Montana
9th Circuit upholds length-of-season restrictions for Montana wolf trapping, snaring • Daily Montanan

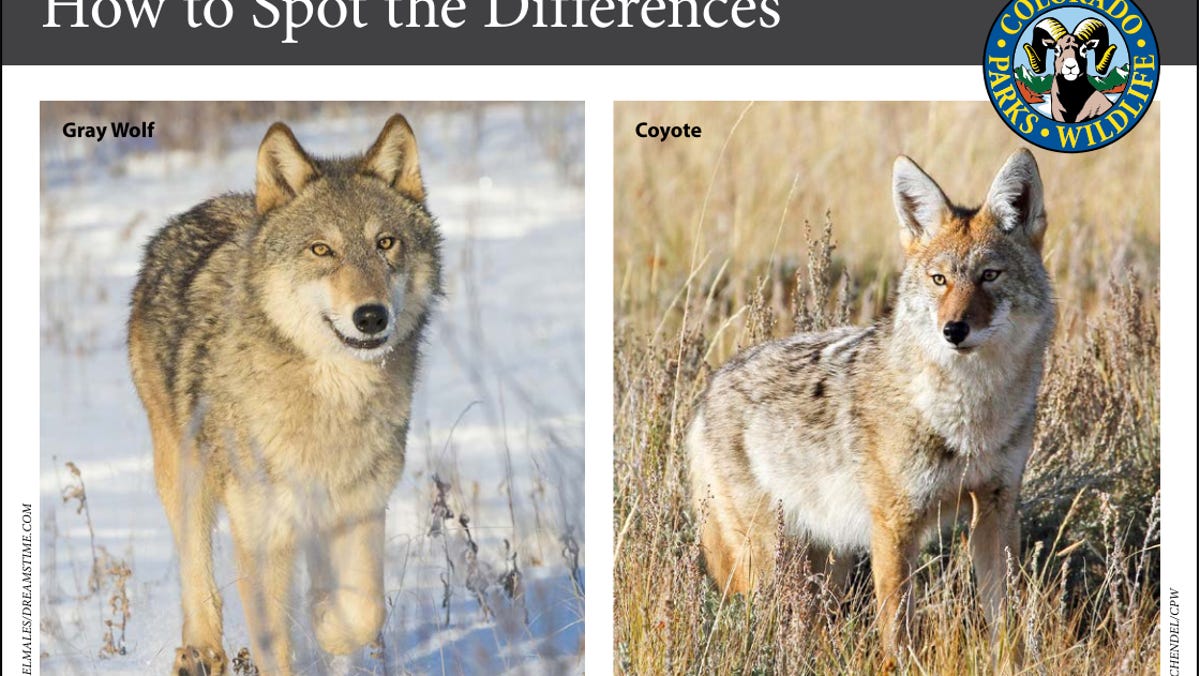
A federal court on Tuesday mostly upheld a judge’s decision last fall to limit Montana’s wolf trapping and snaring season to six weeks in January and February over what he said was the potential for grizzly bears to incidentally get caught in the traps in violation of the Endangered Species Act.
The 9th Circuit Court of Appeals, in a 2-1 decision, upheld the main part of District Court Judge Donald Molloy’s November order, which limited wolf trapping and snaring season to Jan. 1 to Feb. 15 to ensure as many grizzlies were in their dens as possible and could not be caught in the wolf traps.
But the circuit court panel disagreed with the portion of his order that limited the season length in hunting Regions 1 through 5 and in Blaine, Hill, and Phillips counties, and said the lower court needed to modify that part of its original order to only include areas where grizzly bears are known to live.
The panel also vacated the part of the order that the court said appeared to have prohibited Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks from trapping wolves for scientific purposes, which the state says is necessary and often happens during the summer months. The order says plaintiffs’ attorneys had agreed to the injunction not applying to scientific research trapping.
The order comes as the plaintiffs in this case seek a permanent injunction to keep the restrictions on wolf trapping seasons in place, as a judge in Idaho implemented similar restrictions there, and as conservation groups appeal the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s decision that wolves don’t need heightened Endangered Species Act protections in the states that are allowed to manage their wolf populations.
