Health
Mercury In Taurus: What It Means for Your Zodiac Sign
Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.

Health
US pediatricians group reverses decades-old policy, allowing breastfeeding for those with HIV
- People with HIV can breastfeed if they take medications suppressing the AIDS virus, per the American Academy of Pediatrics.
- This marks a significant shift from recommendations since the 1980s.
- Antiretroviral drugs can reduce HIV transmission risk via breast milk to less than 1%.
People with HIV can breastfeed their babies, as long as they are taking medications that effectively suppress the virus that causes AIDS, a top U.S. pediatricians’ group said Monday in a sharp policy change.
The new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics reverses recommendations it had in place since the start of the HIV epidemic in the 1980s.
It recognizes that routinely prescribed drugs can reduce the risk of transmitting HIV via breast milk to less than 1%, said Dr. Lisa Abuogi, a pediatric HIV expert at the University of Colorado and lead author of the report.
BENEFITS OF BREASTFEEDING FOR BOTH MOM AND BABY
“The medications are so good now and the benefits for mom and baby are so important that we are at a point where it is important to engage in shared decision-making,” Abuogi said.
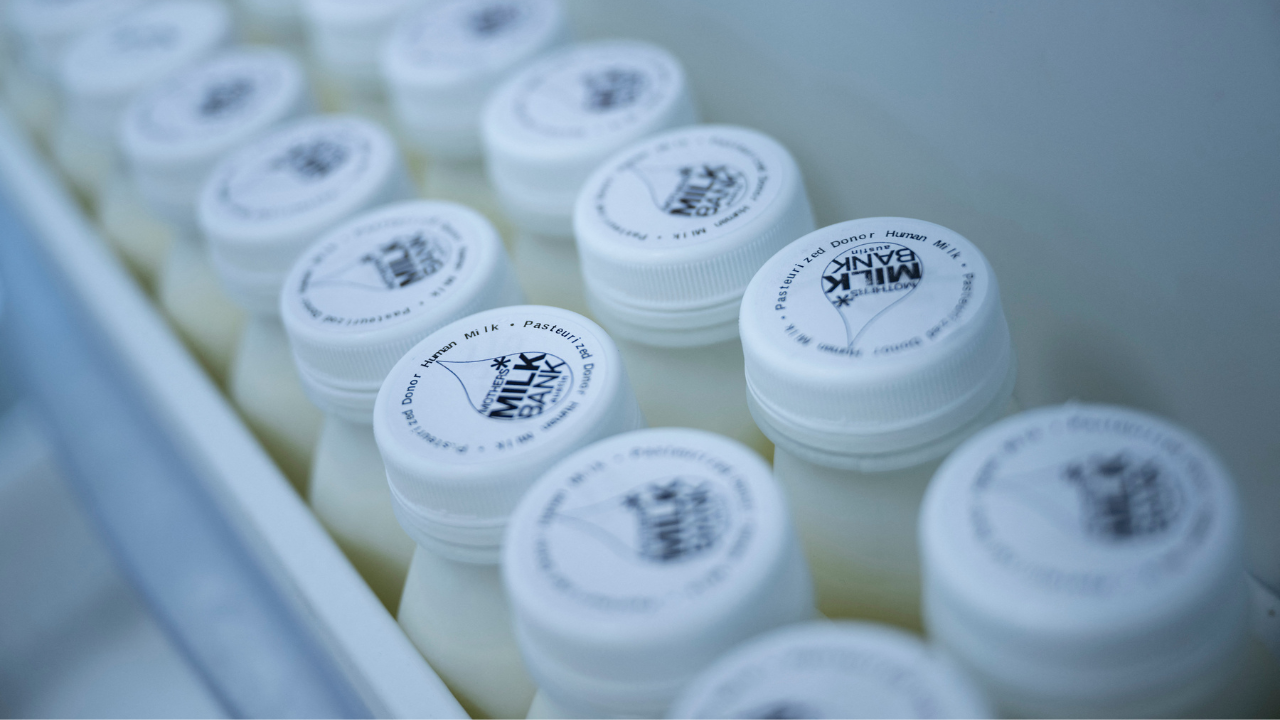
Processed breast milk awaiting distribution is seen at the Breastfeeding Center for Greater Washington on May 19, 2022, in Washington, D.C. People with HIV can breastfeed their babies, as long as they are taking medications that effectively suppress the virus that causes AIDS, a top U.S. pediatricians’ group said on Monday in a sharp policy change. (BRENDAN SMIALOWSKI/AFP via Getty Images)
The drugs, known as antiretroviral therapy, don’t eliminate all risk of transmitting HIV through breast milk. Avoiding breastfeeding is the only certain way to prevent spreading the virus, Abuogi said.
