World
What the Scale of Displacement in Gaza Looks Like

Source: Satellite image by Maxar Technologies
Up to 1.8 million Gazans — around 80 percent of the population — have been forced to leave their homes since Israel began its bombardment in response to Hamas’s attack on Oct. 7. That number is expected to rise after Israel issued a new evacuation order on Saturday for areas in the south.
Total number of people displaced in the Gaza Strip since Oct. 7
Source: United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs via HDX
Note: Estimates for the number of displaced people staying outside the shelter system are difficult to obtain and corrected periodically.
Gaza has never experienced so much internal displacement in such a short time. Earlier conflicts forced hundreds of thousands of Palestinians from their homes, but refugee experts said the current war was unprecedented for the number of people displaced within the enclave’s 140 square miles.
With Israel barring most Gazans from leaving and shelters swelling to many times over their capacity, humanitarian aid workers say there is no safe place to go as the fighting continues.
Where displaced people are staying at United Nations and government shelters
Each circle represents the total number of displaced people in shelters within one square kilometer.
Sources: ReliefWeb Response (shelter populations); Israeli military (evacuation zone boundaries)
Note: Shelter locations shown are primarily schools; data for medical facilities and other buildings serving as shelters was not available. Data is as of Nov. 28.
There are at least 14 government and United Nations shelters within the new evacuation zone that Israeli forces announced on Saturday. These shelters had registered more than 68,000 displaced people as of Nov. 28.
“People are sleeping on the streets and sidewalks without any means of protection,” said Yousef Hammash, an advocacy officer for the Norwegian Refugee Council, who fled from his home in northern Gaza in mid-October to stay with more than 40 relatives in a two-room home in Khan Younis. “And people in the shelters are trying to convince themselves that it’s a bit more safe than being in the street.”
“The situation before was unimaginable, and now they want to move people again,” he added.
Palestinians evacuated their homes damaged by Israeli airstrikes in Gaza City.
Ahmad Hasaballah/Getty Images
A school in Khan Younis where displaced people have found refuge.
Samar Abu Elouf for The New York Times
About 1.4 million Palestinans have found shelter in or outside of Gaza’s schools, medical centers, mosques and churches. The rest — as many as a half a million people — are thought to be staying with relatives and even strangers, often sleeping outside in courtyards or crammed into small apartments.
A majority of the displaced have moved south, as intense air- and ground strikes by Israeli forces have destroyed much of the north, making it unlivable. But tens of thousands are estimated to remain in the north, including many who are unable to travel, such as the sick and disabled.
Humanitarian organizations warn that shelters, even in the south, are not protected from fighting. The U.N. reported on Nov. 23 that since the start of the conflict, an estimated 191 people in shelters had been killed and 798 had been injured.
Many schools housing displaced people have been damaged since the war began, according to a UNICEF tracker, which relies on reports from other organizations on the ground.
Schools that have sheltered displaced people and have been damaged
Sources: UNICEF (shelter damage); Israeli military (evacuation zone boundaries)
Note: Major damage means the building exists but is not usable; moderate damage means the building is usable but damage occurred to the building’s infrastructure; minor damage means damage occurred to windows, doors and other parts of the building. Map includes government schools only. Data is as of Dec. 1.
At least 28 government schools functioning as shelters have sustained major damage in the North Gaza and Gaza regions, making them no longer usable, and 122 others across the territory have sustained moderate or minor damage.
The U.N. has estimated that most of its shelters are at four times their capacity, at minimum, and unable to accommodate more people.
“You have to wait in line for two hours, just to use the bathroom,” Mr. Hammash said. “To have a shower is kind of a dream.”
Number of people staying in shelters in each region since Oct. 7
Many Gazans have moved south, but tens of thousands remain in shelters in the north.
Source: United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs via HDX
The shelter population has soared in the Gaza Strip since the start of the war, especially in the central and southern regions of Deir al Balah, Khan Younis and Rafah, areas to which Israeli forces have told Palestinians to evacuate.
Close quarters and limited access to safe water and bathrooms is contributing to the spread of disease, along with the onset of winter, according to the World Health Organization. The agency has reported thousands of cases of acute respiratory infections, diarrhea and skin rashes in Gaza on average each day.
A tent camp in Khan Younis.
Mohammed Salem/Reuters
A man prepares a fire for cooking at a U.N. school being used as a shelter in Gaza City.
