Business
Is U.S. Employment at Its Peak?

Peak jobs
This morning, the Labor Division will report what number of jobs employers added to their payrolls in March. Economists count on a wholesome acquire. However how for much longer can the labor market stick with it?
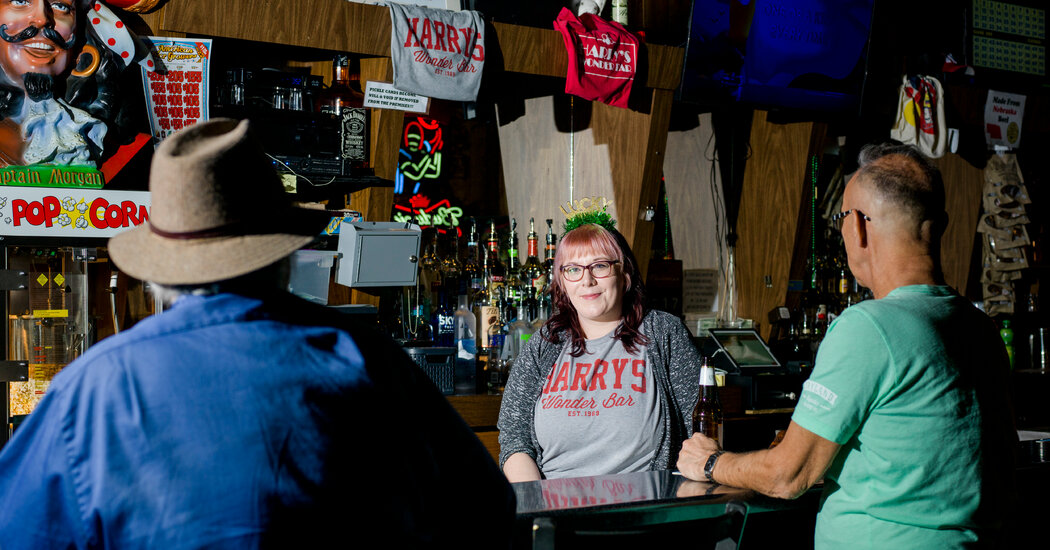
Jobs could also be approaching their as-good-as-it-gets second. Employers have added half 1,000,000 employees monthly to payrolls, on common, for the previous 12 months, with some states near their lowest-ever unemployment ranges. (“I’m in scorching demand, child,” a bartender in Nebraska informed The Instances.) However various economists say that rising inflation and better rates of interest might quickly shift the labor market right into a decrease gear. Goldman Sachs’s prime economist, Jan Hatzius, predicts that the tempo of hiring will sluggish to 200,000 a month over the subsequent quarter, and drift downward from there.
The large drawback is an absence of employees. Lengthy earlier than the pandemic, the proportion of People taking part within the work drive — those that had a job or have been actively on the lookout for one — had been declining. That had so much to do with demographics, specifically retiring Boomers. The participation charge has bounced up from its pandemic low, however has a methods to go to recuperate its prepandemic degree, a lot much less the upper charges of earlier a long time. If the long-term pattern of falling participation charges resumes, “there is not going to be the numbers of individuals on the market to fill these jobs,” Joel Naroff of Naroff Economics informed DealBook.
The pandemic accelerated the drop in participation for all employees, not simply older ones. It has additionally modified attitudes towards conventional methods of working. A latest ballot by the work drive administration firm MBO discovered that 30 % of employees in full-time jobs and 70 % of unbiased contractors assume that they’d have extra job safety in the event that they labored for themselves. That’s up sharply from 2020.
Will the economic system recuperate all the jobs misplaced in the course of the pandemic earlier than the subsequent downturn? The economic system is roughly two million jobs wanting its prepandemic peak. Goldman’s Hatzius forecasts that it might take till January to shut that hole. That’s, until the U.S. slips into recession earlier than then, a risk that extra market watchers have been discussing. “It’s a query of once we could have the subsequent recession,” the Deloitte economist Daniel Bachman informed DealBook. “Someday, and it’s more likely to occur over the subsequent 12 months, we’re going to hit the job market’s higher restrict.”
