South Dakota
Huge underground search for mysterious dark matter begins in South Dakota
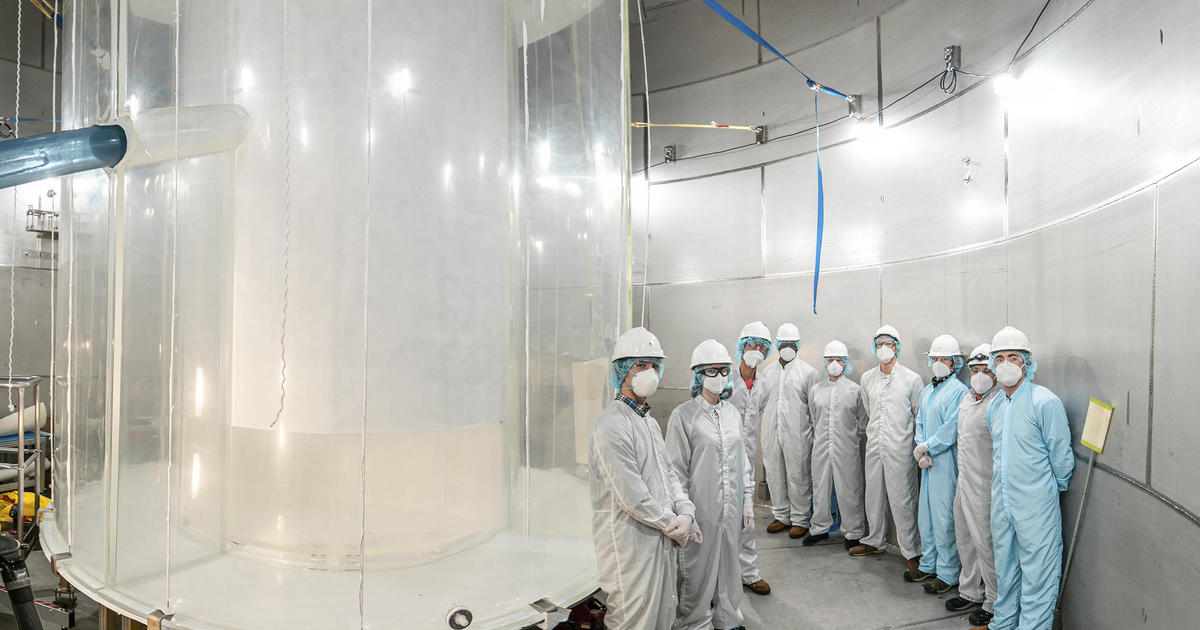

In a former gold mine a mile underground, inside a titanium tank stuffed with a uncommon liquified fuel, scientists have begun the seek for what up to now has been unfindable: darkish matter.
Scientists are fairly certain the invisible stuff makes up many of the universe’s mass and say we would not be right here with out it — however they do not know what it’s. The race to resolve this monumental thriller has introduced one staff to the depths below Lead, South Dakota.
The query for scientists is primary, says Kevin Lesko, a physicist at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory. “What is that this excellent place I dwell in? Proper now, 95% of it’s a thriller.”
The thought is {that a} mile of dust and rock, a large tank, a second tank and the purest titanium on this planet will block almost all of the cosmic rays and particles that zip round — and thru — all of us day-after-day. However darkish matter particles, scientists suppose, can keep away from all these obstacles. They hope one will fly into the vat of liquid xenon within the interior tank and smash right into a xenon nucleus like two balls in a recreation of pool, revealing its existence in a flash of sunshine seen by a tool known as “the time projection chamber.”
Scientists introduced Thursday that the five-year, $60 million search lastly obtained underway two months in the past after a delay brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus far the system has discovered … nothing. No less than no darkish matter.
That is OK, they are saying. The gear seems to be working to filter out many of the background radiation they hoped to dam. “To seek for this very uncommon kind of interplay, job primary is to first do away with all the extraordinary sources of radiation, which might overwhelm the experiment,” mentioned College of Maryland physicist Carter Corridor.
And if all their calculations and theories are proper, they determine they will see solely a pair fleeting indicators of darkish matter a yr. The staff of 250 scientists estimates they will get 20 instances extra information over the subsequent couple of years.
By the point the experiment finishes, the possibility of discovering darkish matter with this system is “most likely lower than 50% however greater than 10%,” mentioned Hugh Lippincott, a physicist and spokesman for the experiment in a Thursday information convention.
