World
How South Africa's former leader Zuma turned on his allies and became a surprise election foe

JOHANNESBURG (AP) — South Africa faces an unusual national election this year, its seventh vote since transitioning from white minority rule to a democracy 30 years ago. Polls and analysts warn that for the first time, the ruling African National Congress party that has comfortably held power since Nelson Mandela became the country’s first Black president in 1994 might receive less than 50% of votes.
One big reason is Jacob Zuma, the former president and ANC leader who stepped down in disgrace in 2018 amid a swirl of corruption allegations but has emerged in recent months with a new political party. It intends to be a major election player as the former president seeks revenge against former longtime allies.
A SOUTH AFRICAN COURT OVERTURNS BAN, RULES THAT FORMER LEADER JACOB ZUMA CAN RUN IN THE ELECTION
Here is what you need to know about the 82-year-old Zuma’s return to the political ring and how it might play a significant election role.
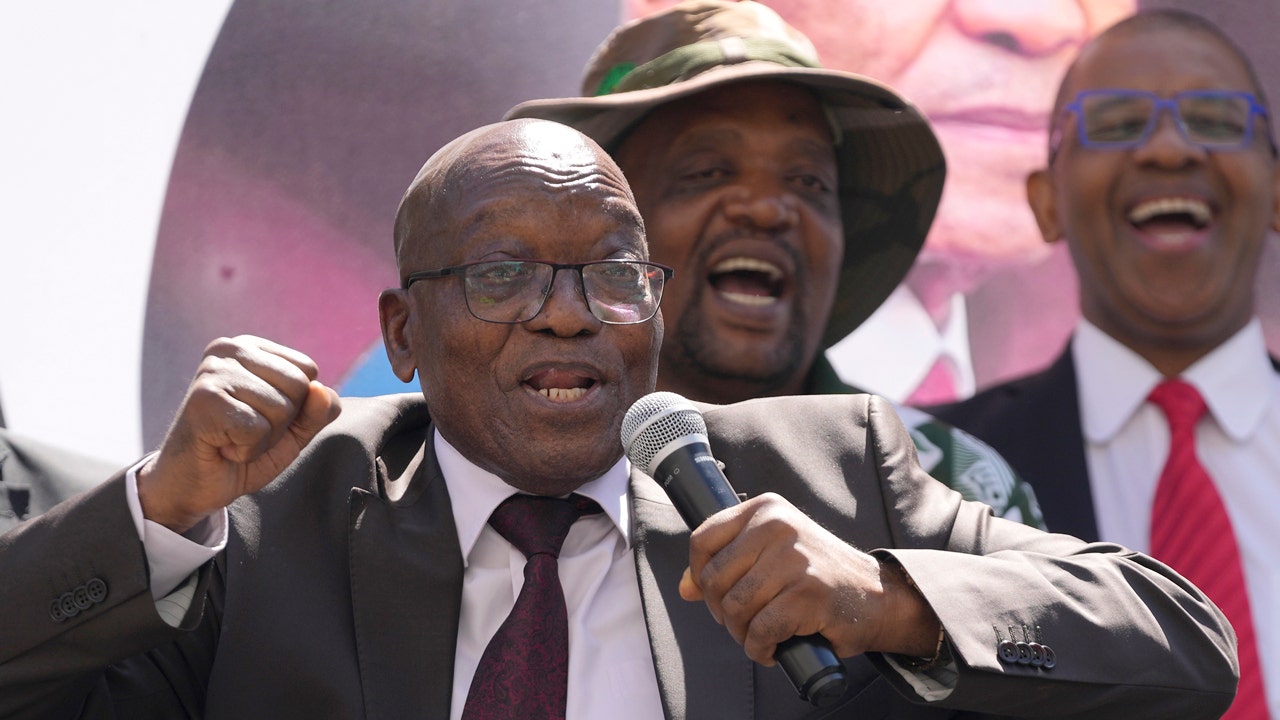
Former South African president, Jacob Zuma, sings and dances after addressing his supporters of the UMkhonto WeSizwe, (MK) party outside the High court in Johannesburg, South Africa, Thursday, April 11, 2024. For the first time since 1994, the ruling African National Congress (ANC) might receive less than 50% of votes after Zuma stepped down in disgrace in 2018 amid a swirl of corruption allegations and has given his support to the newly-formed MK. (AP Photo/Themba Hadebe)
WHO IS JACOB ZUMA?
Zuma has long been one of South Africa’s most recognizable politicians. He was a senior leader in the ANC during the liberation struggle against apartheid. A former ANC intelligence chief, he has repeatedly threatened to reveal some of the party’s secrets. While Zuma was not one of Mandela’s preferred choices to succeed him, Mandela trusted Zuma to play an influential role in ending deadly political violence that engulfed KwaZulu-Natal province before the historic 1994 elections. The province has remained a vocal base of support for Zuma ever since, and members of Zuma’s Zulu ethnic group make up its majority. Zuma became deputy leader of the ANC in 1997 and was appointed South Africa’s deputy president in 1999.