The two groups that challenged Montana’s 2023 wolf trapping regulations, WildEarth Guardians and the Flathead-Lolo-Bitterroot Citizen Task Force, said they see the decision as a small victory as they continue to push for a permanent injunction in the district court.
“We must give grizzly bears a fair shot at recovery, and hostile state management like Montana’s has a long way to go before it measures up to what wildlife and the public need,” said Lizzy Pennock, the carnivore coexistence attorney for WildEarth Guardians.
The defendants in the case, Gov. Greg Gianforte and Fish and Wildlife Commission Chair Lesley Robinson, almost immediately appealed Molloy’s November order to the 9th Circuit. Their attorneys argued the district court wrongly considered new arguments and materials submitted by the two conservation groups, applied the wrong injunction standard, and that the injunction did not prevent irreparable harm and was geographically overbroad.
The circuit court panel, in the majority opinion, disagreed with the state on nearly everything but the geographic overbreadth argument.
Judge Judge Mark J. Bennett and Judge Robert S. Lasnik, a Washington district court judge sitting on the appeals panel for the case, also said that the court’s consideration of a news story highlighting a sighting of a grizzly bear as far east as one had been spotted in 100 years, which was published just before the hearing, was not improper.
The state had also argued that Molloy used the wrong injunction standard by saying the plaintiffs had shown the case involved a serious question on the merits rather than meeting the higher standard of showing that they had a likelihood to succeed in the case.
But Bennett wrote that the 9th Circuit uses the “serious questions” test, and Molloy correctly used that as well. Bennett wrote that the conservation groups had shown evidence grizzly bears are not limited to geographical borders, are attracted to baited traps and can get caught in them. He also said they had shown grizzly bears would be active outside of their dens during the state’s proposed trapping season, which was to start on a floating date sometime between Nov. 27 and Dec. 1 and run through March 15.
“Given all the evidence, it was plausible for the district court to find a reasonably certain threat of imminent harm to grizzly bears should Montana’s wolf trapping and snaring season proceed as planned,” Bennett wrote. “In other words, the district court’s finding was not implausible given plaintiffs’ evidence and the evidence as a whole.”
Judge Richard C. Tallman disagreed with the other two judges on that finding, offering a partial dissent in which he said Molloy based his decision off speculative evidence offered by the plaintiffs and their exhibits.
“The record viewed in totality does not support a finding that irreparable harm is likely, other than just possible,” he wrote. “Of the four exhibits, ten declarations, and nine affidavits submitted by the plaintiffs, the bulk of the information provided is speculative in nature, offering theories about what could happen in the face of climate change or food scarcity, instead of offering any actual evidence that the harm is likely to occur.”
The other two judges disagreed with his assessment however, saying Tallman was giving more weight to evidence that would undermine Molloy’s decision than to the evidence that led him to make his decision.
“Because the district court’s finding of a reasonably certain threat of imminent harm was not implausible on the record, we must affirm that finding,” Bennett wrote.
District court will have to decide new geographic boundaries
But all of the judges agreed that the geographic area to which the season restrictions applied was too broad and said there was not enough evidence in the record to conclude having restrictions across more than half the state was necessary to prevent the accidental capture of grizzly bears.
Molloy’s decision on where the season restrictions would apply seems to have been based on the plaintiffs’ citing of a news release from FWP saying grizzlies have the potential to be found “anywhere in the western two-thirds of Montana” and a news story about the bear being spotted near the Missouri and Judith rivers in eastern Montana. But the judges said those did not constitute enough evidence to close off all wolf trapping west of Billings except for six weeks out of the year.
“The bulletin’s statement is thus couched in speculation and is too hypothetical to support the conclusion that grizzlies will likely be present in all areas of west of Billings such that the injunction’s geographic scope is necessary to protect the grizzlies,” Bennett wrote.
The judges remanded the geographic scope question back to the district court and asked it to make a finding “expeditiously.” But they also ordered that the current geographic scope stay in place until a new one is decided. Montana’s wolf hunting and trapping season concluded on March 15.
Meanwhile, the Montana Trappers Association and Outdoor Heritage Coalition have intervened in the district court case in an attempt to loosen the restrictions. Also, the two conservation groups that are plaintiffs in the case last week filed for summary judgment, asking Molloy to extend the injunction permanently and to include coyote trapping and snaring season restrictions that are identical to the wolf season restrictions – something Molloy declined to do with the preliminary injunction, meaning they can still be trapped and snared year-round for the time being.
