Health
6 energy boosters to help beat the midday slump, from a nutrition expert

Every day, it’s lurking — somewhere in the window between lunch and dinner, waiting to sap your energy and motivation.
It’s the midday slump, that time of afternoon when many people succumb to fatigue, lethargy and a general decline in productivity.
But you don’t have to surrender to the post-lunch “food coma,” according to Dr. Christopher Rhodes, a nutritional biologist and CEO of Mimio Health in Davis, California.
THESE ARE THE WORST DRINKS FOR YOUR HEALTH, ACCORDING TO NUTRITIONISTS
Rhodes — whose mission is to “improve society’s cellular health and longevity through nutrition, vitamins and supplements to reach peak human performance” — revealed some of his practical tips to keep energy levels high all day long.
1. Resist grazing or food ‘teasing’
2. Keep glucose in check
3. Optimize your health with a daily supplement
4. Consider quitting coffee
5. Eat a nutritionally rich lunch
6. Get active after eating
During the midday slump, many people succumb to fatigue, lethargy and a general decline in their productivity. (iStock)
1. Resist grazing or ‘food teasing’
Snacking throughout the day can cause your body to want greater amounts of food, causing a spike in blood sugar and sleepiness, Rhodes cautioned.
“While eating smaller portions throughout the day may seem like a great way to stave off hunger, it can actually have the opposite effect,” he told Fox News Digital.
SNACKS PACK MORE CALORIES THAN A SINGLE MEAL FOR MANY US ADULTS, STUDY FINDS
“Small snacks often don’t meet our body’s satiation thresholds — meaning that while food is coming in, it’s not biologically sufficient to actually make us feel less hungry.”
The opposite can actually be true, he noted, as small amounts of food often stimulate hunger and appetite.
“This isn’t just a side effect of eating, but actually a design feature in almost all manufactured or packaged snacks, which are formulated specifically to cause cravings by giving intense bursts of flavor that fade quickly,” Rhodes said.

Snacking throughout the day can cause the body to want greater amounts of food, causing a spike in blood sugar and sleepiness, a nutritionist warned. (iStock)
“There’s a reason you can’t eat just one potato chip.”
Consistently eating high-carbohydrate snacks or meals can also lead to compounding glucose spikes throughout the day, the expert said — which can lead to brain fog, emotional swings and energy crashes.
“There’s a reason you can’t eat just one potato chip.”
When choosing snacks, the best options are whole-food products like nuts, fruits or jerky, which can provide healthy fats, fiber and protein.
These choices do a better job of slowing digestion, keeping you feeling full and balancing glucose spikes, Rhodes advised.
2. Keep glucose in check
Glucose is the body’s preferred energy source, and its levels are tied to “a thousand different biological processes” that affect everything from energy to mood to metabolism, Rhodes said.
“The body is very good at using and processing glucose within a specific range, but go too low or too high and that’s where you get into trouble,” he warned.

Glucose spikes from high-carb and high-sugar foods can provide a quick burst of energy, but this will soon fade and leave behind sluggishness, brain fog and mood reduction, the expert said. (iStock)
Glucose spikes from high-carb and high-sugar foods can provide a quick burst of energy, but this will soon fade and leave behind sluggishness, brain fog and mood reduction, according to Rhodes.
“The key to sustained energy is keeping your glucose levels balanced in normal ranges throughout the day,” he said.
DRINKING 100% ORANGE JUICE IS LINKED TO SURPRISING HEALTH BENEFITS, STUDY FINDS
The best way to achieve this is to pair carbohydrates with healthy fats, proteins and fibers that help to slow digestion and extend a sharp glucose spike into a smooth, even curve, he said.
3. Optimize your health with a daily supplement
“Outside of glucose spikes, there are plenty of other negative effects caused by or associated with the postprandial (post-meal) state in the body,” Rhodes said.
“Food can be very disruptive to our natural metabolic homeostasis, as it floods our systems with sugars and fats, diverts energy toward digestion and away from other processes, and introduces foreign molecules into the body that trigger immune responses.”
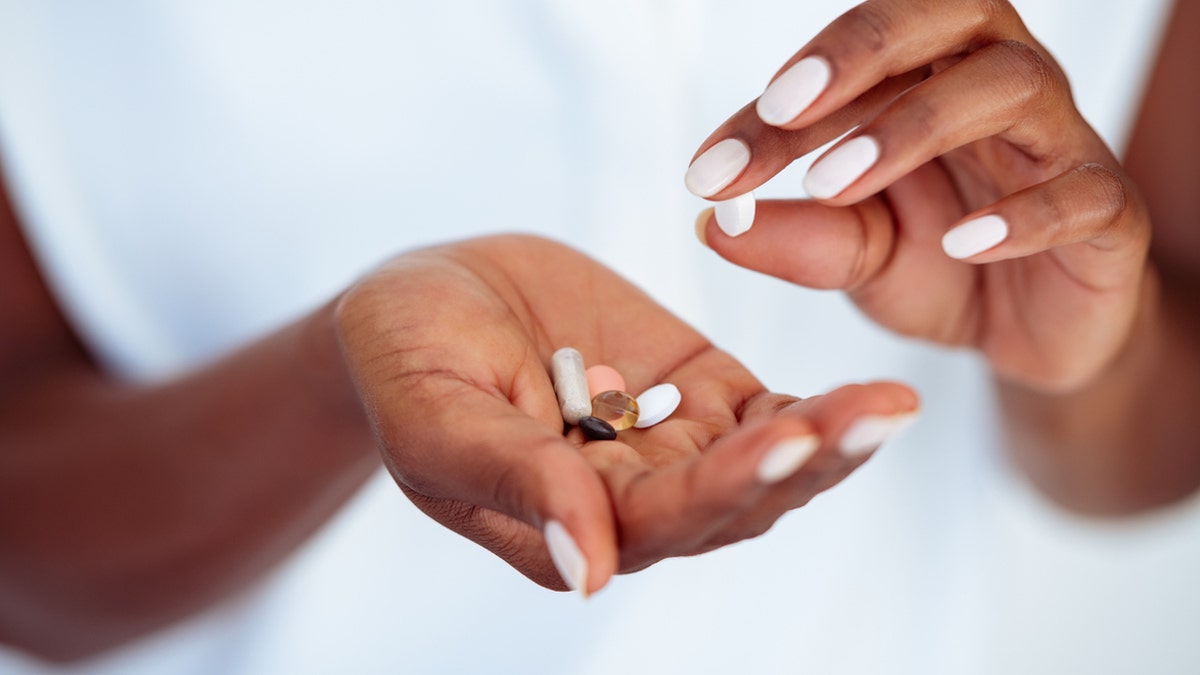

