Science
Your dog can understand what you say better than you think, new study shows

Our dogs understand us better than they’ve been given credit for — and scientists say they have the brain wave evidence to prove it.
By placing electrodes on the heads of 18 pet dogs, researchers found striking evidence that the animals did not merely recognize the patterns of sound that come out of their owners’ mouths but also realized that certain words refer to specific objects.
The findings were reported Friday in the journal Current Biology.
“For decades there has been a debate about whether animals are capable of such a level of abstraction,” said study leader Marianna Boros, a neuroscientist and ethologist at Eotvos Lorand University in Budapest, Hungary. The experiments with dogs knock down the uniqueness of humans “a little bit.”
A few exceptional dogs have been trained to learn the names of hundreds of objects. Among the most esteemed was Chaser, a border collie from South Carolina who could remember the names of more than 1,000 toys.
Boros wondered whether more dogs understand that words have meanings but have no way to show it. Even when dogs succeed in behavioral studies, she said, “you never know exactly what happens in the brain.”
So she took inspiration from researchers who study language processing in humans and got an electroencephalogram machine. The EEG measures brain waves and can gauge the difference between the neural responses to a word that’s expected and a word that seems to come out of left field.
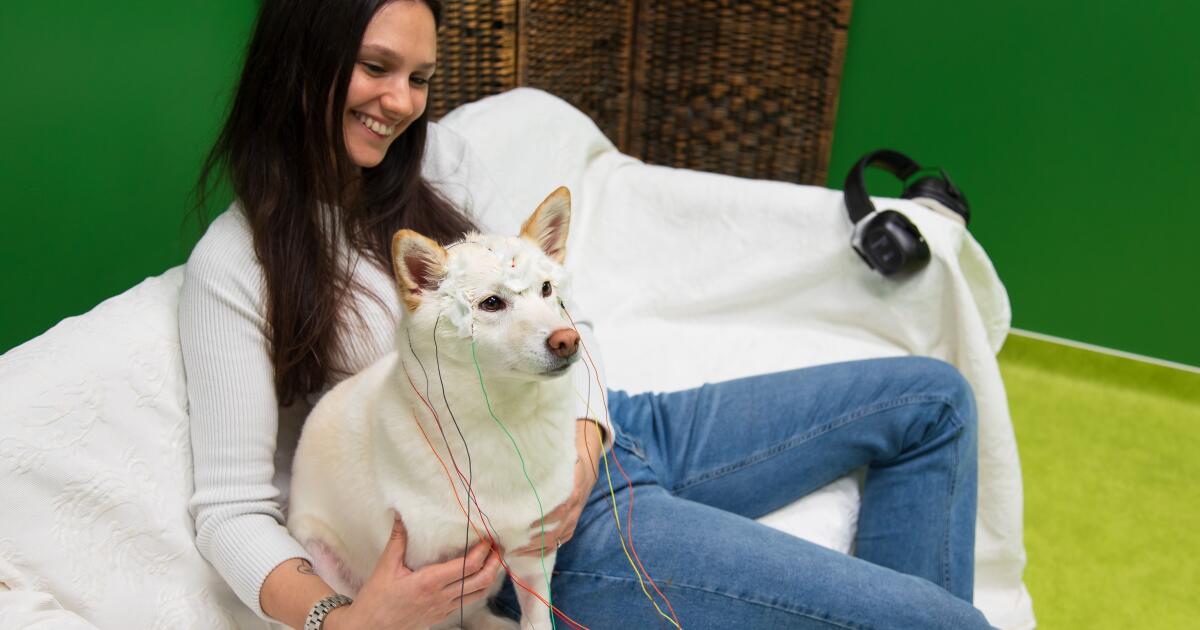
Arbó rests with owner Júlia Vanda Dénes before taking a vocabulary test. The sighthound is wearing electrodes that will measure brain activity during the experiment.
(Oszkár Dániel Gáti)
With a little cleanser, some conductive cream and gauze, the researchers connected the EEG electrodes to the heads of 27 dogs. Then the dogs listened to recordings of their owners using familiar words in simple sentences such as “Luna, here’s the ball.”
After a short pause, the owner appeared behind a window with an object in hand. Sometimes it was the object mentioned in the sentence; sometimes it wasn’t. Either way, the electrodes recorded small voltages from the dogs’ brains as they contemplated what they had heard and seen.
The tests went on for as long as a dog was willing to stay on its mat and participate, Boros said.
“The EEG studies with dogs are quite easy to run,” she said. “They don’t need to do anything. They just lay down.”
The 18 dogs that were able to sit through at least 10 trials were included in the analysis. With all but four of those animals, the EEGs revealed a distinct pattern: The wave signals dipped significantly lower when there was a match between the word and the object than when there wasn’t.
