Science
The Teacher in Room 1214

It was 45 seconds too late, but the teacher had a plan.
A gunman had just barraged her classroom with an AR-15, killing two students and injuring four others before turning to a classroom across the hall. The bullet-riddled walls were crumbling. Ceiling tiles were falling. If the shooter came back to kill more of her students, the teacher decided, she would stand up and shout, “We love you.”
The teacher was Ivy Schamis, whose husband would be waiting at home with a Valentine’s Day dinner; whose son was planning a wedding she couldn’t imagine missing; whose curriculum for this class — History of the Holocaust — had just moments earlier stirred a discussion about hate on campuses.
We love you. These would surely be her final words, Ms. Schamis thought. She knew her plan was futile — irrational, even. But with no stop-the-bleed kit, no shield, no help, words were all she had to show the children that an adult had put up a fight.
The moment never came. The gunman doubled back to the class across the hall, but not to Room 1214. At the command of a SWAT team, Ms. Schamis climbed over bodies and ran with her surviving students down the blood-smeared hallway, out the doors, and into the blinding light.
What waited for her there, in the days and months and years ahead, would be a whole new role in the lives of the 30 students who had survived. For them, she would be what she couldn’t be for the two who died: a lifeline.
She felt she owed them that. She had been the only adult in the room.
Attending to Her Students
The morning after the 2018 massacre at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Parkland, Fla., Ms. Schamis rose before dawn and began cleaning her bloodstained suede boots. Seventeen people had been killed, including Nick Dworet and Helena Ramsay, who had been in her class. Some of the surviving students had abandoned their blood- and glass-caked shoes on the school pavement, but Ms. Schamis had the strange feeling she ought to take hers home and wipe them down, over and over, until they came clean.
She left the boots out by the closet to dry and then phoned the moving company that was set to relocate her family to a new neighborhood in a few weeks. She no longer had time to pack boxes, she explained to the movers. She needed to attend to her students.
Within a few hours, Ms. Schamis was corresponding with her students by text. Today, she adamantly denies that she started the Room 1214 text thread, but everyone else seems to remember it that way. She used it to organize car pools to wakes and funerals, to check in on the wounded and to plan a meet-up at Cold Stone Creamery, just so everyone could be together.
When the school reopened two weeks later, Ms. Schamis was there, shuffling between campus buildings with a cart of teaching supplies. The school’s psychological support offerings for students included coloring books and Play-Doh. She found them useless. She arranged to instead have a service dog, Luigi, a golden retriever, join her classes for the rest of the year.
When Luigi arrived, tail wagging madly, students from throughout the school came to play with him — including some who had otherwise refused to return to campus. The following fall, Ms. Schamis arranged to have everyone from Room 1214 placed in her study hall for support.
Ms. Schamis had known some of the students for only six weeks before the shooting, but she seemed to have a preternatural sense of what each of them needed. Rebecca Bogart, who had been a senior, felt so lost after what she had witnessed that Ms. Schamis encouraged her to apply for a scholarship to go abroad to Ecuador. The physical distance finally gave her mental space from the event.
Ally Allen, who had watched the killer approach through a glass door panel, kept waking in the night with tears pouring down her face. When Ms. Schamis dropped a picture of a German shepherd puppy in the Room 1214 group chat — a future service dog, in need of a home — Ally felt deep down the dog was meant to be hers. She received Dakota the morning after the one-year anniversary of the shooting: a new beginning.
And Kelly Plaur, who had called 911 four times during the shooting, was at a music festival when the crowd began running from what sounded like gunshots. This time, it was Ms. Schamis she called. Keep calm, the teacher coached. Keep me on the phone, and keep running.
Students called and texted her with their grief, their panic attacks, their drug use, their suicidal thoughts. What their own parents could not fully understand — the worst moment of their lives — Ms. Schamis could.
One day, she took some of the students to meet with a survivor of the 1999 Columbine High School shooting in Colorado. His experience of being shot and watching a friend die was remarkably similar to theirs, and Ms. Schamis hoped that his journey toward healing would assure them that together, they could persevere.
