Science
Deadly overdoses stopped surging among L.A. County homeless people. Narcan could be why
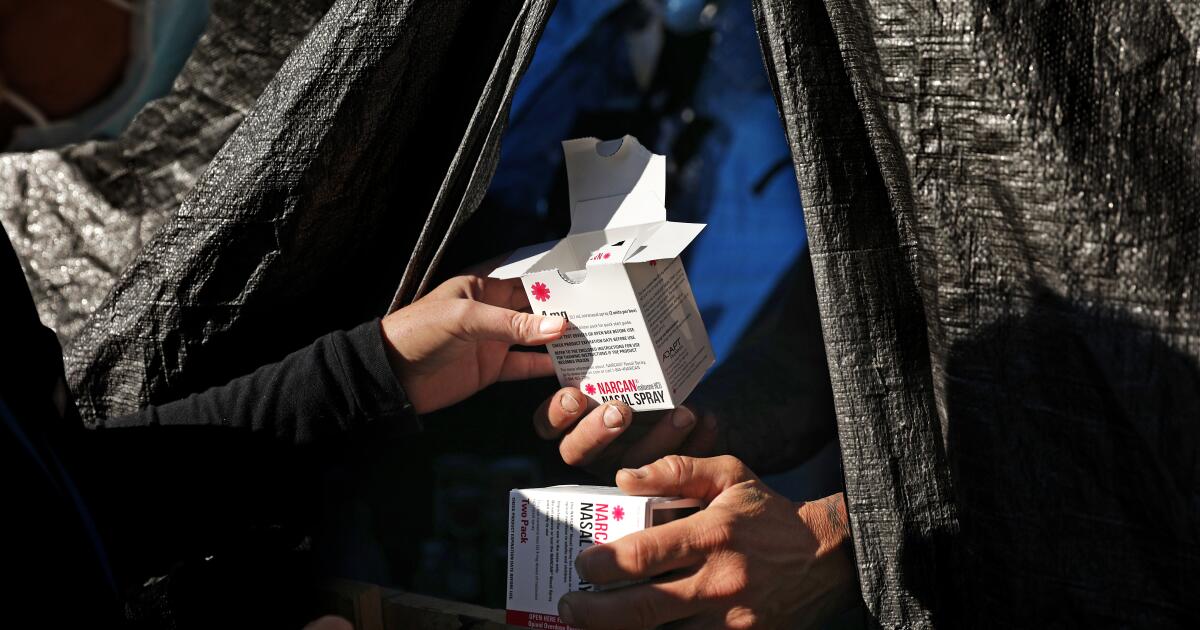

Year after year, Los Angeles County has seen devastating losses on its streets, as homeless people bedding down in tents, under tarps and on sidewalks have lost their lives to drug overdoses at soaring rates.
Now a newly released report shows the death rate from overdoses stopped rising among unhoused people in the county in 2022 — the same year L.A. County was stepping up its efforts to save lives.
Public health officials welcomed the news as a glint of hope, but cautioned it is too soon to say if the numbers are headed for a lasting downturn. They pointed to a county push to dramatically ramp up the distribution of naloxone — a medicine that bystanders can use to stop opioid overdoses — as a likely factor.
In their report, county officials touted a “near doubling” that year in the reported number of overdoses that were thwarted with naloxone, based on figures provided by a county program. The lifesaving medicine is commonly sold as a nasal spray under the brand name Narcan.
Two years ago in North Hollywood, Manny Placeres told The Times he had revived people seven times using Narcan that had been provided to him by a county team, honing his technique with time.
“As they’re knocking on heaven’s door, I pull them back,” Placeres said.
Manny Placeres, who has administered naloxone many times to reverse opioid overdoses on the streets, embraces Leimer in 2022.
(Christina House / Los Angeles Times)
The L.A. County Department of Health Services has handed out Narcan at homeless encampments, given it to community groups and county agencies and set up vending machines to dispense it for free to people leaving county jails.
As of February, the health services department said it had distributed more than 600,000 doses of naloxone since launching its initiative, resulting in more than 25,000 overdoses being stopped. Community groups and syringe programs have bolstered such efforts by handing out their own supplies of free naloxone provided by the state.
Dr. Gary Tsai, director of the public health department’s substance abuse prevention and control bureau, said that after years of alarming increases, “it is encouraging to see a slowing of this leading cause of death for people experiencing homelessness.”
“Efforts to increase access to naloxone and overdose prevention services have undoubtedly helped to bend this curve and provide a blueprint for reducing drug-related fatalities in this very high-risk population,” he said in a statement.
County officials said such efforts had also helped stabilize the death rate for homeless people overall after years of disturbing growth. As deadly overdoses stopped surging and COVID-19 deaths plunged, the overall mortality rate among unhoused people in L.A. County began to level off, the report found.
But homeless people remained far more likely than other county residents to die in a range of ways, including overdoses, traffic collisions, heart disease and homicide.
Their death rate overall was nearly four times higher than that of the broader population — a gap that has widened over time, public health officials found. And although it may have finally hit a plateau, the mortality rate for homeless people in L.A. County was still 60% higher than it had been three years earlier.
“This report highlights the continued need for concerted efforts to reduce the disproportionate burden of mortality among this vulnerable population,” L.A. County Public Health Director Barbara Ferrer said in a statement.
The county report also pointed out some alarming variations in the overall trends in L.A. County: For Black people who were unhoused, for instance, the rate of overdose deaths continued to rise significantly in 2022.
The rate of fatal overdoses also kept rising among homeless people in their 20s and 40s, the report found. That was offset by dropping rates among older people, but the report raised a grim possibility: After so many deadly years, “there may now be fewer surviving fentanyl and other opioid users over 50.”
Narcan can stop overdoses from opioids such as fentanyl, a powerful synthetic drug that has been involved in a rising share of overdose deaths among homeless people in L.A. County.
But fentanyl has not been the only threat: Roughly two-thirds of deadly overdoses among unhoused people involved more than one drug. Among the most commonly mingled were fentanyl and methamphetamine, a combination involved in nearly half of overdose deaths among homeless people in the county in 2022, according to the new report.
L.A. County public health officials called for a number of steps to bring down deaths among unhoused people, including expanding housing options so that people who use drugs will not lose their housing as a result; handing out more naloxone and test strips that detect fentanyl; and expanding preventative care for people who are homeless.