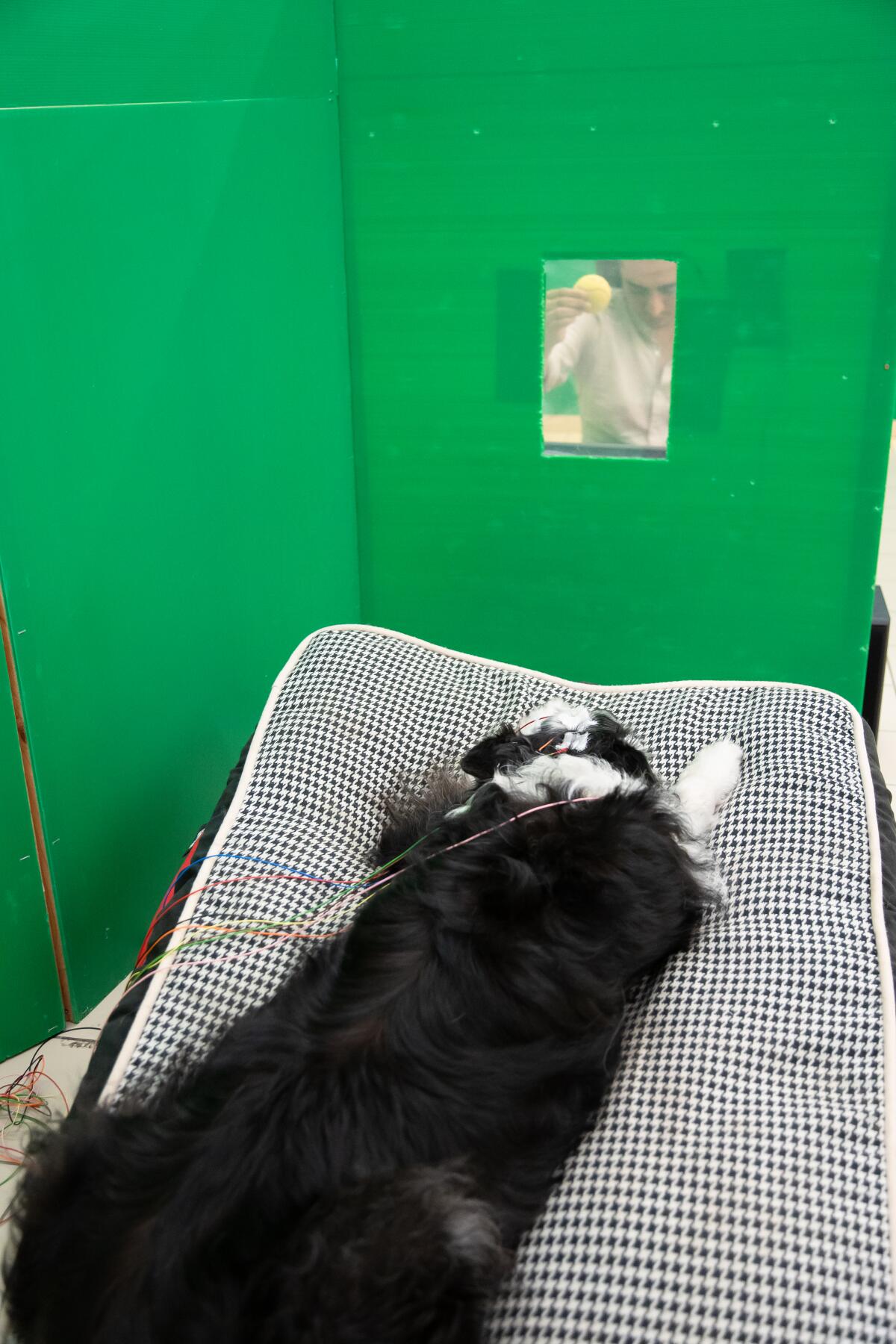

Kun-Kun watches through a window as its owner holds up a tennis ball during the experiment.
(Oszkár Dániel Gáti)
It was reminiscent of the difference seen in EEGs when humans are confronted with a word that seems out of place, such as a request to wash your hands with soap and coffee. Neuroscientists interpret this as a sign that the brain had been expecting another word — “water” instead of “coffee” — and had to do some extra work to understand the sentence.
Boros and her colleagues posit that the same thing happens in the brains of dogs: After hearing their owner use the word for an object, they called it up in their mind in anticipation of seeing it. Then, when an object appeared, it was either the thing they expected or something that threw them for a loop. The reason the dogs could tell something was amiss was that they understood the spoken word.
The gap between hearing the word and seeing the object is key, said Lilla Magyari, a cognitive neuroscientist at the University of Stavanger in Norway, who worked on the study.
If a dog heard the word “ball” while looking at a ball in its owner’s hands, it might guess that the two go together because they are present at the same time, she said. But the experiment’s design prevented that from happening. Instead, the dog must have created an accurate mental representation of the spoken word.
The dog was thinking, “I heard the word, now the object needs to come,” Magyari said.
“Ball” was the most common vocabulary word among the dogs in the study. Several had words for “leash,” “phone” and “wallet.” Most had at least one name for a favorite toy, including one pet that understood four distinct words for different toys in the experiment.
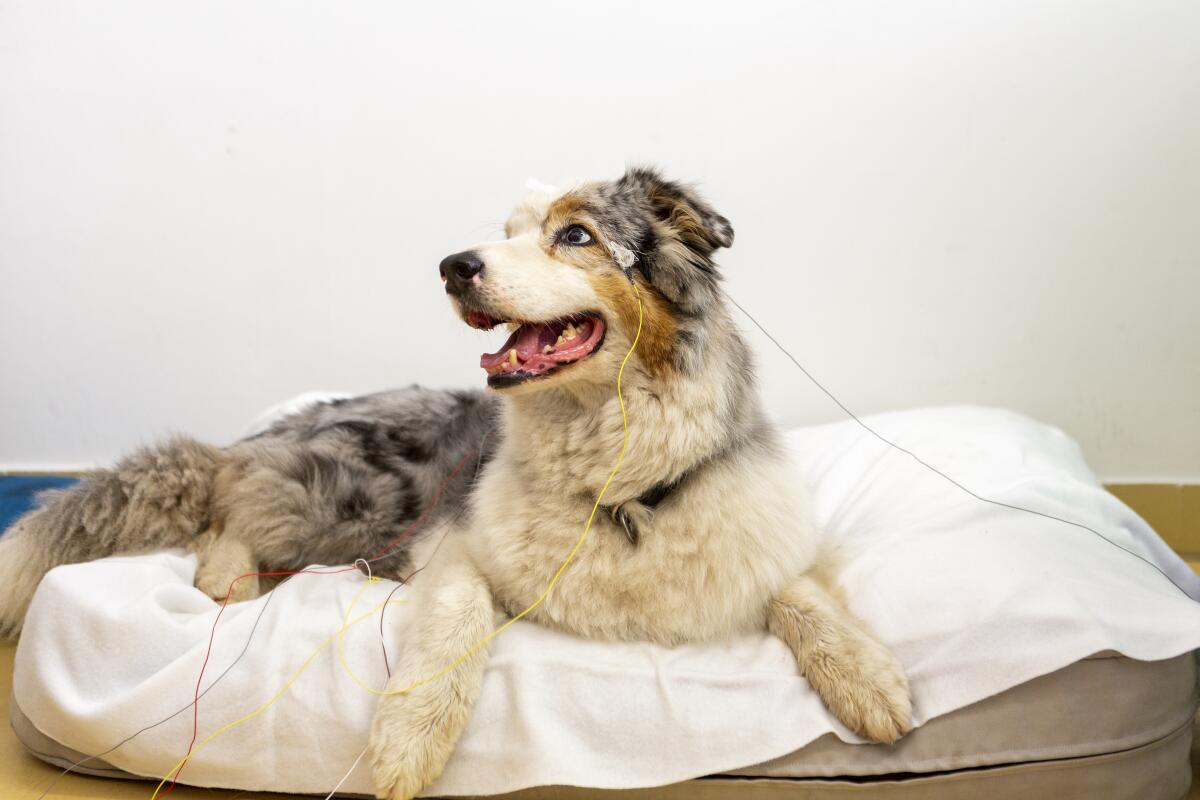

Joey sits on a mat before a participating in a word knowledge experiment.