A fasting supplement is designed to help reduce dietary inflammation, control hunger throughout the day, and reduce the post-meal slump. Before taking any new supplements, it’s always best to consult with a doctor or medical professional. (iStock)
Rhodes recommended taking a fasting supplement like Mimio, which his company designed to improve cellular health, energy, cognition and performance.
“It’s the world’s first fasting mimetic supplement, designed from seven years of clinical fasting research at UC Davis to provide the beneficial protective effects of a prolonged fast in a simple daily pill,” he said.
FASTING-LIKE DIET COULD SLOW THE AGING PROCESS, STUDY SUGGESTS: ‘LIVING LONGER AND HEALTHIER’
A fasting supplement is designed to help reduce dietary inflammation, control hunger throughout the day and reduce the post-meal slump, Rhodes said.
Before taking any new supplements, it’s always best to consult with a doctor or medical professional.
4. Consider quitting coffee
Drinking coffee causes sharp upward and downward energy spikes, as well as creating a false sense of adrenaline, Rhodes said.
“Just like sugar, caffeine can provide short, intense bursts of energy that often leave us feeling even more miserable and sluggish just a few hours later,” Rhodes said.
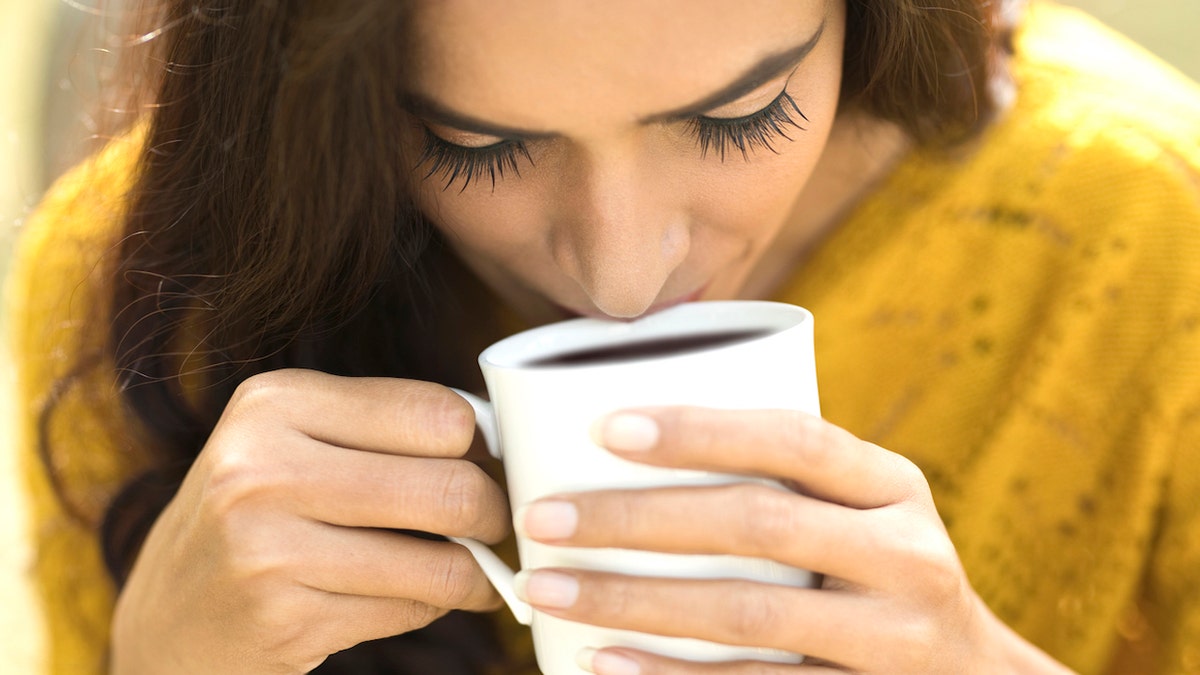

Drinking coffee causes sharp upward and downward energy spikes, as well as creating a false sense of adrenaline, according to the expert. (iStock)
“And just like sugar, the best way to prevent these spikes is to pair caffeine with things that can slow its digestion and smooth out its utilization in the body.”
Instead of coffee, he suggested sipping on green tea, which contains an amino acid called L-Theanine.
CAFFEINE, THE WONDER DRUG? STUDY SUGGESTS MORE COFFEE COULD LOWER BODY FAT AND PREVENT TYPE 2 DIABETES
If you do drink caffeine, Rhodes recommended combining it with a meal that includes healthy fats, fiber and protein — or pairing it with L-Theanine, which has been shown to help reduce the jitteriness and distractibility that can come from caffeine alone.
“Green tea tends to provide a much more balanced experience than coffee.”
“L-Theanine and caffeine are both naturally present in green tea, which is why green tea tends to provide a much more balanced experience than coffee,” Rhodes said.
“It also has a multitude of other benefits, from enhancing cellular stress resistance to improving gut, heart and brain health.”
5. Eat a nutritionally rich lunch
“The best way to keep yourself energized and satisfied throughout the day is to prioritize the nutritional density of your lunches,” Rhodes said.
Low-carb lunches — such as chicken salad, fibrous veggies, and healthy fats like avocado and nuts — will help slow digestion and gastric emptying while providing an energy source for your body, according to the nutritionist.
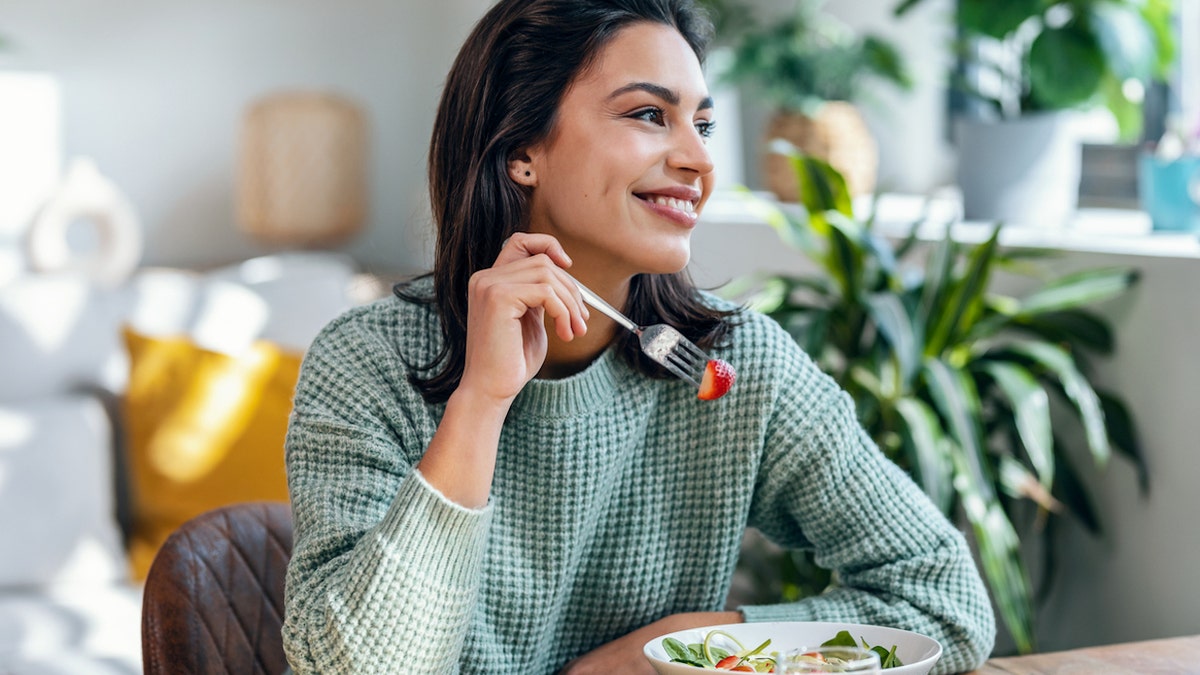