Science
A UCLA doctor is on a quest to free modern medicine from a Nazi-tainted anatomy book
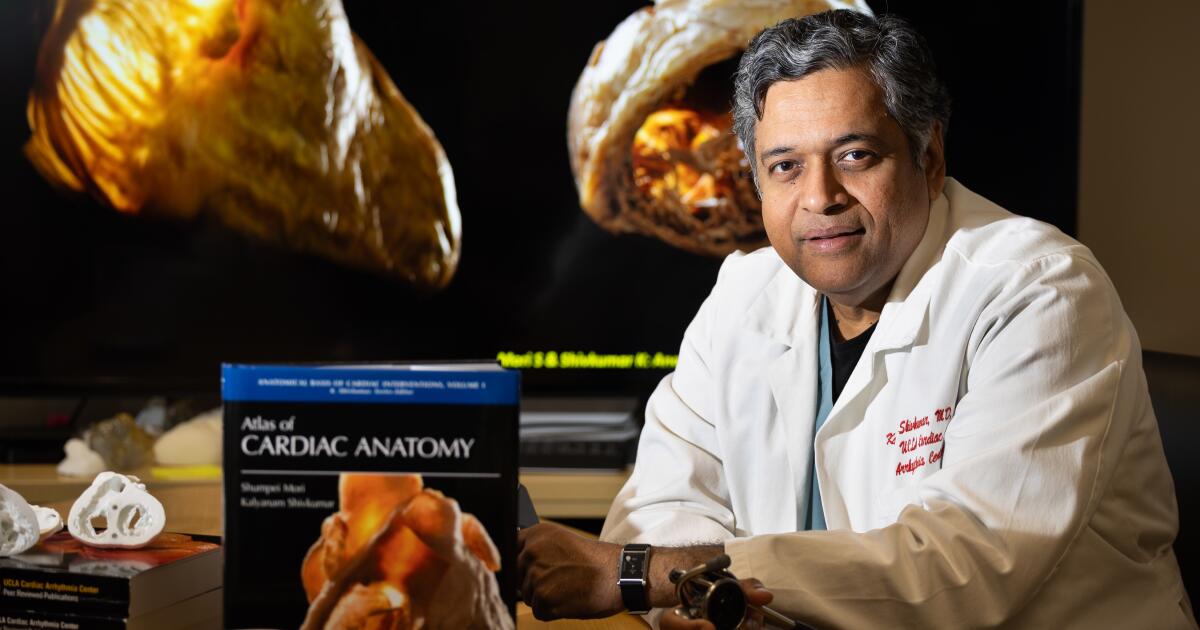

As Dr. Kalyanam Shivkumar pondered how to fix the human heart, he was given a gift laced with horror.
Shivkumar, a cardiac electrophysiologist known as “Shiv” to friends and co-workers at UCLA, was trying to better understand the intricate details of nerves in the chest. He hoped doing so might help him improve treatments for cardiac arrhythmias — aberrant rhythms of the heart — that can prove dangerous and even deadly.
A Canadian colleague sent him a set of anatomy books renowned for the beauty and detail of their drawings, but tipped him off that the “atlas” had an appalling history.
Shivkumar was aghast to learn it was the work of an ardent Nazi whose Vienna institute had dissected the bodies of prisoners, many executed for political reasons after Austria was annexed to Nazi Germany in 1938.
“Every time I open up that book,” he said, “my sense is revulsion.”
Shivkumar is a big thinker, an erudite physician quick with an apt quotation, whose Westwood office is stacked with Sanskrit volumes of the Mahabharata alongside books about late Bruins basketball coach John Wooden.
Dr. Shumpei Mori sets up a donated heart to be photographed at UCLA as part of the Amara Yad project to create new, ethically made anatomical images.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
As he waded into the scholarly debate over using the tainted atlas, the doctor bristled at hearing others praise its illustrations as “unsurpassable.” Much of the soul searching among physicians had revolved around when and how to use it. Shivkumar wanted to put those questions to bed.
“Could we be better?” he asked. “Could we not be making something that’s completely untainted?”
That question would launch Shivkumar on a quest that has lasted more than a decade and is expected to endure for years. He wants to surpass the anatomical atlas created by Dr. Eduard Pernkopf, a fervent supporter of the Nazi regime whose work was fueled by the dead bodies of its victims.
His passion project at the UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center is called Amara Yad, a mashup of Sanskrit and Hebrew meaning “immortal hand.” The work has relied on the generosity of people who have willed their bodies for use at UCLA, as well as hearts that were donated but could not be used for transplant.
So far, Amara Yad has completed two volumes focused on the anatomy of the heart and is enlisting teams at other universities for more. The plan is to draft a freely available, ethically sourced road map to the entire body that eclipses the weathered volumes of watercolors from Pernkopf and honors the Nazis’ victims.
Anatomists have told him, “‘You’re crazy. It’s impossible. How could you ever surpass it?’” Shivkumar said of the Pernkopf atlas in a speech last year before members of the Heart Rhythm Society.
But “can it be beaten? The answer is yes.”
For decades, the origins of the Pernkopf Atlas were unknown to many who turned to its pages for guidance. Swastikas tucked into signatures of an illustrator were airbrushed out in later editions. Its history began to trickle out in journals in the 1980s.
When Dr. Howard Israel finally learned of its roots, he was horrified. Israel, an oral surgeon at Columbia University and self-described “very ordinary American Jew,” told the New York Times he had been relying on the book since he was a medical student.
‘’I felt stupid at using the book,” he told the newspaper, “that I could possibly have benefited from something that sounded so evil.” He and another physician enlisted the Holocaust remembrance group Yad Vashem and publicly pushed for the University of Vienna to investigate whose bodies were depicted in its pages.
The resulting probe found no evidence that the anatomy department under Pernkopf — who had ascended to become dean of the medical faculty at the University of Vienna in 1938 — had received bodies from the Mauthausen concentration camp, as some had wondered.
But the institute had been given at least 1,377 bodies of executed people, most of them sentenced to death for political reasons. Among the charges that led to their executions: “crimes of resistance” and “high treason.”
Using the bodies of executed people was “a centuries-old practice in anatomy,” preferred because anatomists could time their work swiftly after a scheduled death, said Dr. Sabine Hildebrandt, an anatomy educator at Harvard Medical School. What was new under the Nazis, she said, was the sheer number of executions.