(Grzegorz Eliasiewicz)
It’s not clear from the study results whether all dogs have the capacity to learn words. The ones that participated in the experiment were volunteered by their owners, who vouched that their pets knew at least five words for objects. (One dog was said to have a vocabulary of 230 nouns.)
Marie Nitzschner spent a decade studying the cognitive abilities and communication skills of dogs at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Germany. She said she had ever met only one dog that seemed to know words for specific objects. Even so, she said the study makes a strong case that the phenomenon is real.
“It appears to me to be conclusive,” said Nitzschner, who was not involved in the work.
She added that dogs who lack this ability have nothing to worry about “because we still have good communication options. However, if I noticed that my dog had a talent in this direction, I would probably try to encourage this talent.”
Dog lovers are sure to be intrigued by the linguistic capabilities of their best friends. But the researchers see the study as a way to investigate why humans excel at language when other animals don’t.
“It’s kind of a mystery,” Magyari said. “We don’t know why all of a sudden humans were able to use such a complex system.”
By breaking it down into its component parts and studying whether any of them are shared with animals, “we can construct a theory about how language evolved in humans,” she said.
Of all species on Earth, dogs are singular study subjects because they live their entire lives immersed in a world rich with human speech. And unlike with cats, the ancestors of dogs were selected for domestication based on their ability to communicate with humans.
“It’s super-relevant for them,” Boros said.

Science
Canny as a crocodile but dumber than a baboon — new research ponders T. rex's brain power
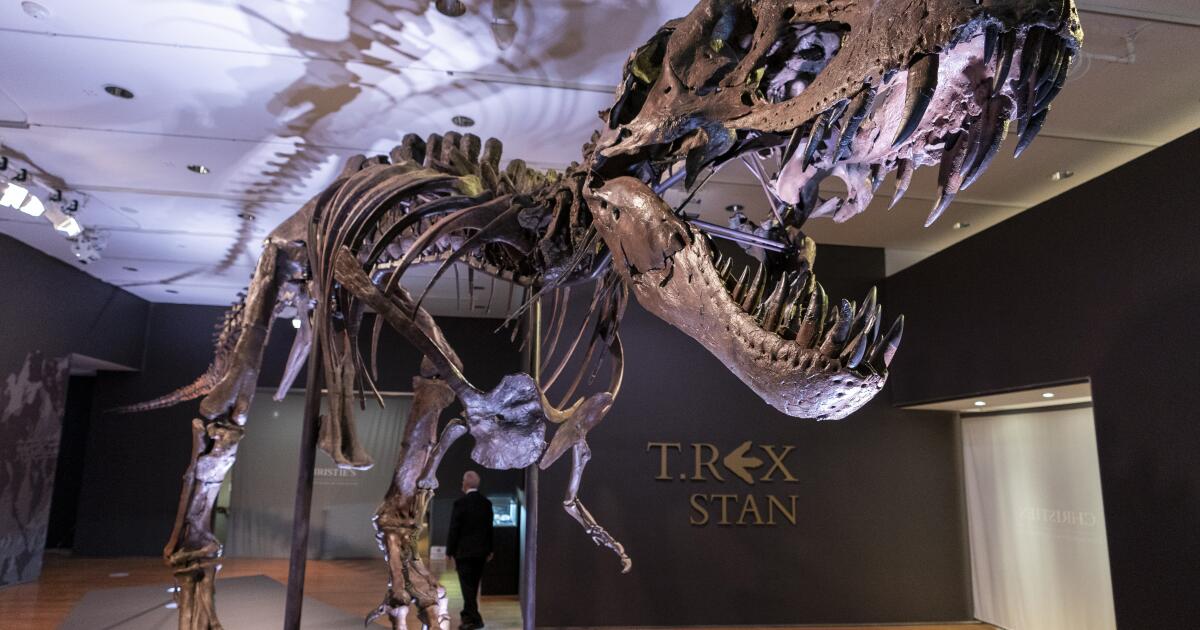

In December 2022, Vanderbilt University neuroscientist Suzana Herculano-Houzel published a paper that caused an uproar in the dinosaur world.
After analyzing previous research on fossilized dinosaur brain cavities and the neuron counts of birds and other related living animals, Herculano-Houzel extrapolated that the fearsome Tyrannosaurus rex may have had more than 3 billion neurons — more than a baboon.
As a result, she argued, the predators could have been smart enough to make and use tools and to form social cultures akin to those seen in present-day primates.
The original “Jurassic Park” film spooked audiences by imagining velociraptors smart enough to open doors. Herculano-Houzel’s paper described T. rex as essentially wily enough to sharpen their own shivs. The bold claims made headlines, and almost immediately attracted scrutiny and skepticism from paleontologists.
In a paper published Monday in “The Anatomical Record,” an international team of paleontologists, neuroscientists and behavioral scientists argue that Herculano-Houzel’s assumptions about brain cavity size and corresponding neuron counts were off-base.
True T. rex intelligence, the scientists say, was probably much closer to that of modern-day crocodiles than primates — a perfectly respectable amount of smarts for a therapod to have.
“What needs to be emphasized is that reptiles are certainly not as dim-witted as is commonly believed,” said Kai Caspar, a biologist at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf and co-author of the paper. “So whereas there is no reason to assume that T. rex had primate-like habits, it was certainly a behaviorally sophisticated animal.”
Brain tissue doesn’t fossilize, and so researchers examine the shape and size of the brain cavity in fossilized dinosaur skulls to deduce what their brains may have been like.