In addition, parents must breastfeed exclusively for the babies’ first six months because research shows that switching between breast milk and formula can disrupt an infant’s gut in ways that increase the risk of HIV infection.
About 5,000 people who have HIV give birth in the U.S. each year. Nearly all take drugs to suppress the virus to very low levels, Abuogi said, though viral levels can rebound if they don’t stay on them.
BREASTFEEDING BAN: GEORGIA MOTHER IS TOLD SHE CAN’T NURSE HER BABY AT WATERPARK, SPARKING DEBATE
Before the medications became widely available starting a decade ago, about 30% of HIV infections transmitted from moms to babies occurred during breastfeeding, said Dr. Lynne Mofenson, an adviser to the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation. In the early 1990s, about 2,000 infections occurred in U.S. infants each year. Today, it’s fewer than 30.
The AAP policy comes more than a year after the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reversed longstanding recommendations against breastfeeding by people with HIV. That guidance said people who have consistent viral suppression should be counseled on their options. It also emphasizes that health care providers shouldn’t alert child protective services agencies if a parent with HIV seeks to breastfeed.
The goal is listening to patients “and not blaming or shaming them,” said Dr. Lynn Yee, a Northwestern University professor of obstetrics and gynecology who helped draft the NIH guidance.
Breastfeeding provides ideal nutrition for babies and protects them against illnesses and conditions such as obesity and Type 2 diabetes, research shows. Nursing also reduces the mother’s risk of breast and ovarian cancer, diabetes and high blood pressure.
The World Health Organization has recommended since 2010 that women with HIV in developing countries breastfeed their infants and have access to antiretroviral therapy. The guidance weighed the risk of infants acquiring HIV through breastfeeding and the risk of babies dying from malnutrition, diarrhea and pneumonia in places where safe replacements for breast milk aren’t available.
In developed nations, however, experts had recommended against breastfeeding because the wide availability of safe water, formula and human donor milk could eliminate the risk of HIV transmission, Yee said.
That frustrated people with HIV who were flatly refused the option of nursing.
Ci Ci Covin, 36, of Philadelphia, said she was diagnosed with HIV at age 20 and not permitted to breastfeed her first child, Zion, now 13.
“I couldn’t understand how come my sister that lives in a place like Kenya, who looks just like me with the same color brown skin, was given the option to breastfeed and how my option was starkly no,” she said.
Not being able to nurse her son sent Covin into a spiral of postpartum depression, she said. When she became pregnant with her now 2-year-old daughter, Zuri, her health care team helped her successfully breastfeed for seven months. Covin took her prescriptions as directed and also gave the baby drugs to prevent infection.
“Breast milk has everything in it that my baby would need,” Covin said. “That’s a beautiful thing.”
Abuogi said the AAP report provides crucial guidance for pediatricians, nurses and lactation specialists who work directly with children and families.
Some providers were already helping people treated for HIV to nurse their babies, despite the earlier recommendations. The new guidance should expand the practice, hopefully quickly, Abuogi said.
“This is a unique situation because it’s not just doctors and providers who are changing,” Abuogi said. “Our patients are pushing this as well.”
Health
Flexitarian vs. Vegetarian — What’s the Difference? | Woman's World

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Many families take patients off life support too soon after traumatic brain injuries: study

Many patients who died after traumatic brain injuries may have survived and recovered if their families had waited to take them off life support, a new study found.
Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School and other universities analyzed “potential clinical outcomes” for patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) who were removed from life support, according to a press release.
The study included 1,392 patients who were treated in 18 trauma centers across the U.S. over a 7½-year period.
HUNDREDS OF RURAL HOSPITALS ARE IN DANGER OF SHUTTING DOWN, STUDY FINDS: ‘AT RISK OF CLOSURE’
Using a mathematical model, the researchers compared patients for whom life support was withdrawn to similar patients who were kept on life support.
Among the group for whom life support was not withdrawn, more than 40% recovered at least some independence, according to a press release.
Many patients who died after traumatic brain injuries may have survived and recovered if their families had waited to take them off life support, a new study has found. (iStock)
The researchers also discovered that the notion of remaining in a vegetative state was an “unlikely outcome” six months after injury.
When designing the study, the team didn’t know what to expect, according to study author Yelena Bodien, PhD, of the Department of Neurology’s Center for neurotechnology and neurorecovery at Massachusetts General Hospital.
HOME HOSPITAL CARE BRINGS ‘PHENOMENAL’ BENEFITS TO PATIENTS AND PROVIDERS, STUDY FINDS
“Our anecdotal experience was that some families are told their loved ones had no chance for recovery, they would never walk, talk, work or have a meaningful relationship again — yet they chose not to discontinue life support and their loved one made a remarkable recovery,” she told Fox News Digital.
