Education
U.S. History Scores Are Falling, but It’s Not Just Because of the Pandemic

Nationwide check scores launched on Wednesday confirmed a marked drop in college students’ data of U.S. historical past and a modest decline in civics, an indication of the pandemic’s alarming attain, damaging pupil efficiency in almost each educational space.
The pandemic plunge in U.S. historical past accelerated a downward pattern that started almost a decade in the past, hitting this latest low at a time when the topic itself has change into more and more politically divisive.
A rising variety of college students are falling under even the fundamental requirements set out on the Nationwide Evaluation of Instructional Progress, a rigorous nationwide examination administered by the Division of Training. About 40 % of eighth graders scored “under fundamental” in U.S. historical past final yr, in contrast with 34 % in 2018 and 29 % in 2014.
Simply 13 % of eighth graders had been thought of proficient — demonstrating competency over difficult subject material — down from 18 % almost a decade in the past.
Questions ranged from the easy — figuring out that manufacturing facility situations within the 1800s had been harmful, with lengthy days and low pay — to the complicated. For instance, solely 6 % of scholars might clarify in their very own phrases how two concepts from the Structure had been mirrored within the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech.
The dip in civics efficiency was smaller however notable: It was the primary decline because the check started being administered within the late Nineties. About 22 % of scholars had been proficient, down from 24 % in 2018.
President Biden’s schooling secretary, Miguel A. Cardona, seized on the outcomes, admonishing politicians for making an attempt to restrict instruction in historical past, typically on subjects of race, a pattern that has performed out in dozens of states, sometimes Republican managed.
“Now just isn’t the time,” he stated, including that “banning historical past books and censoring educators from instructing these necessary topics does our college students a disservice and can transfer America within the flawed course.”
The outcomes, from a nationwide pattern of about 8,000 eighth graders in every topic, observe with scores in math and studying, which additionally decreased in the course of the pandemic. Throughout topics, declines had been typically pushed by the lowest-performing college students, a pattern that has federal officers so involved that they’re now contemplating rewriting check inquiries to zero in on what these college students are lacking.
In historical past, it’s potential that decreased studying comprehension performed some function in pupil efficiency.
However specialists additionally pointed to a unbroken de-emphasis on social research instruction.
Because the implementation of No Little one Left Behind within the early 2000s and its replace in the course of the Obama administration, federal coverage has required states to check college students in studying and math. Periodic testing can also be required for science.
No such mandate exists for social research. (Many state insurance policies round testing and accountability additionally don’t embody social research.)
Whereas some specialists have criticized standardized assessments as restricted in effectiveness and detrimental to college students, most typically agree: What’s examined drives what’s taught.
Educational time for social research declined after the implementation of No Little one Left Behind, a sample that was amplified in the course of the pandemic, when faculties needed to triage educational losses, leading to extra of a concentrate on studying and math.
“It doesn’t bode properly for the way forward for this nation and for the way forward for democracy if we don’t begin doing extra instruction in social research,” stated Kristin Dutcher Mann, a historical past professor on the College of Arkansas at Little Rock, who helps prepare center and highschool social research academics. At one level, she stated, older elementary college college students in her neighborhood obtained an hour of social research every day. Now, she stated, “they are going to be fortunate in the event that they get half-hour for social research twice per week.”
(The Nationwide Council for the Social Research recommends a minimal of 45 minutes of each day instruction in elementary college and an identical equal in center and highschool.)
Instruction has modified, too.
College students spend far much less time memorizing state capitals or the preamble to the Structure — info they might simply Google — and as an alternative focus extra on key expertise, like distinguishing between main and secondary supply paperwork. That’s not essentially a foul factor, Dr. Dutcher Mann stated. College students must be taught to suppose critically.
However she stated that emphasis can contribute to a troubling lack of background data. Even in her faculty courses, she stated, she has seen a “fast and really vital decline” in what college students learn about historical past and geography — like the truth that Africa is a continent, not a rustic.
A base data in historical past and civics is essential for college students to change into engaged, knowledgeable residents, notably amid misinformation on social media platforms, stated Kei Kawashima-Ginsberg, director of Tufts College’s CIRCLE heart, a corporation centered on youth civic engagement.
She cited a latest TikTok marketing campaign towards an Alaska oil undertaking, which resulted in a misguided petition urging President Biden to not promote Alaska.
“You want some fundamentals to grasp what’s even verifiable: ‘Does it even jibe loosely with what I discovered?’” she stated, noting that the president doesn’t have government energy to promote a state.