In their analysis, the authors took issue with Herculano-Houzel’s assumption that dinosaur brains filled their skull cavities in a proportion similar to bird brains. Herculano-Houzel’s analysis posited that T. rex brains occupied most of their brain cavity, analogous to that of the modern-day ostrich.
But dinosaur brain cases more closely resemble those of modern-day reptiles like crocodiles, Caspar said. For animals like crocodiles, brain matter occupies only 30% to 50% of the brain cavity. Though brain size isn’t a perfect predictor of neuron numbers, a much smaller organ would have far fewer than the 3 billion neurons Herculano-Houzel projected.
“T. rex does come out as the biggest-brained big dinosaur we studied, and the biggest one not closely related to modern birds, but we couldn’t find the 2 to 3 billion neurons she found, even under our most generous estimates,” said co-author Thomas R. Holtz, Jr., a vertebrate paleontologist at University of Maryland, College Park.
What’s more, the research team argued, neuron counts aren’t an ideal indicator of an animal’s intelligence.
Giraffes have roughly the same number of neurons that crows and baboons have, Holtz pointed out, but they don’t use tools or display complex social behavior in the way those species do.
“Obviously in broad strokes you need more neurons to create more thoughts and memories and to solve problems,” Holtz said, but the sheer number of neurons an animal has can’t tell us how the animal will use them.
“Neuronal counts really are comparable to the storage capacity and active memory on your laptop, but cognition and behavior is more like the operating system,” he said. “Not all animal brains are running the same software.”
Based on CT scan reconstructions, the T. rex brain was probably “ a long tube that has very little in terms of the cortical expansion that you see in a primate or a modern bird,” said paleontologist Luis Chiappe, director of the Dinosaur Institute at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.
“The argument that a T. Rex would have been as intelligent as a primate — no. That makes no sense to me,” said Chiappe, who was not involved in the study.
Like many paleontologists, Chiappe and his colleagues at the Dinosaur Institute were skeptical of Herculano-Houzel’s original conclusions. The new paper is more consistent with previous understandings of dinosaur anatomy and intelligence, he said.
“I am delighted to see that my simple study using solid data published by paleontologists opened the way for new studies,” Herculano-Houzel said in an email. “Readers should analyze the evidence and draw their own conclusions. That’s what science is about!”
When thinking about the inner life of T. rex, the most important takeaway is that reptilian intelligence is in fact more sophisticated than our species often assumes, scientists said.
“These animals engage in play, are capable of being trained, and even show excitement when they see their owners,” Holtz said. “What we found doesn’t mean that T. rex was a mindless automaton; but neither was it going to organize a Triceratops rodeo or pass down stories of the duckbill that was THAT BIG but got away.”
Science
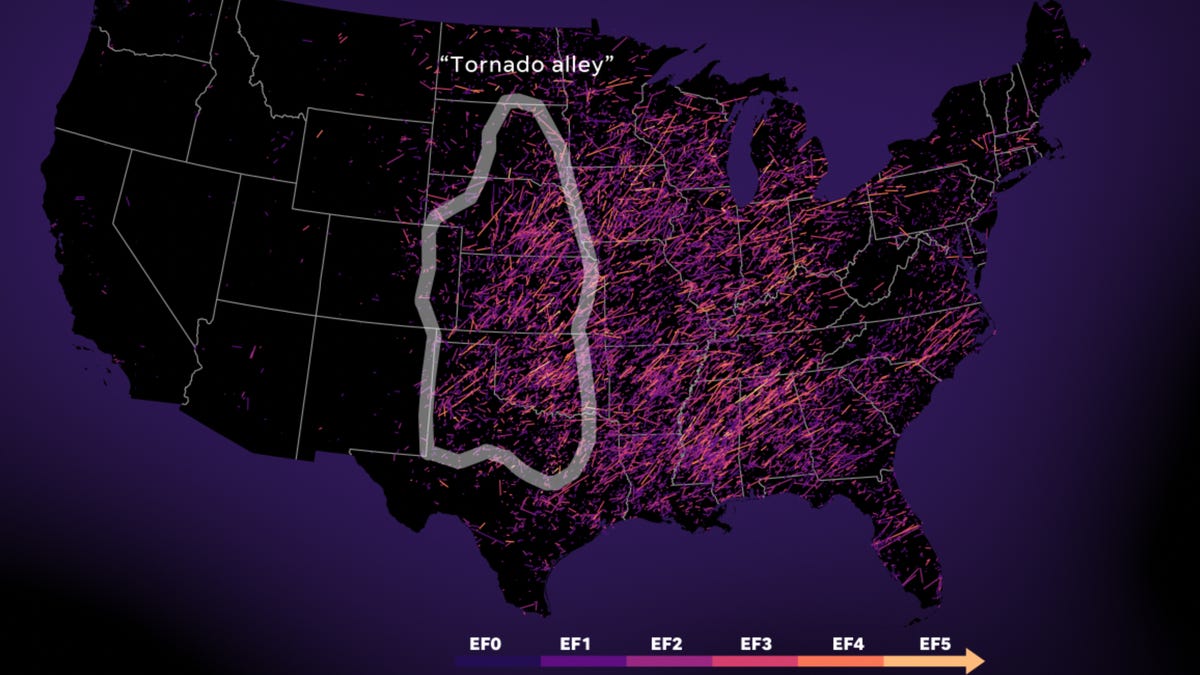
You're gonna need a bigger number: Scientists consider a Category 6 for mega-hurricane era

In 1973, the National Hurricane Center introduced the Saffir-Simpson scale, a five-category rating system that classified hurricanes by wind intensity.
At the bottom of the scale was Category 1, for storms with sustained winds of 74 to 95 mph. At the top was Category 5, for disasters with winds of 157 mph or more.
In the half-century since the scale’s debut, land and ocean temperatures have steadily risen as a result of greenhouse gas emissions. Hurricanes have become more intense, with stronger winds and heavier rainfall.
With catastrophic storms regularly blowing past the 157-mph threshold, some scientists argue, the Saffir-Simpson scale no longer adequately conveys the threat the biggest hurricanes present.