Whereas that is removed from a certain factor, “you want a little bit enthusiasm,” Lawrence Berkeley’s Lesko mentioned. “You do not go into uncommon search physics with out some hope of discovering one thing.”
Two hulking Melancholy-era hoists run an elevator that brings scientists to what’s known as the LUX-ZEPLIN experiment within the Sanford Underground Analysis Facility. A ten-minute descent ends in a tunnel with cool-to-the-touch partitions lined with netting. However the outdated, musty mine quickly results in a high-tech lab the place dust and contamination is the enemy. Helmets are exchanged for brand new cleaner ones and a double layer of child blue booties go over steel-toed security boots.
The guts of the experiment is the enormous tank known as the cryostat, lead engineer Jeff Cherwinka mentioned in a December 2019 tour earlier than the system was closed and crammed. He described it as “like a thermos” fabricated from “maybe the purest titanium on this planet” designed to maintain the liquid xenon chilly and preserve background radiation at a minimal.
Xenon is particular, defined experiment physics coordinator Aaron Manalaysay, as a result of it permits researchers to see if a collision is with considered one of its electrons or with its nucleus. If one thing hits the nucleus, it’s extra more likely to be the darkish matter that everybody is on the lookout for, he mentioned.
These scientists tried an analogous, smaller experiment right here years in the past. After arising empty, they figured they needed to go a lot larger. One other large-scale experiment is underway in Italy run by a rival staff, however no outcomes have been introduced up to now.
The scientists are attempting to know why the universe just isn’t what it appears.
One a part of the thriller is darkish matter, which has by far many of the mass within the cosmos. Astronomers know it is there as a result of after they measure the celebs and different common matter in galaxies, they discover that there’s not almost sufficient gravity to carry these clusters collectively. If nothing else was on the market, galaxies could be “rapidly flying aside,” Manalaysay mentioned.
“It’s primarily unattainable to know our commentary of historical past, of the evolutionary cosmos with out darkish matter,” Manalaysay mentioned.
Lippincott, a College of California, Santa Barbara, physicist, mentioned “we might not be right here with out darkish matter.”
So whereas there’s little doubt that darkish matter exists, there’s a number of doubt about what it’s. The main principle is that it includes issues known as WIMPs — weakly interacting huge particles.
If that is the case, LUX-ZEPLIN may have the ability to detect them. We need to discover “the place the wimps may be hiding,” Lippincott mentioned.

South Dakota
History 605 S4, Ep 6: Citibank and South Dakota

In this episode we speak with Sean Vanatta who has written “Plastic Capitalism: Banks, Credit Cards, and the End of Financial Control.” Vanatta describes how Citibank and South Dakota changed the credit card industry in the United States. An unconnected series of events that involves the US Supreme Court, the Federal Reserve, the South Dakota Legislature and the national demand for credit cards brings together two very different but desperate entities: the state of South Dakota led by Governor Bill Janklow, and Citibank, a large international New York bank led by President Walter Wriston. Their desperate need for one another changed South Dakota’s economy as well as consumer credit for millions of Americans. It’s all an amazing story of coincidences that’s important to part of South Dakota’s history. For more, the book can be found here: Plastic Capitalism (yale.edu)
South Dakota
Kristi Noem Made Yet Another False Claim in Her Book

Kristi Noem just can’t get her facts straight. After a flopped press tour for her new book—where she confronted questions over anecdotes on meeting North Korean ruler Kim Jong Un (she didn’t) and killing her dog (she did)—Noem also falsely claimed in her book that Sen. Mike Rounds (R-SD) called for former President Donald Trump to drop out in 2016. Noem claimed that Rounds and the “entire delegation in South Dakota was not supportive of Trump” after the Access Hollywood tape came out. “Every one of the Republicans called for Trump to drop out of the race, which meant they believed Hillary Clinton should be the next president. Amazing, right?” she wrote. But Rounds’ camp is contesting this. “We have not read the book, but someone pointed out that among the inaccuracies, there was one that referenced Sen. Rounds,” Rounds spokeswoman Lydia Hall told The Dakota Scout. “We’ve asked the publisher to correct that error in their next revision and they confirmed that they are making the correction after reviewing the facts.”
Read it at The Dakota Scout
South Dakota
Survey says nearly two-thirds of SD educators use Indigenous standards • South Dakota Searchlight

Survey results indicate nearly two-thirds of South Dakota public school educators are teaching the Oceti Sakowin Essential Understandings, but the number of respondents is lower than the last survey.