Low-carb lunches — such as chicken salad, fibrous veggies, and healthy fats like avocado and nuts — will help slow digestion and gastric emptying while providing an energy source for your body, according to the nutritionist. (iStock)
“While carbohydrate-rich foods will provide you with a quick burst of energy, they can lead to glucose spikes that can throw your systems out of balance — and they typically contain fewer micronutrients and bioactives that support cognition, energy production and productivity.”
Instead, Rhodes recommended crafting meals that are rich in healthy fats, fiber and proteins.
“The best way to keep yourself energized and satisfied throughout the day is to prioritize the nutritional density of your lunches.”
Some examples are protein-rich salads, hearty vegetable soups, or more traditional rice and noodle dishes that replace the carbs with veggie alternatives, like cauliflower “rice” and zucchini “noodles.”
“Fiber helps to provide volume to a meal without contributing any extra calories, and forms a gel-like matrix in your stomach that helps to trap other nutrients, so they’re released more slowly during digestion,” Rhodes noted.
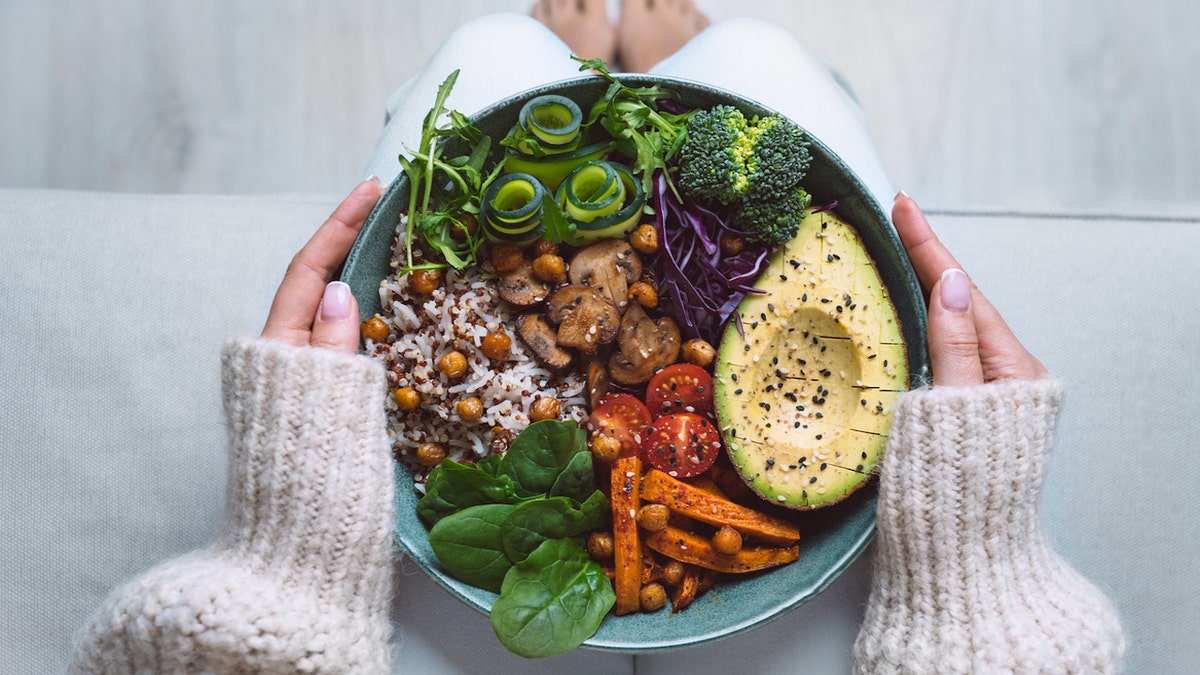

“Fiber helps to provide volume to a meal without contributing any extra calories,” a nutritionist said. (iStock)
Fats like avocado and nuts help to keep you fuller for longer.
“Proteins are the most slowly digested macronutrient — and as an added bonus, they have the highest ‘thermic effect,’ meaning the body has to burn more calories to digest proteins than any other nutrient,” Rhodes said.
6. Get active after eating
When you eat, your glucose level spikes, and it is best to use up that consumed energy quickly to keep your levels balanced, according to Rhodes.
“This is also a great time to take advantage of a brain break, so you can return to work refreshed,” he said.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Physical activity immediately after eating can help balance out glucose spikes.
“After a meal, your body naturally reprioritizes its energy toward digestion and metabolism, putting other organ systems like your muscles and brain on the back burner,” he told Fox News Digital.

Performing any physical activity after a meal will help to shift energy utilization back to your muscles and brain, the expert said. (iStock)
Performing any physical activity after a meal — whether it’s taking a walk, climbing stairs, gardening or even doing household chores will help to shift energy use back to your muscles and brain, Rhodes said.
“Instead of breaking down the nutrients in your meal and storing the energy for later (usually as fat), post-meal exercise helps shuttle the newly created energy directly to your cells for immediate use — and has been shown to help smooth out glucose absorption curves to provide more balanced, stable energy,” he added.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.