For full protection of immediately’s jobs report, see The Instances’s particular briefing, which will probably be up to date all through the day.
HERE’S WHAT’S HAPPENING
Mortgage charges hit a four-year excessive. The common charge for a 30-year fastened mortgage rose to 4.67 %, its highest degree since 2018, in line with Freddie Mac. Whereas charges had been anticipated to rise, they’ve accelerated greater than anticipated. Analysts stated, nonetheless, that this was unlikely to discourage consumers for now.
European leaders reject Moscow’s demand to pay for Russian fuel in rubles. President Vladimir Putin has insisted that international consumers open ruble accounts with Russian banks by immediately, in a probable effort to shore up his nation’s forex. However Germany and Italy, Russia’s two largest vitality clients in Europe, stated they’d proceed to pay in euros. It’s unclear how the standoff will probably be resolved.
The Senate nears a deal on a $10 billion Covid support package deal. That’s lower than half the White Home’s authentic request, however would advance the stalled laws after President Biden requested for more cash to fund vaccinations and therapeutics.
A Important Yr for Electrical Autos
The recognition of battery-powered vehicles is hovering worldwide, whilst the general auto market stagnates.
“No” votes are narrowly forward in an Amazon warehouse union election. Thus far, 875 votes have been forged in favor of unionizing an Alabama warehouse, versus 993 towards, although over 400 ballots are being challenged. However pro-union votes are main at one other Amazon warehouse, on Staten Island, which is anticipated to be finalized immediately.
Scientists introduce the primary totally mapped human genome. The brand new outcomes, introduced this week, fill in gaps and proper errors within the preliminary 2003 map. The accomplishment, made potential by advances in genetic sequencing know-how, might result in future breakthroughs in medical analysis.
Why aren’t excessive fuel costs serving to E.V. shares?
Lately, when U.S. fuel costs have risen, so have gross sales of hybrid, electrical and compact autos. But with the common value of a gallon operating at its highest in a few years, S.U.V.s and different fuel guzzlers are nonetheless being pushed off tons.
It’s about trade-offs: A scarcity of fuel-efficient vehicles has pushed the worth of these out there to the purpose the place fewer shoppers see a payoff in making the swap. That’s additionally mirrored within the subdued efficiency of the shares of many electrical automobile makers. Regardless of a spike in fuel costs, shares of Lucid and Rivian have lagged the market this 12 months. It was the identical for Tesla till not too long ago, with a giant acquire in latest days linked to a inventory cut up.
E.V. buyers are extra apprehensive about provide than demand. Nickel, a key Russian export, is a significant part in electrical automobile batteries. Dan Ives, who covers E.V. shares for Wedbush Securities, estimated {that a} scarcity of nickel and different rising prices might drive E.V. makers to boost costs by $1,200 per automobile. That’s weighing on the sector, he stated, even when larger fuel costs finally result in larger demand for electrical vehicles. The pandemic additionally continues to be a problem: Volkswagen and Tesla briefly shut factories in Shanghai this week, because of a lockdown there.
Policymakers try to do one thing about it. Yesterday, President Biden invoked the Protection Manufacturing Act to extend home manufacturing of minerals wanted for electrical autos, like nickel, lithium and cobalt. The president stated that the nation relied on “unreliable international sources” for a lot of supplies essential for transitioning to using clear vitality. The motion isn’t anticipated to incorporate loans or direct purchases, and should face opposition from environmentalists, together with some in Biden’s personal celebration.
“It is a transition, and transitions are painful. However near-zero rates of interest weren’t sustainable. Will probably be a great factor if charges are larger. That ought to enhance the outlook for shares and bonds over the long run, as soon as we get by way of it.”
— Joe Davis, the chief economist for Vanguard, on the outlook for the market as rates of interest rise and bonds get pummeled.
Deal-making takes a success
World M.&A. was value simply over $1 trillion within the first quarter, down 20 % from the identical time a 12 months in the past, in line with Refinitiv. Deal makers had anticipated a slowdown from 2021’s record-setting tempo, as rising inflation and the warfare in Ukraine made corporations extra cautious about what they do with their money.