Earlier this year, two climate scientists published a paper that compared historical storm activity to a hypothetical version of the Saffir-Simpson scale that included a Category 6, for storms with sustained winds of 192 mph or more.
Of the 197 hurricanes classified as Category 5 from 1980 to 2021, five fit the description of a hypothetical Category 6 hurricane: Typhoon Haiyan in 2013, Hurricane Patricia in 2015, Typhoon Meranti in 2016, Typhoon Goni in 2020 and Typhoon Surigae in 2021.
Patricia, which made landfall near Jalisco, Mexico, in October 2015, is the most powerful tropical cyclone ever recorded in terms of maximum sustained winds. (While the paper looked at global storms, only storms in the Atlantic Ocean and the northern Pacific Ocean east of the International Date Line are officially ranked on the Saffir-Simpson scale. Other parts of the world use different classification systems.)
Though the storm had weakened to a Category 4 by the time it made landfall, its sustained winds over the Pacific Ocean hit 215 mph.
“That’s kind of incomprehensible,” said Michael F. Wehner, a senior scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and co-author of the Category 6 paper. “That’s faster than a racing car in a straightaway. It’s a new and dangerous world.”
In their paper, which was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Wehner and co-author James P. Kossin of the University of Wisconsin–Madison did not explicitly call for the adoption of a Category 6, primarily because the scale is quickly being supplanted by other measurement tools that more accurately gauge the hazard of a specific storm.
“The Saffir-Simpson scale is not all that good for warning the public of the impending danger of a storm,” Wehner said.
The category scale measures only sustained wind speeds, which is just one of the threats a major storm presents. Of the 455 direct fatalities in the U.S. due to hurricanes from 2013 to 2023 — a figure that excludes deaths from 2017’s Hurricane Maria — less than 15% were caused by wind, National Hurricane Center director Mike Brennan said during a recent public meeting. The rest were caused by storm surges, flooding and rip tides.
The Saffir-Simpson scale is a relic of an earlier age in forecasting, Brennan said.
“Thirty years ago, that’s basically all we could tell you about a hurricane, is how strong it was right now. We couldn’t really tell you much about where it was going to go, or how strong it was going to be, or what the hazards were going to look like,” Brennan said during the meeting, which was organized by the American Meteorological Society. “We can tell people a lot more than that now.”
He confirmed the National Hurricane Center has no plans to introduce a Category 6, primarily because it is already trying “to not emphasize the scale very much,” Brennan said. Other meteorologists said that’s the right call.
“I don’t see the value in it at this time,” said Mark Bourassa, a meteorologist at Florida State University’s Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies. “There are other issues that could be better addressed, like the spatial extent of the storm and storm surge, that would convey more useful information [and] help with emergency management as well as individual people’s decisions.”
Simplistic as they are, Herbert Saffir and Robert Simpson’s categories are the first thing many people think of when they try to grasp the scale of a storm. In that sense, the scale’s persistence over the years helps people understand how much the climate has changed since its introduction.
“What the Saffir-Simpson scale is good for is quantifying, showing, that the most intense storms are becoming more intense because of climate change,” Wehner said. “It’s not like it used to be.”
Science
Opinion: America's 'big glass' dominance hangs on the fate of two powerful new telescopes
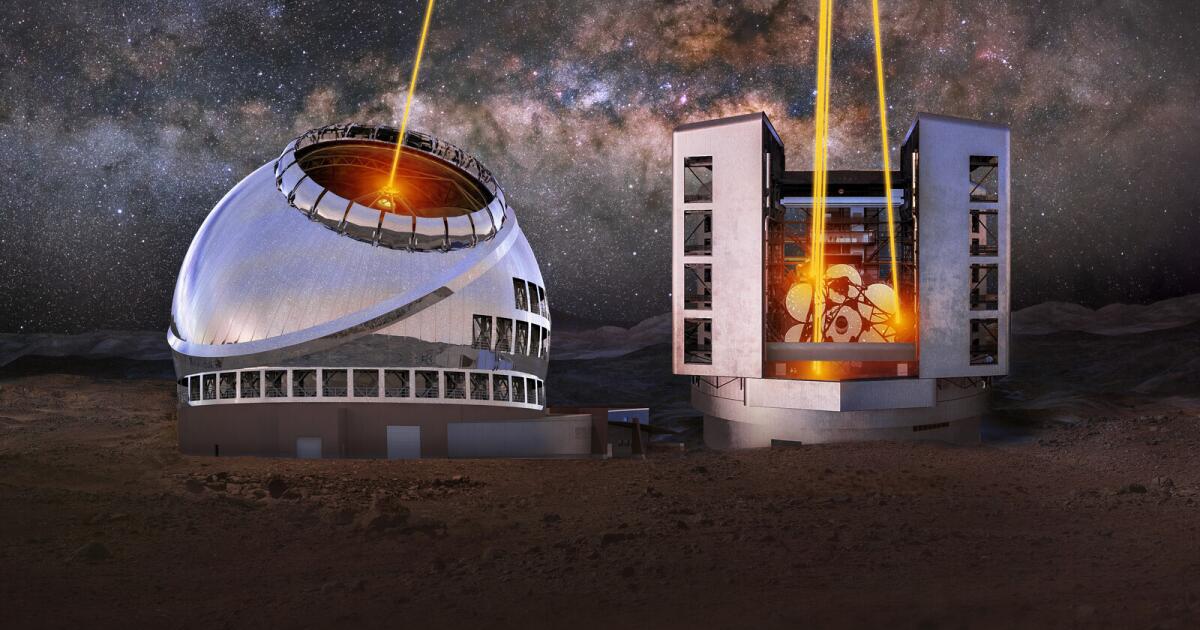
More than 100 years ago, astronomer George Ellery Hale brought our two Pasadena institutions together to build what was then the largest optical telescope in the world. The Mt. Wilson Observatory changed the conception of humankind’s place in the universe and revealed the mysteries of the heavens to generations of citizens and scientists alike. Ever since then, the United States has been at the forefront of “big glass.”
In fact, our institutions, Carnegie Science and Caltech, still help run some of the largest telescopes for visible-light astronomy ever built.