Health
“I Lost 130 lbs at Age 53!” — Here's the Protein Combo That Builds Muscle + Boosts Weight Loss

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Cancer immunity gets a boost from one common nutrient, study finds: ‘Intrigue and optimism’

Vitamin D could be a surprise weapon against cancer, new research suggests.
A study of mice published in the journal Science last week found that eating a diet rich in vitamin D changed the gut microbiome in a way that boosted cancer immunity.
The micronutrient increased levels of the bacterium Bacteroides fragilis, which has been shown to improve cancer immune response.
BE WELL: PREPARE A DINNER RICH IN VITAMIN D FOR GOOD HEALTH
The mice that received vitamin D showed improved responses to cancer immunotherapy and greater immunity to new tumor development, according to researchers at the Francis Crick Institute in London, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), and Aalborg University in Denmark.
“What we’ve shown here came as a surprise — vitamin D can regulate the gut microbiome to favor a type of bacteria that gives mice better immunity to cancer,” said senior study author Caetano Reis e Sousa, head of the Immunobiology Laboratory at Crick, in a press release.
Dietary vitamin D, found in foods including salmon, increased levels of the bacterium Bacteroides fragilis, which has been shown to improve cancer immune response. (iStock)
“This could one day be important for cancer treatment in humans.”
The researchers aren’t yet sure why vitamin D seems to foster a “good” microbiome.
WHY IMMUNOTHERAPY IS EMERGING AS THE ‘FOURTH PILLAR’ OF CANCER TREATMENTS, EXPERTS SAY
“If we can answer this, we might uncover new ways in which the microbiome influences the immune system, potentially offering exciting possibilities in preventing or treating cancer,” said co-author Evangelos Giampazolias, former postdoctoral researcher at the Crick and now group leader of the Cancer Immunosurveillance Group at the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute, in the release.

Previous studies have linked vitamin D to improved immunity against cancer. (iStock)
Shama Farooq, M.D., a neuro-oncologist at Hackensack Meridian Neuroscience Institute at Jersey Shore University Medical Center, was not involved in the study but shared his comments on the findings.
“As a doctor who treats patients with cancer, my initial reaction to this study was one of intrigue and optimism,” he told Fox News Digital.
IN POTENTIAL CANCER BREAKTHROUGH, NEWLY FOUND ‘KILL SWITCH’ TRIGGERS DEATH OF CANCER CELLS: ‘ONE-TWO PUNCH’
“The findings suggest a potential link between vitamin D levels, the microbiome and cancer immunity, offering potential new avenues for improving cancer treatment and prevention strategies.”
Continued research into improving the body’s immunity against cancer is “crucial,” Farooq noted.
“Cancer is a complex disease with diverse mechanisms of evasion,” he said.
The micronutrient increased levels of the bacterium Bacteroides fragilis, which has been shown to improve cancer immune response. (iStock)
“By exploring new ways to boost the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells, researchers can develop more effective and targeted treatments, ultimately improving patient outcomes and survival rates.”
Based on the findings of this study, Farooq said he recommends people make sure their vitamin D levels are adequate, “as part of a comprehensive approach to potentially lowering their risk of cancer.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship, maintaining optimal levels of vitamin D is generally beneficial for overall health and may contribute to reducing cancer risk,” he added.
Studies in humans are needed to learn more about the link between vitamin D and cancer immunity, the researchers acknowledged.

