World
The US is facing a loneliness ‘epidemic’. Can art help reverse the trend?

Early one morning in the spring of 1969, Jeremy Nobel went downstairs to the living room of his family home in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to get ready for school.
There, he found his father sitting on the sofa, looking as white as a sheet and clearly in pain. He instructed Nobel, who was 15 years old at the time, to wake his mother and have her call for help.
The police soon arrived. They slipped an oxygen mask on his father’s face, loaded him onto a stretcher and whisked him off to the local medical centre.
That was the last time Nobel saw his father alive. He died of a heart attack at 47 years old.
After his father’s death, Nobel felt despondent, rudderless. Though he kept up with his school activities and friends, Nobel experienced what he calls spiritual or existential loneliness. He questioned his self-worth and how he could lead a safe and secure life.
He did not talk at all about his father’s death with his friends. “The loneliness was below the surface,” he said.
Looking back, Nobel sees that day in 1969 as pivotal to who he is today: a primary-care physician, public health practitioner and faculty member at Harvard Medical School. But he wishes he had received guidance at the time to help him cope with the loneliness he felt.
Now, more than 50 years later, he has written a book to do just that for others. Published last month, Project UnLonely: Healing Our Crisis of Disconnection aims to unravel how loneliness can affect physical and mental health — and how it can be addressed.
A national epidemic
The book comes at a time when health experts are raising the alarm on loneliness. In May, the United States Surgeon General, Vivek Murthy, released an advisory highlighting loneliness as an “epidemic” and a public health “crisis”.
The advisory defined loneliness as a “distressing experience” arising from “perceived isolation or inadequate meaningful connections”. It added, however, that loneliness is subjective, happening when there is a discrepancy between “an individual’s preferred and actual experiences”.
Still, the Surgeon General said loneliness is “more widespread than other major health issues in the US”, including diabetes and obesity.
Even before COVID-19, about half of American adults said they were experiencing loneliness, the advisory explained. The situation only got worse during the pandemic, when many people were cut off from friends and family and lost work or loved ones.
Though most people feel lonely sometimes, a chronic sense of isolation can have vast health ramifications, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, dementia, stroke, depression, anxiety and premature death.
A Meta-Gallup poll from October indicated that the problem was worldwide. Nearly one in four people, surveyed from across 140 countries, identified as “very” or “fairly lonely”.
“Loneliness is not an illness or a disease. It’s a brain state, it’s a mood, it’s an emotion,” Nobel said.
“The human experience of loneliness can be perhaps best viewed as a biologic signal that there’s something you need, just as thirst is a biologic signal that you need hydration. It’s very good that we’re thirsty, and yet if you become toxically thirsty or dehydrated, you could die from that.”
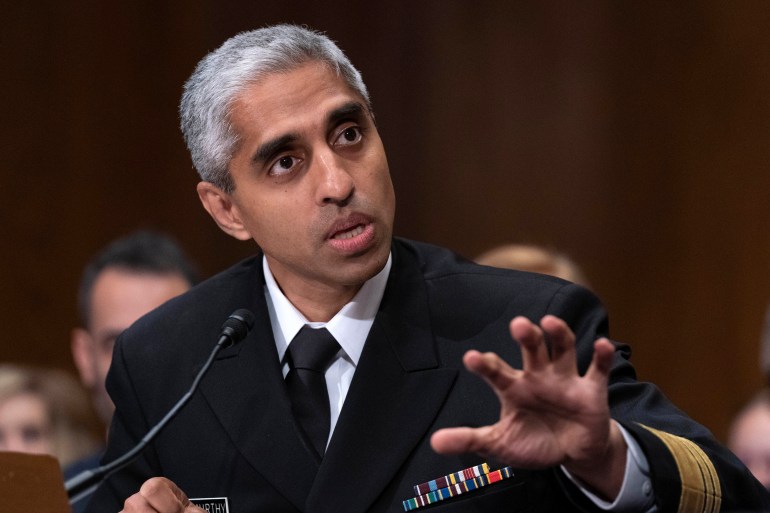

Nobel has studied loneliness for almost 20 years. He even developed a course on the subject, entitled Loneliness and Public Health, and founded and leads a nonprofit that helps address loneliness through community programming.
His interest in social isolation began in the early 1980s when he was working as a primary care physician in Boston.