The institute “was drowned in bodies,” and “the source for these bodies was mostly connected with the apparatus of repression of the Nazi regime,” said historian Herwig Czech, a member of the Lancet Commission on Medicine, Nazism, and the Holocaust, at a recent forum.
By the time those findings emerged, the publisher of the anatomy book had stopped printing it.
1
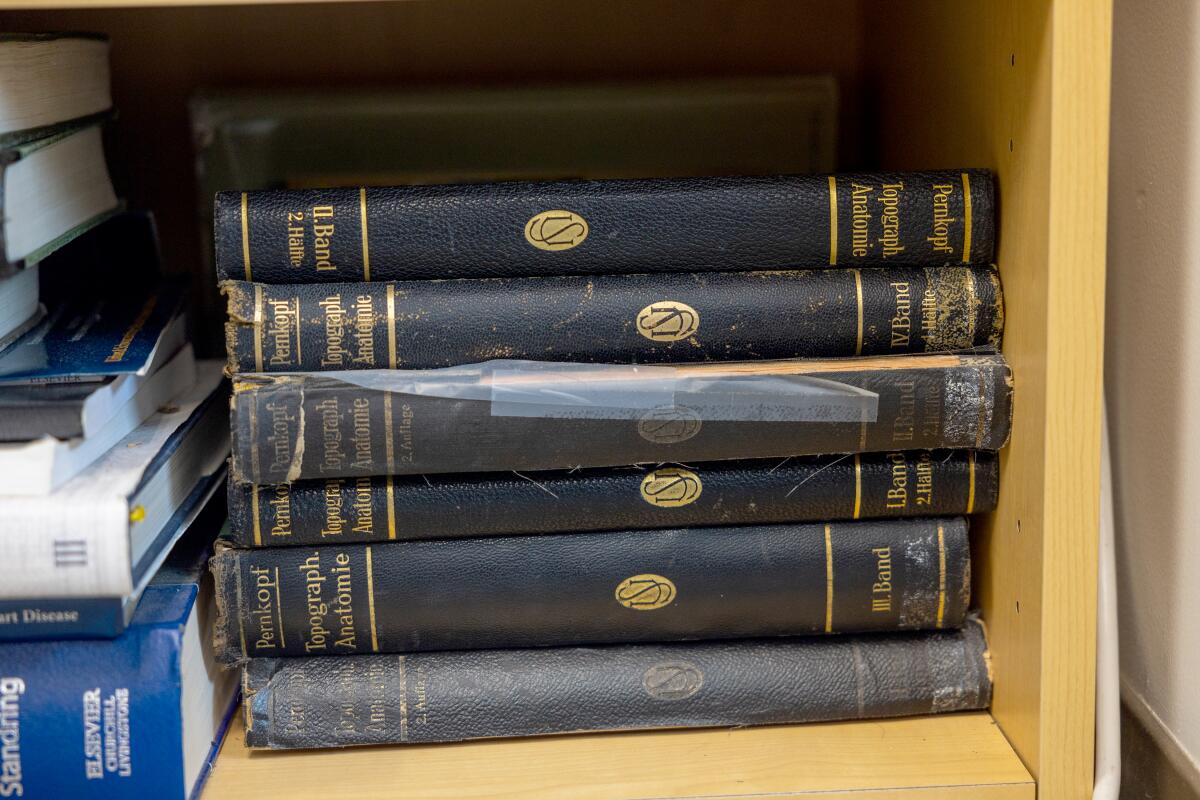

2

1. A stack of volumes of the Pernkopf atlas on a shelf in Dr. Kalyanam Shivkumar’s UCLA office. 2. Erich Lepier, one of the Pernkopf atlas illustrators, repeatedly included a swastika after the cursive R in his signature. (Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
Yet use of the atlas persisted. Hildebrandt said that a decade ago, dental students in her classes “were basically giving each other thumb drives with bootlegged copies of the head and neck.”
Other anatomical atlases exist, but these illustrations had especially fine details, including of the nerves extending beyond the brain and spiral cord. One survey of nerve surgeons found that 13% of respondents were using the atlas. Among those who have publicly grappled with it is Dr. Susan Mackinnon, a surgery professor at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis known as a pioneer in nerve regeneration.
“I used this textbook for years before I knew the history of it,” she said. “My brain is contaminated with that. I can’t undo that.”
Mackinnon sought ethical guidance. Rabbi Joseph Polak, a Boston University assistant adjunct professor of health law who survived the concentration camps as a child, said one dilemma involved a patient in excruciating pain.
Polak recalled that the patient had told Mackinnon that “if you can’t find the nerve to stop the pain, then I want my leg amputated.” The rabbi walked through Jewish teachings that applied to the ethical quandary and conferred with other experts, penning a set of recommendations called the Vienna Protocol.
Among his urgings to doctors: If you use these drawings, make it clear to patients where they came from.
The Third Reich wanted “to extinguish them and to extinguish eventually all memory of them,” the rabbi said of Holocaust victims, speaking at a recent forum about the atlas. But when a doctor tells patients about what happened to the people depicted in the drawings, he said, “they’re being called out of that darkness.”
Mackinnon now keeps the atlas locked away. In the rare cases she feels she needs to consult it to operate, she tells patients and co-workers about the man behind it. His firings of Jewish doctors. The grim details in its pages — shorn hair, emaciated bodies — that began to raise suspicions about its terrible origins.
The only reason to use it, she said, is to save someone from misery — and only if “nothing else will help you.”