HOW DID HE BECOME PRESIDENT?
Zuma’s path to power included legal challenges. In 2006, he was found not guilty of raping the daughter of a comrade at Zuma’s home in Johannesburg. A year earlier, he was fired as South Africa’s deputy president after his financial advisor was convicted for corruption for soliciting bribes for Zuma during an infamous arms deal. Alleging a political witch hunt, Zuma launched an aggressive political campaign that saw him elected ANC president in 2007. His campaign appealed to widespread discontent with then-President Thabo Mbeki, who was often described as autocratic and aloof. The corruption charges against Zuma were later dropped, amid controversy, and he was elected South Africa’s president in 2009.
HOW DID HE LOSE POWER?
Zuma’s presidency was often under fire. His close friends and allies, the Gupta family, were accused of influencing appointments to key cabinet positions in exchange for lucrative business deals. The allegations of corruption in government and state-owned companies eventually led the ANC force Zuma to resign in 2018. A judicial commission of inquiry uncovered wide-ranging evidence, and Zuma in 2021 was convicted and sentenced to 15 months in jail for refusing to testify. Zuma remains aggrieved with the ANC and his successor, President Cyril Ramaphosa. But few South Africans expected the break to go so far.
HOW HAS HE REEMERGED?
Zuma shocked the country in December by denouncing the ANC and campaigning against a party that had been at the heart of his political career. His new political party, UMkhonto WeSizwe, was named after the ANC’s military wing, which was disbanded at the end of the struggle against white minority rule. The ANC has launched a legal case seeking to stop the new party from using a name and logo that are similar to those of the military wing. The charismatic Zuma continues to crisscross the country, delivering lively speeches, and an image of his face will represent the party on ballots.
WHAT ARE ZUMA’S ELECTION CHANCES?
The ANC already had been facing pressure from other opposition parties. But Zuma’s new party threatens to draw support from within the often divided ANC. South Africa’s electoral body has cleared him to run for a parliament seat, despite his past conviction. Polls suggest the new party may emerge as one of the country’s biggest opposition parties and could play a significant role if the weakening ANC must form coalitions to run the country. Addressing his supporters at a recent rally, Zuma declared that “I need to return so that I can fix things.”

World
Most Americans See TikTok as a Chinese Influence Tool, Reuters/Ipsos Poll Finds
World
Biden admin sanction waivers give Iran access to billions in funds to keep war efforts going, expert says
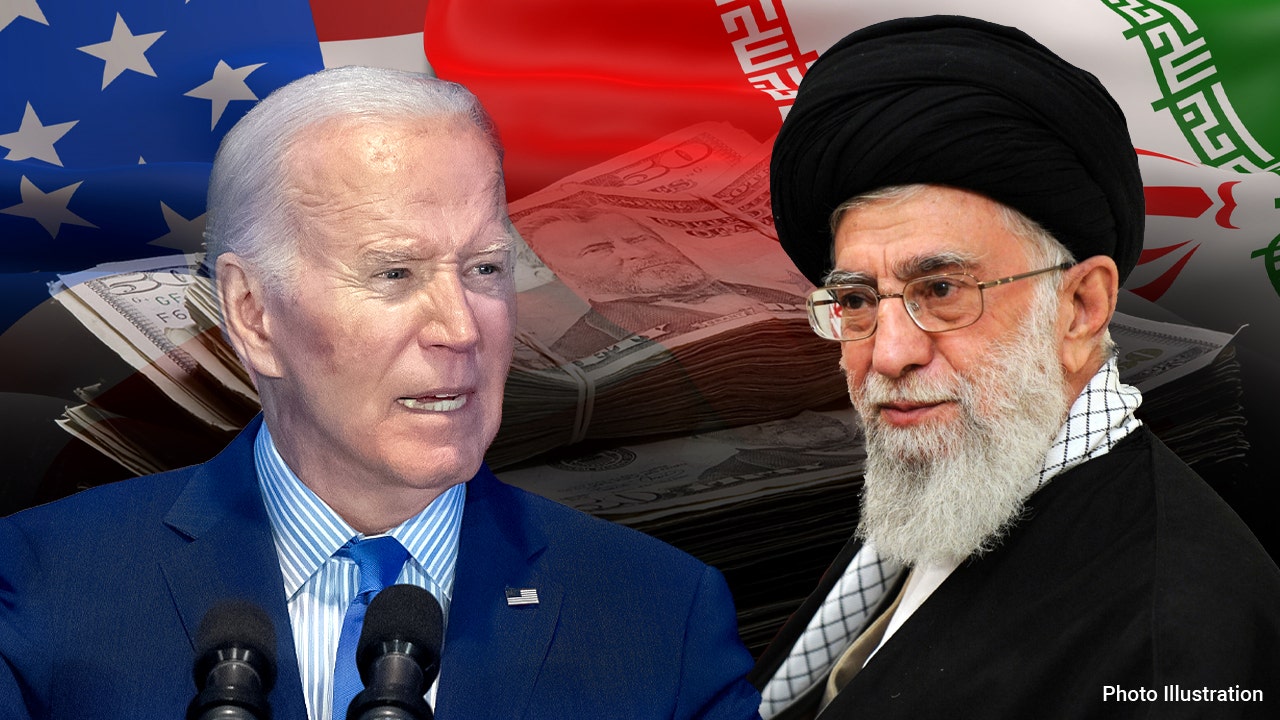

The Biden administration has allowed billions in sanctions waivers that benefit Iran, with estimated billions more in unsanctioned oil sales, which allows the Iranian government to continue diverting money to its drone factories and funding proxy groups, an expert told Fox News Digital.