As he treated patients of different ages and backgrounds, he started to notice how loneliness can have direct effects on other aspects of their healthcare. They skipped taking their prescribed medications, for instance, or did not schedule follow-up visits.
“Loneliness changes how we behave,” Nobel said. “Our motivation for self-care, taking medications in a timely and appropriate way, partnering with the healthcare delivery system in effective ways — that ability and the motivation to do that becomes weaker as people become lonely.”
While many experts agree that loneliness is a serious health problem, some question calling it an epidemic.
Eric Klinenberg, a sociology professor at New York University, said that “epidemic” implies a significant spike in loneliness. He explained there is not strong enough evidence to support that claim.
“Studies of loneliness are all over the map, and the trends over time are hard to assess,” he said.
“If we call it an epidemic, we signal that it requires extra attention and also that it requires less attention when it ebbs. I think it’s more accurate, and more helpful, to define it as a durable health problem, one that is tied up in modern life and has been for ages.”

Creativity fosters connection
However loneliness is labelled, organisations and individuals are adopting different strategies to tackle it.
The Surgeon General’s report outlines a framework to advance social connections. It includes strengthening community infrastructure like parks and libraries, educating healthcare providers and reducing the potential harms of socialising online.
For Nobel, part of the solution lies in the arts. His interest in that approach was piqued after visiting a 2002 art show. The pictures on display were from children in New York City, depicting what they had experienced during the attacks on September 11, 2001.
Nobel noticed that even if the young artists could not discuss their feelings, they could talk about their art. Studies show that creativity can help foster social connections.
“One of the ways creative arts can be healing is because it allows people to re-explore various things consciously and unconsciously that may be holding them back and causing loneliness,” Nobel said.
After the art show, he felt a renewed passion to explore his creative side, including through poetry. Art allowed him to identify and shape his own story. “I couldn’t have told this story about my dad as few as 10 years ago, but you write it enough, you explore it enough.”
The link between arts and health also intrigued student Diana Shaari, currently a senior at Harvard College.
Shaari experienced loneliness firsthand during her first year of college in 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic moved classes online, restricted campus visitors and closed most school buildings.
As a freshman, she knew no one on campus, and it was her first time living away from her parents. It was a solitary experience for Shaari, who describes herself as someone who thrives on social interaction.
“Every day you would wake up by yourself. You wouldn’t run into kids going to and from class. If I wanted to, I could spend an entire week or even more without seeing anyone,” Shaari said. “That all contributed to these overall feelings of loneliness. Also, just being with your own thoughts for too long is never great.”
To counter the social isolation she and her fellow students were facing, Shaari teamed up with Nobel and others to pilot a workshop at Harvard College in 2021 called Colors & Connection.
It was the first in-person event she was able to attend since starting college and her most memorable, she said. The workshop combines art-making and conversations to bring people together. It has since expanded to 31 campuses across the country.
“It was almost therapeutic,” she said. “There are certain universal elements to art and artistic expression that are really key in allowing people to connect and to feel connected with others.”
The pandemic may have exacerbated loneliness, but Nobel said there is a bright side.
Loneliness often comes with shame and stigma, which can prevent people from seeking help. But during the pandemic, loneliness was ubiquitous, Nobel said — allowing people to speak up about it more easily.
“We had a common experience of isolation. We were lonely together,” Nobel said. “That opened the window to talk about loneliness in a very healthy way.”