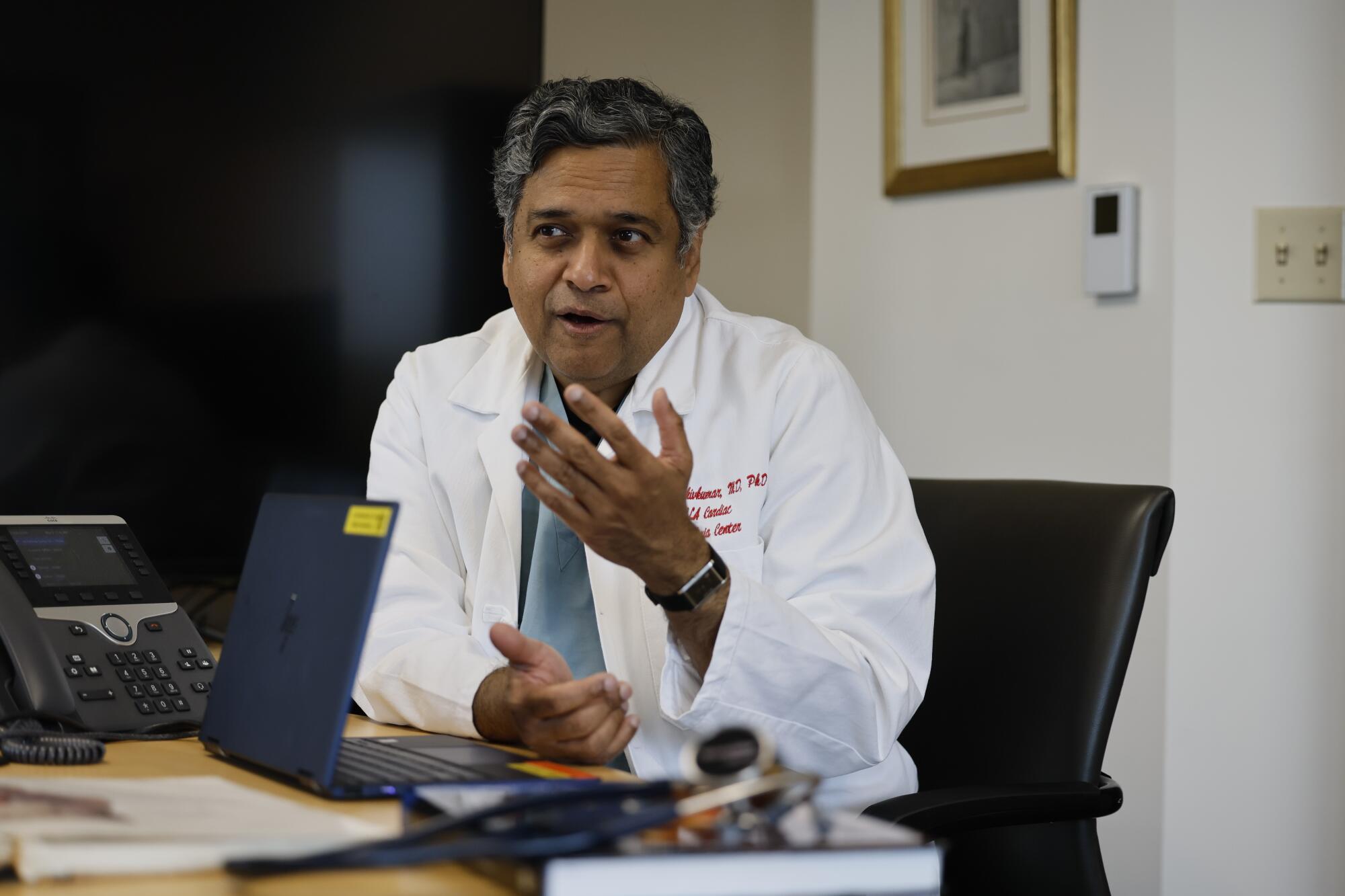

“Could we be better” than Pernkopf? Shivkumar asked. “Could we not be making something that’s completely untainted?”
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
Shivkumar said his goal is to eliminate the need to consult those pages at all. Inside UCLA’s Center for the Health Sciences in Westwood, he showed off a donated heart, prepped and ready for its close-up in a corner of the lab outfitted with a black backdrop and brilliant lights.
A spent heart normally wilts like a deflated balloon, but this one had been pumped with chemicals to imitate the fullness of life. The team first puts the organs to use in research, then carefully dissects them for imaging.
Bringing out a bisected piece of a heart, Dr. Shumpei Mori displayed how its inner architecture could be captured on camera, threading a catheter through the organ as a co-worker snaked in an endoscope.
“The internal structure is really fine and delicate,” said Mori, a specialist in cardiac anatomy who had jumped at the chance to do something new in the field.
“Even Pernkopf simplified the anatomy” in its drawings, Mori said. “What we are doing is more complicated.”
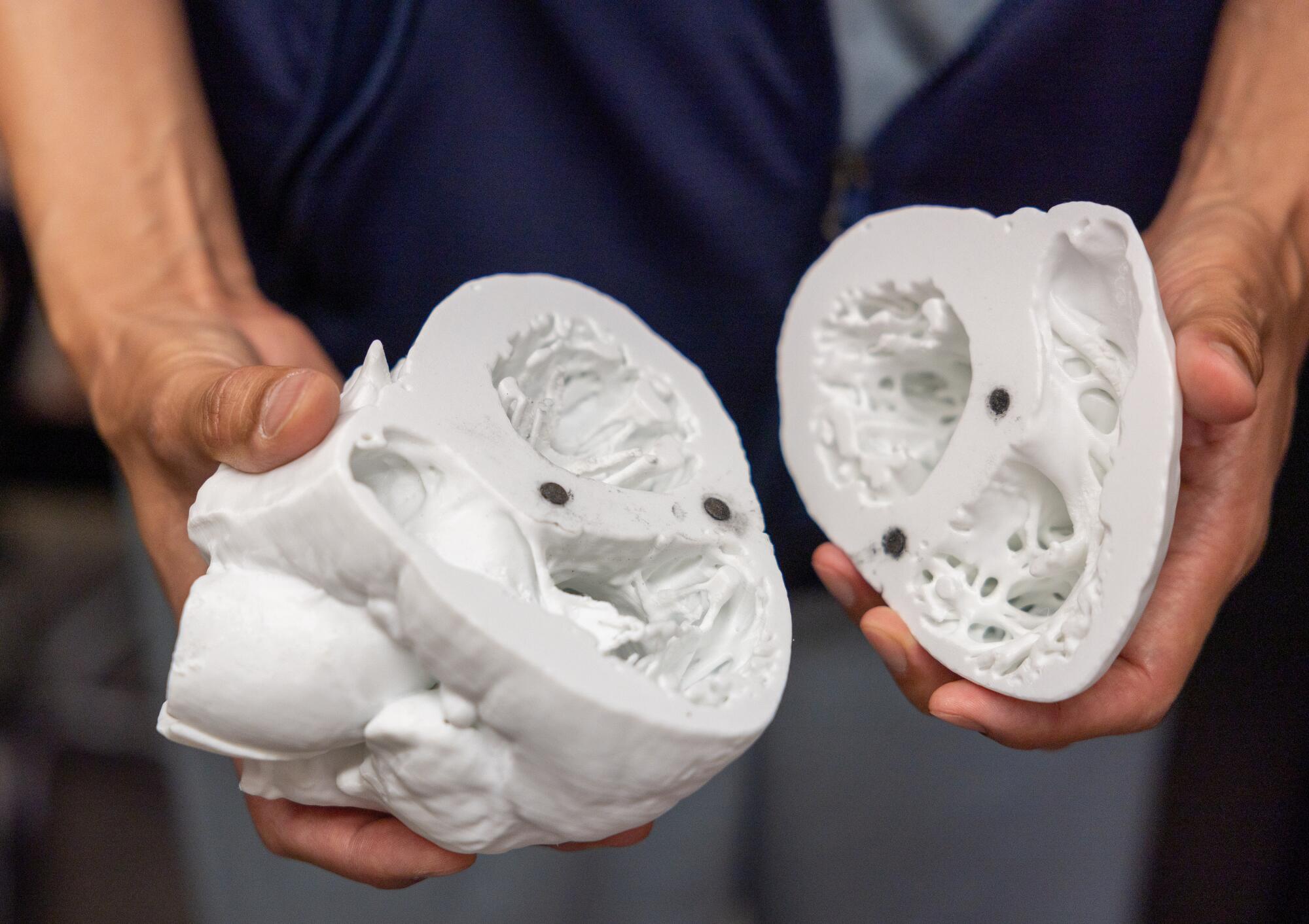
Dr. Shumpei Mori holds a detailed model of a heart. “Even Pernkopf simplified the anatomy,” he said. “What we’re doing is more complicated.”