However the information additionally reveals a noteworthy urge for food for very large offers: The worth and quantity of takeovers value $10 billion was up sharply within the first quarter regardless of elevated scrutiny from antitrust regulators and different components that dampened enthusiasm for smaller offers.
Brokers of change
Can the ability of popular culture be harnessed to advertise democracy? This query is what drove the CAA Basis — the philanthropic arm of the Hollywood expertise company CAA — to crew up with Democracy Works and create the Civic Alliance, a coalition of greater than 1,250 corporations supporting election engagement. Members embody Amazon, Coca-Cola, Levi’s, McDonald’s, Microsoft and Starbucks.
“2020 was a tipping level,” Natalie Tran, the CAA Basis’s govt director, informed DealBook. “I don’t assume we will return from that. The expectations for civic engagement from companies have reworked within the final two years.”
The origin story: Forward of the 2020 presidential election, Tran had been searching for steerage on civics by way of an organization lens. She wished to advertise engagement at CAA however wasn’t an skilled and shortly found that individuals in her place at different corporations have been seeking comparable data. They discovered little. “It’s not possible for companies to answer the engagement expectations with out instruments and sources,” Tran stated. The alliance not too long ago revealed the Company Civic Playbook, a information it developed for members.
The playbook makes the enterprise case for engagement. Based mostly on the efficiency of the alliance’s publicly traded corporations, civic engagement pays off: These corporations outperformed the S&P 500 in the course of the 2020 election marketing campaign and in “the consequential moments for our democracy within the months that adopted,” in line with the alliance. “Folks all the time say democracy is nice for enterprise,” Tran stated. “We wished to show that with information.”
The midterms are producing “presidential election vitality,” Tran stated. The alliance’s aim is to make civic engagement an day-after-day, each election sort of factor, right down to the native degree, Tran stated: “We’re equipping corporations to construct a sustainable tradition of civic participation.”
THE SPEED READ
Russia-Ukraine warfare
-
The U.S. imposed sanctions on Russian know-how corporations to crack down on efforts to evade current restrictions. (NYT)
-
Moscow is encouraging illicit imports of Western items. (Fortune)
-
The results of sanctions on Russia are being felt all through the start-up world. (FT Lex)
Offers
-
The Justice Division is investigating no less than one assembly between Activision Blizzard’s C.E.O., Bobby Kotick, and a stepson of Barry Diller as a part of an inquiry into uncommon choices buying and selling days earlier than the online game large’s sale to Microsoft. (WSJ)
-
Carmakers searching for to compete with Tesla in electrical autos are more and more weighing shopping for a few of their suppliers to hurry up analysis and manufacturing. (Reuters)
-
SPACs are off to a sluggish begin on the Hong Kong and Singapore inventory markets. (FT)
Coverage
-
U.S. antitrust officers reaffirmed their dedication to harder scrutiny of tech giants. (Bloomberg)
-
“The investigation that threatens to sink U.S. photo voltaic” (FT)
-
A plan by Senator Rick Scott, Republican of Florida, that might impose revenue taxes on many People who now pay none, is drawing opposition from his personal celebration. (NYT)
-
“She Took the White Home Pictures. Trump Moved to Take the Revenue.” (NYT)
Better of the remaining
-
“This Is What Occurs When Globalization Breaks Down” (NYT)
-
Some Ivy League universities are taking part in down their low acceptance charges. (WSJ)
-
“Reverse Mortgages Are No Longer Only for Owners Quick on Money” (NYT)
-
How the celeb-spotting Instagram account DeuxMoi is altering New York’s restaurant scene. (The Lower)
-
Patrick Demarchelier, the style photographer recognized for his portraits of supermodels and Princess Diana, has died. He was 78. (NYT)
We’d like your suggestions! Please electronic mail ideas and options to dealbook@nytimes.com.

Business
130,000 Igloo Coolers Recalled After Fingertip Amputations From Handle

About 130,000 Igloo coolers were recalled on Thursday after consumers reported 78 fingertip injuries from the cooler’s tow handle, 26 of which led to fingertip amputations, bone fractures or cuts, according to the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission.
This warning expands an initial recall issued in February of more than one million 90-quart Igloo Flip & Tow Rolling Coolers because the tow handle was crushing and seriously injuring people’s fingertips.