Omar El-Qattaa/Agence France-Presse — Getty Images
During the seven-day cease-fire that ended on Friday, some people temporarily left shelters to return to their homes to investigate any damage. Some people displaced in the south even tried to go back to the north, according to the U.N.
The safety of displaced people is uncertain as the fighting continues into its ninth week, and people are once again forced to move to new locations.
“We are going to a new level of madness and bombardment,” Mr. Hammash said. “Now it’s the turn of the south.”

World
As Superman Hits Theaters, James Gunn Is Reportedly Eyeing at Least Two TV Spinoffs

You will be redirected back to your article in seconds
ad
World
Missing teen surfer found alive on remote island miles from shore: 'Didn't give up hope'

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
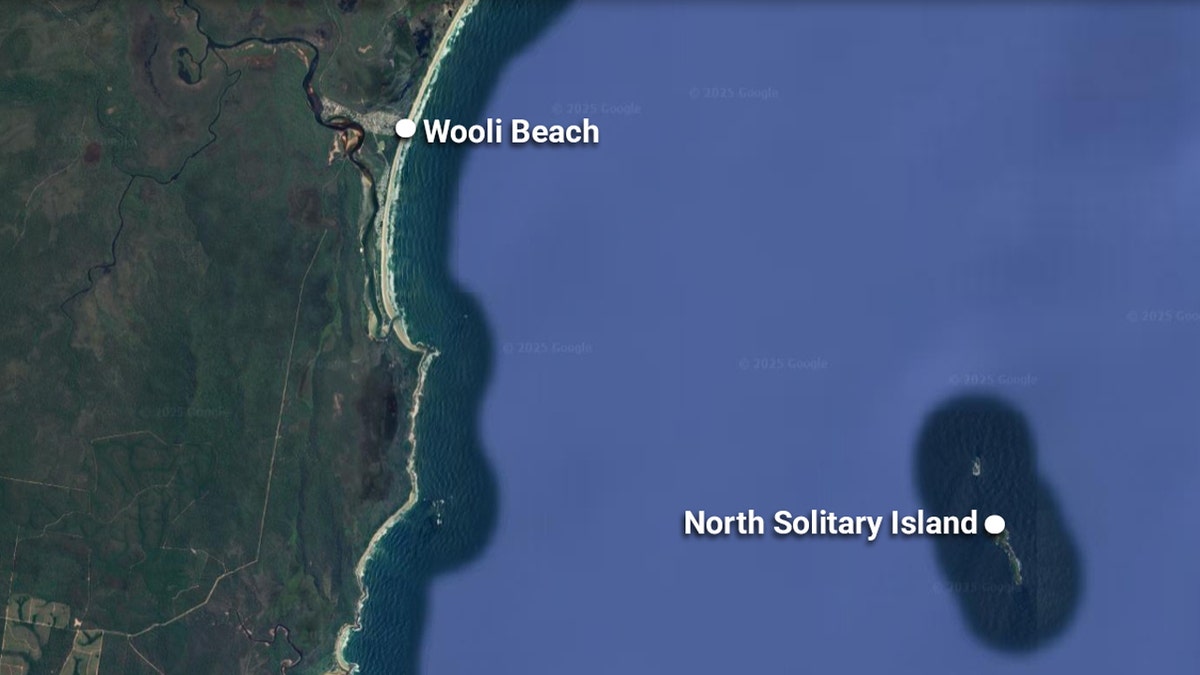
A surfer who went missing after paddling out in the ocean Wednesday afternoon was located the next day on a remote island roughly 8 miles from where his bicycle and clothes were found at a beach access point in New South Wales, Australia.
The New South Wales Police Force said in a news release Thursday morning the 19-year-old man, later identified as surfer Darcy Deefholts, had been located after being swept away and going missing the day before.
Police said Deefholts left his home in Wooli on a bicycle at about 2:30 p.m. Wednesday toward Wooli Beach.
After failing to return home, concerned family members contacted police, and a search on land and sea commenced around Wooli Beach.