But that legacy is being threatened as the National Science Foundation, the federal agency that supports basic research in the U.S., considers whether to fund two giant telescope projects. What’s at stake is falling behind in astronomy and cosmology, potentially for half a century, and surrendering the scientific and technological agenda to Europe and China.
In 2021, the National Academy of Sciences released Astro2020. This report, a road map of national priorities, recommended funding the $2.5-billion Giant Magellan Telescope at the peak of Cerro Las Campanas in Chile and the $3.9-billion Thirty Meter Telescope at Mauna Kea in Hawaii. According to those plans, the telescopes would be up and running sometime in the 2030s.
NASA and the Department of Energy backed the plan. Still, the National Science Foundation’s governing board on Feb. 27 said it should limit its contribution to $1.6 billion, enough to move ahead with just one telescope. The NSF intends to present their process for making a final decision in early May, when it will also ask for an update on nongovernmental funding for the two telescopes. The ultimate arbiter is Congress, which sets the agency’s budget.
America has learned the hard way that falling behind in science and technology can be costly. Beginning in the 1970s, the U.S. ceded its powerful manufacturing base, once the nation’s pride, to Asia. Fast forward to 2022, the U.S. government marshaled a genuine effort toward rebuilding and restarting its factories — for advanced manufacturing, clean energy and more — with the Inflation Reduction Act, which is expected to cost more than $1 trillion.
President Biden also signed into law the $280-billion CHIPS and Science Act two years ago to revive domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors — which the U.S. used to dominate — and narrow the gap with China.
As of 2024, America is the unquestioned leader in astronomy, building powerful telescopes and making significant discoveries. A failure to step up now would cede our dominance in ways that would be difficult to remedy.