The essential understandings are a set of standards approved in 2018 for teaching students about Native American culture and history. “Oceti Sakowin” is the collective term for Lakota, Dakota and Nakota speaking Native Americans, many of whom live in South Dakota. There are nine tribal nations within the state.
About 62% of teachers are using the standards, based on a survey conducted by the state Department of Education in 2023 — a “remarkable increase” from 45% in 2021, said Fred Osborn, director of the Office of Indian Education, which is under the supervision of the state Department of Tribal Relations. He presented the survey results to the Indian Education Advisory Council earlier this month.
Use of the standards is optional. The survey is used to understand how the standards are being implemented, and to help state officials encourage statewide adoption.
“The key is there’s improvement,” Osborn said. “It’s not perfect yet. There’s still work to be done, but we’ve come a long way from 45% of teachers. We hope that increases every year.”
Osborn added that the Office of Indian Education provided 10,000 copies of books on the Oceti Sakowin Essential Understandings through a Bush Foundation grant since the first survey, and sent out education packets for all grade levels last fall.
Fewer survey responses
Only about 385 educators took part in the 2023 survey, compared to 554 in 2021.
The 2023 survey also does not list how many public school districts were represented in the survey, whereas 2021’s survey had responses from 125 of the state’s 149 school districts. The school district identification question was changed between 2021 and 2023, said department spokesperson Nancy Van Der Weide. The department does not have any data to determine how many school districts were represented in the latest survey.
Removing the school district identification question allowed participants more anonymity, Van Der Weide told South Dakota Searchlight.
Navajo leaders outraged after a Lakota student’s tribal regalia was removed at graduation
Neither Osborn nor any members of the council addressed the potential impact of fewer responses on the validity of the survey results. The survey was voluntary and available for one month, Van Der Weide said, with a notice placed in a newsletter sent to teachers throughout the state.
“Those educators who did respond provided informed recommendations,” Van Der Weide said in an emailed statement. “Some of those were educators who already incorporate a lot of OSEUs in their classrooms, while others were those who wanted to make them a part of their instruction and responded with ideas for tools that would help them to incorporate the standards into their classrooms.”
Advisory council member Sherry Johnson, tribal education director for the Sisseton Wahpeton Oyate, helped shaped the standards and is participating in the standards update. She doubts the survey is an accurate representation of how the standards are being used in the state.
“We have pockets of the state that are doing well, but it’s not pervasive. It’s not required,” Johnson said. “If nothing else, there should be direct teacher training and a mandate to have this Indian education for all.”
Megan Deal, a second-grade teacher in Pierre and a member of the advisory council, said her school participated in a pilot program to help create lesson plans for standards at each grade level, but not all teachers incorporated the teachings into their classrooms.
“I don’t think they’re being taught at very many schools around the state at this time,” Deal said.
Council member Brian Wagner, tribal education director with the Lower Brule Sioux Tribe, said he is concerned about the lack of “teeth” with the standards. Lawmakers have introduced bills to require use of the Oceti Sakowin Essential Understandings in classrooms, but those efforts have failed in the Legislature.
“Knowledge is power,” Wagner said. “If people don’t learn about history, then we risk repeating it, and unfortunately the history repeating would be the racism and the discrimination that many tribal members have experienced because people don’t understand tribal sovereignty or the treaties and the treaty rights.”
Impact expected from social studies standards
Though the standards are optional, said Secretary of South Dakota Department of Education Joseph Graves, the new social studies standards that will be implemented by 2025 will include references to the Oceti Sakowin Essential Understandings. Those will encourage more teachers to use the cultural standards, he said.
“We’re going to find more Native American history and culture being taught in the schools than ever before,” Graves said. “This is actually a move forward, not a move back. I think the social studies standards have gotten an unfair black eye, and I think once you see these in place you’ll find we’re teaching more of it rather than less and, I think, from an enlightened perspective.”
States were adding lessons about Native American history. Then came the anti-CRT movement
The social studies standards controversy started in 2021 because the department removed more than a dozen references to the Oceti Sakowin from a committee’s draft revision of social studies standards. After Gov. Kristi Noem formed a new work group and ordered the process to start over, the group produced standards that drew criticism for an emphasis on rote memorization over inquiry-based learning.
Graves added that the department plans to provide teachers with weekly materials to help them utilize the social studies standards and encourage them to use the Oceti Sakowin Essential Understandings.