“The tow handle can pinch consumers’ fingertips against the cooler, posing fingertip amputation and crushing hazard,” the recall said.
In the February recall, the safety commission said that Igloo had received 12 reports of fingertip injuries from the coolers. Since then there have been an additional 78 reports, according to the commission.
The recalled coolers, all of which have the word “IGLOO” on the side of them, were manufactured before January 2024 and come in different colors. The manufacture date can be found on the bottom of the cooler.
The commission said the latest recall also affected about 20,000 coolers in Canada and 5,900 in Mexico, which is in addition to the tens of thousands recalled from each country in February.
Igloo said that owners who bought the coolers between January 2019 and January 2025 should stop using them and contact the company for a free replacement handle.
The company said in a statement that it stood behind the quality of its products and that consumer “safety and satisfaction” were its top priorities.
The coolers were sold at Academy, Costco, Dick’s, Target and other retailers and online stores and were usually priced between $80 and $140.
Business
Insurance commissioner signals possible probe into State Farm's handling of L.A. wildfire claims

After fielding a storm of complaints at a community meeting about how State Farm General is handling Los Angeles wildfire claims, California Insurance Commissioner Ricardo Lara said Saturday that regulators might launch a formal inquiry into the company’s practices.
Lara made his comments during a Zoom session attended by more 200 survivors of the Palisades and Eaton fires, who complained about delays in handling their claims, difficulty in getting testing for toxic substances and low cash offers to fix damaged homes and replace those destroyed.
“It’s not off the table,” said Lara, referring to the department’s authority to conduct what is called a “market conduct” exam into the company’s response to the fires. “We are not necessarily opposed to that.”
The department has previously conducted such investigations following other large fires.
The Zoom session was organized by the Pali Strong community group, which was formed by Pacific Palisades residents after the Jan. 7 fires.
State Farm, on Sunday, said in response that it has the largest claims force in the industry and it is “focused on our customers and helping them recover from the largest fire event we have ever experienced in the state.”
“We actively work with each of our customers to resolve their claim by understanding the facts of their loss, identifying the damages and applicable coverage,” the statement said.
The company said that as of May 5 it had received more than 12,600 claims and paid more than $3.4 billion to customers.
Separately, Tony Cignarale, deputy commissioner of consumer services and market conduct, told the fire victims that the department sent the California FAIR Plan Assn. a letter last week seeking information into how the insurer of last resort is handling smoke damage claims.
The FAIR Plan was sued last month by policyholders in both fire zones, who allege the state’s insurer is refusing to properly investigate and pay for smoke damage as required by state law. Also named as defendants are State Farm and other California licensed home insurers, who run the plan.
The threat to conduct a market conduct exam into State Farm General’s claims handling practices comes as California’s largest home insurer awaits a decision on its request for an emergency rate hike in response to its losses from the Jan. 7 fires.
The company originally filed for a 22% rate hike for its homeowner policies, but trimmed that down to 17% during a hearing last month before an administrative law judge.
The judge is expected to make a recommendation as early as this week to Lara, who can then accept, reject or revise the ruling. It also could be sent back for reconsideration.
Joy Chen, whose Altadena home was damaged by soot and ash, asked Lara to defer granting the company any rate hike until he “fully” investigates the complaints.
“We’d be happy to submit them to you,” said Chen, a leader of the Eaton Fire Survivors Network.
Lara said that he could not tie any investigation into the complaints to consideration of the rate hike, which he said was a “separate judicial process that is currently underway.” However, he asked the fire survivors to submit all their complaints to the department so it could examine them.
“What I commit to doing is collecting all the data that I’m going to receive … and sending it to our law enforcement team, because I really want to look at … all the allegations that were talked about today,” he said.
Chen, who said her home was effectively remediated by her insurer, USAA, later told The Times, “Lara’s most important job is to protect California families but he is saying the department does not consider claims management when approving rate hikes — but this is one of the few legal powers he actually has to regulate the industry.”
Last week, the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health announced it found high levels of lead and other toxic metals at homes destroyed by the wildfires whose topsoil had been scraped by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, particularly in the Altadena area with its older housing stock.