But weeks later, Ms. Schamis’s phone began buzzing incessantly. It was the Room 1214 text thread. The Columbine survivor had died of an overdose.
Leaving Parkland
Ms. Schamis committed herself to staying at Marjory Stoneman Douglas until every surviving student from Room 1214 graduated in the spring of 2019. It was not easy. On her commute each morning, she had the same troubling premonition: her car plummeting off the expressway overpass. Finally, her husband, Jeff, suggested a daily ritual. When she approached the bridge, she was to call him to discuss something grounding and ordinary, like what they would have for dinner.
At the 2019 graduation ceremony, Ms. Schamis wept: Helena should have received a diploma. Ms. Schamis found Helena’s brother and hugged him, but Helena’s mother stood back. Ms. Schamis wondered what the woman felt seeing the teacher who had been with her daughter.
That fall, she took the semester off and then moved to Washington, D.C., forgoing her full pension in search of peace.
Washington was where Ms. Schamis truly began to mourn. She joined a two-year waiting list for therapy. She reached out to Ally Allen, whom she had referred to a breeder for a service dog, realizing for the first time she needed one of her own.
But two Parkland survivor charities she approached for financial aid to train a dog said they could not help her. As a teacher, she wasn’t entirely surprised: She didn’t recall a school administrator ever once checking in on her. She had never heard any school official admit that she had not received active shooter training, or that her classroom had no stop-the-bleed kit. And she had never been able to reclaim mementos of almost 20 years of teaching that remained inside Room 1214.
Ms. Schamis, who has a master’s degree in education and specialized in Holocaust studies, had spent almost her entire career at Marjory Stoneman Douglas. She had loved teaching social studies in part because it allowed her to watch students see themselves anew: As they made sense of current events in the context of history, she witnessed their opinions changing and their prejudices being renounced.
There was nothing more meaningful to her. But she could not return to another classroom.
So she took a job as an office manager at a small private school, accepting a major pay cut to avoid being in a classroom where she would again be responsible for students’ safety.
When she started, she discovered the office manager station was in the front foyer of the building — in a way, the first line of defense.
‘Always Available’
The students, too, scattered around the country, but the Room 1214 text thread bound them together. Over time, there were updates: Ally Allen, inspired by Ms. Schamis, was preparing to become a teacher. Hannah Carbocci was pursing a career in criminal justice and writing her thesis on warning signs in school shooters. Catie Krakow was getting a degree in mental health counseling and shared tips on how the others could care for themselves as another anniversary approached.
I hope everyone is doing as well as they could be, wrote Elena Blanco, who had been assigned to the seat behind Nick.
You guys are forever family, replied Matt Walker, whose desk had been next to Helena’s.
As long as I am breathing, Ms. Schamis told them, I will always be available for you.
A year later, soon after the Uvalde, Texas, shooting, Ms. Schamis woke up to a message on the thread that had landed during the night: Uvalde was one too many, a student wrote; he couldn’t take his anguish anymore.
Ms. Schamis had taken a suicide prevention course the summer after the massacre. She knew the steps. She called the former student, asking if he had a specific plan to end his life. He did. She kept him engaged with questions — what was something he was looking forward to? — while she sought emergency help for him from five states away.
She spent the next five hours in a maze of dead ends. She tried the suicide hotline, but they could not help her, since she was not the person in distress. She did a 40-minute intake call with a Florida behavioral health center, only to learn they did not serve his region. She connected with a mental health hospital, but it turned out to be private. By now, she was weeping.
Eventually she reached the instructor of her suicide prevention class from all those years ago, who told her to call the West Palm Beach Police Department and explain that the distressed young man was a survivor of Parkland’s school shooting.
The boy ultimately received emergency care and survived. But not before the dispatcher who answered Ms. Schamis’s call admitted that with all the school shootings, she could not specifically recall what happened in Parkland.
‘That’s My Girl.’