“What happens when you end up releasing that money is that it goes into the general funds, which can then be used in lots of different ways,” Jonathan Schanzer, senior vice president for research at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD), explained.
“If they are using the sanctions relief to fund their general budget, then ultimately [they] are to the benefit of the IRGC because the IRGC partakes in that regular budget,” Schanzer said, noting the Biden administration has often argued that any waivers do not ultimately and directly benefit the Iranian military and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
“Let me put it this way: There is no way to do it without ultimately benefiting the regime and its ultimate objective, which is to fund its malign activities abroad,” Schanzer, a former terrorism finance analyst at the U.S. Department of the Treasury noted.
TEHRAN ‘RELIGIOUSLY’ BROADCASTING ANTI-ISRAEL UNREST AT US SCHOOLS FOR PROPAGANDA, EXPERT SAYS
A State Department spokesperson told Fox News Digital that the Biden administration “has not lifted a single sanction on Iran. Rather, we continue to increase pressure.”
“Our extensive sanctions on Iran remain in place, and we continue to enforce them,” the spokesperson said. “Over the last three years, the U.S. has sanctioned over 600 individuals and entities connected to the full range of Iran’s problematic and dangerous behaviors, UAV and missile proliferation, terrorism, terrorist financing and other forms of illicit trade, horrific human rights abuses and support for proxy terrorist groups.”
President Biden, left, and Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. (Getty Images)
“We have even seen the regime fail to meet its own revenue expectations as it struggles to evade our sanctions and find illicit buyers for its oil,” the spokesperson said, not commenting on the fact Iran does find buyers for its oil. The spokesperson insisted that the U.S. sanctions, in combination with “Iran’s economy and regime mismanagement,” have brought the country’s currency “to the lowest it has ever been against the U.S. dollar.”
A second State Department spokesperson reiterated the fact that the sanctions waiver allowing Iraq to buy electricity from Iran has been renewed 21 times since the Trump administration first issued the waiver in 2018 and that “any notion” that money goes to Iran due to the waivers “is false and misleading.”
THERE IS ‘NO DOUBT’ THAT ANTI-ISRAEL PROTESTS ARE ‘HIGHLY COORDINATED’ ACROSS SENIOR LEVELS IN US: MIKE POMPEO