Vitamin D has been linked to improved responses to cancer immunotherapy and greater immunity to new tumor development. (iStock)
“More work is needed before we can conclusively say that correcting a vitamin D deficiency has benefits for cancer prevention or treatment,” said Sousa.
Farooq echoed the need for more research.
“Moving forward, I would like to see further research delve deeper into the mechanisms underlying the interaction between Vitamin D, the microbiome and cancer immunity,” he said.
Fox News Digital reached out to the study researchers for comment.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
Cancer trends revealed, including most common types of the disease and biggest risk factors
Almost 40% of Americans will receive a cancer diagnosis at some point in their lifetime — but certain types are more common than others, statistics show.
USAFacts, a Washington-based nonprofit that compiles government data and reports on it, took a deep dive into the latest cancer data to identify trends — and shared the results with Fox News Digital.
Of the 1.96 million new cancer cases in 2023, half were made up of five types: breast cancer (15%), prostate cancer (15%), lung and bronchus cancer (12%), colorectal cancers (8%) and all other types (50%).
CANCER CAUSES: THESE 10 HIDDEN CARCINOGENS CAN RAISE THE RISK, ACCORDING TO AN ONCOLOGY EXPERT
Among the 609,820 cancer deaths in 2023, nearly half were made up of lung and bronchus cancer (21%), colorectal cancers (9%), pancreatic cancer (8%) and breast cancer (7%).
The remaining 55% of deaths were attributed to other cancers.
Almost 40% of Americans will receive a cancer diagnosis at some point in their lifetime — but certain types are more common than others. USAFacts, a Washington-based nonprofit that compiles government data and reports on it, studied the numbers and shared trends with Fox News Digital. (iStock)
While cancer cases have risen overall due to a growing population, the share of people getting diagnosed and dying from the disease has decreased.
“Between 2000 and 2019, the incidence rate — or the rate of new cancer cases per 100,000 people — declined by 5.4%, while the annual mortality rate fell by more than 26%,” the report stated.
The share of people getting diagnosed and dying from cancer has actually decreased.
“This suggests improvements in cancer prevention, detection and treatment,” Dr. Brett Osborn, a Florida neurologist and longevity expert, told Fox News Digital in a statement.
Osborn was not involved in the report, but commented on the findings.
Here are five standout observations.
1. Gender-specific risk
As of 2019, men were about 15.4% more likely to receive a new cancer diagnosis and 37.5% more likely to die from the disease than women.
That gap has narrowed since 2000, however, when the cancer incidence rate was more than 37% higher for men.
FOODS TO EAT, AND NOT EAT, TO PREVENT CANCER, ACCORDING TO A DOCTOR AND NUTRITIONIST
For men, the most common cancers are prostate, lung and colorectal cancers, the USAFacts report stated.
Those types made up 50.8% of new cancer cases and 45.9% of cancer deaths in 2023 among males.
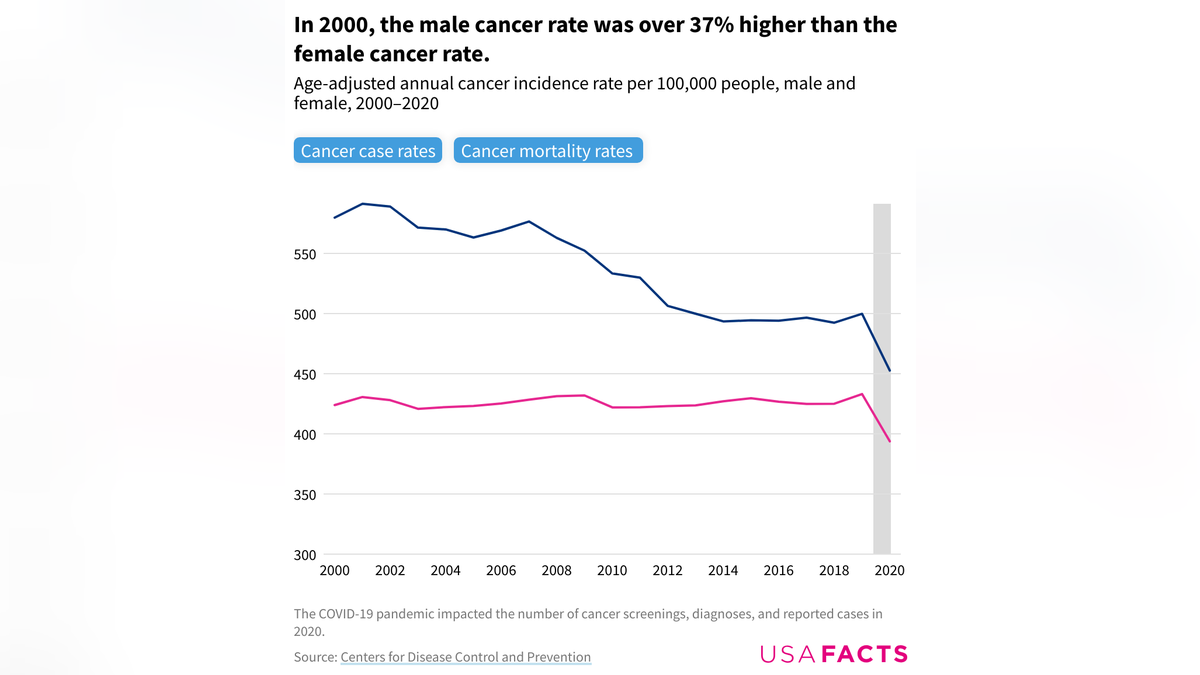
As of 2019, men were about 15.4% more likely to receive a new cancer diagnosis and 37.5% more likely to die from the disease than women. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention )
Among women, the most prevalent types are breast cancer, lung cancer and colorectal cancer.
Those three types comprised 54.6% of new cancer cases and 50.1% of cancer deaths in 2023 for females.
2. Cancer rates across ethnic groups
White Americans have the highest rate of new cancer diagnoses, followed by non-Hispanic Black Americans, the report stated.
Among cancer deaths, however, non-Hispanic Black Americans are at the highest risk.
SOME BREAST CANCER PATIENTS COULD BE AT RISK OF ANOTHER TYPE OF CANCER, STUDY REVEALS
Non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander Americans have the lowest risk of diagnosis and mortality.