According to the 2023 survey results, about 84% of educators said they were aware of the standards, and 77% said it is important to implement the standards in every classroom. Only 55% of teachers said they knew the concepts well enough to teach them, but that was an 18 point increase from 2021.
Nearly 40 administrators took part in their administrator survey in 2023, compared to 164 in 2021. The 2023 survey does not list how many public school districts were represented in the administrator survey.
Nearly 80% of administrators said it’s important to implement the standards in every classroom, but two-thirds of administrators indicated a lack of confidence to implement the standards in their schools, while 56% reported an uncertainty about how to integrate the standards and 44% cited a concern for the appropriateness of the content — an increase of 28 points from the 2021 survey.
The survey does not address how using the standards affects Native American student achievement, but Osborn said it would be “interesting to cross analyze” that.
GET THE MORNING HEADLINES DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX
-
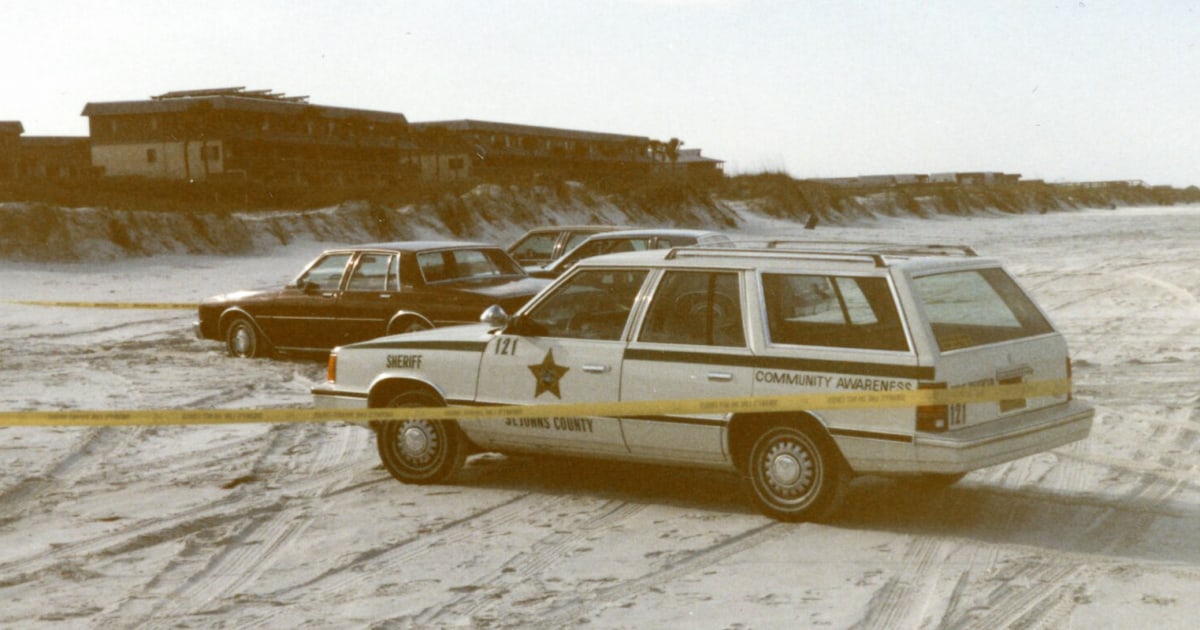

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSkeletal remains found almost 40 years ago identified as woman who disappeared in 1968
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIndia Lok Sabha election 2024 Phase 4: Who votes and what’s at stake?