“We have been in ongoing engagement with allies and partners, including at the G-7 and with the EU, on ways to increase pressure on Iran,” the second spokesperson said.
A Fox News Digital analysis, in combination with the FDD’s research, determined that Iran has received between $16 billion and $20 billion in sanctions waivers, with billions more gained through the sale of Iranian oil, which the U.S. has sanctioned but has not managed to totally prevent due to a mixture of lax government oversight and more sophisticated evasion methods.
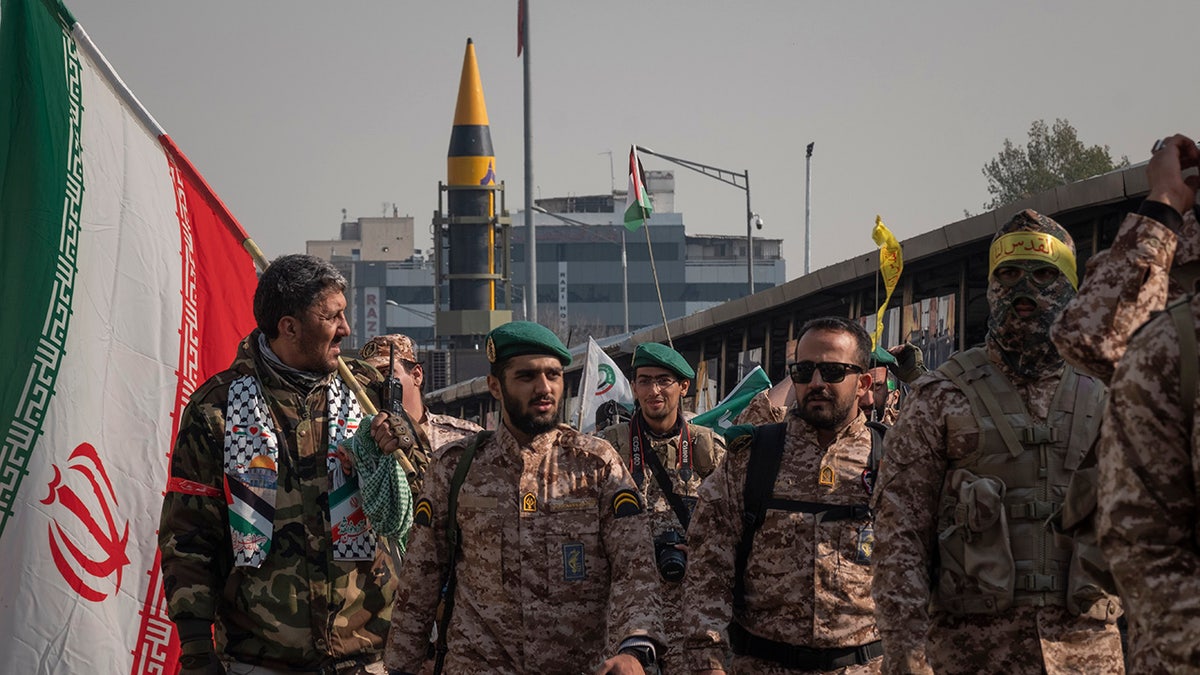

Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps military personnel are walking along Enghelab (Revolution) Avenue as an Iranian Kheibar Surface-to-Surface missile is being unveiled during the Ela Beit Al-Moghaddas (Al-Aqsa Mosque) military rally in Tehran, Iran, on Nov. 24, 2023. (Morteza Nikoubazl/NurPhoto via Getty Images)
That includes a $10 billion sanctions waiver so Iraq can trade to obtain electricity from Iran, a $6 billion sanctions waiver agreed for South Korea to transfer money in exchange for the release of five Americans and $3.8 billion gained through the sale of petrochemicals in order to dodge a Trump-era sanction.
The U.S. State Department in March came under fire for resuming a sanctions waiver, which had been renewed since the Trump administration first issued the waiver in 2018. Some experts estimated the waiver as having a valuation of around $10 billion for Iran.
IRAN COURT SENTENCES POPULAR RAPPER TO DEATH FOR INVOLVEMENT IN PROTESTS, LAWYER SAYS
That waiver particularly allowed for the transfer of funds between Iran and Iraq so that Iraq, which remains a U.S. ally, could continue to use electricity imported from Iran – but critics saw it merely as another easement on sanctions against Iran.
“None of this money goes to the mullahs. None of this money goes into Tehran. The sanctions relief that is provided actually goes to vendors that provide humanitarian assistance to the Iranian people,” White House national security advisor John Kirby told reporters at the time.
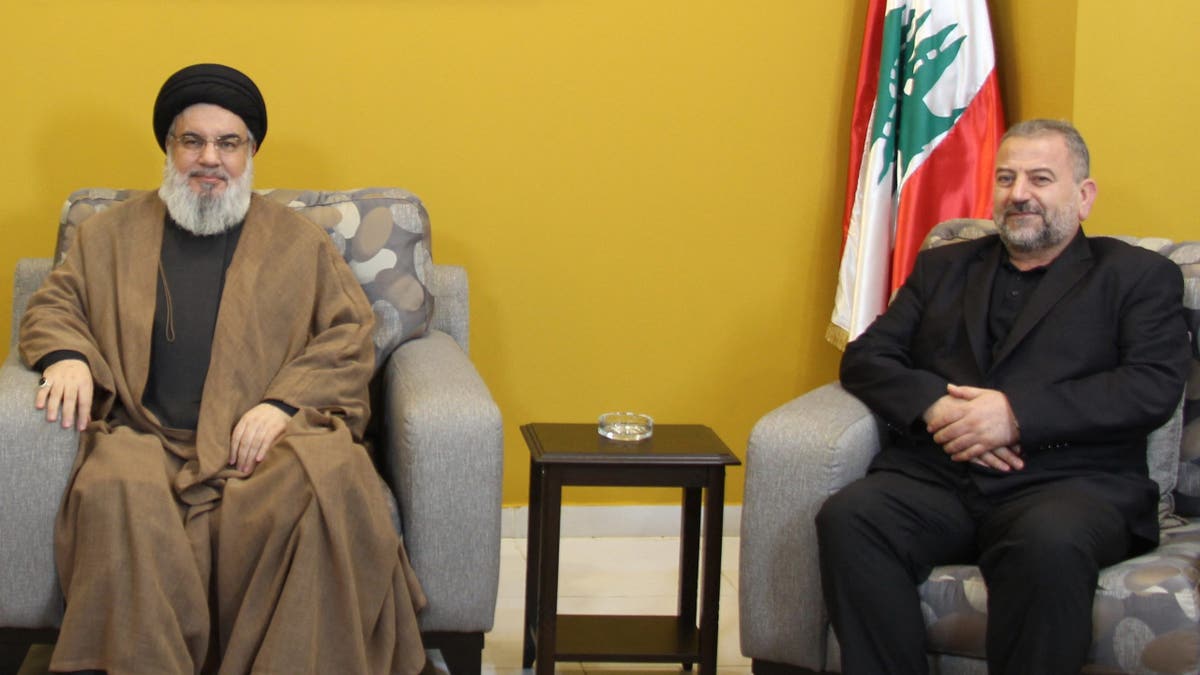

This file handout picture provided by Hezbollah’s media office on Sept. 2, 2023 shows the Lebanese Shiite group’s Secretary General Hassan Nasrallah, left, during a meeting with the deputy chief of the Palestinian Hamas movement, Saleh al-Aruri, at an undisclosed location in Lebanon. (Hezbollah’s Media Office/AFP via Getty Images)
“Not only do the Iraqi people not suffer because of this, the Iranian people aren’t going to suffer because of this,” Kirby added. “That allows for Iraq to be able to work its way off of Iranian energy so that they can keep the lights on.”