AT LEAST 2 DEAD, 43 MISSING AFTER FERRY SINKS NEAR BALI
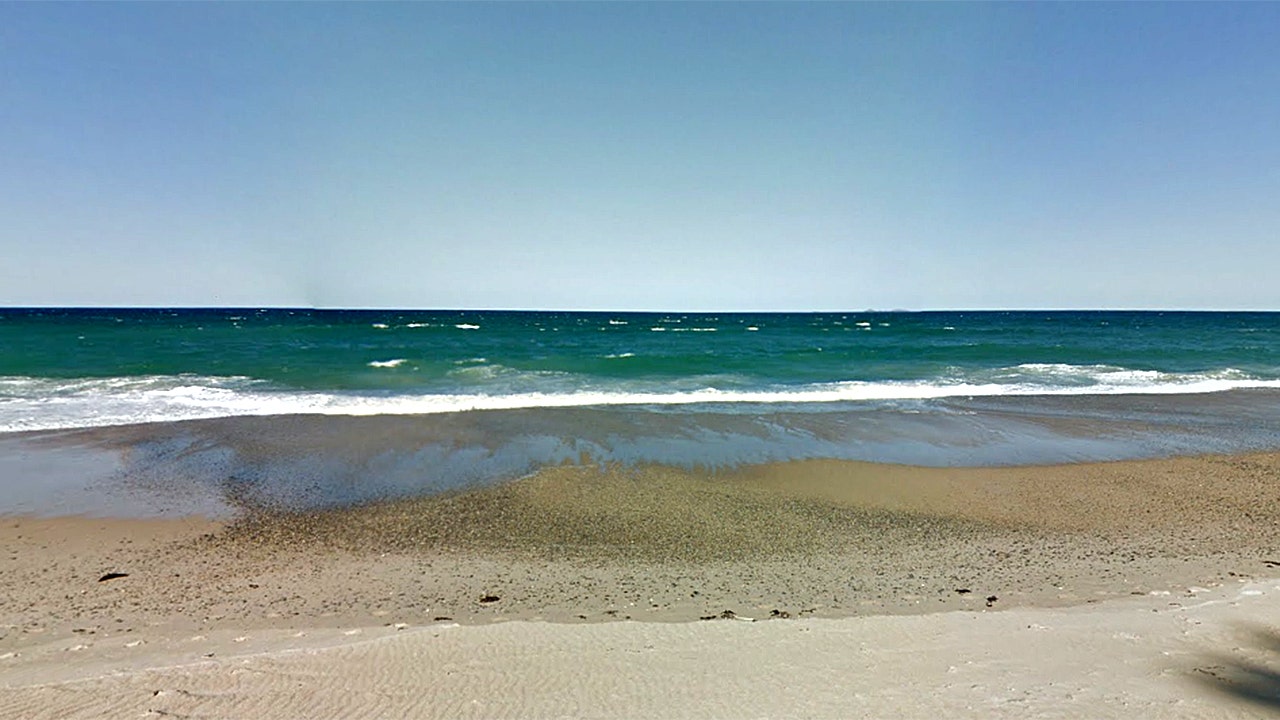
An Australian surfer who went missing Wednesday was found Thursday on an island nearly 8 miles from shore. (Google Maps)
The next morning, Deefholts was located safely on a small island called North Solitary, about 8 miles southeast of Wooli Beach.
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) reported Darcy’s father, Terry Deefholts, could not believe the news Darcy had been found at about 9 a.m. Thursday.
“It’s kind of surreal. I was at the point of thinking the absolute worst,” Terry Deefholts told the station. “I didn’t give up hope, but, jeez, I was close.”
Earlier in the day, the teenager was seen riding his bike around town and fishing at the Wooli breakwall.
Family members became concerned Wednesday night after Darcy’s clothes and bicycle were located at a beach access point in Wooli, just east of Grafton.
AMERICAN TOURIST VANISHES IN TROPICAL PARADISE AFTER EARLY MORNING WALK FROM VACATION RENTAL
An Australian surfer who went missing Wednesday was found on an island nearly 8 miles away off the coast of Wooli Beach in New South Wales July 10, 2025. (Google Earth)
Melissa Smith, a family member, told the station Darcy likely went out too far on his surfboard and could not get back to shore.
“He’s a survivor, a strong boy. He would have known that was a safe place, I guess,” she said.
ABC reported that family members believed Darcy had a Malibu surfboard with him, though his smartwatch and cellphone were left at home in Wooli.
Search efforts continued through about 1 a.m. Thursday and commenced at first light.
FREAK ACCIDENT AT THE BEACH SENDS TEEN TO ICU AS MOM WARNS OF WATERFRONT DANGER

Police joined search efforts after a 19-year-old surfer went missing at Wooli Beach in New South Wales, Australia. (iStock)
Thursday morning’s efforts included six private vessels and a Marine Rescue team, though what was puzzling to some was how calm the sea conditions were and the small amount of wind and swell.