-
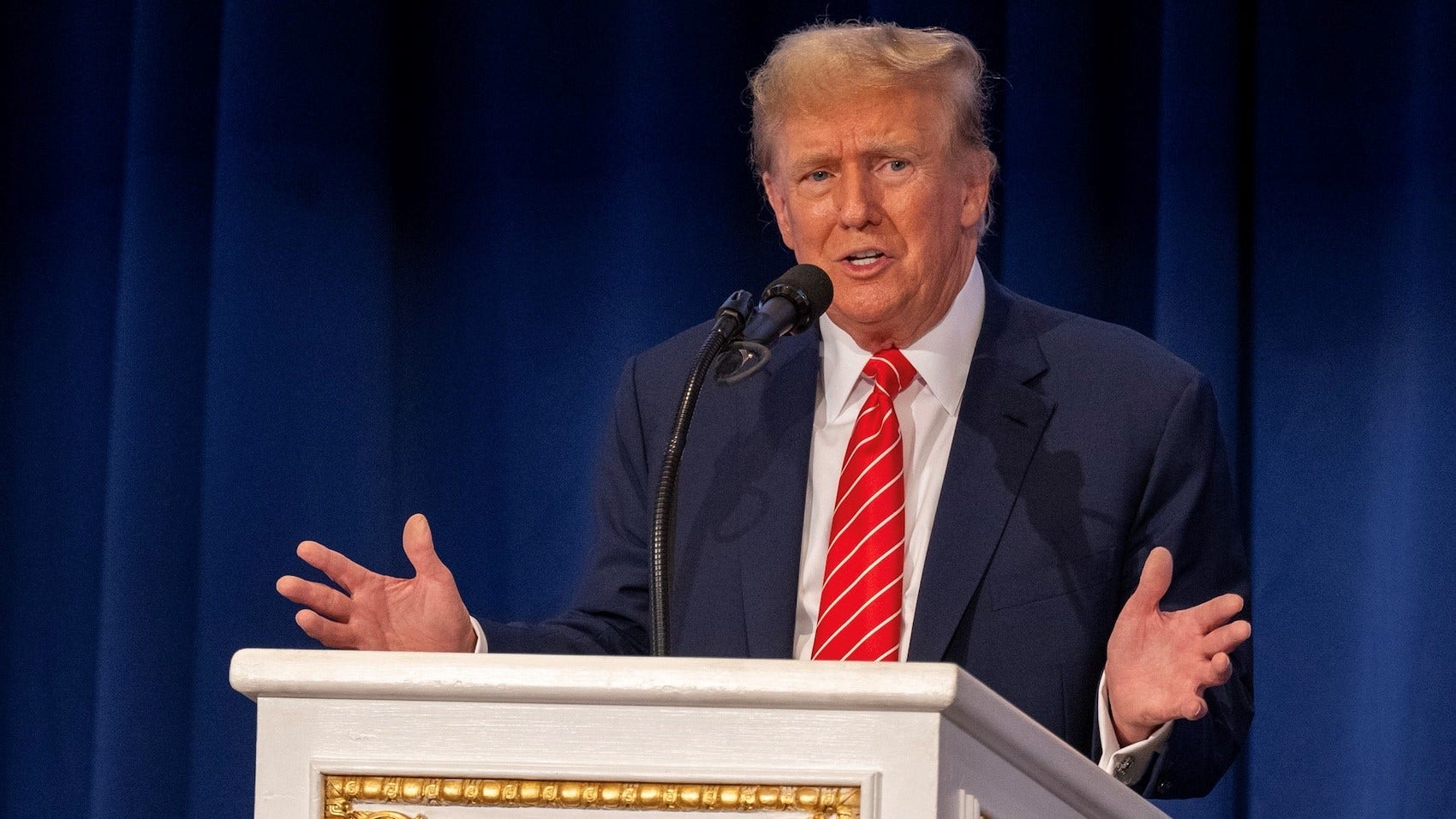

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTales from the trail: The blue states Trump eyes to turn red in November
-
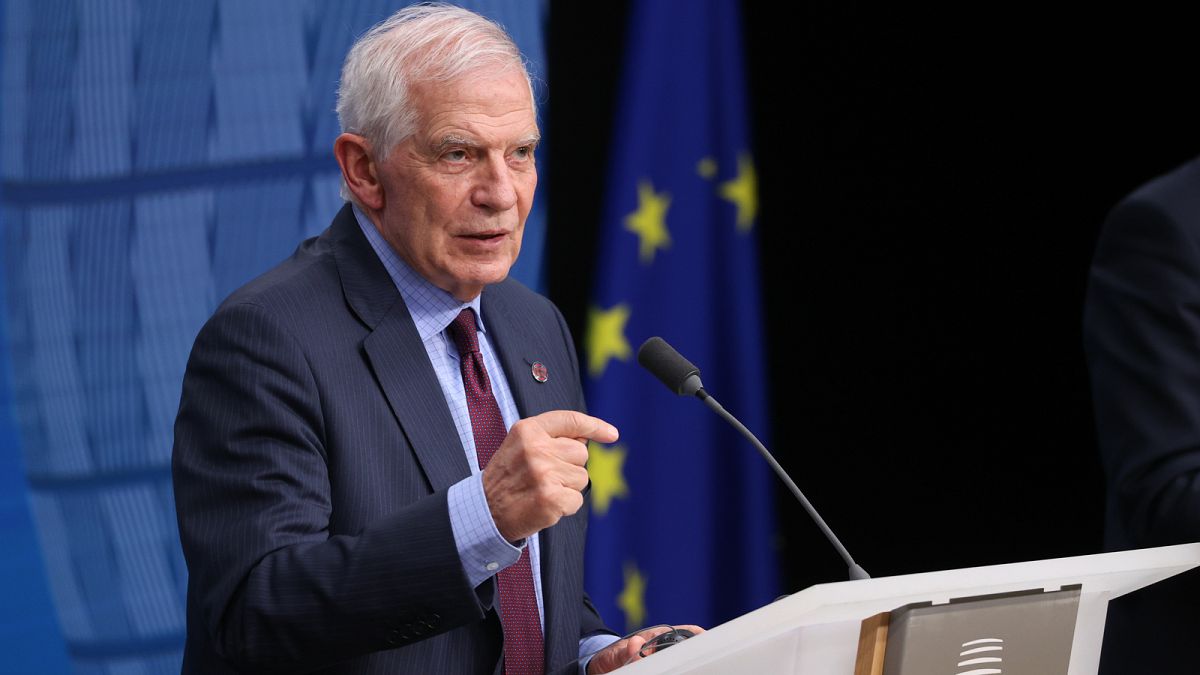

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoBorrell: Spain, Ireland and others could recognise Palestine on 21 May
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago“Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes”: Disney's New Kingdom is Far From Magical (Movie Review)