Schanzer countered the administration’s argument by noting that “as soon as [money] hits the system, it is going to be diverted or used in a cynical way,” even taking what humanitarian aid gets into the country through third-party vendors and reselling it to the civilian population, effectively laundering the assistance into money.
IRAN REJECTS ARGENTINA’S PUSH TO ARREST INTERIOR MINISTER FOR 1994 JEWISH CENTER BOMBING
“When we talk about dual-use goods or even things that they need in order to feed their fighters things along those lines, it is a consistently cynical diversion scheme,” Schanzer said. “Whether we’re talking about Iran itself or we’re talking about Iran’s proxies.”
“When the administration was saying that we shouldn’t be putting sanctions on the Houthis because it would ultimately block humanitarian assistance from getting into Yemen – guess what?” Schanzer continued. “When that humanitarian assistance gets to Yemen, who benefits? The people that control the territory in question, which right now a large chunk of Yemen is controlled by the Houthis.”
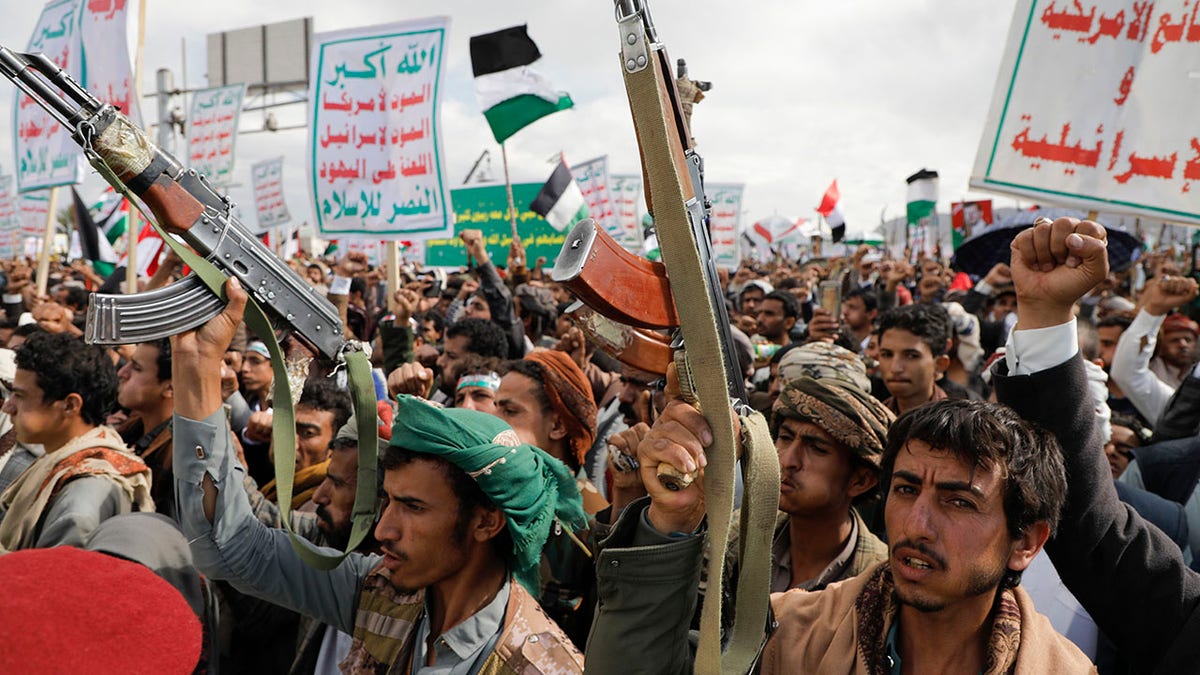

Houthi supporters attend a rally in Sanaa, Yemen, on March 8. (AP/Osamah Abdulrahman)
The New York Times in February published the results of an investigation that determined Iran had managed to sell “oil worth billions of dollars” thanks to “a significant gap in U.S. oversight.” Shipping vessels owned by shell companies and using “spoofing” methods to hide their location made dozens of trips throughout 2023 to ferry Iran’s oil under the sanctions.
The lack of a total crackdown on Iran’s oil shipments has led a significant number of experts to argue that the Biden administration may have started willfully turning a blind eye to Iran’s activities – partially since the surge in oil sales is clear and evident.