World
Borrell: Spain, Ireland and others could recognise Palestine on 21 May
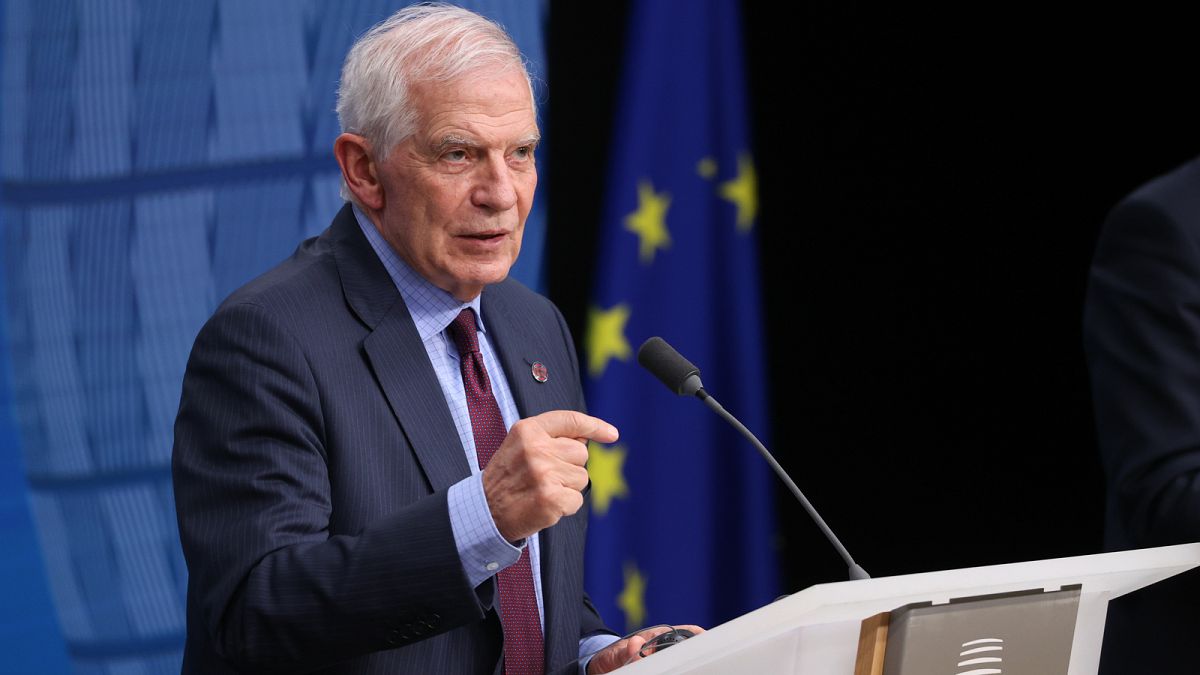

Spain, Ireland and other like-minded EU member states could recognise the State of Palestine on 21 May, the EU’s High Representative for Foreign Affairs, Josep Borrell, has said.
In an interview on Spanish national radio RNE on Thursday, Borrell was asked to confirm reports in Irish media that Spain, Ireland and a handful of other EU member states could formally recognise the State of Palestine on May 21.
Borrell confirmed the plans, adding that the Spanish foreign minister, José Manuel Albares, had told him that 21 May was the proposed date.
Borrell had been attending an event to celebrate Europe Day in Madrid along with Albares hours earlier.
Irish diplomatic sources have confirmed to Euronews that a group of European countries is proposing to recognise a Palestinian state during the month of May, with the 21st a possible date, but not set in stone.
The source added that the date could shift to allow other countries, including non-EU country Norway, to move in tandem.
Borrell also mentioned Slovenia as one of the countries that could join the joint recognition after the government in Ljubljana passed a decree on recognising the Palestinian state earlier on Thursday.
The EU’s top diplomat also added that Belgium could soon follow suit, as it was delaying the recognition while waiting for more countries to get on board.
Malta could also join, having backed a declaration of intent during a March summit of the European Council.
It comes as the UN General Assembly votes on Friday on a resolution to make the State of Palestine a full member of the United Nations, where they currently hold observer status.
Nine of the EU’s 27 member states currently recognise Palestinians’ right to a state according to the so-called 1967 borders, which include the West Bank, the Gaza Strip and East Jerusalem.
Malta, along with eastern states such as Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Romania and Slovakia, have recognised the Palestinians’ right to statehood since 1988. In 2014, Sweden became the first member state to unilaterally recognise Palestinians’ right to statehood while a member of the bloc.
Although the European Union supports the so-called two-state solution – which would deliver statehood for Palestinians – and is the single biggest donor of aid to Palestinians, it has not yet unanimously backed the recognition of a Palestinian state.
European Council President Charles Michel told Euronews in April that member states willing to recognise the State of Palestine should move in tandem in order to “trigger significant progress” in building peace in the war-torn region.
World
The Other Black Girl Cancelled at Hulu

ad
World
State Department criticizes Israel’s attempts at ‘mitigating civilian harm’ in Gaza war: report

The U.S. State Department on Friday criticized Israel’s use of U.S-supplied arms in a way that may be “inconsistent” in “mitigating civilian harm” in the war in Gaza.