Overall cancer incidence rates have dropped between 2000 and 2019 for every group except American Indian/Alaska Native people, who experienced a nearly 35% increase in diagnoses.
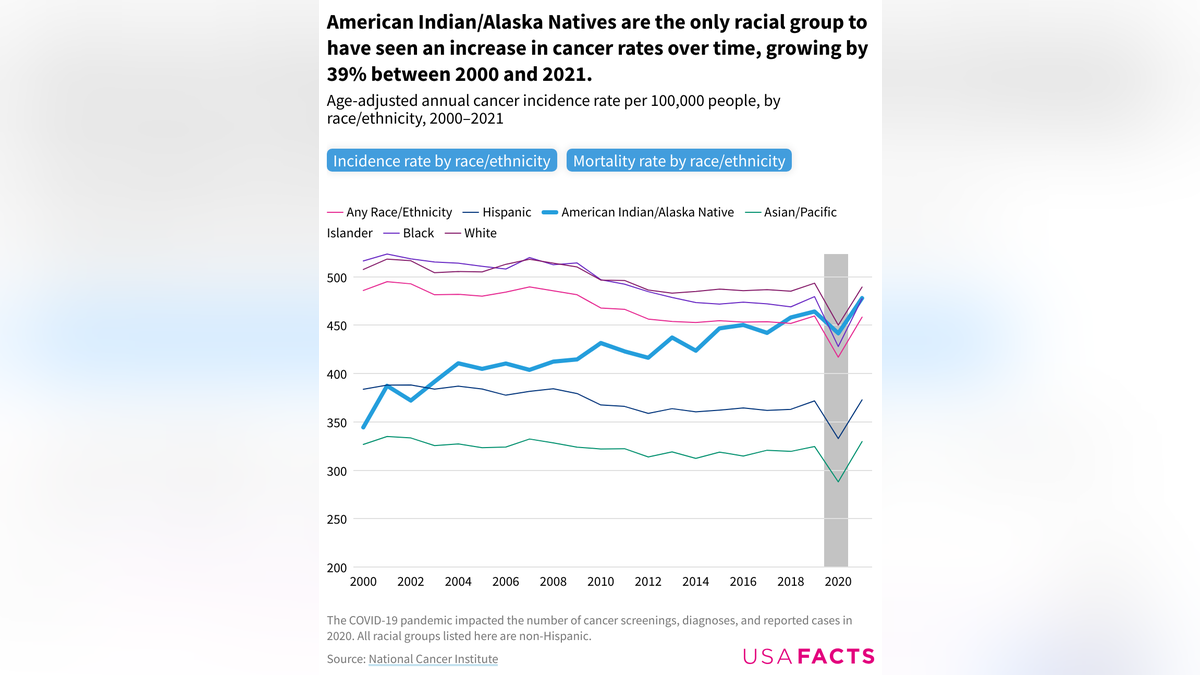
White Americans have the highest rate of new cancer diagnoses, followed by non-Hispanic Black Americans, the report stated. (National Cancer Institute)
“While the reason behind these disparities is hard to pin down, contributing factors include access to health care, environmental conditions, lifestyle behaviors and genetics,” the report states.
3. Cancer survival rates
The five-year cancer survival rate has risen, going from 63.5% in 2000 to 68.4% in 2015 — and is expected to continue its upward trend.
“This improvement is credited to better prevention, early detection and advancements in treatment,” according to Osborn.
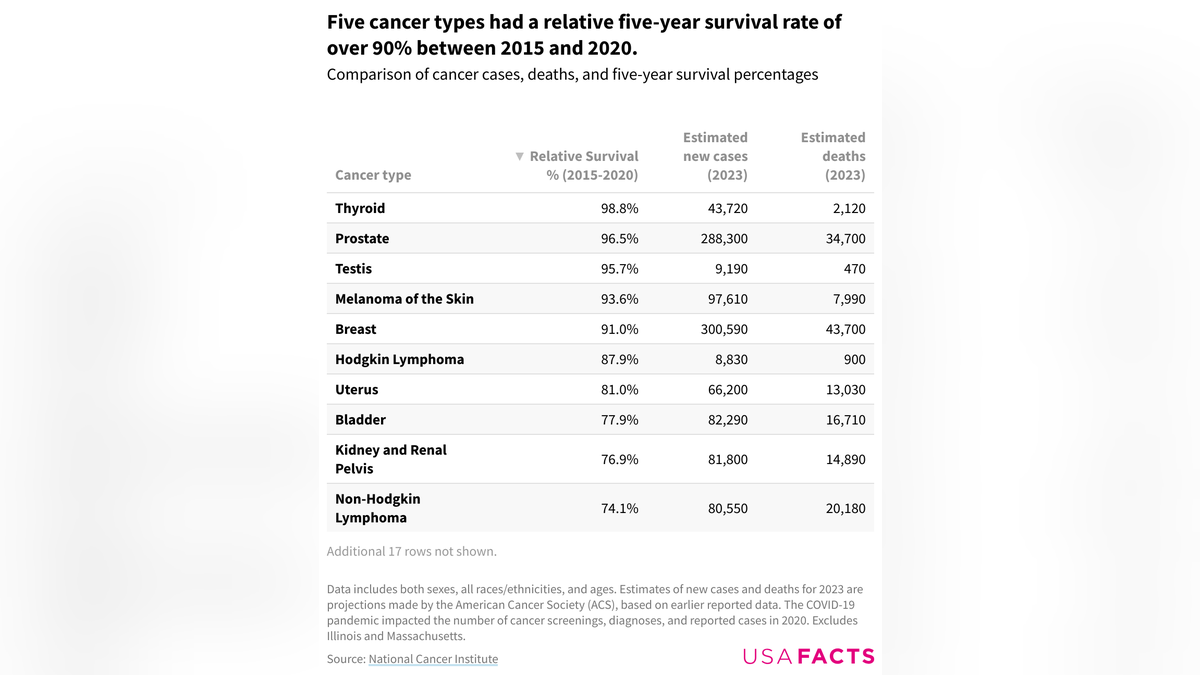
The five-year cancer survival rate has risen, going from 63.5% in 2000 to 68.4% in 2015, and is expected to continue its upward trend. (National Cancer Institute)
Survival rates vary by cancer type.
The cancers with the highest five-year survival rate are thyroid (98.8%), prostate cancer (96.5%), testicular cancer (95.7%), skin cancer (93.6%) and breast cancer (91.0%).
CANCER RATES RISING IN YOUNG PEOPLE DUE TO ‘ACCELERATED AGING,’ NEW STUDY FINDS: ‘HIGHLY TROUBLING’
“It should be noted that estimated cancer deaths in 2023 do not reflect the five-year survival rate between 2015 and 2020, as deaths in 2023 may result from cancer cases diagnosed prior to the five-year window,” the report stated.
4. Average age of cancer diagnosis
Age is the most prevalent risk factor for a cancer diagnosis, according to the report.
Diagnosis rates rise steadily for each decade of life.
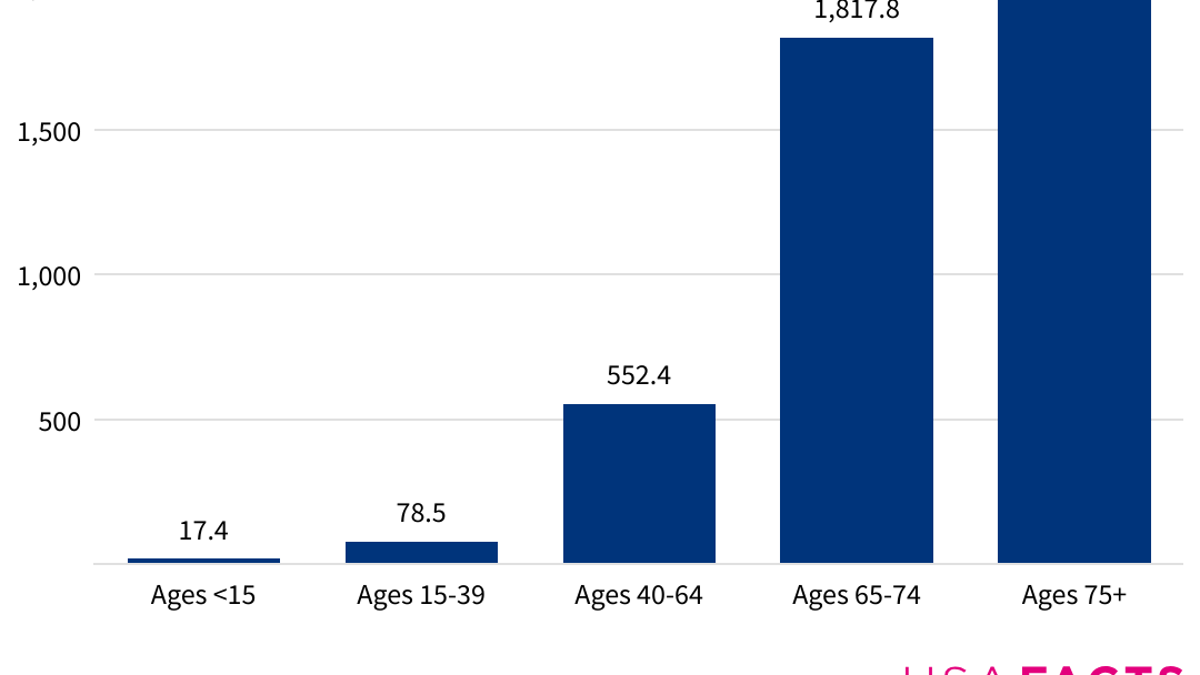
Age is the most prevalent risk factor for a cancer diagnosis, according to the new report. (National Cancer Institute)
The average age of diagnosis is 66 and the average age of death is 72, according to data gathered by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) between 2016 and 2020.
The disease can occur at any age, however — which is why experts recommend early screenings to reduce mortality rates.
5. Importance of guarding against ‘complacency’
Despite the improvements in cancer incidence and mortality rates, Osborn warned that Americans “should not be lulled into complacency.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“According to 2024 data from the American Cancer Society, the incidence of six of the most common cancers – namely those related to excess body weight, such as endometrial, liver, kidney, pancreas, colorectal and breast – are on the rise and may temper the declining mortality rate in the future,” he warned.
Rising obesity rates in the U.S. are a direct cancer driver, Osborn indicated.
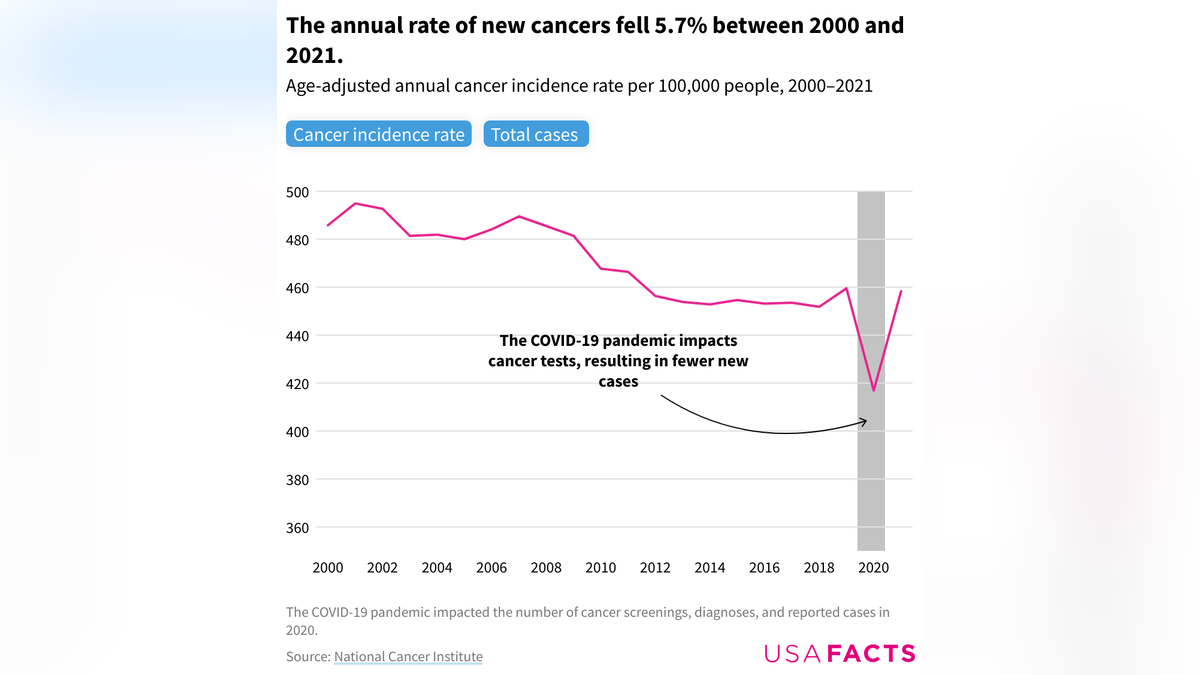
While cancer cases have risen overall due to a growing population, the share of people getting diagnosed and dying from the disease has decreased. (National Cancer Institute)
“It is estimated that more than two in five adults (42.4%) have obesity – a gateway disease to cancer — according to recent data from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases,” said Osborn.
“One can only hope that we are not headed in the wrong direction.”
“Unless the tide is turned and the obesity epidemic is addressed, the observed reduction in the annual rate of new cancers and associated mortality will slow and potentially be extinguished,” he continued.
“One can only hope that we are not headed in the wrong direction.”
USAFacts compiled its report using data from the NCI, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS).
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIs this fictitious civil war closer to reality than we think? : Consider This from NPR
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoShipping firms plead for UN help amid escalating Middle East conflict
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoICE chief says this foreign adversary isn’t taking back its illegal immigrants
-
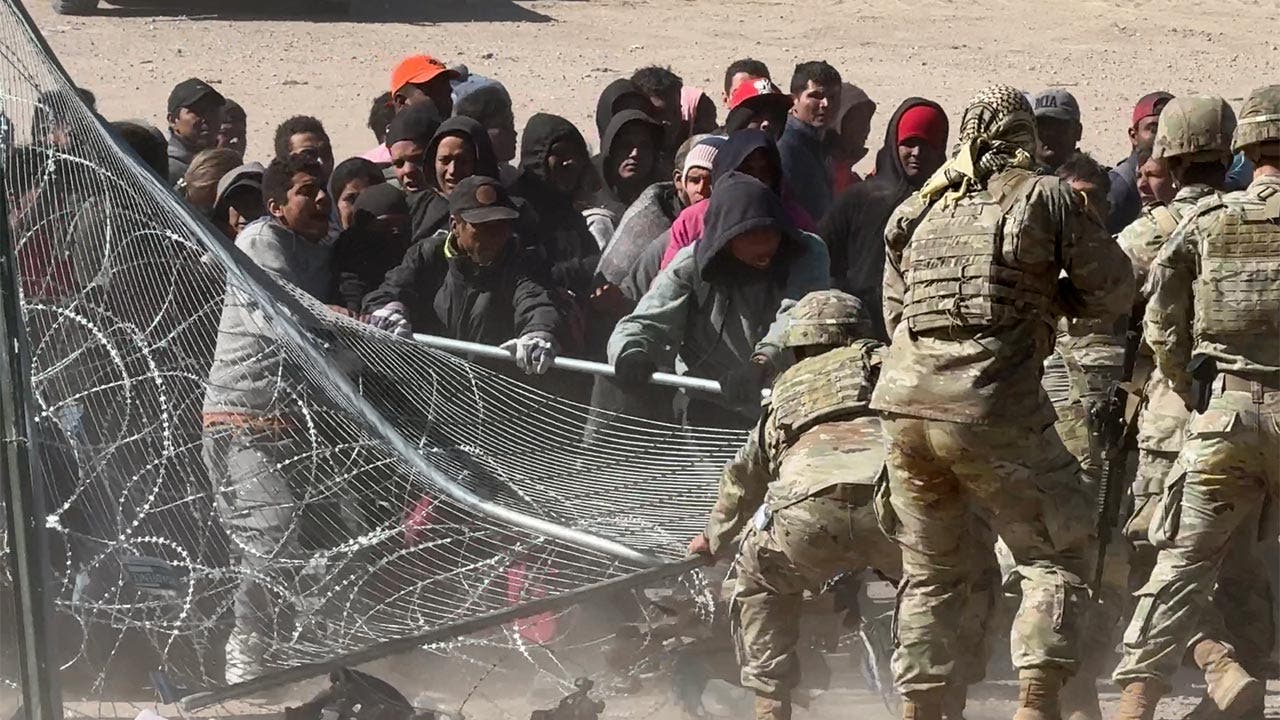