Javier Blas, a long-time energy and commodities reporter, wrote in a Bloomberg op-ed that “the conspiracy theorist inside me says the White House has turned a blind eye to the Iranian sales because it’s more worried about inflation … not only has Iran boosted oil production, but its exports have surged even more because it’s been able to sell a large chunk of the crude it was forced to put in the past into storage, both onshore and into tankers turned into floating storage facilities.”
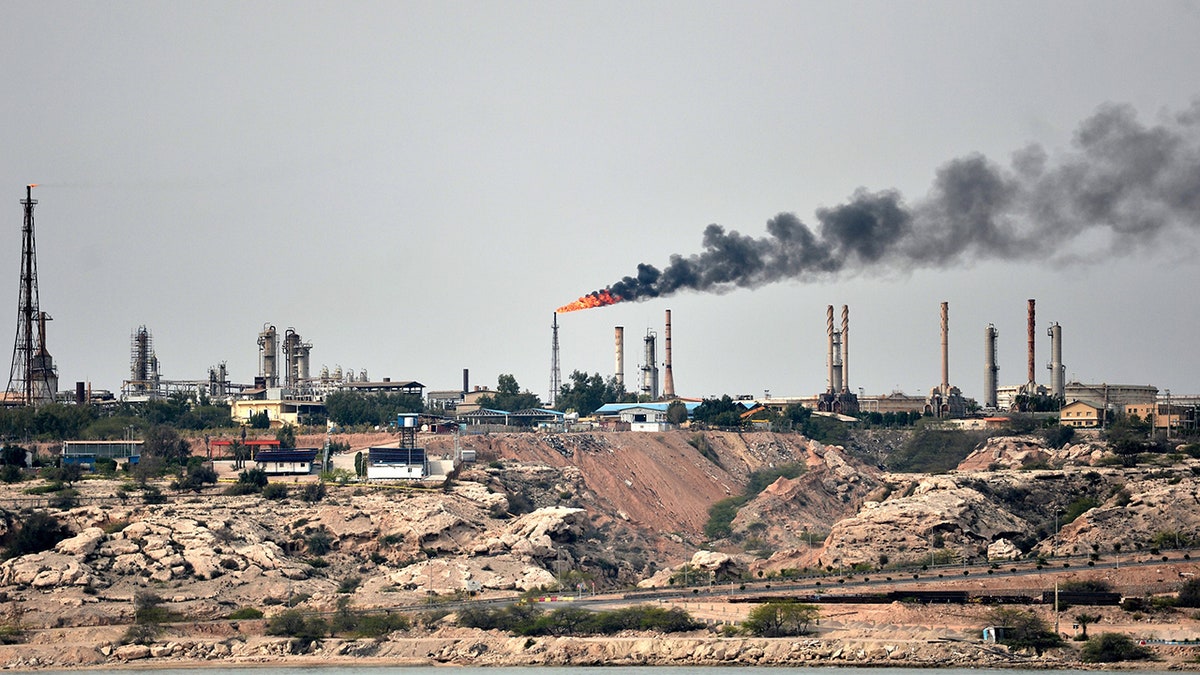

A general view of the Port of Kharg Island Oil Terminal, 25 kilometeres from the Iranian coast in the Persian Gulf and 483 kilometers northwest of the Strait of Hormuz, in Iran on March 12, 2017. (Fatemeh Bahrami/Anadolu Agency/Getty Images)
Iran’s growing cooperation with China also plays a significant role in how the country has managed to dodge sanctions, according to Foreign Policy, which cited a 25-year economic cooperation agreement the two countries agreed to in March 2021, as well as Iran’s decision to join the Beijing-led BRICS economic bloc, which gives Iran access to other currencies and trading options.
“There’s no question that Russia, China and others are working to provide assistance to the Iranians,” Schanzer claimed. “We know this to be the case, but, with the Russians and Chinese, it’s often done in trade or in arms purchases, oil … if they get remuneration in rubles or in RMB (Chinese Yuan) in trade surplus where they can cash in for other products that’s not the same as dollars, and it’s not the same as some of the goods that will come through American channels.”
Fox News Digital’s Caitlin McFall contributed to this report.