A report obtained by Fox News Digital, which was sent to Congress on Friday, admitted that “Israel has had to confront an extraordinary military challenge: Hamas has embedded itself deliberately within and underneath the civilian population to use civilians as human shields.”
The report added that “it is often difficult to determine facts on the ground in an active war zone of this nature and the presence of legitimate military targets across Gaza.”
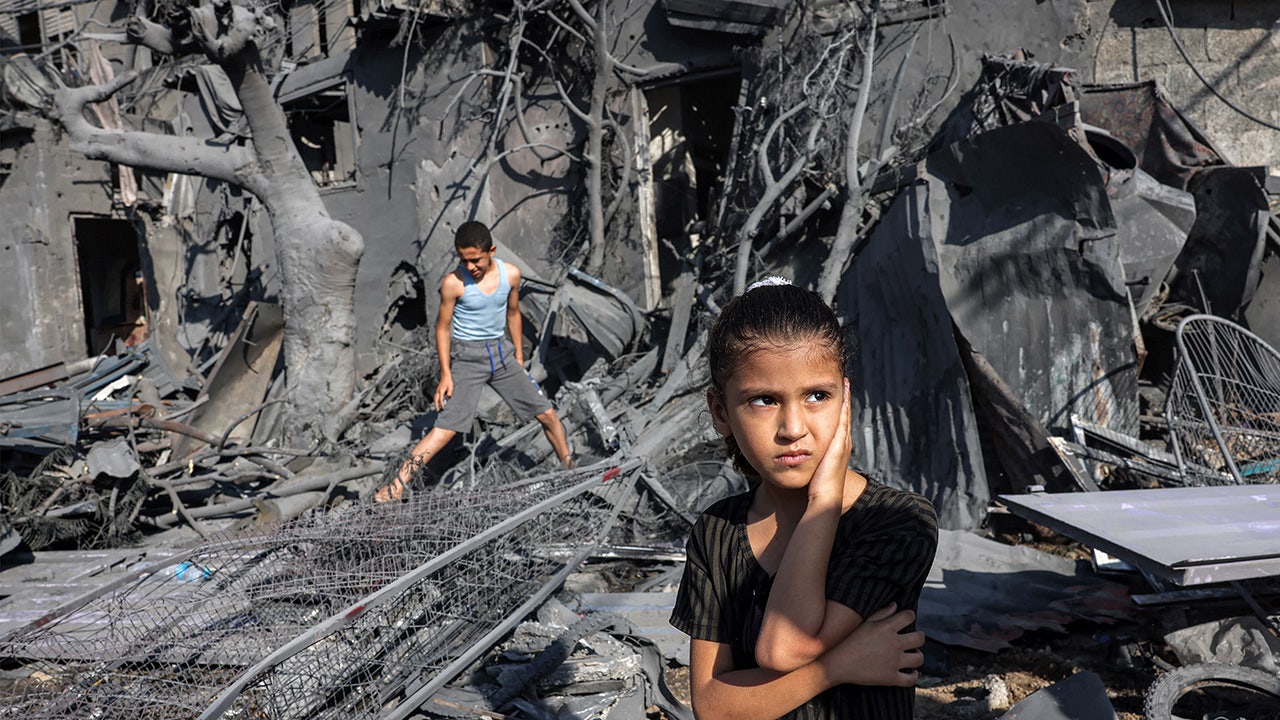
Nearly 35,000 Palestinians have been killed in the conflict, including many women and children, according to the Palestinian government.
HAMAS KINGPIN HOLED UP DEEP BELOW GAZA, SURROUNDED BY HOSTAGES USED AS HUMAN SHIELDS, SAYS EXPERT
A girl looks on as she stands by the rubble outside a building that was hit by Israeli bombardment in Rafah in the southern Gaza Strip, Oct. 31, 2023. (Mohammed Abed/AFP via Getty Images)
The report was commissioned by President Biden to assess if Israel and other U.S. allies are adhering to international humanitarian law.
Israeli officials have said the country is complying with international law “and have identified a number of processes for ensuring compliance that are embedded at all levels of their military decision-making,” the report said, including giving advanced warnings, using specific weapons and avoiding places like schools, hospitals and places of worship.
“Although we have gained some insight into Israel’s procedures and rules, we do not have complete information to verify whether” U.S. arms “were specifically used in actions that have been alleged as violations of [international humanitarian law] or international human rights law during the period of the report,” the report continued. “The nature of the conflict in Gaza makes it difficult to assess or reach conclusive findings on individual incidents.”