“There is a fair bit of current running north to south further out, so I suspect he has ended up in [a] current and drifted south,” Marine Rescue skipper Matthew McLennan told ABC.
Later that morning, one of the search crews found Darcy and reported that he was cold and suffering from exposure, though he was not injured.
Darcy was transported to a nearby hospital after returning to shore.
A spokesperson from the local health district in Northern New South Wales said in a statement obtained by the station that Darcy was in stable condition and “in good spirits and being supported by family.”
World
New amnesty law for human rights abuses in Peru prompts fury, action

Lawyers for victims of human rights abuses committed during Peru’s decades-long armed conflict have pledged to appeal to international bodies to overturn a law passed by the country’s Congress, which would grant amnesty to prosecuted military and police members, as well as other forces.
“We’re not only going to the domestic arena to seek its invalidation, but we’ve already taken some action at the international level,” lawyer Gloria Cano, director of the Pro Human Rights Association, said during a news conference on Thursday.
A congressional commission on Wednesday approved the bill granting amnesty to members of the armed forces, national police and local self-defence committees, said legislator Alejandro Cavero, third vice president of the country’s Congress.
Cano also said her association had already alerted the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights and Inter-American Court of Human Rights, and planned to go to the United Nations, as well.
After the Peruvian Congress passed the bill, Volker Turk, the UN’s national human rights coordinator, said on X that “impunity does not hide the crime, it magnifies it.”
Amnesty International earlier urged the legislature to side with victims and reject the bill. “The right to justice of thousands of victims of extrajudicial executions, forced disappearances, torture, and sexual violence would be violated,” the rights group said on X.
A coalition of human rights organisations in Peru said the new law could wipe out 156 convictions and another 600 cases that are being prosecuted.
The law, which awaits President Dina Boluarte’s approval, benefits uniformed personnel who were accused, are still being investigated or are being tried for crimes stemming from their participation in the country’s armed conflict from 1980 to 2000 against left-wing rebels. Boluarte has not made any comment on the amnesty, even before its passage.
The bill was presented by Congressman Fernando Rospigliosi, from the right-wing Popular Force party of Keiko Fujimori, daughter of the late former leader Alberto Fujimori.
Fujimori’s decade as president from 1990 was marked by ruthless governance.
He was jailed for atrocities – including the massacre of civilians by the army – but released from prison in 2023 on humanitarian grounds.
The new law specifies that a humanitarian amnesty will be granted to people more than 70 years old who have been sentenced or served a prison sentence.
Critics have warned that the legislation would hinder the search for truth about the period of violent conflict, which pitted state forces against Shining Path and Tupac Amaru rebels, and killed about 70,000 people.
“Granting amnesty to military and police officers cannot be a reason for impunity,” Congressman Alex Flores of the Socialist Party said during debate on the bill.
There have been numerous attempts in recent years to shield the military and police from prosecution in Peru for crimes committed during the conflict – but opponents of amnesty have found success before at international bodies.
The Inter-American Court of Human Rights has at least twice previously declared amnesty laws in Peru invalid for violating the right to justice and breaching international human rights standards.
Human rights advocates believe that Peru’s membership of the Inter-American System of Human Rights and the obligations this entails make the amnesty law unconstitutional.
Amnesty laws passed in 1995 in Peru shielded military and police personnel from prosecution for human rights abuses committed during the conflict, including massacres, torture, and forced disappearances.
Peru’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission found that the majority of the conflict’s victims were Indigenous Peruvians caught between security forces and the Shining Path. It also found that there are more than 4,000 clandestine graves across the country as a result of the two decades of political violence.
In August 2024, Peru adopted a statute of limitations for crimes against humanity committed before 2002, shutting down hundreds of investigations into alleged crimes committed during the conflict.
The initiative benefitted the late Fujimori and 600 prosecuted military personnel.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoSee How Trump’s Big Bill Could Affect Your Taxes, Health Care and Other Finances
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week ago16 Mayors on What It’s Like to Run a U.S. City Now Under Trump
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoVideo: Trump Signs the ‘One Big Beautiful Bill’ Into Law
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Who Loses in the Republican Policy Bill?
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoFederal contractors improperly dumped wildfire-related asbestos waste at L.A. area landfills
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeet Soham Parekh, the engineer burning through tech by working at three to four startups simultaneously
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCongressman's last day in office revealed after vote on Trump's 'Big, Beautiful Bill'
-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoRussia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 1,227