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUkraine’s military chief admits ‘difficult situation’ in Kharkiv region
-
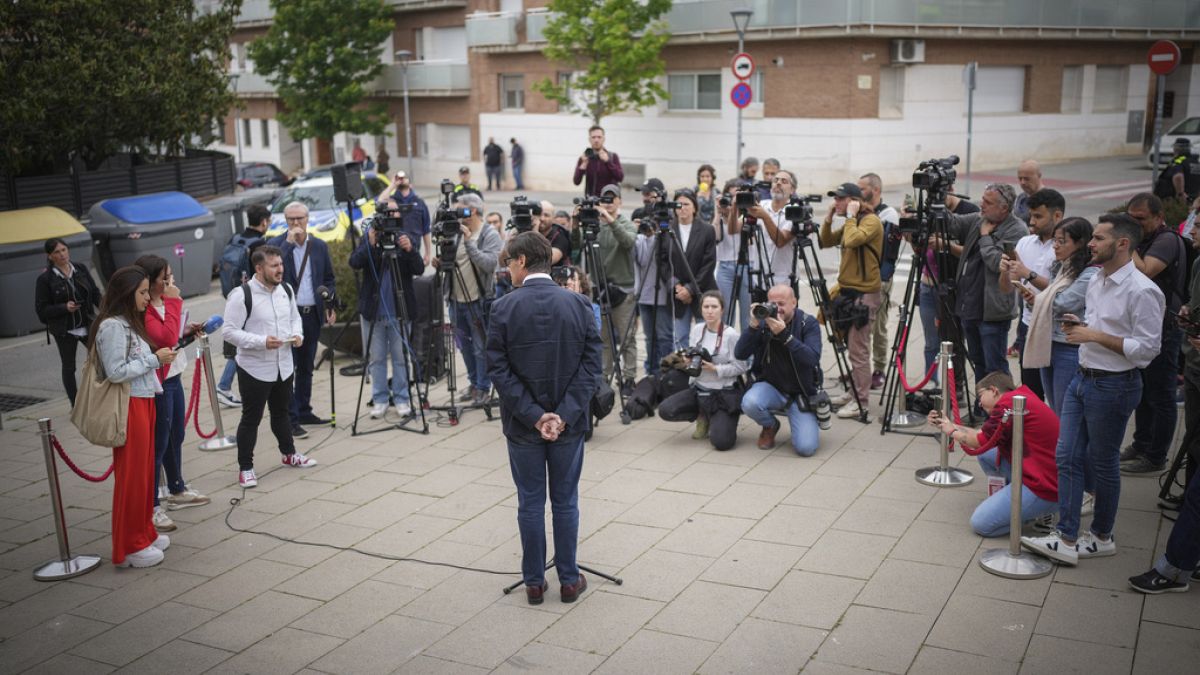

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCatalans vote in crucial regional election for the separatist movement
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNorth Dakota gov, former presidential candidate Doug Burgum front and center at Trump New Jersey rally











/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22461385/vpavic_4547_20210421_0067.jpg)