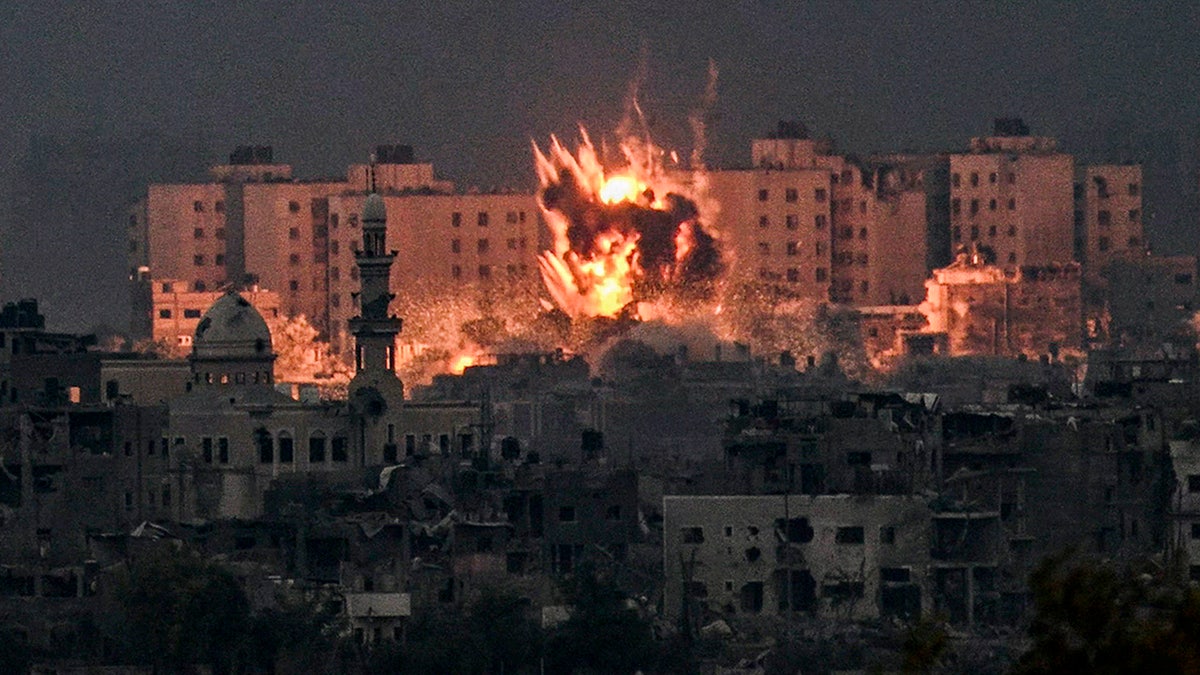

A fireball erupts during Israeli bombardment in the northern Gaza Strip, Oct. 14, 2023. (Aris Messinis/AFP via Getty Images)
It said, however, that the United Nations, humanitarian organizations and international humanitarian law experts “have reported Israeli civilian harm mitigation efforts as inconsistent, ineffective, and inadequate, failing to provide protection to vulnerable civilians who cannot or chose not to relocate.”
BIDEN VOWS TO WITHHOLD WEAPONS FROM ISRAEL IF NETANYAHU GOES FORWARD WITH RAFAH INVASION
Israel has the capability, experience and tools to mitigate civilian harm, the report said, adding, however, “the results on the ground, including high levels of civilian casualties, raise substantial questions as to whether the IDF is using them effectively in all cases.”