“On the other hand, clinicians are under a lot of pressure to make early prognoses and do not want to commit someone to a life that would never be acceptable to them, so it could be that those patients who died after life support was withdrawn would have had very significant impairments otherwise.”

“Our anecdotal experience was that some families are told their loved ones had no chance for recovery … yet they chose not to discontinue life support and their loved one made a remarkable recovery,” a researcher said. (iStock)
“I think there are two stories here,” said Bodien.
“One is that some patients with traumatic brain injury who died because life support was withdrawn may have recovered, but the other is that many would have died even if life support was continued.”
A patient’s prognosis after severe traumatic brain injury is highly uncertain, she noted. “Sometimes patients with the most devastating injuries survive and make meaningful recoveries.”
“Families can advocate for delaying a decision to discontinue life support if this is aligned with what they believe their loved one would want.”
The problem, Bodien said, is that health care providers lack the tools required to determine which patients with devastating injuries will recover, to what extent they will recover — and how long that will take.
‘Very important’ study
Dr. Marc Siegel, clinical professor of medicine at NYU Langone Medical Center and a Fox News medical contributor, was not involved in the research but said it was a “very important” study.
“Previous research shows a high-level recovery from mild TBI and a significant recovery percentage even with moderate to severe injury,” Siegel told Fox News Digital.
HEAD INJURY ASSOCIATED WITH DOUBLED MORTALITY RATE, 30-YEAR STUDY REVEALS
“After head trauma, the brain may swell, and the use of mannitol and steroids and even sometimes surgery — where the top of the skull is removed — can be used to decrease pressure on the brain and increase chance of a full recovery,” he continued.
Rehabilitation is also crucial, Siegel added.
“All of these tools should be given a chance to work in most cases.”
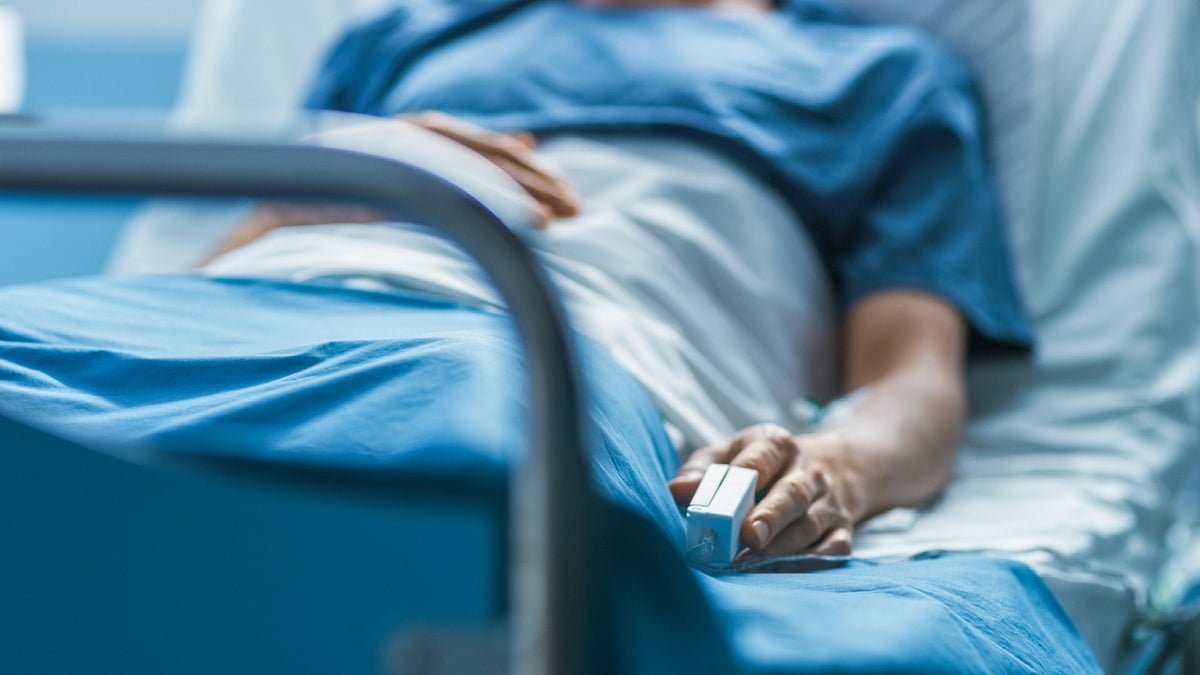
Health care providers lack the tools required to determine which patients with devastating injuries will recover, to what extent they will recover and how long that will take, a researcher said. (iStock)
Based on the study findings, Bodien recommended that clinicians should be “very cautious” with “irreversible decisions” like withdrawing life support in the days following traumatic brain injury.