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
The camera is far from their only tool: The team has generated 3-D images to illustrate the dimensions of the inner structures of the heart; done CT scans to produce hand-held models; and used sophisticated imaging from a microscope to reveal the lattice of nerves connecting to the organ — part of the signaling system that Shivkumar calls “the internet of the human body.”
In another lab, Mori carefully unzipped a bag on a metal gurney to reveal the stripped-down interior of a cadaver diligently dissected over a year and a half, its rib cage cracked open like a weighty book. Shivkumar pointed out the pale web of nerves stretching up through the neck. Mori had painted them yellow by hand.
The human body might seem like well-traveled territory, but as physicians work to find less invasive ways of healing, such as attacking a cancer with ultrasound, Shivkumar said there is “a volcanic desire for this kind of information.” Snip the right nerve, he said, and you can avert the need for a heart transplant.
“Pernkopf never did nerves like this,” he said with pride.
Amara Yad is also an act of “moral repair” meant to honor the victims, said Dr. Barbara Natterson-Horowitz, a UCLA cardiologist and evolutionary biologist who helped support the project. The Nazi atlases “were like documents of death. The atlases that Shiv is creating are really living, interactive tools to support life.”
When Shivkumar decided to launch the project, he had been inspired by the words of USC emeritus professor of rheumatology Dr. Richard Panush, who had pushed to set the atlas aside in the library of the New Jersey medical center where he had worked, moving it to a display case that explained its history.
Panush said the old atlas should be preserved only as “a symbol of what we should not do, and how we should not behave, and the kind of people that we cannot respect.”
Doctors need to know that history to understand their own moral fallibility, Hildebrandt said. Physicians in Nazi Germany “still thought they were doing the right thing,” she said, even as they failed to see some people as human.
Rabbi Polak stressed that doctors at the time “had the deepest, most profound respect of the masses.”
Yet when the Nazis took power, “it turned out that a vast proportion of them were moral sleazeballs,” Polak said. “They were the first to join when they saw that it could promote their careers.”
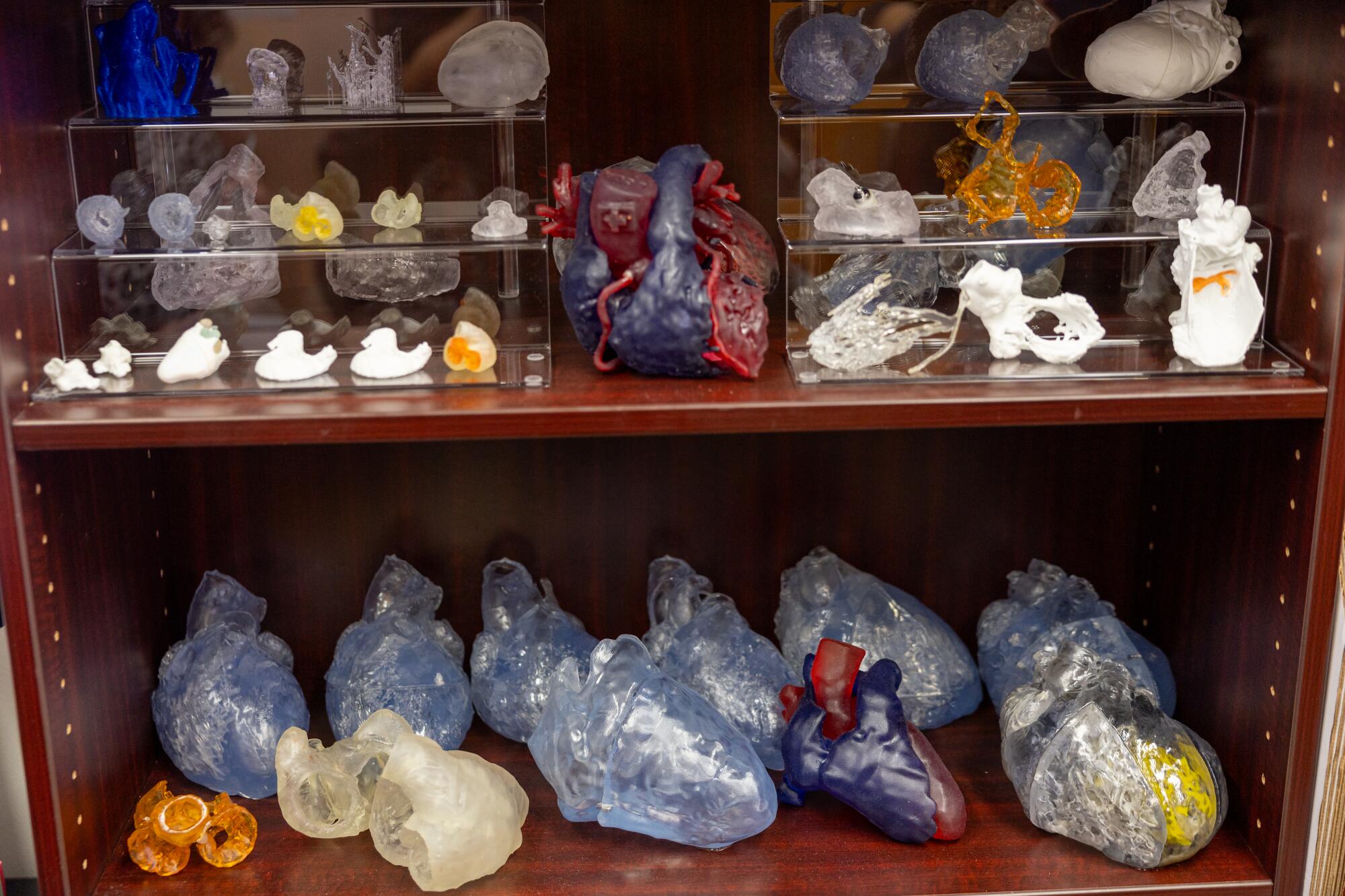

Model hearts line a bookshelf at UCLA. The Amara Yad project is working with other universities to tackle other parts of human anatomy.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
Shivkumar said that beyond making new tools for physicians, the Amara Yad project is working with Oxford University to develop an accompanying curriculum that will explore ethical failures in medicine. Pernkopf’s anatomy book is only one example.