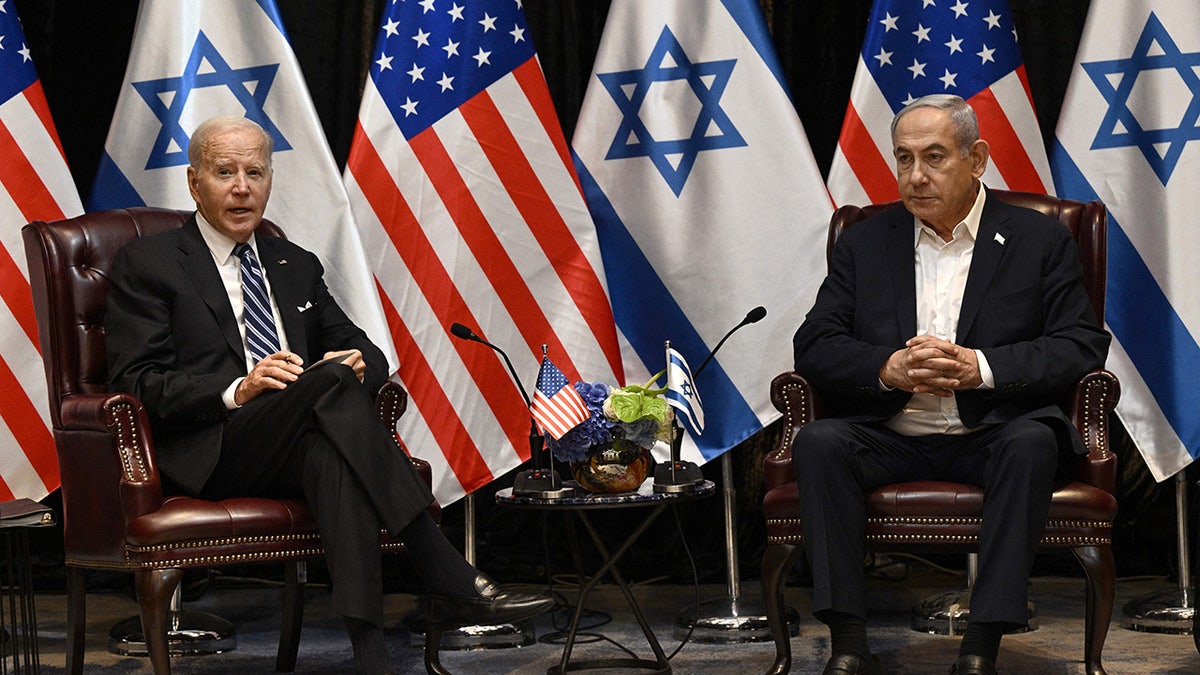

President Biden speaking with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in Tel Aviv last October. (Brendan Smialowski/AFP via Getty Images)
Despite misgivings, the State Department said it found Israel’s assurances that it had followed international law in the use of U.S. weapons “credible and reliable” and will continue supplying arms.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoThe White House has a new curator. Donna Hayashi Smith is the first Asian American to hold the post