“Families should also be aware of our results so that they can advocate for delaying a decision to discontinue life support if this is aligned with what they believe their loved one would want,” she added.
Limitations of the research
There were some limitations to the study, Bodien said.
“The sample size of the study was small, which made it difficult to find an adequate number of participants who did not have life support discontinued and were clinically similar, or ‘matched,’ to those who had life support discontinued,” she told Fox News Digital.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Among the participants who did not have life support discontinued, the researchers were not able to follow all of them for a six-month period.
Another limitation is that the researchers used clinical variables that were available on the day of, or the day after, hospitalization — but sometimes decisions to discontinue life support are made several days later.
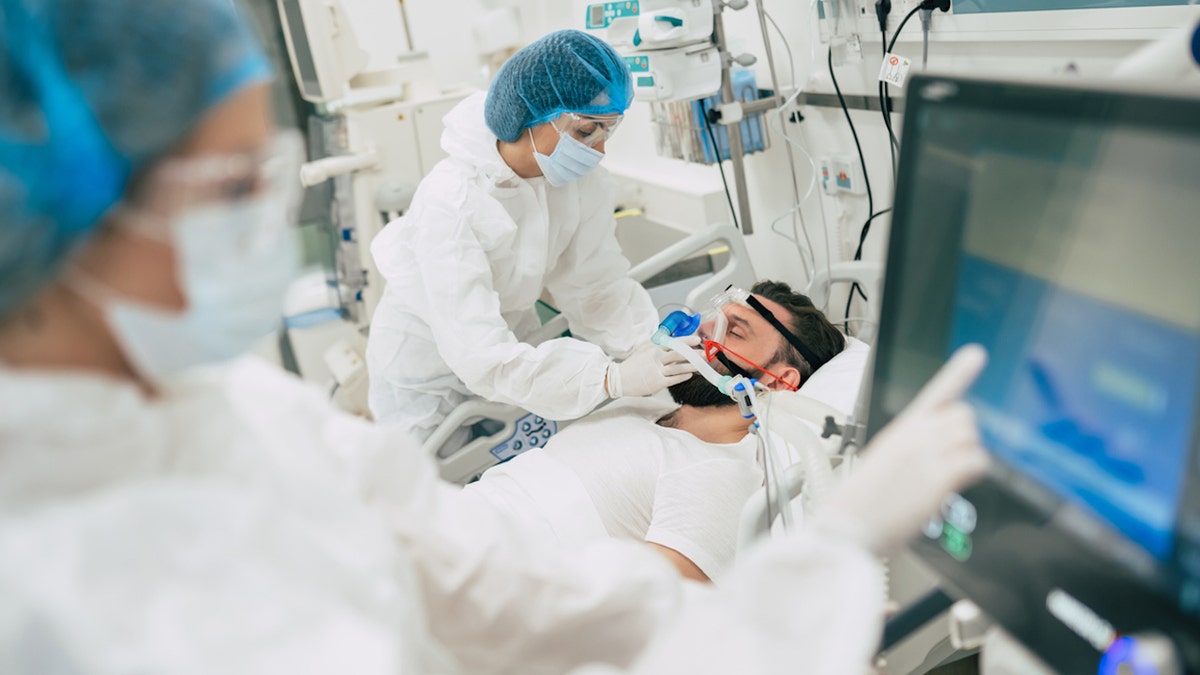
Based on the findings, study author Yelena Bodien (not pictured) recommended that clinicians should be “very cautious” with “irreversible decisions” such as withdrawing life support in the days following traumatic brain injury. (iStock)
“There are many considerations that may lead to a decision to discontinue life support after traumatic brain injury that we were unable to factor into our analyses,” she continued.
“For example, personal beliefs, religion and advanced directives could all affect decision-making but were not captured in our study.”
Bodien also noted that the Harvard study was focused on traumatic brain injury and cannot be generalized to other injuries and illnesses.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSkeletal remains found almost 40 years ago identified as woman who disappeared in 1968
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIndia Lok Sabha election 2024 Phase 4: Who votes and what’s at stake?
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago“Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes”: Disney's New Kingdom is Far From Magical (Movie Review)
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUkraine’s military chief admits ‘difficult situation’ in Kharkiv region
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTales from the trail: The blue states Trump eyes to turn red in November
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoBorrell: Spain, Ireland and others could recognise Palestine on 21 May
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCatalans vote in crucial regional election for the separatist movement
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNorth Dakota gov, former presidential candidate Doug Burgum front and center at Trump New Jersey rally