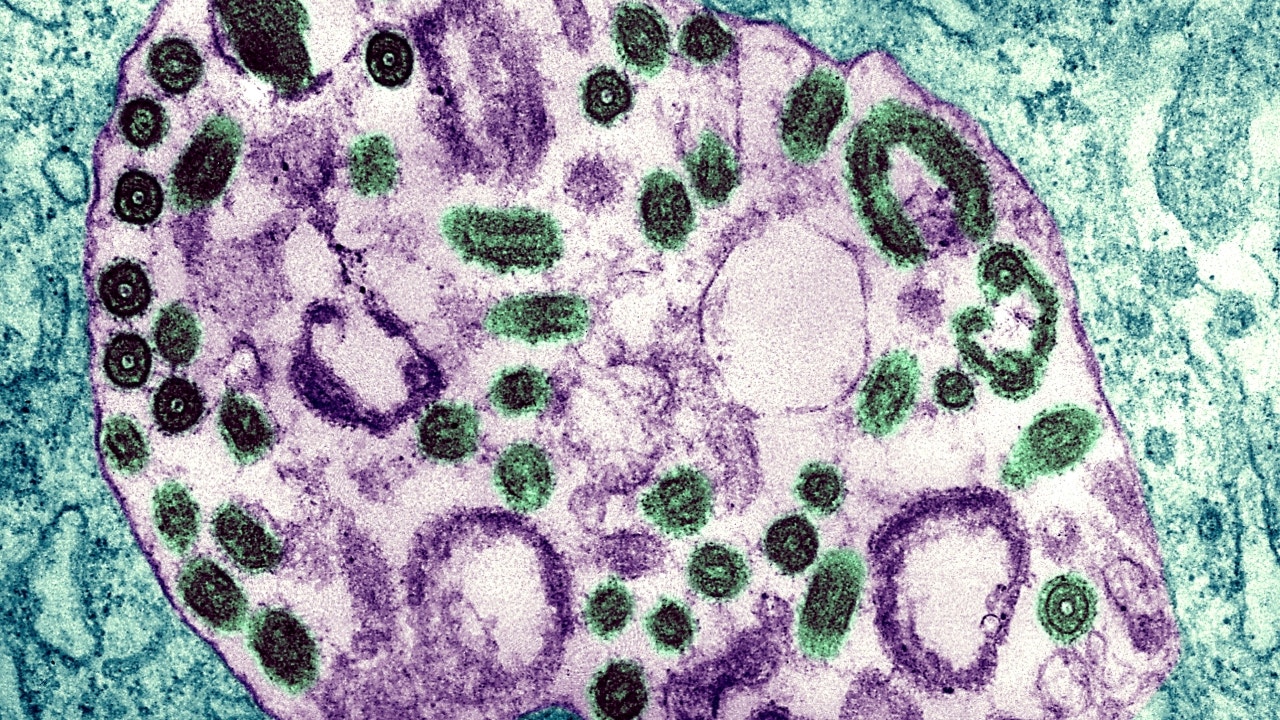
Electron Micrograph Of The Marburg Virus. Marburg Virus, First Acknowledged In 1967, Causes A Sever Kind Of Hemorrhagic Fever, Which Impacts People, As Nicely As Non Human Primates.
“At present, the danger of MVD in america is low; nevertheless, clinicians ought to pay attention to the potential for imported circumstances,” the CDC mentioned.
The illness has epidemic potential, in keeping with the World Well being Group (WHO). It has excessive fatality charges — out of eight Tanzanian circumstances reported thus far, 5 of the sufferers died.
Equatorial Guinea officers reported their first outbreak Feb. 13, the place there have been 14 confirmed circumstances and 10 deaths. The Tanzanian authorities introduced its first-ever outbreak of MVD on March 21.
SILENT PANDEMIC’ WARNING FROM WHO: BACTERIA KILLING TOO MANY PEOPLE DUE TO ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
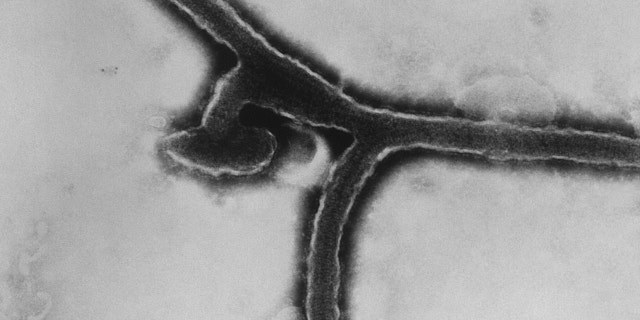
This transmission electron micrograph (TEM) revealed among the ultrastructural morphology exhibited by the Marburg virus, the reason for Marburg hemorrhagic fever.
Signs embrace headache, fatigue, sudden fever, unexplained bleeding and gastrointestinal signs. Muscle and joint ache and lack of urge for food are additionally frequent.
The incubation interval is normally two to 21 days. The CDC famous that the illness is usually tough to diagnose.
“Most of the indicators and signs of MVD are just like different infectious ailments (equivalent to malaria or typhoid fever) or viral hemorrhagic fevers which may be endemic within the space (equivalent to Lassa fever or Ebola),” the CDC mentioned. “That is very true if solely a single case is concerned.”
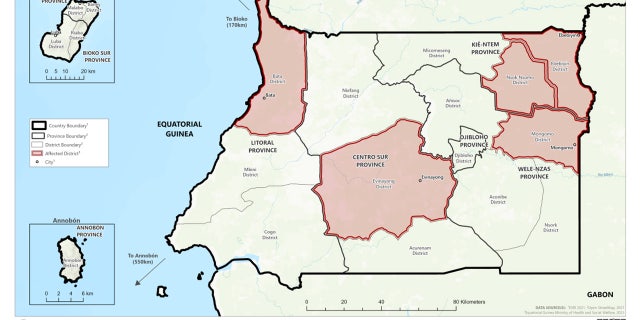
Equatorial Guinea officers reported their first outbreak on February 13, the place have been 14 confirmed circumstances and 10 deaths. (Heart of Illness Management)
The CDC says the illness’s mortality fee is anyplace from 23% to 90%. There isn’t any Meals and Drug Administration (FDA) authorised vaccine for the illness, however fluid alternative and intensive supportive care in its early phases will be profitable.