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPolice enter UCLA anti-war encampment; Arizona repeals Civil War-era abortion ban
-
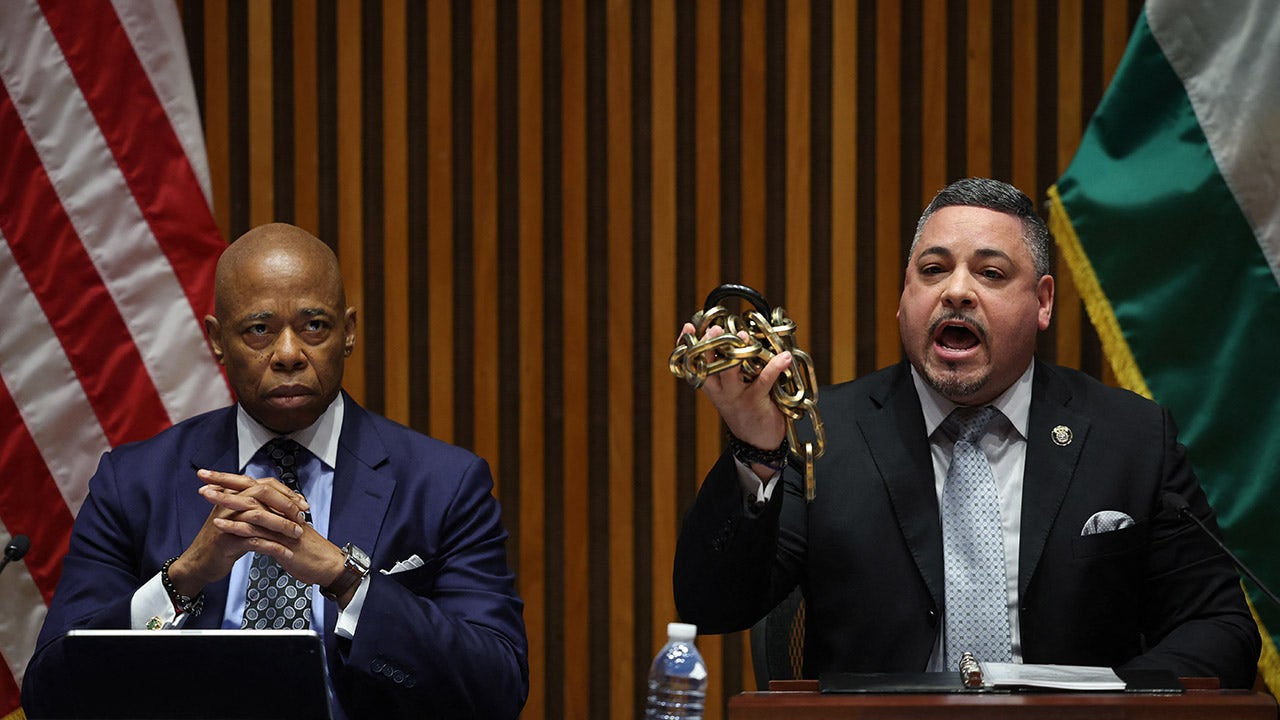

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoAdams, NYPD cite 'global' effort to 'radicalize young people' after 300 arrested at Columbia, CUNY
-
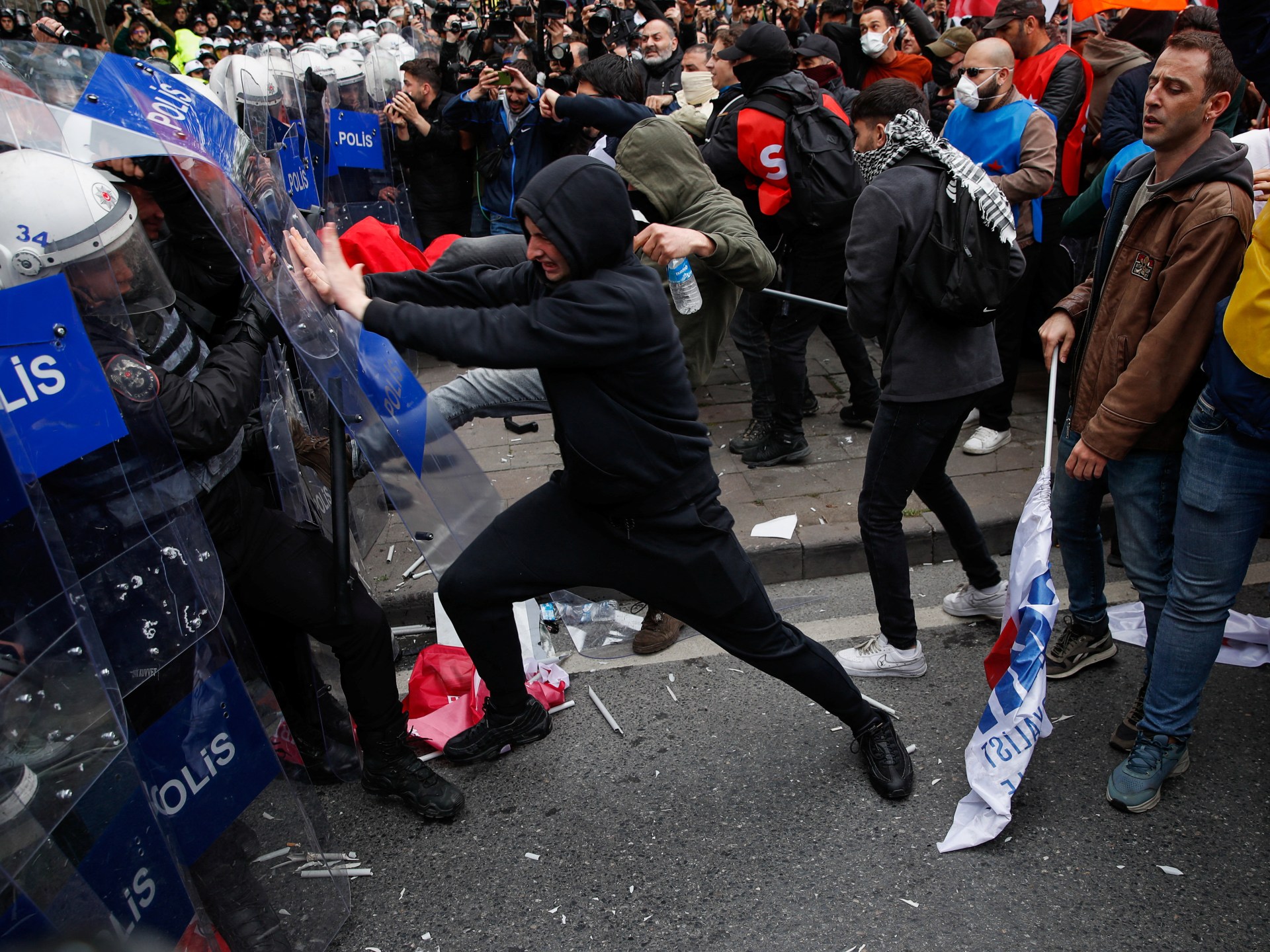

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTurkish police arrest hundreds at Istanbul May Day protests
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Police Arrest Columbia Protesters Occupying Hamilton Hall