In regards to the FAIR Plan, Cignarale said the department’s letter to the insurer asked them “for very specific information as to the very steps that are being taken to resolve these smoke claims.”
Lara told the fire victims that he had issued a bulletin to state insurers in March stating that the department expected them to “fully investigate and pay legitimate smoke claims.” He said if that was not happening, fire victims should submit their complaints to the state so the department’s investigative unit could look into them.
He also said the department planned to convene health experts to develop state standards for smoke damage remediation. “Absent any set standards, then the insurance companies will do anything to get you back in your home as quickly as possible,” he said.
The FAIR Plan did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Business
Why America’s ‘Beautiful Beef’ Is a Trade War Sore Point for Europe

Hendrik Dierendonck, a second-generation butcher who has become, as he describes it, “world famous in Belgium” for his curated local beef, thinks Europe’s way of raising cattle results in varied and delicious cuts that European consumers prize.
“They want hormone-free, grass-fed,” Mr. Dierendonck explained recently as he cut steaks at a bloody chopping block in his Michelin-starred restaurant, which backs onto the butchery his father started in the 1970s. “They want to know where it came from.”
Strict European Union food regulations, including a ban on hormones, govern Mr. Dierendonck’s work. And those rules could turn into a trade-war sticking point. The Trump administration argues that American meat, produced without similar regulations, is better — and wants Europe to buy more of it, and other American farm products.
“They hate our beef because our beef is beautiful,” Howard Lutnick, the commerce secretary, said in a televised interview last month. “And theirs is weak.”
Questions of beauty and strength aside, the administration is right about one thing: European policymakers are not keen on allowing more hormone-raised American steaks and burgers into the European Union.
Further opening the European market to American farmers is just one ask on a laundry list of requests from the Trump team. American negotiators also want Europe to buy more American gas and trucks, to change their consumption taxes and to weaken their digital regulations.
Trade officials within the European Union are willing to make many concessions to avert a painful and protracted trade war and to avert higher tariffs. They have offered to drop car tariffs to zero, to buy more gas and to increase military purchases. Negotiators have even suggested they could buy more of certain agricultural products, like soy beans.
But Europeans have their limits, and those include America’s treated T-bones and acid-washed chicken breasts.
“E.U. standards, particularly as they relate to food, health and safety, are sacrosanct — that’s not part of the negotiation, and never will be,” Olof Gill, a spokesman for the European Commission, the E.U. administrative arm, said at a recent news conference. “That’s a red line.”
It is not clear how serious the Americans are about pushing for farm products like beef and chicken. But the topic has surfaced repeatedly. When U.S. officials unveiled a trade deal with Britain on Thursday, for instance, beef was part of the agreement.
But according to Britain, the deal would simply make it cheaper for Americans to export more hormone-free beef to the country and would not weaken British health and safety rules, which are similar to those in the E.U.
When it comes to the European Union, the United States can already export a large amount of hormone-free beef without facing tariffs, so an equivalent deal would do little to help American farmers.
But diplomats and European officials have repeatedly insisted that there is no wiggle room to lower those health and safety standards. And when it comes to meat-related trade restrictions more broadly, there is very little. Chicken, for instance, faces relatively high tariffs, and there is limited appetite to lower those rates.
That’s because Europe is protective of both its food culture and its farms.
Where America tends to have massive agricultural businesses, Europeans have maintained a more robust network of smaller family operations. The 27-nation bloc has about nine million farms, compared with about two million in the United States.
Subsidies and trade restrictions help to keep Europe’s agricultural system intact. The European Union allocates a big chunk of its budget to supporting farmers, and a mix of tariffs and quotas limit competition in sensitive areas. E.U. tariffs on agricultural products are around 11 percent overall, based on World Trade Organization estimates, though they vary hugely by product.
And the bloc could place higher tariffs on U.S. farm goods if trade negotiations fall through. Their list of products that could face retaliatory levies, published Thursday, includes beef and pork, along with many soy products and bourbon.
But it’s not just tariffs limiting European imports of American food. Strict health and safety standards also keep many foreign products off European grocery shelves.