The history of the atlas “invites the contemplation of how doctors and medical scientists and anatomists are related to a regime,” said Sari J. Siegel, who heads the Center for Medicine, Holocaust and Genocide Studies at Cedars-Sinai. Thinking about it underscores that “medicine is political.”
“It can’t be divorced from the larger contexts in which it exists.”
Shivkumar, born to a Hindu family in the southernmost state of India, is used to people wondering why he became “possessed” with this project. He recalls first learning about the Holocaust from a photographer friend of his grandfather, a former newspaper editor once imprisoned for sedition against the British Empire.
He was 11 when the photographer showed him images dating to World War II, and it chilled him “to see that human beings could be so brutal to other humans.” As a child, his parents had told him they owed the world because their part of India was lucky to be long spared from such conflict.
In Amara Yad, we “get a rare opportunity in history to correct an unbelievably depressing stain that was placed in our field,” he told the Heart Rhythm Society.
It irritates him to think of the abundant resources that a Nazi had at hand to do this sort of work. “Imagine having five Shumpeis!” he exclaimed at one point, gesturing at his colleague who hand painted the nerves. At UCLA, the project has piggybacked on ongoing research and relied on donations. He is hoping to garner $500,000 annually to continue and expand the work.
But Shivkumar likes to quote the Emperor Ashoka on that point: “To do good is difficult. One who does good first does something hard to do. … Truly, it is easy to do evil.”
Science
Opinion: Wait times go down. Patient satisfaction goes up. What's the matter with letting apps and AI run the ER?

My resident describes our next emergency room patient — a 32-year-old female with severe, crampy mid-abdominal pain, vomiting and occasional loose stools. The symptoms have been present for nearly a week, and there is tenderness to both sides of the upper abdomen. It could be a gallbladder problem, the resident says, hepatitis, pancreatitis, diverticulitis or an atypical appendicitis. She proposes routine blood tests along with an ultrasound and an abdominal CT scan.
This is the time-honored approach to an undifferentiated patient complaint: Generate a list of possible diagnoses, decide which represent a “reasonable” concern and use the results from further testing to conclude what’s going on. Yet increasingly the second phase of this process — evaluating which diagnoses represent a reasonable concern — is getting short shrift. It is the heavy lift of any patient encounter — weighing disease probabilities, probing for details. It’s often simpler, and faster, to cast a wide net, click the standard order for blood work and imaging, and wait for the results to pop up.
The issue of the “busy doctor ordering too many tests” has plagued medicine for decades. Now, as hospitals inject algorithms and technology into their workflow, it’s much worse. Medicine is moving inexorably away from the deductive arts, becoming more technology- and test-dependent and less patient-centric.
Go to an emergency room today and you will likely be met within minutes by a doctor whose sole role is to perform a “rapid medical evaluation.” The provider asks a few questions, ticks boxes on a computer screen and, shazam, you are in line for the most likely series of tests and scans, all based on typically a less than 60-second encounter.
This strategy seems obvious. When workups are initiated as soon as the patient arrives, wait times go down, patient satisfaction goes up, and fewer patients leave out of frustration before even being seen. These are the metrics that put smiles on administrators’ faces and give hospitals high marks in national surveys.
But is it good doctoring? Without the luxury of time, these gateway providers typically lump patients into broad, generic categories: the middle-aged person with chest pain, the short-of-breath asthmatic, the vomiting pregnant patient, the septuagenarian with cough and fever, and so forth. The diagnosis is then reverse-engineered with tests to cover all possible bases for that particular complaint.
In essence this is flipping the script on traditional doctoring while incentivizing doctors to use testing as a surrogate for critical thinking, dumbing down the practice of medicine and throwing gasoline on the problem of over-testing.
Since rapid evaluation became the norm, use of laboratory, CT and ultrasound services at my hospital has increased nearly 20%. Just the other day, a pregnant woman in my ER went through a full battery of time-consuming, expensive and invasive tests even though she’d been through all of them at another hospital the day before. As far as I can tell, the only reason we did that was because that’s what an algorithm told us to do.
This has real effects on patients. Contrary to popular perception, more tests may not supply more answers. That’s because the accuracy of any test depends on the likelihood that the patient has the disease in question before the test is performed. Testing performed without the appropriate indication or context can produce incidental or even spurious results that may have your doctor looking in entirely the wrong direction.
The basic problem with hospitals’ growing obsession with efficiency is this: Algorithmic systems treat all patients the same, expecting precise, like-for-like responses to every question with just the right amount of detail. Except every patient is unique. And they tend to give up their stories at their own pace, in broken, non-linear fits and starts, sometimes conflating truth and fiction in ways that can be counterproductive and frustrating, but also uniquely human. I am often reminded of Jack Webb in the old TV series “Dragnet” imploring a witness to offer “just the facts, ma’am, just the facts.” In real life, whether from situational stress, self-delusion, superstition, health illiteracy, mental illness, drugs or alcohol, my patients’ initial version of their complaint is rarely “just the facts” or the final word on the subject.