Four years after the shooting, a process server arrived at Ms. Schamis’s home with a subpoena calling on her to testify at the killer’s sentencing trial. Ms. Schamis hid.
The text thread began to buzz with messages from former students who would also be required to appear. Ms. Schamis reverted to her usual role. I’m with you as you testify, she wrote.
Daniela Menescal, who had gone on to study psychology in Boston and still had shrapnel embedded in her leg and back, was distressed about going alone.
I’ll ask if I can be with you, Ms. Schamis told Daniela.
As the sun rose on a Wednesday morning, she texted the group that it was her turn. Dylan Kraemer, who had already taken the stand, replied fast.
You got this! If you look straight when u testify, he wrote, you can’t see the shooter.
On the witness stand, Ms. Schamis spoke with the tone of a teacher in front of a class, nodding for emphasis and gesturing around the room. Her gold necklace glimmered under the lights as she described the layout of Room 1214, the lesson she had been teaching, the first deafening blasts.
Her eyes trailed over to the defense table. There he was, the man who had stolen Nick’s chance to swim at the Olympics; who had robbed Helena of her plans to attend college in England.
The killer kept his head down. The prosecutor, Mike Satz, brought over a photograph, Exhibit 3S, and asked Ms. Schamis to name the subject.
“That’s my girl,” she said, putting her hand over her mouth, her voice cracking. “Helena. Helena Ramsay.”
Then he brought over another, Exhibit 3R.
“And that’s Nicholas Dworet,” she said. “Handsome boy.”
Parents in the courtroom shifted in their seats. Others shook their heads. Ms. Schamis looked up to the ceiling, blinking the tears from her eyes, patting her cheeks with a tissue and adjusting her glasses back on her nose where they had been.
Hannah Carbocci — watching the trial live from home — knew her teacher wouldn’t see the group chat until later, but she sent an encouraging message anyway: Mrs Schamis you’re a rockstar, she wrote.
There were no further questions, the lawyer in the courtroom said.
Ms. Schamis climbed down from the stand. That afternoon, she typed a response in the thread: Love you so.
A Demolition
As the sixth anniversary of the shooting approached last year, Lexi Gendron was struggling. She had tried to go to college, but like many of the others, found herself too preoccupied with classroom seating arrangements to focus. She couldn’t have her back to the door, but facing it meant watching for a killer.
After one class, she dropped out, instead working at a casino and a winery before moving to Texas. Now, she was about to start nursing school in hopes of a career in pediatrics — which meant returning to a classroom once again.
Just spilling my heart out, she wrote on the thread one night. Lexi had thrown away all her #MSDStrong memorabilia in search of a fresh start in Texas — only to realize that those tangible objects had been her puzzle pieces to a day that had never fully sunk in.
I’m so upset with myself for letting that stuff go, she wrote. I can’t believe I did that.
Ms. Schamis was the first to reply, offering to send T-shirts, bracelets, buttons and pins. Let me know whatever will make you feel better, she wrote.
She understood the pull of Parkland. When the school’s 1200 building was set to be demolished, Ms. Schamis had reached out to the school board, desperate to return to her classroom one more time. The jury, bereaved parents, journalists, and even Vice President Kamala Harris were granted permission to enter the building, but Ms. Schamis was not. Instead, prosecutors sent a package to her home in Washington: a five-year-old box of stale Valentine’s Day chocolates from her desk in Room 1214.
On the morning the demolition was set to begin, Ms. Schamis heard a radio segment as she drove to her new school in Washington. Bereaved families in Parkland were cathartically hammering off bits of the school building before the team came in to clear it away.
Ms. Schamis, shaking, called Jeff. They discussed the weather.
Her last mental image of her own classroom comes from a press pool report in which strangers described the artifacts left inside her fourth-period Holocaust class: a 2017-18 school year planner; a whiteboard bearing Ms. Schamis’s learning objective, “to be aware of the world and its surroundings”; bullet strike marks across the desks; and the dried blood of Nick and Helena coating a book titled “Tell Them We Remember.”
