Science
Opinion: America's 'big glass' dominance hangs on the fate of two powerful new telescopes
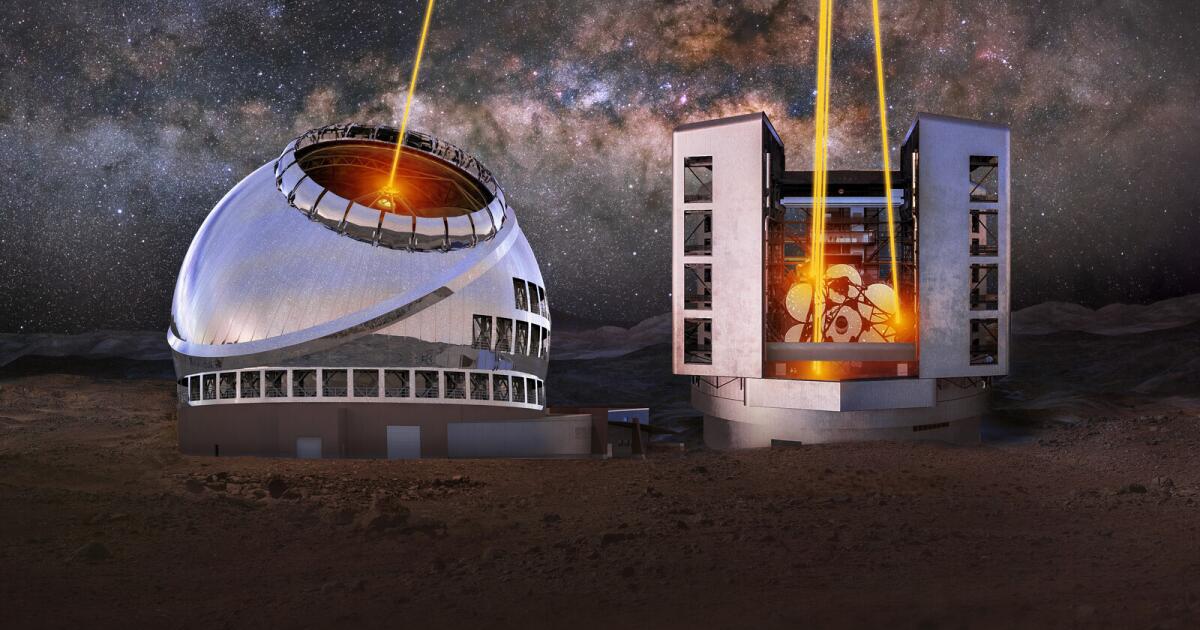
More than 100 years ago, astronomer George Ellery Hale brought our two Pasadena institutions together to build what was then the largest optical telescope in the world. The Mt. Wilson Observatory changed the conception of humankind’s place in the universe and revealed the mysteries of the heavens to generations of citizens and scientists alike. Ever since then, the United States has been at the forefront of “big glass.”
In fact, our institutions, Carnegie Science and Caltech, still help run some of the largest telescopes for visible-light astronomy ever built.
But that legacy is being threatened as the National Science Foundation, the federal agency that supports basic research in the U.S., considers whether to fund two giant telescope projects. What’s at stake is falling behind in astronomy and cosmology, potentially for half a century, and surrendering the scientific and technological agenda to Europe and China.
In 2021, the National Academy of Sciences released Astro2020. This report, a road map of national priorities, recommended funding the $2.5-billion Giant Magellan Telescope at the peak of Cerro Las Campanas in Chile and the $3.9-billion Thirty Meter Telescope at Mauna Kea in Hawaii. According to those plans, the telescopes would be up and running sometime in the 2030s.
NASA and the Department of Energy backed the plan. Still, the National Science Foundation’s governing board on Feb. 27 said it should limit its contribution to $1.6 billion, enough to move ahead with just one telescope. The NSF intends to present their process for making a final decision in early May, when it will also ask for an update on nongovernmental funding for the two telescopes. The ultimate arbiter is Congress, which sets the agency’s budget.
America has learned the hard way that falling behind in science and technology can be costly. Beginning in the 1970s, the U.S. ceded its powerful manufacturing base, once the nation’s pride, to Asia. Fast forward to 2022, the U.S. government marshaled a genuine effort toward rebuilding and restarting its factories — for advanced manufacturing, clean energy and more — with the Inflation Reduction Act, which is expected to cost more than $1 trillion.
President Biden also signed into law the $280-billion CHIPS and Science Act two years ago to revive domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors — which the U.S. used to dominate — and narrow the gap with China.
As of 2024, America is the unquestioned leader in astronomy, building powerful telescopes and making significant discoveries. A failure to step up now would cede our dominance in ways that would be difficult to remedy.
The National Science Foundation’s decision will be highly consequential. Europe, which is on the cusp of overtaking the U.S. in astronomy, is building the aptly named Extremely Large Telescope, and the United States hasn’t been invited to partner in the project. Russia aims to create a new space station and link up with China to build an automated nuclear reactor on the moon.