It’s currently unclear how the court will handle the remanded geographic question in conjunction with the request for a permanent injunction, but attorneys for Gianforte and Robinson will have until May 6 to file their opposition to the request, and the two sides will have about another month to fully brief their arguments, at which time the decision would rest in the court’s hands.
Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks spokesperson Greg Lemon said FWP agreed the geographic area of the original injunction was too broad and said the state was focused back on the district court case.
Pennock and Mike Bader, a consultant to the Flathead-Lolo-Bitterroot Citizen Task Force, said the state needed to acknowledge how climate change was shortening grizzlies’ den times and start to better acknowledge how some of its hunting and trapping policies could harm animals, like grizzlies, that do still have protections under the Endangered Species Act.
“The State of Montana cannot be entrusted with management responsibility for grizzly bears because they are acting irresponsibly towards carnivores and predators,” Bader said.

Montana
I moved to Montana after getting priced out of California. I work in the trades — not all transplants are rich remote workers buying up property.
- Ian Baylon moved to Montana in April 2022 after watching “Yellowstone” and visiting the state.
- The 34-year-old said you get more bang for your buck renting in Montana than in the Bay Area.
- Baylon said not all Montana transplants are remote workers buying property and driving up prices.
This is an as-told-to essay based on a conversation with 34-year-old Ian Baylon, a tradesman who moved from California to Montana in April 2022. The essay has been edited for length and clarity.
I was born and raised in the Bay Area, San Francisco. Later as an adult I lived in Crockett, which is a beautiful little coastal Bay Area town. Even in Crockett the housing was expensive.
When my girlfriend, now wife, and I moved in together, the cheapest thing we could find for ourselves was in Vallejo, which is super busy, super violent. But that’s what we could afford, even though I was a manager at a granite shop and my wife was working as an esthetician.
During COVID, we got sucked into “Yellowstone,” watched the whole series, and decided to book a trip to Montana in February 2022 just to see how it is.
We stayed in West Yellowstone and had a blast here. One of the days, I decided to look for a job, just to see who was hiring and what they were willing to pay. I googled a couple of granite spots and a company was hiring in Bozeman. I went in for an interview. They asked me, “What will it take for you to move up here?”
They were willing to pay me my $89,000 a year salary plus moving costs, plus a deposit on the place we rented.
From March to April, within a month, I got the job, we rented the house, and we packed up and moved here.
Jacob Boomsma/Getty Images
The culture shock has mostly been good
Moving up here was a little bit of a culture shock, but more in a good way.
People are a lot nicer up here. I’m Mexican American, my wife is white, and no one says anything racist or out of pocket to us. I was super worried about that. A gentleman the other day opened the door for me at the gas station. He was wearing a MAGA hat.
Montana is not what people think. There’s a huge diversity. I equate Bozeman to Berkeley.
I tell people I’m from California and they say “boo” at first, but it’s more of a tit-for-tat. They make fun of me, I make fun of them, and we still get along.
One not good culture shock has been the younger generation. It’s a college town, and they’re not as friendly as my generation is or the generation before me.
Here in the Gallatin Valley where we live now, which includes Bozeman, the housing market is ridiculous. There’s a huge shortage of housing and everything is really expensive.
We thought we were going to be able to come in here and buy property. Or buy a ranch with some land and have animals. Nope. There’s a reason why they call it Boz Angeles. But renting you do get more bang for your buck up here.
Here in Montana there’s a huge shortage of labor too.
While it was very competitive in California, there’s a lot of demand for the trades up here, but nobody up here really wants to learn the trades. The young kids coming into the trades don’t know jack diddly and they expect everything to be handed to them and not work hard.
Gordon Calhoun/Getty Images
Not all Montana transplants are the same
One thing that native Montanans don’t like is that a lot of people that live here in the Gallatin Valley are from out of state, not only from California, but from Washington, New York, Texas, you name any state, they’re here.
I’ve seen both types of transplants. The ones that got out of California because they couldn’t afford it, and the ones that have that expendable money.
That’s where the problem lies. The people that move in and buy up the properties, drive up the cost for the locals, and who don’t really need to work or contribute to the economy here. A lot work in tech or finance, and there’s no need for them to work locally. They can work from home remotely.