‘The only adult in there.’
Last summer, Ms. Schamis sat on the patio of a Mexican restaurant in Washington, recounting that day in 2018. Her German shepherd, Sayde, sprawled beneath her chair. All these years later, she still seemed uneasy. “That’s what keeps me up at night, thinking I was the only adult in there,” she said.
Jeff sat across from her. He reminded her of the bonds she had forged with her students: the pancake breakfasts at their place; the letters of recommendation for graduate schools; the tattoos that several had gotten — Room 1214 — including one who had it drawn in Ms. Schamis’s handwriting.
“But I didn’t save them — I didn’t save them,” she said. Her words hung in the air, jarring against the faint mariachi music coming through the patio speakers.
Jeff leaned forward and said with a seasoned assurance, “How could anybody save somebody from an AR-15?”

Science
Federal EPA moves to roll back recent limits on ethylene oxide, a carcinogen

The Trump administration on Friday moved to roll back Biden-era limits on emissions of ethylene oxide, a cancer-causing chemical often used in the sterilization of medical devices.
The Environmental Protection Agency said repealing the rules, which fall under the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants, would “safeguard the supply of essential medical equipment” — saving approximately $630 million for companies over 20 years. California is home to about a dozen such facilities.
The government said the pollution is an inevitable part of protecting people from “lethal or significantly debilitating infections that would result without properly sterilized medical equipment,” arguing that the technology does not readily exist to meet the more stringent rules.
“The Trump EPA is committed to ensuring life-saving medical devices remain available for the critical care of America’s children, elderly, and all patients without unnecessary exposure to communities,” EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin said in a statement.
Supporters of the Biden rule reject that argument and say companies could have complied using existing technology and that the public was not at risk of losing sterilized equipment.
An estimated 50% of sterile medical devices in the U.S. are treated with ethylene oxide, or EtO, particularly those that can’t be cleaned using steam or radiation. The colorless gas is also used to make chemicals found in products such as antifreeze, detergents, plastics and adhesives.
EtO poses health risks. Short-term exposure by inhalation can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, fatigue respiratory irritation and other adverse health effects, according to the federal Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
Longer-term exposure increases the risk of cancers of the white blood cells, such as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, as well as breast cancer. A now-deleted page from the EPA’s website stated, “EtO is a human carcinogen. It causes cancer in humans.”
Friday’s proposal specifically targets updated rules for EtO emissions that were passed by the Biden administration in 2024 following pressure from environmental justice groups, particularly those in Louisiana’s heavily industrialized “Cancer Alley.” The change sought to reduce the amount of EtO released from commercial sterilizers by 90% and lessen the hazards for nearby communities.
The tighter rules were in part based on EPA’s own scientific study that found it to be 60 times more carcinogenic than previously thought, which the agency now says should be reassessed.
If finalized, the plan would give facilities a choice between installing continuous real-time monitoring systems for EtO emissions or complying with modified pollution control requirements at facilities that emit more than 10 tons a year, the EPA said.
The proposal follows other moves by the Trump administration to rescind regulations it says are burdensome and costly for industries, such as those governing emissions from coal power plants. Last month, the EPA repealed the endangerment finding, which affirmed the dangers of greenhouse gas emissions and underpinned the agency’s ability to regulate those emissions from vehicles.
The action around ethylene oxide would affect about 90 commercial sterilization facilities owned and operated by approximately 50 companies. Three California companies applied for and received presidential exemptions for their EtO emissions in July.
The Sterigenics facility, center, in Vernon is pictured in 2022.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
They are located in Ontario and Vernon and operated by the company Sterigenics, which provides industrial sterilization technology for medical devices and other commercial products.
In January, a coalition of environmental and community groups challenged the EtO exemptions in federal court. The lawsuit from the Southern Environmental Law Center and the Natural Resources Defense Council argues that technology exists for facilities to comply with the tighter Biden-era standards without raising costs, and many facilities are already using it.