World
Ireland to begin sending asylum seekers back to the UK 'by end of May'
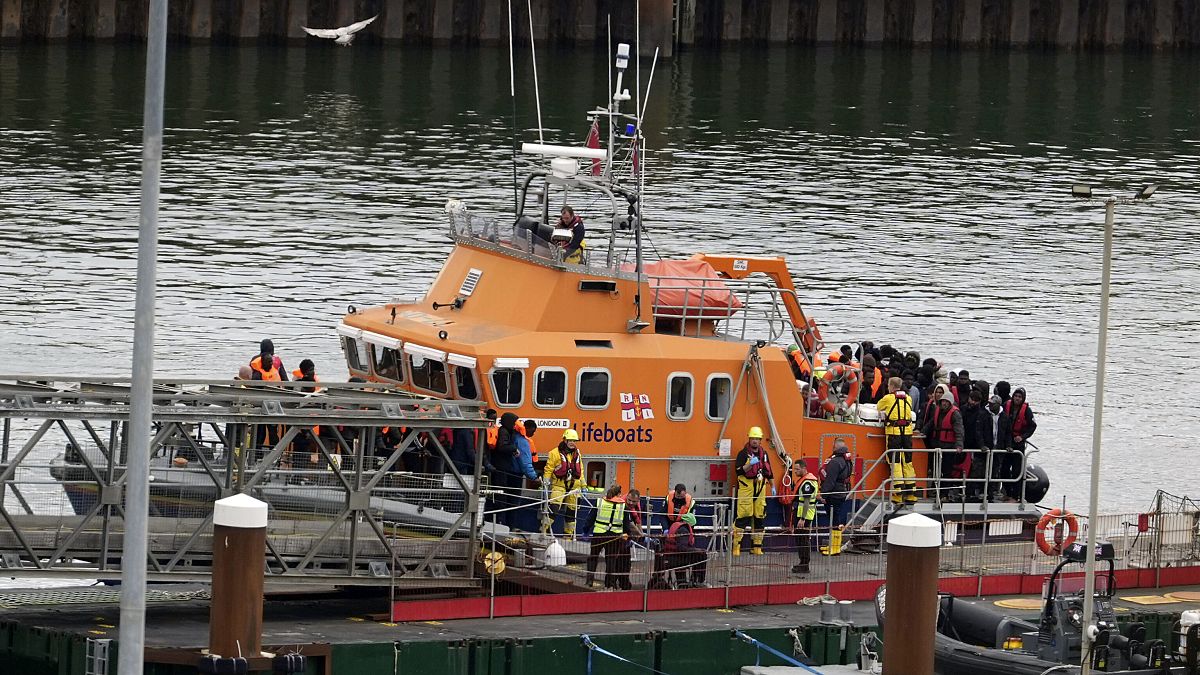

British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak say the increase in migrant numbers crossing over to Ireland proves that his controversial Rwanda policy is working.
The Irish government has said it is planning to enact legislation by the end of May that would allow it to resume sending asylum seekers who arrive over the border with Northern Ireland back to the United Kingdom.
Justice Minister Helen McEntee said the emergency legislation would allow for faster processing of migrants.
“This has never been a panacea when we talk about returns, the most effective way that we can have an immigration system that’s firm but fair is a fast processing system and what this means is that people’s applications are turned around much more quickly,” she said.
Ireland’s High Court ruled last month that Ireland could not send back people who arrive from the UK seeking asylum because the Irish government had not specified whether they would be at risk after their return.
Taoiseach Simon Harris said the legislation is about giving practical legal meaning to an agreement in place between the UK and Ireland since 2020.
Harris has urged Westminster to stand by the agreement, which allows asylum seekers to be returned in either direction.
Helen McEntee said that Ireland hadn’t returned anyone to the UK since 2020 as the agreement had been suspended during the coronavirus pandemic.
Immigration is an increasingly hot topic in Ireland, where asylum applications have been rising sharply.