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago'Nothing more backwards' than US funding Ukraine border security but not our own, conservatives say
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoThe San Francisco Zoo will receive a pair of pandas from China
-
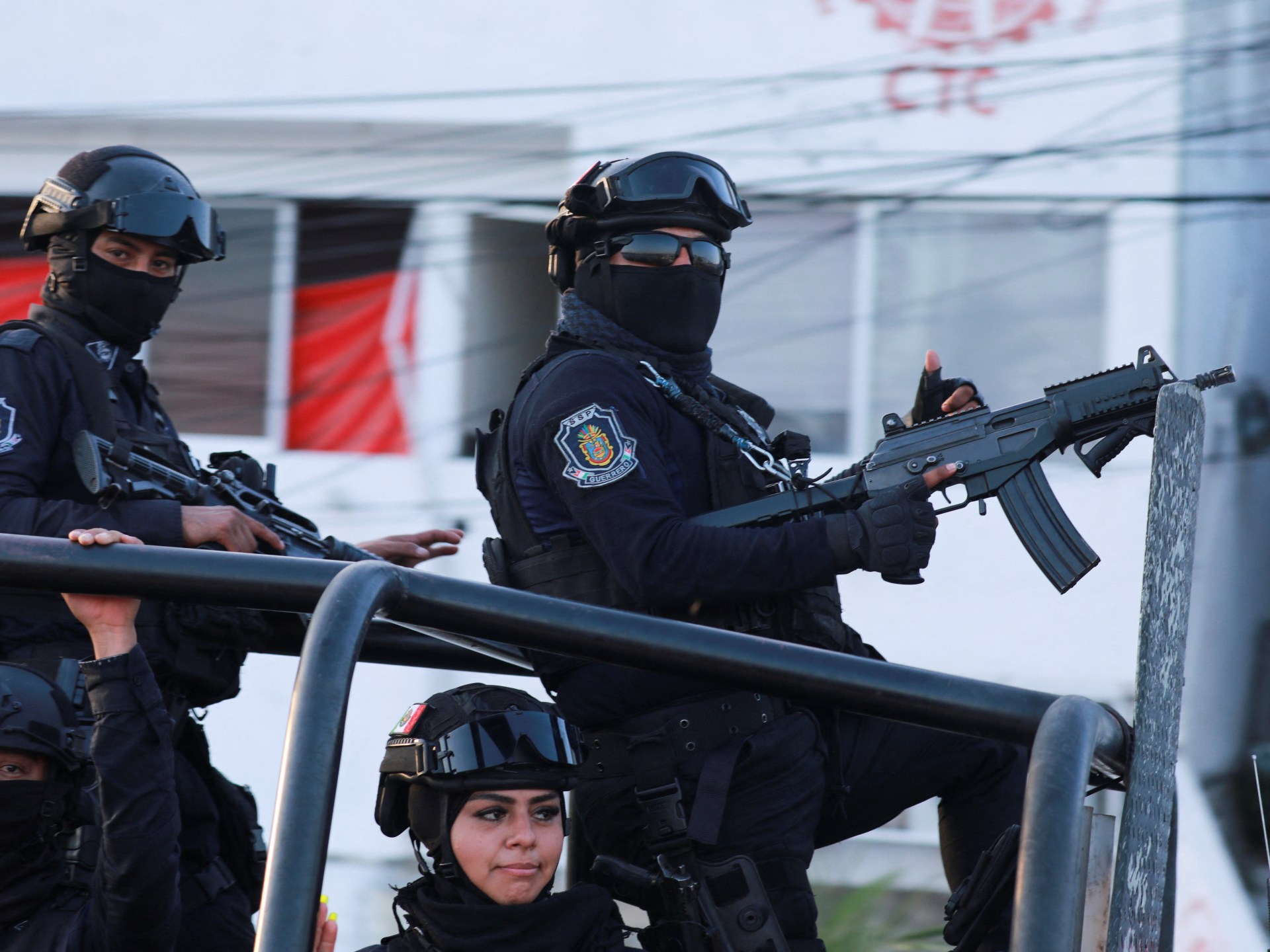