Take beef. Mr. Dierendonck and other European farmers are banned from using growth stimulants, unlike in the United States, where cattle are often raised on large feedlots with the use of hormones. European safety officials have concluded that they cannot rule out health risks for humans from hormone-raised beef.
To Mr. Dierendonck, the rules also fit European preferences. The lack of hormones results in a less homogenous product. “Every terroir has its taste,” he explains, describing the unique “mouth feel” of the West Flemish Red cow he raises on his farm on the Belgian coast.
But farming beef without hormones is more expensive. And American exporters have to adhere to hormone limitations when they send steaks, hamburgers or dairy products to E.U. countries, which European farmers argue is only fair. Otherwise, imports produced using cheaper methods could put European farmers out of business.
“We cannot accept import products that do not meet our production standards,” said Dominique Chargé, a cattle farmer from the west of France who is also president of La Coopération Agricole, a national federation representing French agricultural cooperatives.
The result is that the United States does not sell much beef to Europe. It makes more economic sense for U.S. farmers to sell into markets that allow hormone-raised cattle.
One frequent American complaint is that European health standards are more about preference than actual health.
American scientists have called the risks of hormone use in cows minimal. And though E.U. officials and consumers frequently sneer at America’s “chlorinated chickens,” that rallying cry is a bit dated. American farmers have for years been using a vinegar-like acid, and not chlorine, to rinse poultry and kill potential pathogens.
Some studies in Europe have suggested that such treatments are not a replacement for raising a chicken in a way that makes it pathogen-free from the start. American scientists have concluded that the rinses do their job and are not harmful to humans.
“I don’t know that it’s really about the science,” said Dianna Bourassa, a microbiologist specializing in poultry at Auburn University. “In my microbiological opinion, there are no health implications.”
From the perspective of European farmers, though, whether the health risks are genuine is besides the point. So long as European voters oppose chemical-treated chicken and hormone-treated beef, Europe’s farmers cannot use those farming techniques.
“When you speak to our farmers, it’s about fairness,” explained Pieter Verhelst, a member of the executive board of a Belgian farmers’ union, Boerenbond. “The policy framework we start with is totally different, and those issues are mostly totally out of the hands of farmers.”
And European consumers do seem to support E.U. food and farming rules.
Farmer protests last year loudly opposed more beef imports from South American countries, in part over concerns that the cows might be raised with a growth hormone. An Obama-era trade deal died in part thanks to popular anger over “chlorine chicken” (“Chlorhünchen,” to derisive Germans.)
E.U. public opinion polling has suggested that policies that promote farming and farmers are very popular. In a 2020 poll fielded in-person across the bloc, nearly 90 percent of Europeans agreed with the idea that agricultural imports “should only enter the E.U. if their production has complied with the E.U.’s environmental and animal welfare standards.”
In Europe, including at Mr. Dierendonck’s butchery and farm, there’s a value placed on the old-fashioned, small-scale way of doing things, policymakers and farmers agreed. Mr. Dierendonck does buy some American beef for customers who ask for it — it’s easy to cook, he said — but it’s a small part of the business.
“I like American beef very much, but I don’t like it too much,” said Mr. Dierendonck, explaining that to him, the beef his European suppliers provide is varied, like a fine wine. “For me, it’s about keeping traditions alive.”