A colleague recently described her role in a clinical encounter as 9 parts translator to 1 part doctor. One question leads to another, and then another, and another until she successfully translates the patient’s lived experience into a language modern medicine and its algorithms might begin to understand. My experience is similar. Properly choreographed, the doctor-patient interaction becomes a pas de deux — two people in sync, jointly trying to solve a puzzle with each sharing their perspective and expertise. In the transition to front-loaded care, I worry health decisions will be made with information that may be incomplete or, at times, totally unreliable.
Algorithmic medicine also seems tailor-made for an AI takeover. The logic is obvious. Use “big data” to assist doctors and nurses struggling to keep up with the demands of modern medicine. AI can ensure a level, consistent floor of care that avoids errors of omission by considering a deliberately broad list of diagnostic possibilities. In an ideal world, a synergy of human and machine intelligence could amplify the patient-doctor encounter. As likely, AI will lead doctors to abdicate judgment and responsibility to the automated response of the machine.
And so, I complimented my resident on her list of concerns but suggested that we spend a little more time with the patient. The story of her symptoms didn’t feel complete. I recommended my resident grab a chair and simply ask the patient about her life. What emerged was the chaotic picture of an exhausted part-time student by day, working two evening waitressing jobs and surviving on pizza, pasta and energy drinks. She had always had a “fragile stomach.”
Our list of reasonable diagnoses was expanding and contracting, replaced with irritable bowel syndrome, food intolerances, gut motility issues, all overlying a stressed individual barely keeping it together. The labs, ultrasound or CT scan initially proposed now seemed irrelevant.
The result: The patient got out of the hospital faster. She received helpful suggestions about stress reduction, diet and sleep habits. She got an appointment with a primary care physician and avoided thousands of dollars in tests. Had we just relied on tests instead of asking a few more questions, there is a good chance we would have missed the best approach to her problem entirely.
ER waiting rooms and wards are bursting at the seams, and the streamlining of care has never felt more essential. But this is not an excuse for doctors to relinquish their humanity or their “method.” We should tweak the process: Allow more time for doctors to get the story right, do less testing until we have weighed the risks and rewards, prioritize asking questions rather than merely looking for answers.
Sociologists coined the term “pre-automation” to describe the transitional phase in which humans lay the groundwork for automation, often by acting in increasingly machine-like ways. As providers, we must not fall in line.
Put another way, with AI primed to take on a substantial role in how doctors deliver care, we should remind ourselves: If we behave like machines, we certainly won’t be missed when machines replace us.
Eric Snoey is an ER doctor at Alameda Health System-Highland Hospital in Oakland.
Science
Column: Democrats show that they're no better than Trump in allowing politics to interfere with science

Anyone who cares about the importance of science in the making of government policy had to be deeply dispirited by the hearing into the origins of COVID-19 staged by a Republican-led House subcommittee on May 1.
The sole witness at the hearing, and its target, was Peter Daszak, the head of EcoHealth Alliance, a nongovernmental organization tasked with overseeing international virus research funded by federal agencies.
It wasn’t just that the GOP majority used the occasion to promote the ignorant, imbecilic and 100% evidence-free notion that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that caused the COVID pandemic, originated in a Chinese laboratory, through work funded by the U.S. government, and overseen by EcoHealth.
Science is a myth-buster…Because of this, science has become a nuisance, even an enemy to some industries and many of the most powerful actors in the new attention economy.
— Science blogger Philipp Markolin
It was that the Democratic minority showed itself to be complicit with the GOP attack on EcoHealth.
As I wrote at the time, the Democrats threw Daszak and by extension science itself under the bus: “Perhaps they hoped that by allowing Daszak to be drawn and quartered, they might persuade the Republicans to climb down from their evidence-free claims about government complicity in the pandemic’s origins.”
The Democrats’ craven and shameful performance hinted that EcoHealth’s government funding, which had been blocked by the Trump administration and restored, though delayed, under Biden, was pretty much doomed.
On Wednesday, the bell tolled. EcoHealth received a notice from the Department of Health and Human Services, the parent agency of the NIH, that it was immediately suspending all funding to the organization and moving to “debar” it from federal funding going forward.
It’s impossible to overstate what a serious blow this is for EcoHealth and research into the origins of pathogens that could cause illness and death on a global scale — the central purpose of EcoHealth’s work.
The organization, which has operated with a budget of about $16 million, cannot receive a contract from any federal agency or even serve as a subcontractor of another awardee. All organizations with federal contracts that have affiliated with EcoHealth will be “carefully examined.”
EcoHealth says it will appeal the proposed debarment, as is its right. But that process could take years. In the meantime, the organization will be effectively out of money, and very likely out of business. The HHS action effectively turns one of the leading organizations in the quest to protect humankind from the next pandemic into a pariah, completely unjustifiably.
The debarment threat “will mean the demise of EcoHealth, one of the most scientifically productive and internationally respected groups conducting field surveillance for potential pandemic viruses,” says Gerald T. Keusch, a former associate director of international research at the NIH. “And that means our national security will be compromised.”
Let’s be clear about what has happened here. EcoHealth has been made a scapegoat for the pandemic for partisan reasons. The process started with President Trump. At a news conference on April 17, 2020, a reporter from a right-wing organization mentioned that the NIH had given a $3.7-million grant to the Wuhan Institute of Virology. (Actually, the WIV grant, which was channeled from a larger EcoHealth grant, was only $600,000.)
Trump, sensing an opportunity to show a strong hand against China and advance his effort to blame the Chinese for the pandemic, responded: “We will end that grant very quickly.” The NIH terminated the grant one week later, prompting a backlash from the scientific community, including an open letter signed by 77 Nobel laureates who saw the action as a flagrantly partisan interference in government funding of scientific research.
The HHS inspector general found the termination to be “improper.” The NIH reinstated the grant, but immediately suspended it until EcoHealth met several conditions that were manifestly beyond its capability, as they involved its demanding information from the Chinese government that it had no right to receive. The grant was reinstated last year under Biden, but NIH bureaucrats, perhaps worried about their careers in a new Trump administration, continued to put administrative obstacles in the way of EcoHealth’s work.
The attacks on Daszak and his organization are simply instruments of the GOP project to pin blame for the pandemic on Anthony Fauci, one of the world’s most respected public health figures.
The context is a battle for the minds of uninformed and misinformed Americans over the origin of COVID-19. The hypothesis favored by most qualified virologists and epidemiologists is that the virus reached humans the way most viruses do — as spillovers from wildlife. The alternative hypothesis, for which absolutely not a speck of evidence has ever been presented, is that the virus emerged from a laboratory—specifically the Wuhan Institute of Virology in China, whether deliberately or through sloppy lab practices.