The National Science Foundation’s decision will be highly consequential. Europe, which is on the cusp of overtaking the U.S. in astronomy, is building the aptly named Extremely Large Telescope, and the United States hasn’t been invited to partner in the project. Russia aims to create a new space station and link up with China to build an automated nuclear reactor on the moon.
Although we welcome any sizable grant for new telescope projects, it’s crucial to understand that allocating funds sufficient for just one of the two planned telescopes won’t suffice. The Giant Magellan and the Thirty Meter telescopes are designed to work together to create capabilities far greater than the sum of their parts. They are complementary ground stations. The GMT would have an expansive view of the southern hemisphere heavens, and the TMT would do the same for the northern hemisphere.
The goal is “all-sky” observation, a wide-angle view into deep space. Europe’s Extremely Large Telescope won’t have that capability. Besides boosting America’s competitive edge in astronomy, the powerful dual telescopes, with full coverage of both hemispheres, would allow researchers to gain a better understanding of phenomena that come and go quickly, such as colliding black holes and the massive stellar explosions known as supernovas. They would put us on a path to explore Earth-like planets orbiting other suns and address the question: “Are we alone?”
Funding both the GMT and TMT is an investment in basic science research, the kind of fundamental work that typically has led to economic growth and innovation in our uniquely American ecosystem of scientists, investors and entrepreneurs.
Elon Musk’s SpaceX is the most recent example, but the synergy goes back decades. Basic science at the vaunted Bell Labs, in part supported by taxpayer contributions, was responsible for the transistor, the discovery of cosmic microwave background and establishing the basis of modern quantum computing. The internet, in large part, started as a military communications project during the Cold War.