-
)
) Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoThe Idea of You Movie Review: Anne Hathaway’s honest performance makes the film stand out in a not so formulaic rom-com
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSome Republicans expected to join Arizona Democrats to pass repeal of 1864 abortion ban
-
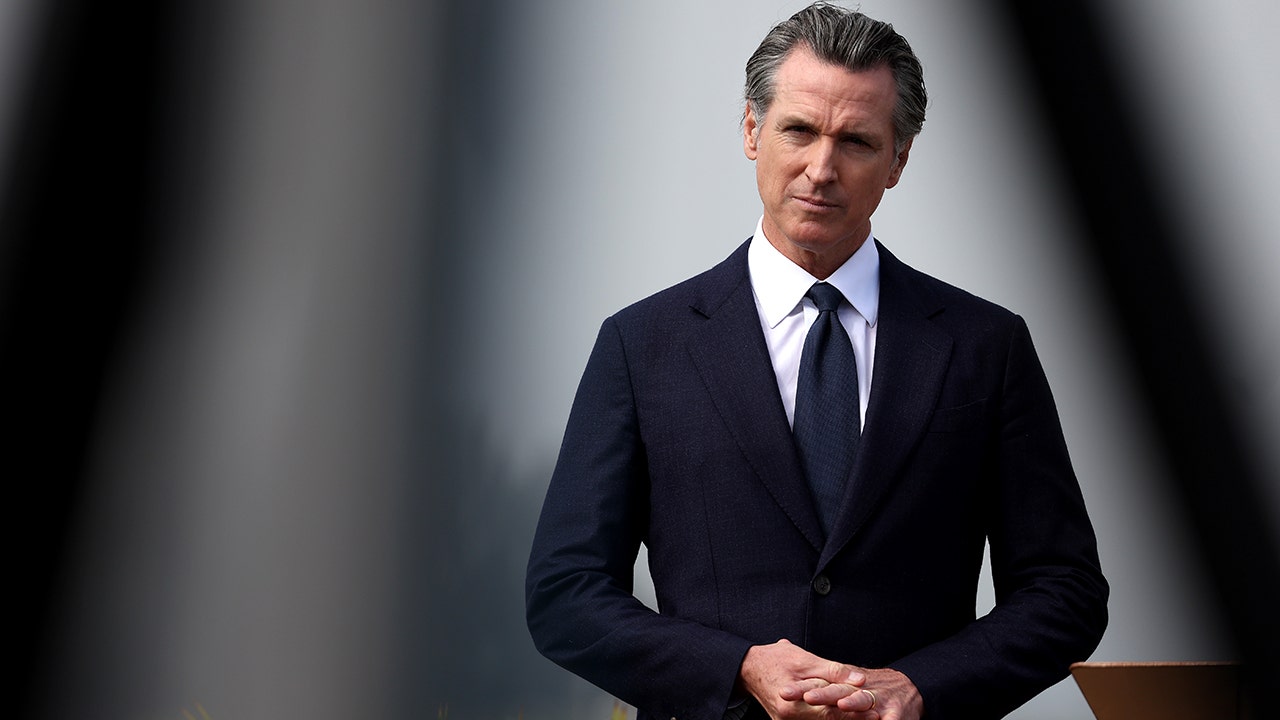

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNewsom, state officials silent on anti-Israel protests at UCLA