With American belief in establishments falling to new lows, however with younger voter turnout and political engagement up, many see this as a pivotal second for re-emphasizing historical past and civics schooling.
Sheila Edwards, a center college historical past trainer in Los Angeles County, stated after latest college shootings, college students had inundated her with detailed questions concerning the Second Modification. On the day of the Jan. 6 assault on the Capitol, she needed to give you a brand new homework task to handle her college students’ curiosity within the information.
“Children appear to be extra concerned with historical past and civics than ever earlier than,” she stated.

Education
Video: Police Use Pepper Spray on Protesters on G.W.U.’s Campus

new video loaded: Police Use Pepper Spray on Protesters on G.W.U.’s Campus
transcript
transcript
Police Use Pepper Spray on Protesters on G.W.U.’s Campus
Police officers arrested 33 pro-Palestinian protesters and cleared a tent encampment on the campus of George Washingon University.
-
“The Metropolitan Police Department. If you are currently on George Washington University property, you are in violation of D.C. Code 22-3302, unlawful entry on property.” “Back up, dude, back up. You’re going to get locked up tonight — back up.” “Free, free Palestine.” “What the [expletive] are you doing?” [expletives] “I can’t stop — [expletives].”
Recent episodes in Israel-Hamas War
Education
How Counterprotesters at U.C.L.A. Provoked Violence, Unchecked for Hours

A satellite image of the UCLA campus.
On Tuesday night, violence erupted at an encampment that pro-Palestinian protesters had set up on April 25.
The image is annotated to show the extent of the pro-Palestinian encampment, which takes up the width of the plaza between Powell Library and Royce Hall.
The clashes began after counterprotesters tried to dismantle the encampment’s barricade. Pro-Palestinian protesters rushed to rebuild it, and violence ensued.
Arrows denote pro-Israeli counterprotesters moving towards the barricade at the edge of the encampment. Arrows show pro-Palestinian counterprotesters moving up against the same barricade.
Police arrived hours later, but they did not intervene immediately.
An arrow denotes police arriving from the same direction as the counterprotesters and moving towards the barricade.
A New York Times examination of more than 100 videos from clashes at the University of California, Los Angeles, found that violence ebbed and flowed for nearly five hours, mostly with little or no police intervention. The violence had been instigated by dozens of people who are seen in videos counterprotesting the encampment.
The videos showed counterprotesters attacking students in the pro-Palestinian encampment for several hours, including beating them with sticks, using chemical sprays and launching fireworks as weapons. As of Friday, no arrests had been made in connection with the attack.
To build a timeline of the events that night, The Times analyzed two livestreams, along with social media videos captured by journalists and witnesses.
The melee began when a group of counterprotesters started tearing away metal barriers that had been in place to cordon off pro-Palestinian protesters. Hours earlier, U.C.L.A. officials had declared the encampment illegal.
Security personnel hired by the university are seen in yellow vests standing to the side throughout the incident. A university spokesperson declined to comment on the security staff’s response.
Mel Buer/The Real News Network
It is not clear how the counterprotest was organized or what allegiances people committing the violence had. The videos show many of the counterprotesters were wearing pro-Israel slogans on their clothing. Some counterprotesters blared music, including Israel’s national anthem, a Hebrew children’s song and “Harbu Darbu,” an Israeli song about the Israel Defense Forces’ campaign in Gaza.
As counterprotesters tossed away metal barricades, one of them was seen trying to strike a person near the encampment, and another threw a piece of wood into it — some of the first signs of violence.
Attacks on the encampment continued for nearly three hours before police arrived.
Counterprotesters shot fireworks toward the encampment at least six times, according to videos analyzed by The Times. One of them went off inside, causing protesters to scream. Another exploded at the edge of the encampment. One was thrown in the direction of a group of protesters who were carrying an injured person out of the encampment.
Mel Buer/The Real News Network
Some counterprotesters sprayed chemicals both into the encampment and directly at people’s faces.
Sean Beckner-Carmitchel via Reuters
At times, counterprotesters swarmed individuals — sometimes a group descended on a single person. They could be seen punching, kicking and attacking people with makeshift weapons, including sticks, traffic cones and wooden boards.
StringersHub via Associated Press, Sergio Olmos/Calmatters
In one video, protesters sheltering inside the encampment can be heard yelling, “Do not engage! Hold the line!”
In some instances, protesters in the encampment are seen fighting back, using chemical spray on counterprotesters trying to tear down barricades or swiping at them with sticks.