“EPA’s 2024 rule was an important and overdue step to reduce toxic ethylene oxide pollution and protect communities,” said Irena Como, senior attorney at the Southern Environmental Law Center, in a statement Friday. “Repealing this rule that is proven to significantly lower pollution exposure and cancer risks will subject even more people who work, live, and send their children to schools located near these facilities to harm that is entirely preventable.”
Sterilization and chemical industry groups support the plan.
“The EPA rule concerning ethylene oxide use in commercial sterilizers threatens to severely restrict access to vital medical products nationwide,” the American Chemistry Council said in a statement. “We commend the EPA for their commitment to reevaluating these policies.”
The EPA will hold a 45-day comment period about the proposal after it is published in the federal register. A final decision is expected sometime this year.
Science
H5N1 bird flu spreads to sea otters and sea lions along San Mateo coast, wildlife experts say

Researchers say the H5N1 bird flu outbreak in California elephant seals has spread to other marine mammals, including a sea otter and sea lion.
However, wildlife officials are cautiously optimistic the outbreak will remain contained. It has so far only been detected on beaches in San Mateo County, although testing is being conducted along the coastline.
The strain the animals have contains a mutation allowing it to more easily transmit between mammals. It is also a different variation than the ones found in dairy cows and commercial poultry. This one is Eurasian in origin, first seen in 2022. It has been detected in birds that fly along the Pacific Flyway, and is responsible for a mass mortality event in 2023 in northern fur seals on an island in eastern Russia, said Christine Johnson, director of UC Davis’ Center for Pandemic Insights, during a press conference Thursday morning.
Johnson said researchers think this is the first detection of the A3 variation of the virus on the Pacific Coast and therefore likely a new introduction into North America, she said.
In late February, a team of researchers from UC Davis, UC Santa Cruz, the California Department of Fish and Wildlife and the Marine Mammal Center announced they had found the virus in seven dead elephant seal pups collected from the beach at Año Nuevo State Park. That number is now 16, but Johnson said likely more will be confirmed in the weeks to come.
“This count reflects only the animals that have gone through sampling and confirmatory testing in multiple labs,” she said. “We know there are more animals with signs of infection that we have sampled that are being tested across the different laboratory systems.”
She said no other otters have been found, but a “handful” of California sea lions are “in the queue.” This kind of spillover, she said, is not unusual.
“Outbreaks affect a wide range of birds and mammals, and these animals all share the near shore ecosystem,” she said, although it’s “especially tragic” when infections affect less common species in the southern sea otter.
Patrick Robinson, the Año Nuevo reserve director, and a marine biologist at UC Santa Cruz, said 47 elephant seals on the mainland have died since the outbreak began, and the wildlife team is finding two new symptomatic and two dead animals every day.
Symptoms of bird flu in mammals include tremors, convulsions, seizures and muscle weakness.
He said it is normal for some individuals to die of natural causes, so testing is critical. And he said the percentage of animals that have died in the Año Nuevo rookery is relatively small: Only about 5% of weaned pups and 6% of adult males have died. Still, in the case of pups, that’s four times higher than last year’s death rates. And he said, the death of large males is “basically nonexistent in most males.”
He said 80% of the adult females had departed by the time the outbreak began, and nearly all of them are now gone. No adult females have died, and none have been observed with symptoms.
“The outbreak is not over, and we’re not really sure what’s going to happen in the future,” he said. “I remain hopeful about this thing right now.”
In late 2022, the H5N1 bird flu virus decimated southern elephant seal populations in South America and several sub-Antarctic Islands. At some colonies in Argentina, 97% of pups died, while on South Georgia Island, researchers reported a 47% decline in breeding females between 2022 and 2024. Researchers believe tens of thousands of animals died.
More than 30,000 sea lions in Peru and Chile died between 2022 and 2024. In Argentina, roughly 1,300 sea lions and fur seals perished.
At the time, researchers were not sure why northern Pacific populations were not infected, but suspected previous or milder strains of the virus conferred some immunity.