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTwo Mexican mayoral contenders found dead on same day
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoBrussels, my love? The EU single market is not sexy enough for voters
-
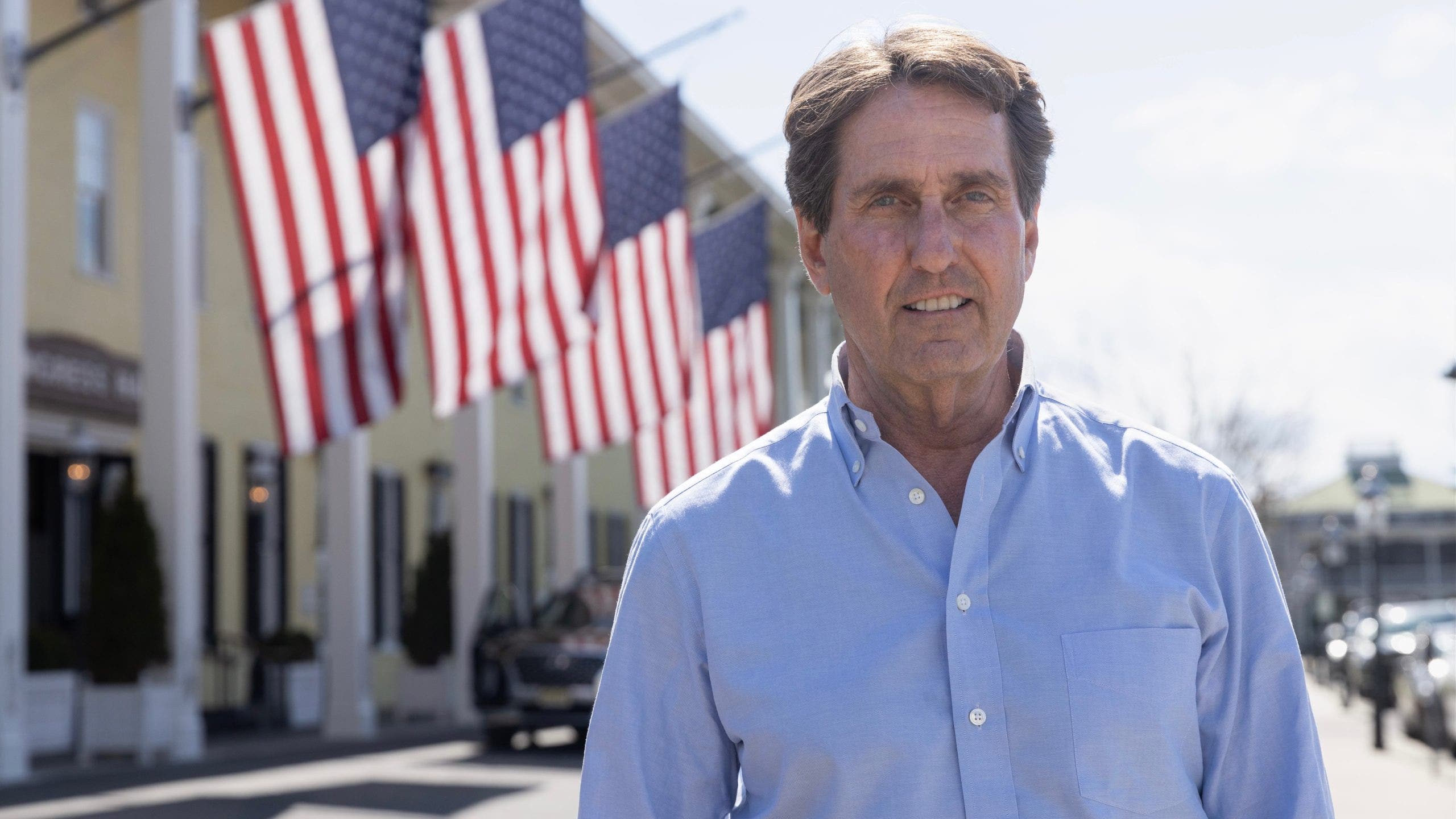

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRepublican aims to break decades long Senate election losing streak in this blue state