The latter hypothesis was initially promoted by an anti-China cabal in the Trump-era State Department. Although they never produced any grounds for the conspiracy theory, it remains favored by anti-vaccine agitators and in the Republican anti-science camp. It has a certain appeal for uninformed people susceptible to sinister explanations of complicated, troubling events; but it’s not science.
Daszak calls the government actions “fundamentally unfair” and “based on a set of false assumptions about COVID-19 origins and on persistent mischaracterizations and misunderstandings of our research…Our work has been at the forefront of understanding pandemic risk for over two decades, and it’s a very cruel irony that because we knew that China was a potential hotspot for the next coronavirus pandemic, we’re now being targeted in a political backlash caused by exactly the type of pandemic we were concerned about preventing.”
An outgrowth of the lab-leak fantasy is the asinine claim that as head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Fauci funded research in China that created the pandemic virus and let it loose on the world, and then concealed his complicity. This is a favorite meme among lab-leak fanatics. Among the research bodies that received NIAID funding to conduct field work in China was EcoHealth. (Fauci retired last year as director of NIAID, which is part of the National Institutes of Health.)
On May 1, the GOP-led Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemic brought things to a head with its grilling of Daszak. It was a circus featuring posturing politicians intent on smearing Daszak and EcoHealth on the pretext of getting to the bottom of the pandemic’s cause. The committee Democrats participated fully, hammering Daszak as a “poor steward of the taxpayers’ dollars,” based on transparent trivialities.
During a follow-up subcommittee hearing Thursday, ranking member Raul Ruiz (D-Indio) alluded to the dishonestly of the GOP attack on Fauci. But, perhaps inadvertently, he also exposed the dishonesty of his caucus’ attack on Daszak.
The committee Republicans, Ruiz said, “still have not succeeded in substantiating their allegations that NIH and NIAID through a grant to EcoHealth Alliance created SARS-CoV-2 and conspired to cover it up. … No evidence demonstrates that work performed under the EcoHealth grants, including at the Wuhan Institute of Virology, led to the creation of SARS-CoV-2.”
Does Ruiz ever listen to the words coming out of his mouth? The very goal of the GOP’s dragging Daszak and EcoHealth into this controversy was to fabricate a link in the chain between Fauci and COVID-19; by rejecting the GOP position, Ruiz demolished the case against EcoHealth.
Yet Ruiz didn’t walk the last mile. “EcoHealth has defied its obligations to be a transparent steward of taxpayer dollars,” he said, repeated the lame case against the organization that he first aired, in connivance with the Republicans, during the public interrogation of Daszak on May 1.
Legitimate scientists, such as virology experts uninfected by the conspiratorial fantasy that the virus originated in the lab, are aghast at the suspension of EcoHealth’s funding and the organization’s likely debarment, as well as the Democrats’ supine behavior.
The Democrats, as Stuart Neil, a professor of virology at Kings College London, wrote on X, “have made some shoddy back room deal to allow them to look tough to the conspiracy theorists.” Neil is right. There is no rational explanation for the Democrats’ behavior than some sort of deal with the Republican majority to give them cover to challenge the lab leak theory.
Put it all together, and it looks like HHS started with a politically driven impulse to cut off EcoHealth’s funding, followed by an effort to assemble every justification for doing so, no matter how trivial. The absurdity of its action drips from the closing words of the notice issued by H. Katrina Brisbon, an HHS “suspension and debarment official.” She wrote that “the immediate suspension of EHA is necessary to protect the public interest and due to a cause of so serious or compelling a nature that it affects EHA’s present responsibility.”
The notice was accompanied by an 11-page bill of particulars, but they all boil down to two key purported offenses — that EcoHealth had missed a 2019 deadline for an annual report of its activities to NIH, and that work EcoHealth had funded in China had produced a recombinant version of a virus that grew fast enough to trigger a safety halt in the work.
The first was tantamount to a traffic violation. EcoHealth maintained that it hadn’t been able to file the report on time because it had been locked out of NIH’s onlline reporting portal, which NIH denies. On the second, there were legitimate disagreements over whether the subject virus’ growth actually did trigger the halt requirement; in any case, the virus wasn’t a threat to human health. The work at issue took place in 2018.
HHS cited several other supposed offenses, including EcoHealth’s failure to submit lab notebooks from the Wuhan institute that NIH has requested in November 2021. But since NIH had ordered EcoHealth to stop funding the institute as of April 2020, those notebooks were plainly out of its reach.
Daszak says EcoHealth will respond to the HHS and the subcommittee “with documentary evidence…refuting every single allegation that’s been levied against us.”
The roots of anti-science slant of Trump and others on the far right isn’t hard to discern. It’s aimed at protecting the economic establishment from new ideas and realities such as global warming, while providing financial and personal opportunities for grifters and charlatans.
Swiss scientist and science blogger Philipp Markolin has put his finger on this phenomenon.
“Science is a myth-buster,” he writes. “Its debunking activity reduces the value of information products that too many media manipulators rely on for their business. Because of this, science has become a nuisance, even an enemy to some industries and many of the most powerful actors in the new attention economy.”
Why did the Democrats agree to participate in this charade? In joining the Daszak smear, they have shredded their credibility as of scientific truth, at the very moment when science is most in need of their protection.
The time has come to ask this question of Ruiz, his Democratic colleagues on the coronavirus subcommittee — Debbie Dingell of Michigan, Kwesi Mfume of Maryland, Deborah Ross of North Carolina, Robert Garcia of Long Beach, Ami Bera of Sacramento and Jill Tokuda of Hawaii — along with Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra: How can you live with yourselves?
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSkeletal remains found almost 40 years ago identified as woman who disappeared in 1968
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIndia Lok Sabha election 2024 Phase 4: Who votes and what’s at stake?
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTales from the trail: The blue states Trump eyes to turn red in November
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoBorrell: Spain, Ireland and others could recognise Palestine on 21 May
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago“Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes”: Disney's New Kingdom is Far From Magical (Movie Review)
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUkraine’s military chief admits ‘difficult situation’ in Kharkiv region
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCatalans vote in crucial regional election for the separatist movement
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNorth Dakota gov, former presidential candidate Doug Burgum front and center at Trump New Jersey rally





/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22461385/vpavic_4547_20210421_0067.jpg)