Except for a brief attempt to capture a loudspeaker used by counterprotesters, and water bottles being tossed out of the encampment, none of the videos analyzed by The Times show any clear instance of encampment protesters initiating confrontations with counterprotesters beyond defending the barricades.
Shortly before 1 a.m. — more than two hours after the violence erupted — a spokesperson with the mayor’s office posted a statement that said U.C.L.A officials had called the Los Angeles Police Department for help and they were responding “immediately.”
Officers from a separate law enforcement agency — the California Highway Patrol — began assembling nearby, at about 1:45 a.m. Riot police with the L.A.P.D. joined them a few minutes later. Counterprotesters applauded their arrival, chanting “U.S.A., U.S.A., U.S.A.!”
Just four minutes after the officers arrived, counterprotesters attacked a man standing dozens of feet from the officers.
Twenty minutes after police arrive, a video shows a counterprotester spraying a chemical toward the encampment during a scuffle over a metal barricade. Another counterprotester can be seen punching someone in the head near the encampment after swinging a plank at barricades.
Fifteen minutes later, while those in the encampment chanted “Free, free Palestine,” counterprotesters organized a rush toward the barricades. During the rush, a counterprotester pulls away a metal barricade from a woman, yelling “You stand no chance, old lady.”
Throughout the intermittent violence, officers were captured on video standing about 300 feet away from the area for roughly an hour, without stepping in.
It was not until 2:42 a.m. that officers began to move toward the encampment, after which counterprotesters dispersed and the night’s violence between the two camps mostly subsided.
The L.A.P.D. and the California Highway Patrol did not answer questions from The Times about their responses on Tuesday night, deferring to U.C.L.A.
While declining to answer specific questions, a university spokesperson provided a statement to The Times from Mary Osako, U.C.L.A.’s vice chancellor of strategic communications: “We are carefully examining our security processes from that night and are grateful to U.C. President Michael Drake for also calling for an investigation. We are grateful that the fire department and medical personnel were on the scene that night.”
L.A.P.D. officers were seen putting on protective gear and walking toward the barricade around 2:50 a.m. They stood in between the encampment and the counterprotest group, and the counterprotesters began dispersing.
While police continued to stand outside the encampment, a video filmed at 3:32 a.m. shows a man who was walking away from the scene being attacked by a counterprotester, then dragged and pummeled by others. An editor at the U.C.L.A. student newspaper, the Daily Bruin, told The Times the man was a journalist at the paper, and that they were walking with other student journalists who had been covering the violence. The editor said she had also been punched and sprayed in the eyes with a chemical.
On Wednesday, U.C.L.A.’s chancellor, Gene Block, issued a statement calling the actions by “instigators” who attacked the encampment unacceptable. A spokesperson for California Gov. Gavin Newsom criticized campus law enforcement’s delayed response and said it demands answers.
Los Angeles Jewish and Muslim organizations also condemned the attacks. Hussam Ayloush, the director of the Greater Los Angeles Area office of the Council on American-Islamic Relations, called on the California attorney general to investigate the lack of police response. The Jewish Federation Los Angeles blamed U.C.L.A. officials for creating an unsafe environment over months and said the officials had “been systemically slow to respond when law enforcement is desperately needed.”
Fifteen people were reportedly injured in the attack, according to a letter sent by the president of the University of California system to the board of regents.
The night after the attack began, law enforcement warned pro-Palestinian demonstrators to leave the encampment or be arrested. By early Thursday morning, police had dismantled the encampment and arrested more than 200 people from the encampment.
Education
Video: President Biden Addresses Campus Protests

new video loaded: President Biden Addresses Campus Protests
transcript
transcript
President Biden Addresses Campus Protests
President Biden defended the right of demonstrators to protest peacefully, but condemned the “chaos” that has prevailed at many colleges nationwide.
-
Violent protest is not protected. Peaceful protest is. It’s against the law when violence occurs. Destroying property is not a peaceful protest. It’s against the law. Vandalism, trespassing, breaking windows, shutting down campuses, forcing the cancellation of classes and graduations — none of this is a peaceful protest. Threatening people, intimidating people, instilling fear in people is not peaceful protest. It’s against the law. Dissent is essential to democracy, but dissent must never lead to disorder or to denying the rights of others, so students can finish the semester and their college education. There’s the right to protest, but not the right to cause chaos. People have the right to get an education, the right to get a degree, the right to walk across the campus safely without fear of being attacked. But let’s be clear about this as well. There should be no place on any campus — no place in America — for antisemitism or threats of violence against Jewish students. There is no place for hate speech or violence of any kind, whether it’s antisemitism, Islamophobia or discrimination against Arab Americans or Palestinian Americans. It’s simply wrong. There’s no place for racism in America.