Health
Treating Other Diseases With Ozempic? Experts Weigh In | Woman's World

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
FDA bans red food dye due to potential cancer risk

FDA looks to ban red food dye
Celebrity fitness trainer Jillian Michaels joins ‘Hannity’ to discuss the possibility of the FDA banning red food dye.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has officially banned red dye — called Red 3, or Erythrosine — from foods, dietary supplements and ingested medicines, as reported by the Associated Press on Wednesday.
Food manufacturers must remove the dye from their products by January 2027, while drug manufacturers will have until January 2028 to do so, AP stated.
Any foods imported into the U.S. from other countries will also be subject to the new regulation.
RED FOOD DYE COULD SOON BE BANNED AS FDA REVIEWS PETITION
“The FDA is taking action that will remove the authorization for the use of FD&C Red No. 3 in food and ingested drugs,” said Jim Jones, the FDA’s deputy commissioner for human foods, in a statement.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has officially banned red dye — called Red 3, or Erythrosine — from foods, dietary supplements and ingested medicines (iStock)
“Evidence shows cancer in laboratory male rats exposed to high levels of FD&C Red No.3,” he continued. “Importantly, the way that FD&C Red No. 3 causes cancer in male rats does not occur in humans.”
The synthetic dye, which is made from petroleum, is used as a color additive in food and ingested drugs to give them a “bright cherry-red color,” according to an online statement from the FDA.

Food manufacturers must remove the dye from their products by January 2027, while drug manufacturers will have until January 2028 to do so. (iStock)
The petition to ban the dye cited the Delaney Clause, which states that the agency cannot classify a color additive as safe if it has been found to induce cancer in humans or animals.
The dye was removed from cosmetics nearly 35 years ago due to potential cancer risk.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“This is a welcome, but long overdue, action from the FDA: removing the unsustainable double standard in which Red 3 was banned from lipstick but permitted in candy,” said Dr. Peter Lurie, director of the group Center for Science in the Public Interest, which led the petition effort, as reported by AP.

Nearly 3,000 foods are shown to contain Red No. 3, according to Food Scores, a database of foods compiled by the Environmental Working Group. (iStock)
Dr. Marc Siegel, clinical professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health and Fox News senior medical analyst, applauded the FDA’s ban.
“It was a long time coming,” he told Fox News Digital. “It’s been more than 30 years since it was banned from cosmetics in the U.S. due to evidence that it is carcinogenic in high doses in lab rats. There needs to be a consistency between what we put on our skin and what we put into our mouths.”
“There needs to be a consistency between what we put on our skin and what we put into our mouths.”
Siegel said he believes the FDA’s decision could be tied to the incoming new head of the Department of Health and Human Services, Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
“They knew it would have happened anyway under RFK Jr.,” he said. “It is already banned or severely restricted in Australia, Japan and the European Union.”

The food additive also “drew kids in” to a diet of empty calories and ultraprocessed foods, one doctor stated. (iStock)
The food additive also “drew kids in” to a diet of empty calories and ultraprocessed foods, Siegel added.
“It has also been linked to behavioral issues in children, including ADHD.”
Nearly 3,000 foods are shown to contain Red No. 3, according to Food Scores, a database of foods compiled by the Environmental Working Group.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
The National Confectioners Association provided the below statement to Fox News Digital.
“Food safety is the number one priority for U.S. confectionery companies, and we will continue to follow and comply with FDA’s guidance and safety standards.”
The petition to remove Red No. 3 from foods, supplements and medications was presented in 2022 by the Center for Science in the Public Interest and 23 other organizations and scientists.
Health
How Yvette Nicole Brown Lost Weight and Got Her Diabetes Under Control

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science6 days ago
Science6 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoAmazon Prime will shut down its clothing try-on program
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoMapping the Damage From the Palisades Fire
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoMourners Defy Subfreezing Temperatures to Honor Jimmy Carter at the Capitol
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25826211/lorealcellbioprint.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25826211/lorealcellbioprint.jpg) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoL’Oréal’s new skincare gadget told me I should try retinol
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25832751/2192581677.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25832751/2192581677.jpg) Technology2 days ago
Technology2 days agoSuper Bowl LIX will stream for free on Tubi
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoWhy TikTok Users Are Downloading ‘Red Note,’ the Chinese App