-
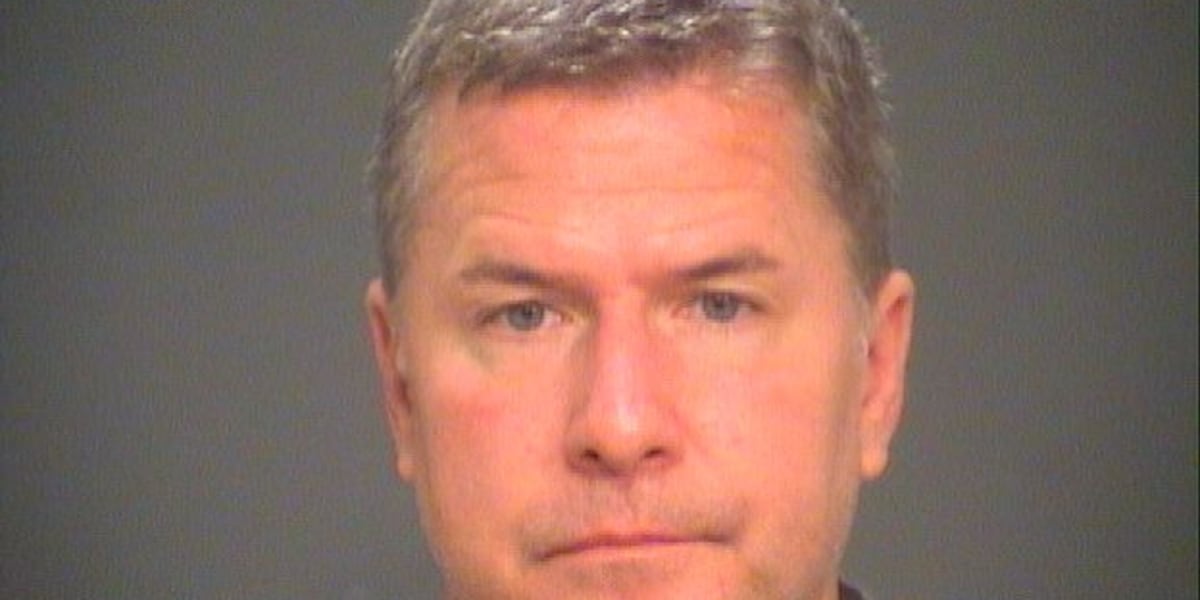

 Cleveland, OH1 week ago
Cleveland, OH1 week agoWho is Gregory Moore? Former divorce attorney charged for murder of Aliza Sherman in downtown Cleveland
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoU.S. and China Dig In on Trade War, With No Plans for Formal Talks
-
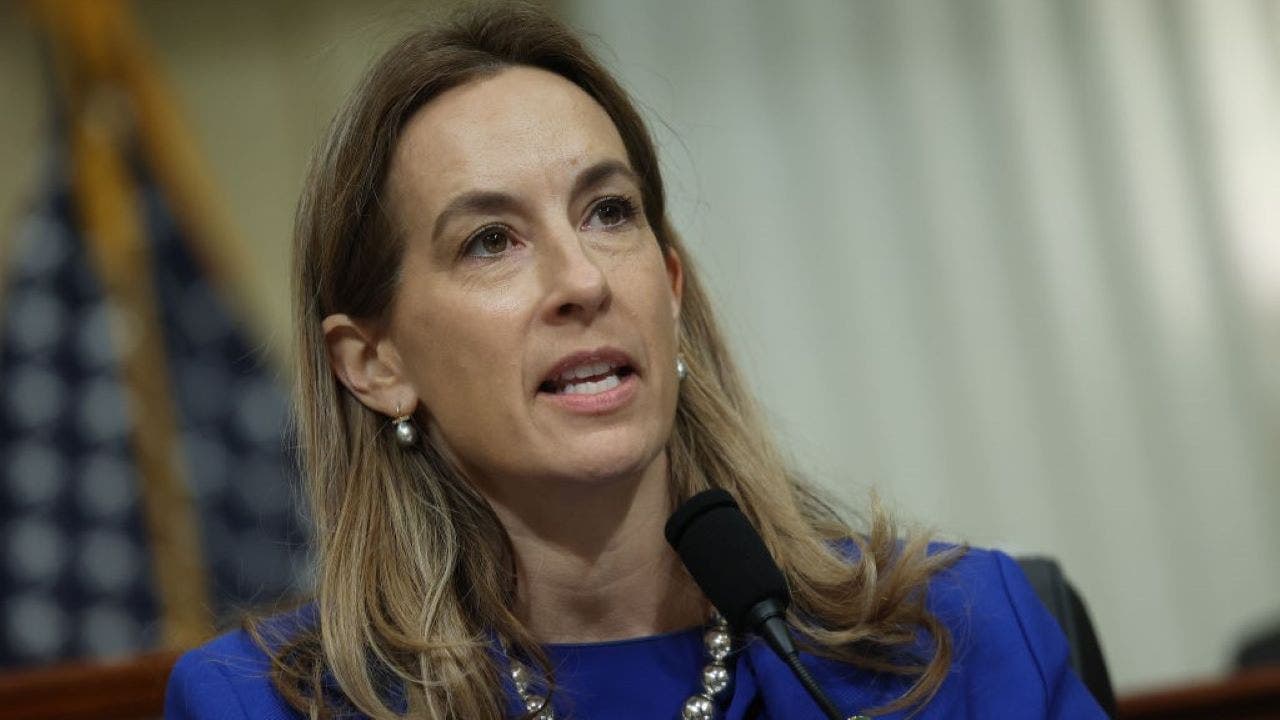

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRep. Mikie Sherrill suggests third Trump impeachment as she campaigns to be next New Jersey governor
-
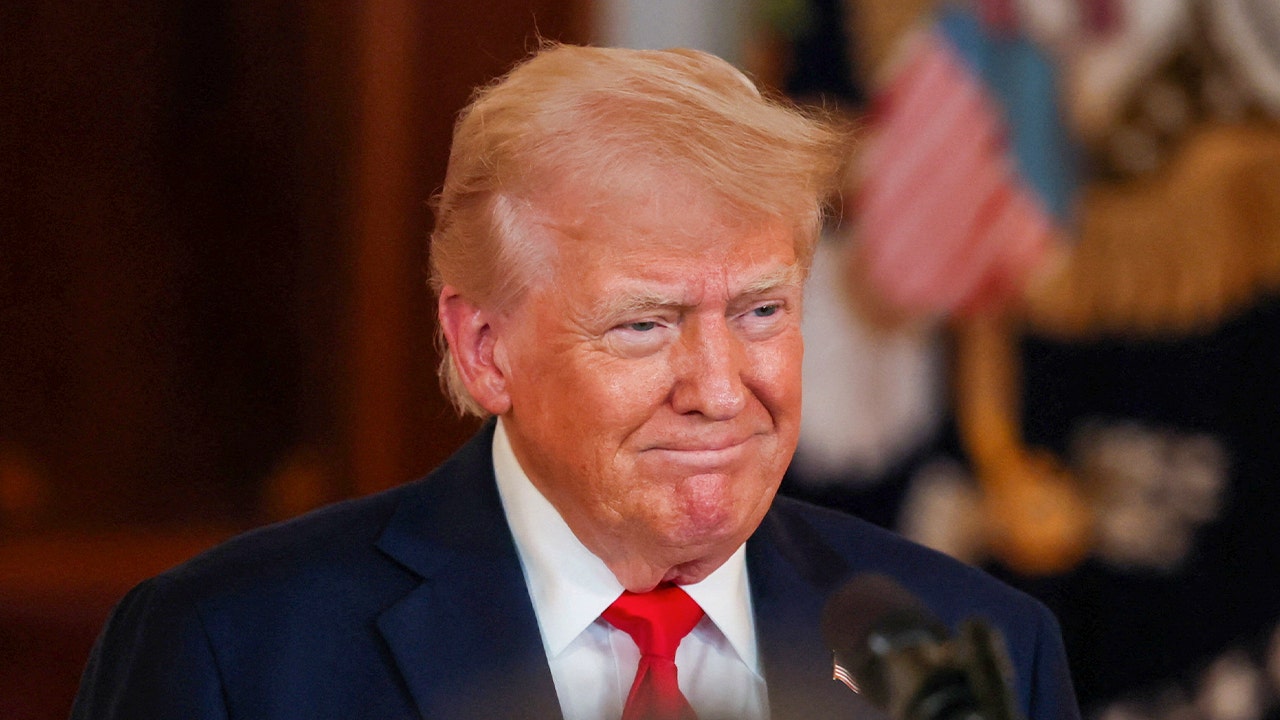

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump posts AI image of himself as Pope amid Vatican's search for new pontiff
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoFamily statement: Rodney Hinton Jr. walked out of body camera footage meeting with CPD prior to officer death
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAre Politicians Too Old? California Democrats Want to Debate an Age Cap.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago‘Don’t see a major war with India, but have to be ready’: Pakistan ex-NSA
-
News1 week ago
Stock market today: Dow, S&P 500, Nasdaq futures jump amid jobs report beat, hopes for US-China talks