The virus is better known in the U.S. for sweeping through dairy herds, where it infected dozens of dairy workers, millions of cows and thousands of wild, feral and domestic mammals. It’s also been found in wild birds and killed millions of commercial chickens, geese and ducks.
Two Americans have died from the virus since 2024, and 71 have been infected. The vast majority of infected people were dairy or commercial poultry workers. One death was that of a Louisiana man who had underlying conditions and was believed to have been exposed via backyard poultry or wild birds.
Science
Nearly 40% of California produce contains PFAS pesticides, report finds
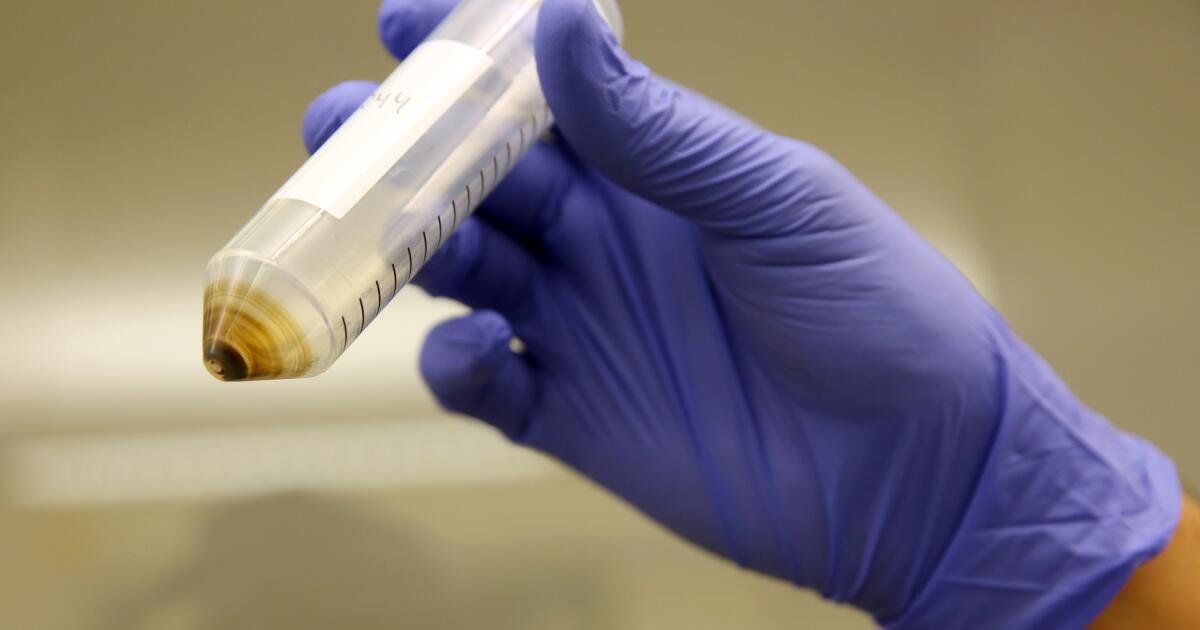
A new report shows that nearly 40% of conventionally grown fruits and vegetables tested by California regulators have residues of “forever” or PFAS chemicals, a family of compounds that can be lasting and harmful.
The Environmental Working Group, an advocacy group based in Washington, D.C., reviewed California’s own test data and found PFAS pesticide residues on peaches, grapes and strawberries, and about three dozen other types of fruits and vegetables.
The chemicals have have increasingly been used in agricultural chemicals in recent years.
“Here’s the thing: This is an emerging threat,” said Nathan Donley, environmental health science director for the Center for Biological Diversity, who was not involved in the report. “PFAS pesticides went from being the exception to now they’re the rule.”
More than 90% of nectarine, peach and plum samples tested contained the PFAS fungicide fludioxonil. The fungicide is sprayed on the fruits after harvest to prevent mold. More than 80% of the cherries, strawberries and grapes sampled carried PFAS residue.
The group relied on data collected in 2023 by California’s Department of Pesticide Regulation, a branch of CalEPA.