But a lot of people moving up here from California are not your techies or your white collar people. It’s people like me, who work in the trades.
We’re just regular people, just like you guys. We got priced out of our own native place.
You do have your trust fund babies from back east and your techies from the West Coast, but the bulk of us are escaping that chokehold. Just to still chase the American dream.
I think we are more happy here than we would’ve been in California, even though we miss it. We do miss our friends, the diversity, and everything that California has to offer.
But living there 24/7 kind of overwhelmed us. The lifestyle was always hurry up and go. Here we work, but there’s so much natural beauty around you. We’re in the valley surrounded by mountains.
On my way home after an 11-hour day, looking at the beautiful mountains and the meadows and the streams and the rivers and the snow-capped Bridgers, how can you be angry? It’s just so soothing.
Montana
EPA to send over $28 million to Montana to replace lead pipes in drinking water system

The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is sending more than $28 million to Montana to help identify and replace lead pipes in drinking water infrastructure.
The funding comes from a $15 billion allocation in the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law for nationwide lead pipe removal. Funds are administered by the state.
The extent of lead pipes in Montana is not yet known, but the EPA estimates they are present in less than two tenths of a percent of the state’s drinking water infrastructure.
The Montana Department of Environmental Quality is working to complete a full inventory of lead service lines in Montana by October and soliciting project proposals from communities.
Separately, during the state’s last legislative session Montana lawmakers set aside millions of dollars to remove lead from school drinking water supplies.
Montana
Montana Shed Hunter Shoots Charging Grizzly with a Handgun

A Montana shed hunter escaped a harrowing bear attack thanks to quick thinking and good marksmanship. According to a Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks (FWP) press release, a man was shed hunting on private property near Wolf Creek, Montana, on April 25 when he encountered a grizzly.
“The man was walking along a ridge covered with low trees and brush with his two dogs at his side and the wind at his back,” explained an FWP spokesperson. “After seeing a fresh grizzly bear track in a snow patch, he continued along his path and a few minutes later, he first saw the bear standing near the top of the ridge about 20 yards away.”
What happened next is the stuff of nightmares. The grizzly sow immediately dropped to all fours and charged. Thankfully, the man, whose identity has not been released, was carrying a handgun for self-defense. He fired five shots off at the bear, grazing it with one bullet and dropping and killing it with another. According to the FWP, the bear charged from 30 feet to 10 feet before it was killed.
The man was uninjured in the incident. The female grizzly appeared to be in good health and weighed around 300 pounds. It was estimated to be 12 years old. FWP officials reported to the scene of the incident, where they located and captured a lone cub-of the-year. The cub was taken to a licensed wildlife rehab center and will likely be placed at an accredited zoo. Because grizzlies are still considered endangered in the Lower 48, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is also investigating the incident.
Grizzlies bears can grow up to 500 pounds. Today, Montana is home to the largest population of grizzlies in the Continental U.S.—and the state’s grizzly population is spreading into central Montana. Sows with cubs are known to be territorial and aggressive when defending young, which appears to be what spurred the recent incident.