Beyond its economic ripple effect, basic research in space and about the cosmos has played an outsized role in the imagination of Americans. In the 1960s, Dutch-born American astronomer Maarten Schmidt was the first scientist to identify a quasar, a star-like object that emits radio waves, a discovery that supported a new understanding of the creation of the universe: the Big Bang. The first picture of a black hole, seen with the Event Horizon Telescope, was front-page news in 2019.
We understand that competing in astronomy has only gotten more expensive, and there’s a need to concentrate on a limited number of critical projects. But what could get lost in the shuffle are the kind of ambitious projects that have made America the scientific envy of the world, inspiring new generations of researchers and attracting the best minds in math and science to our colleges and universities.
Do we really want to pay that price?
Eric D. Isaacs is the president of Carnegie Science, prime backer of the Giant Magellan Telescope. Thomas F. Rosenbaum is president of Caltech, key developer of the Thirty Meter Telescope.
-

 Kentucky1 week ago
Kentucky1 week agoKentucky first lady visits Fort Knox schools in honor of Month of the Military Child
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoShipping firms plead for UN help amid escalating Middle East conflict
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIs this fictitious civil war closer to reality than we think? : Consider This from NPR
-
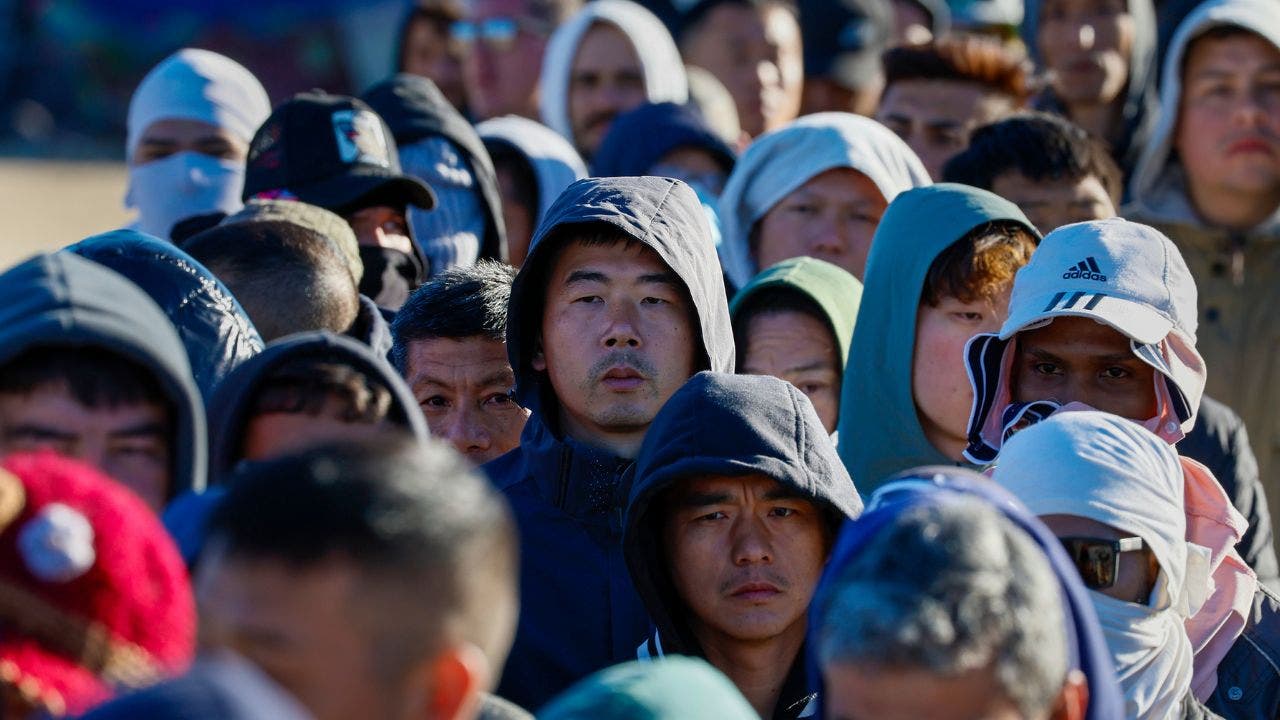

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoICE chief says this foreign adversary isn’t taking back its illegal immigrants
-
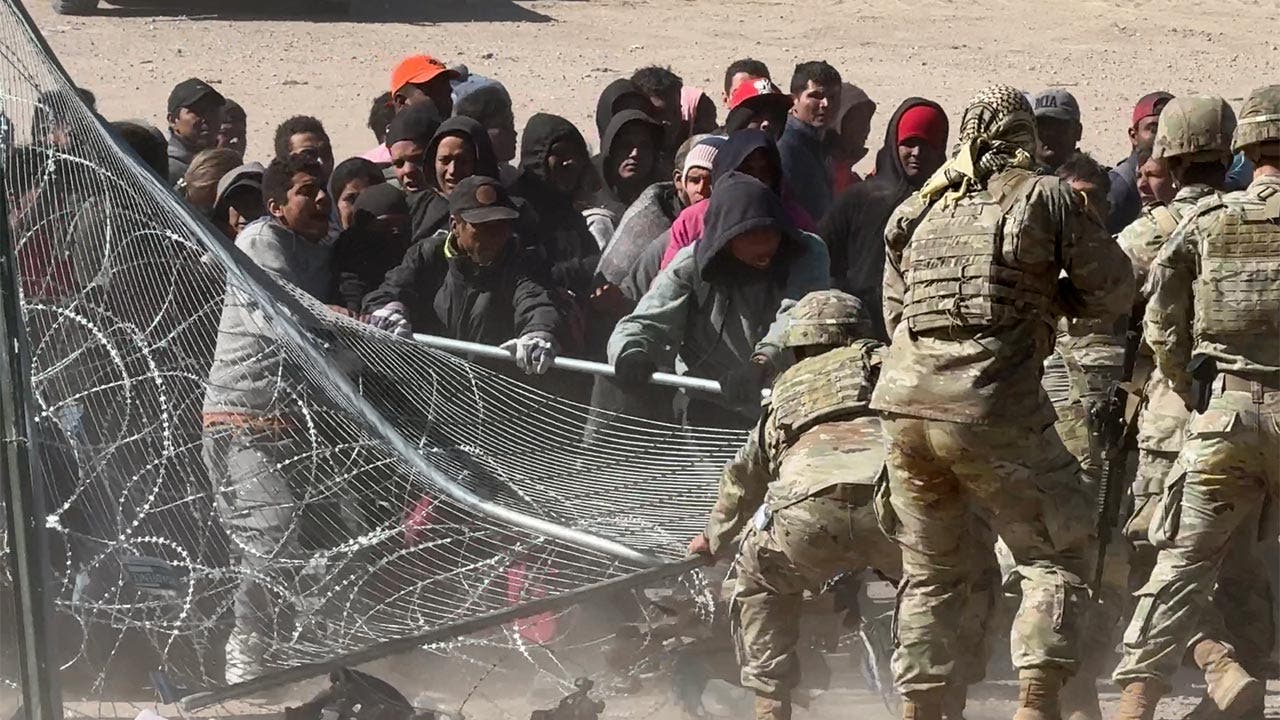

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago'Nothing more backwards' than US funding Ukraine border security but not our own, conservatives say
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoThe San Francisco Zoo will receive a pair of pandas from China
-
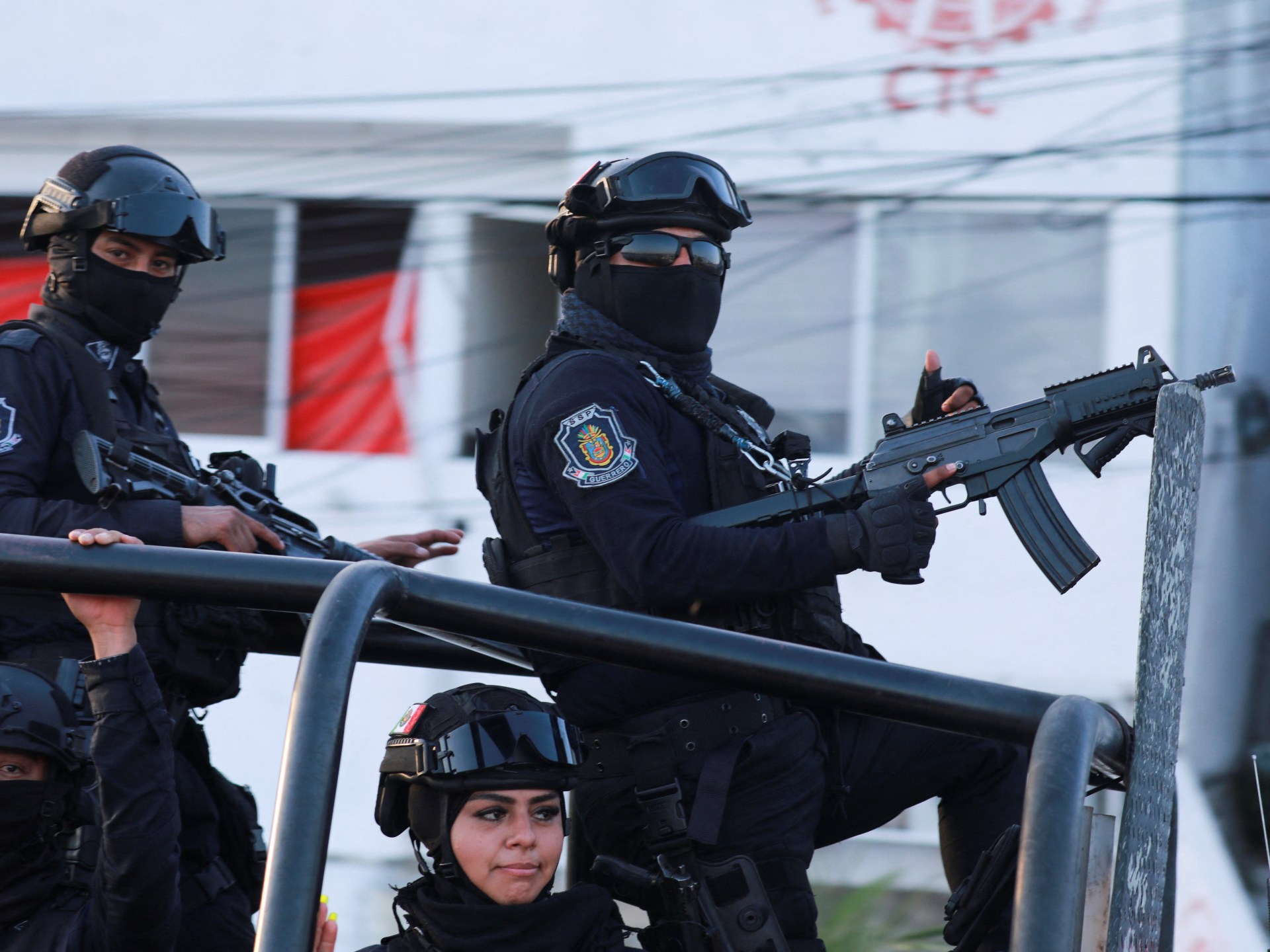

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTwo Mexican mayoral contenders found dead on same day
-
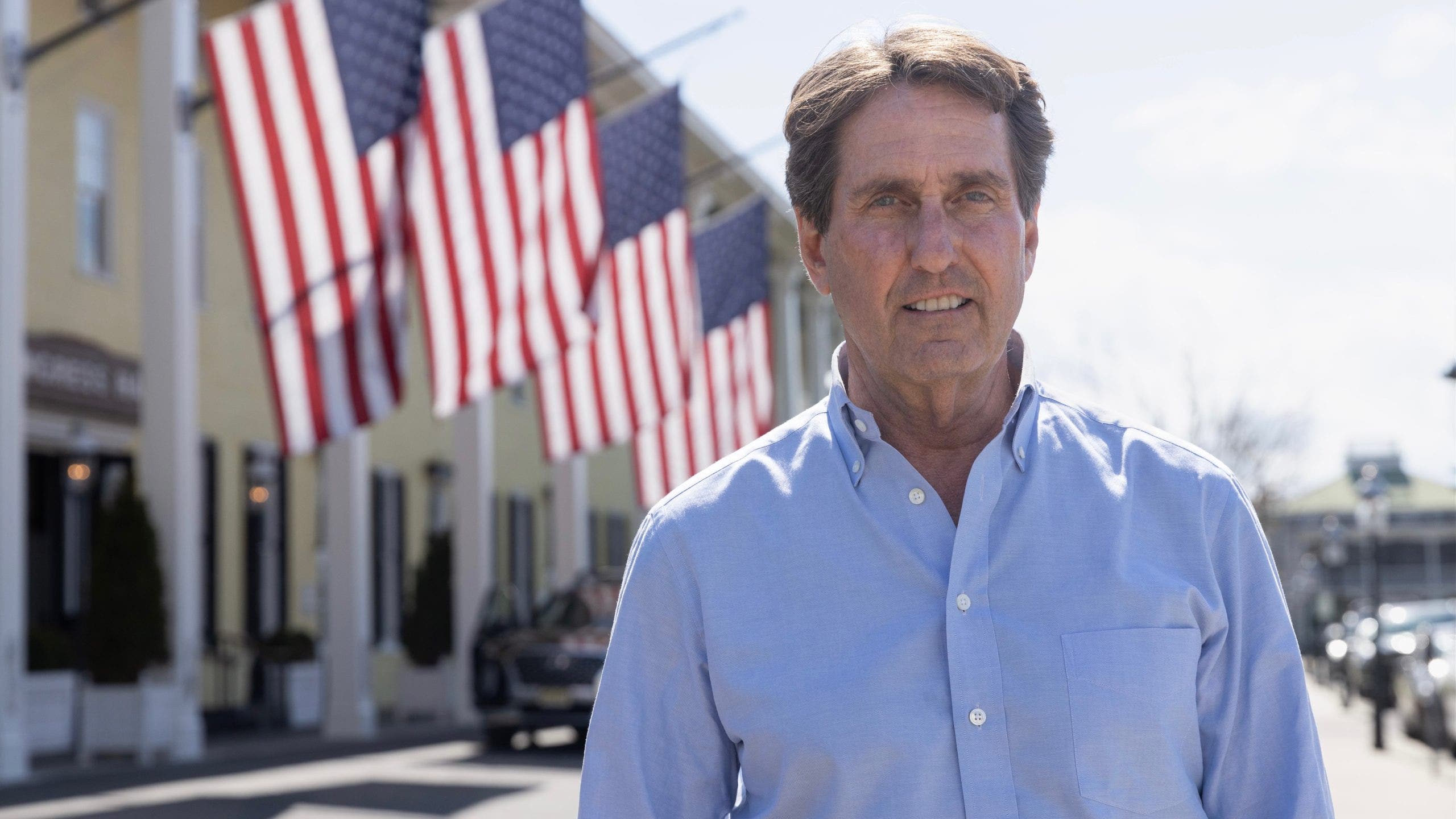

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRepublican aims to break decades long Senate election losing streak in this blue state