There are thousands of PFAS chemicals used in consumer products, electronics, pharmaceuticals and pesticides. They are prized by product manufacturers for their strength, persistence and water resistance. However, many are considered highly toxic, even at very low levels. They’ve been linked to immune suppression, cancer and reproductive and developmental health disruptions and toxicity. They’ve also been linked to ecosystem damage, harming aquatic animals and wildlife.
The vast majority of PFAS chemicals have not been tested for human health effects.
“At a time when most industries are transitioning away from PFAS chemicals, the pesticide industry is actually doubling down on them,” said Donley, who has published papers on the issue. “I think that the persistence of these chemicals is certainly playing a role” in why industries find them desirable, he said.
“But then again, you get a whole heck of a lot more collateral damage when you have a pesticide that sticks around as long as DDT does,” he said.
Regulators say that not all PFAS chemicals are the same. While some can persist for thousands of years, others break down much more quickly. They also say the ones used in approved pesticides are vetted for human health impacts, as well as ecosystem impacts — such as how they could affect pollinators, aquatic organisms and other wildlife. There are also strict usage requirements that limit the amount of chemicals applied to food, they say.
“Before any pesticide can be sold or used in California, DPR (Department of Pesticide Regulation) conducts a thorough scientific review. This includes evaluating both the active ingredients and full product formulations to understand how long the chemicals remain in the environment and how they break down, which is a key concern for PFAS compounds,” said Amy MacPherson, a spokeswoman for the pesticide agency.
In addition, she said, while the report looks at “detections” of PFAS chemicals, her agency “looks at how those detections compare to federal tolerance levels.”
She said this is important because “detection alone … does not necessarily mean there’s a health risk. Tolerance levels consider lifelong, daily exposure that pose a reasonable certainty of no harm, inclusive of chronic risk.”
Varun Subramaniam, a co-author of the report and a health data specialist with the Environmental Working Group, said he focused on California for two reasons: California’s pesticide department is one of the few, if not only, state agencies to do this kind of testing; and the state is one of the nation’s largest producers of fruits and vegetables.
“Things that are grown in California tend to spread across the country,” said Subramaniam, who is working on a national report documenting the use of these pesticides. “We thought California was a good starting point.”
Roughly 70 PFAS pesticides are registered with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, accounting for about 14% of all active pesticide ingredients. California has registered 53 PFAS pesticides.
According to the report, about 2.5 million pounds of PFAS pesticides are applied annually on California cropland.
Both Subramaniam and Donley said states such as Maine, Rhode Island, Minnesota and North Carolina are “way ahead” of California in considering the harm these chemicals pose to people and ecosystems, and are trying to ban them.
“These chemicals are really top of mind in the East Coast, especially in New England states where … this story has been going on for decades,” he said.
Subramaniam said people should wash their produce before eating, and opt for organic fruits and vegetables when they can — organic farmers cannot use these chemicals on their produce.
-

 Detroit, MI1 week ago
Detroit, MI1 week agoU.S. Postal Service could run out of money within a year
-

 Miami, FL1 week ago
Miami, FL1 week agoCity of Miami celebrates reopening of Flagler Street as part of beautification project
-

 Pennsylvania1 week ago
Pennsylvania1 week agoPa. man found guilty of raping teen girl who he took to Mexico
-
Oklahoma6 days ago
OSSAA unveils Class 6A-2A basketball state tournament brackets, schedule
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoKeith Olbermann under fire for calling Lou Holtz a ‘scumbag’ after legendary coach’s death
-

 Michigan5 days ago
Michigan5 days agoOperation BBQ Relief helping with Southwest Michigan tornado recovery
-

 Southeast4 days ago
Southeast4 days ago‘90 Day Fiancé’ alum’s boyfriend on trial for attempted murder over wild ‘Boca Bash’ accusations
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoAncient herb known as ‘nature’s Valium’ touted for improving sleep and anxiety
