Recent episodes in Politics
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoThe White House has a new curator. Donna Hayashi Smith is the first Asian American to hold the post
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPolice enter UCLA anti-war encampment; Arizona repeals Civil War-era abortion ban
-
)
) Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoThe Idea of You Movie Review: Anne Hathaway’s honest performance makes the film stand out in a not so formulaic rom-com
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSome Florida boaters seen on video dumping trash into ocean have been identified, officials say
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUN, EU, US urge Georgia to halt ‘foreign agents’ bill as protests grow
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIn the upcoming European elections, peace and security matter the most
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: President Biden Addresses Campus Protests
-
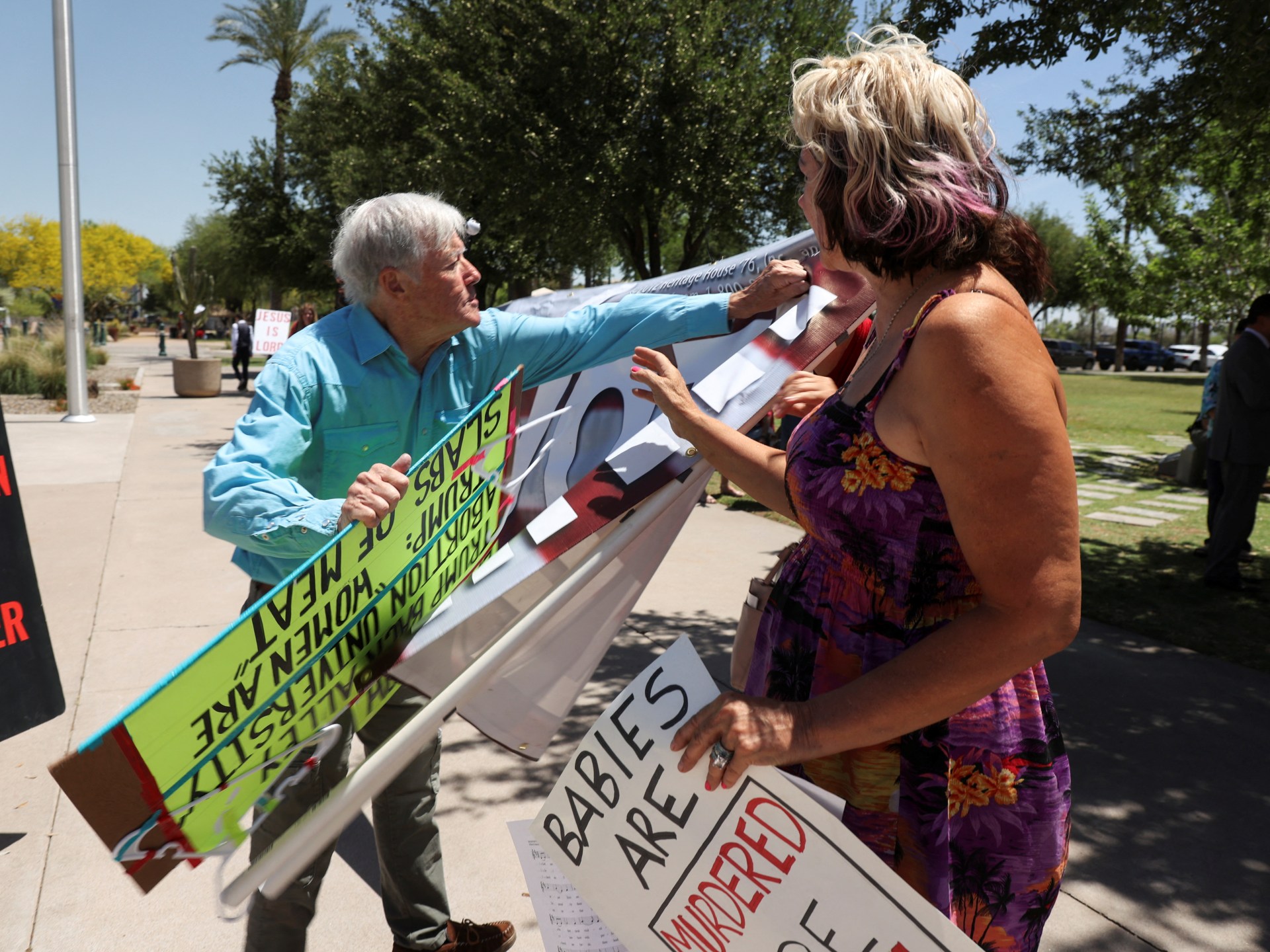
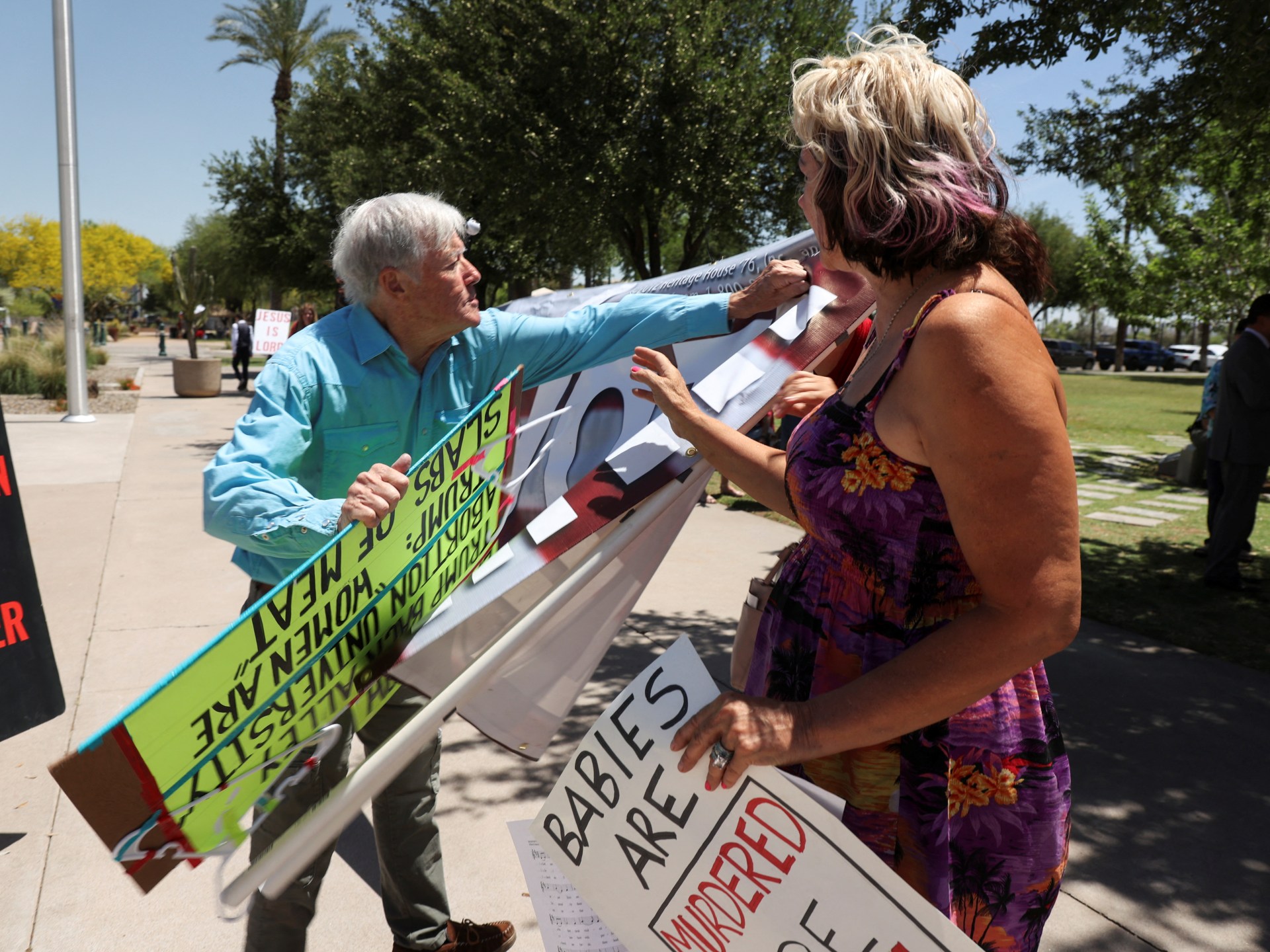 World1 week ago
World1 week agoArizona Senate repeals near-total 1864 abortion ban in divisive vote