British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak claims that the increase in migrants crossing over to Ireland proves that his controversial Rwanda policy, which aims to send some asylum seekers arriving in Britain on a one-way trip to the African country, is working.
Human rights activists and migrants’ groups call the policy unethical, inhumane and costly.
Irish officials estimate that more than 80% of arrivals into Ireland came via the land border with Northern Ireland, which is part of the UK.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Dozens of Yale Students Arrested as Campus Protests Spread
-
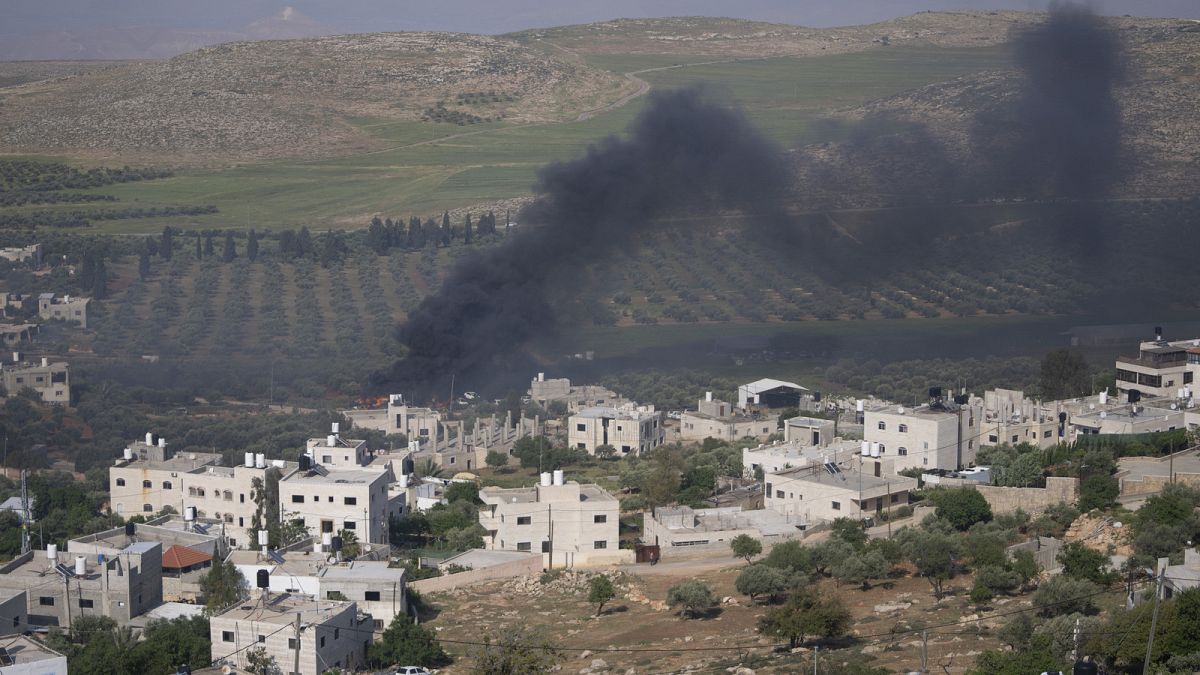

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoEU sanctions extremist Israeli settlers over violence in the West Bank
-
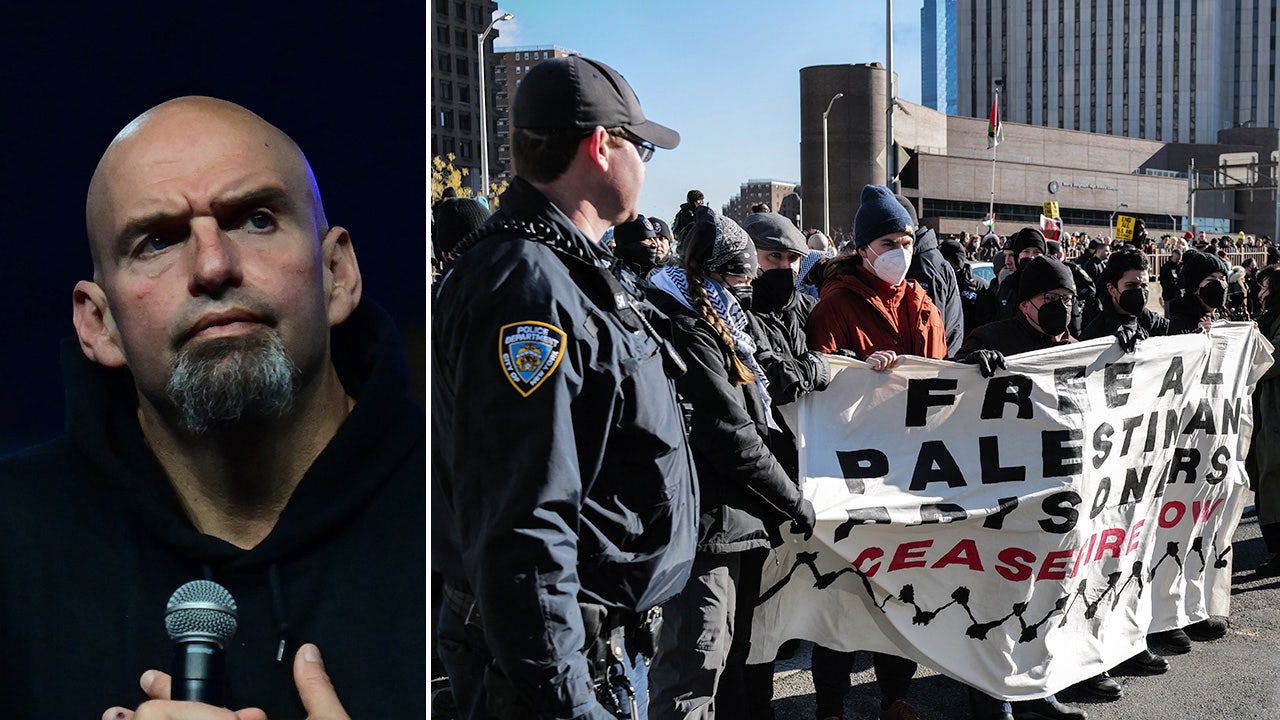

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFetterman hammers 'a–hole' anti-Israel protesters, slams own party for response to Iranian attack: 'Crazy'
-
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDemocrats hold major 2024 advantage as House Republicans face further chaos, division
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPeriod poverty still a problem within the EU despite tax breaks
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoA battle over 100 words: Judge tentatively siding with California AG over students' gender identification
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoShort Film Review: Wooden Toilet (2023) by Zuni Rinpoche
-

 World6 days ago
World6 days agoHaiti Prime Minister Ariel Henry resigns, transitional council takes power