Read Next: How to Survive a Bear Attack
While grizzly attacks on humans are rare, they do occur. Last fall, Field & Stream reported on a bird hunter who shot and wounded a grizzly while hunting upland birds near Choteau, not far from where the recent attack took place. And in 2021, a grizzly mauled and killed a camper in Ovando. Montana, along with neighboring Wyoming, are petitioning the feds to remove grizzlies in the region from the Endangered Species Act as those populations have surpassed recovery goals.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoLarry Webb’s deathbed confession solves 2000 cold case murder of Susan and Natasha Carter, 10, whose remains were found hours after he died
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoFirst cargo ship passes through new channel since Baltimore bridge collapse
-
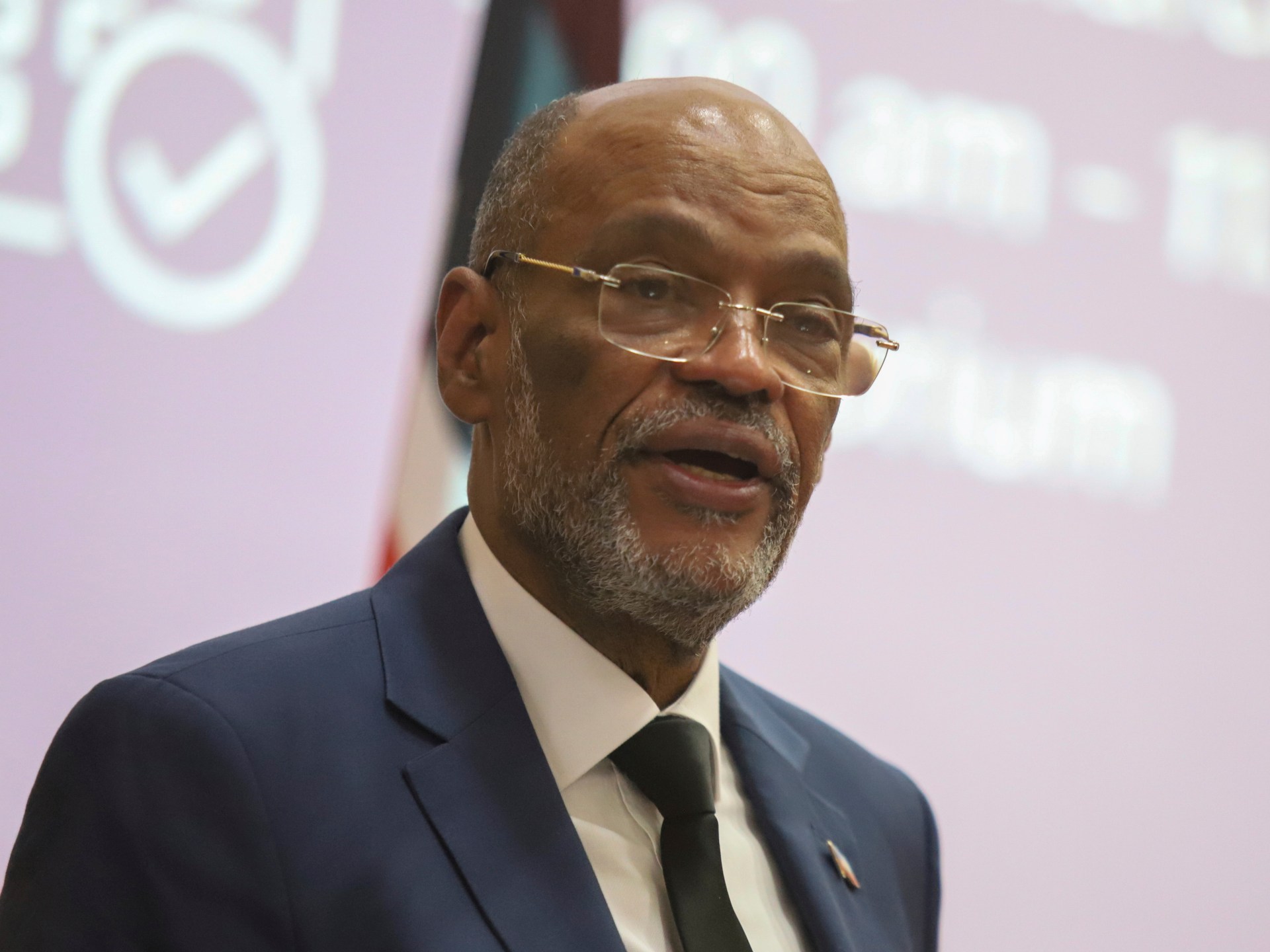

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHaiti Prime Minister Ariel Henry resigns, transitional council takes power
-
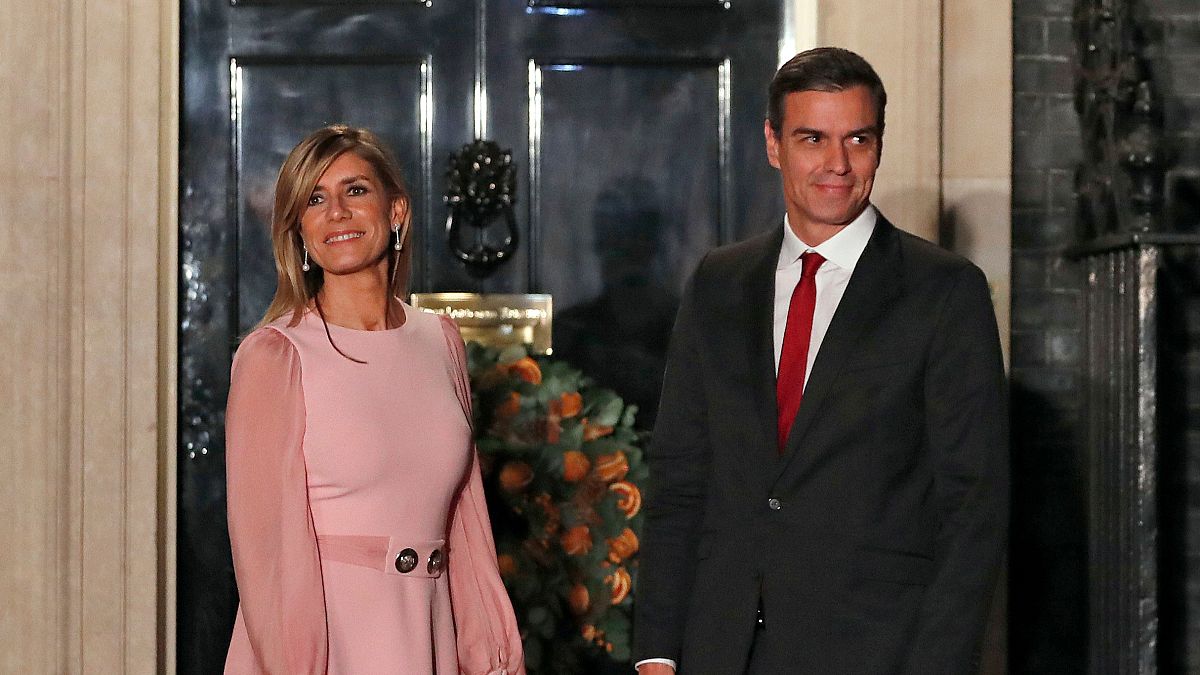

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSpanish PM Pedro Sanchez suspends public duties to 'reflect'
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUS secretly sent long-range ATACMS weapons to Ukraine
-
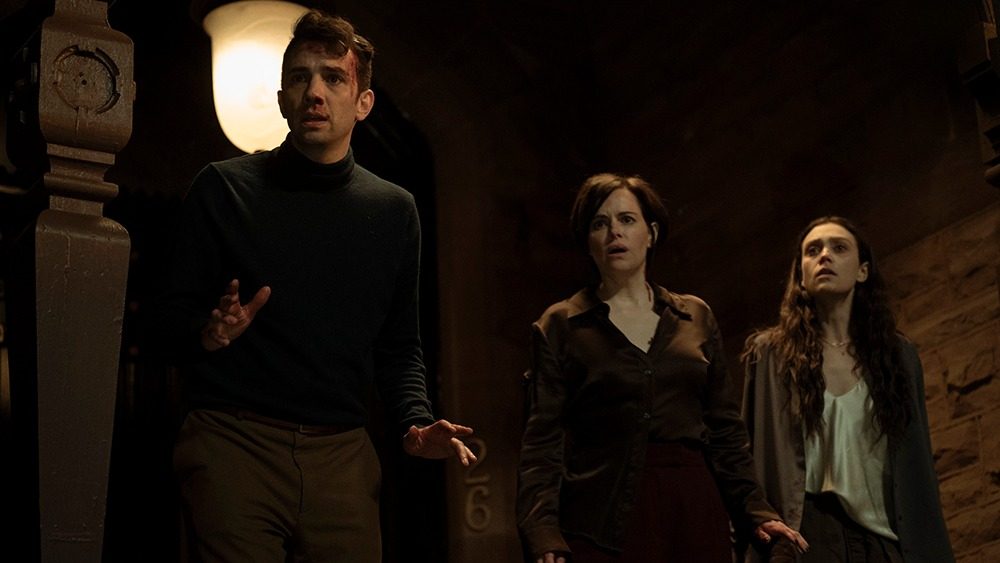

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoHumane (2024) – Movie Review
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAmerican Airlines passenger alleges discrimination over use of first-class restroom
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Johnson Condemns Pro-Palestinian Protests at Columbia University