Although we welcome any sizable grant for new telescope projects, it’s crucial to understand that allocating funds sufficient for just one of the two planned telescopes won’t suffice. The Giant Magellan and the Thirty Meter telescopes are designed to work together to create capabilities far greater than the sum of their parts. They are complementary ground stations. The GMT would have an expansive view of the southern hemisphere heavens, and the TMT would do the same for the northern hemisphere.
The goal is “all-sky” observation, a wide-angle view into deep space. Europe’s Extremely Large Telescope won’t have that capability. Besides boosting America’s competitive edge in astronomy, the powerful dual telescopes, with full coverage of both hemispheres, would allow researchers to gain a better understanding of phenomena that come and go quickly, such as colliding black holes and the massive stellar explosions known as supernovas. They would put us on a path to explore Earth-like planets orbiting other suns and address the question: “Are we alone?”
Funding both the GMT and TMT is an investment in basic science research, the kind of fundamental work that typically has led to economic growth and innovation in our uniquely American ecosystem of scientists, investors and entrepreneurs.
Elon Musk’s SpaceX is the most recent example, but the synergy goes back decades. Basic science at the vaunted Bell Labs, in part supported by taxpayer contributions, was responsible for the transistor, the discovery of cosmic microwave background and establishing the basis of modern quantum computing. The internet, in large part, started as a military communications project during the Cold War.
Beyond its economic ripple effect, basic research in space and about the cosmos has played an outsized role in the imagination of Americans. In the 1960s, Dutch-born American astronomer Maarten Schmidt was the first scientist to identify a quasar, a star-like object that emits radio waves, a discovery that supported a new understanding of the creation of the universe: the Big Bang. The first picture of a black hole, seen with the Event Horizon Telescope, was front-page news in 2019.
We understand that competing in astronomy has only gotten more expensive, and there’s a need to concentrate on a limited number of critical projects. But what could get lost in the shuffle are the kind of ambitious projects that have made America the scientific envy of the world, inspiring new generations of researchers and attracting the best minds in math and science to our colleges and universities.
Do we really want to pay that price?
Eric D. Isaacs is the president of Carnegie Science, prime backer of the Giant Magellan Telescope. Thomas F. Rosenbaum is president of Caltech, key developer of the Thirty Meter Telescope.

Science
A virus without a vaccine or treatment is hitting California. What you need to know

A respiratory virus that doesn’t have a vaccine or a specific treatment regimen is spreading in some parts of California — but there’s no need to sound the alarm just yet, public health officials say.
A majority of Northern California communities have seen high concentrations of human metapneumovirus, or HMPV, detected in their wastewater, according to data from the WastewaterScan Dashboard, a public database that monitors sewage to track the presence of infectious diseases.
A Los Angeles Times data analysis found the communities of Merced in the San Joaquin Valley, and Novato and Sunnyvale in the San Francisco Bay Area have seen increases in HMPV levels in their wastewater between mid-December and the end of February.
HMPV has also been detected in L.A. County, though at levels considered low to moderate at this point, data show.
While HMPV may not necessarily ring a bell, it isn’t a new virus. Its typical pattern of seasonal spread was upended by the COVID-19 pandemic, and its resurgence could signal a return to a more typical pre-coronavirus respiratory disease landscape.
Here’s what you need to know.
What is HMPV?
HMPV was first detected in 2001, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s transmitted by close contact with someone who is infected or by touching a contaminated surface, said Dr. Neha Nanda, chief of infectious diseases and hospital epidemiologist for Keck Medicine of USC.
Like other respiratory illnesses, such as influenza, HMPV spreads and is more durable in colder temperatures, infectious-disease experts say.
Human metapneumovirus cases commonly start showing up in January before peaking in March or April and then tailing off in June, said Dr. Jessica August, chief of infectious diseases at Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa.
However, as was the case with many respiratory viruses, COVID disrupted that seasonal trend.
Why are we talking about HMPV now?
Before the pandemic hit in 2020, Americans were regularly exposed to seasonal viruses like HMPV and developed a degree of natural immunity, August said.
That protection waned during the pandemic, as people stayed home or kept their distance from others. So when people resumed normal activities, they were more vulnerable to the virus. Unlike other viruses, there isn’t a vaccine for human metapneumovirus.
“That’s why after the pandemic we saw record-breaking childhood viral illnesses because we lacked the usual immunity that we had, just from lack of exposure,” August said. “All of that also led to longer viral seasons, more severe illness. But all of these things have settled down in many respects.”
In 2024, the national test positivity for HMPV peaked at 11.7% at the end of March, according to the National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System. The following year’s peak was 7.15% in late April.
So far this year, the highest test positivity rate documented was 6.1%, reported on Feb. 21 — the most recent date for which complete data are available.
While the seasonal spread of viruses like HMPV is nothing new, people became more aware of infectious diseases and how to prevent them during the pandemic, and they’ve remained part of the public consciousness in the years since, August and Nanda said.
What are the symptoms of HMPV?
Most people won’t go to the doctor if they have HMPV because it typically causes mild, cold-like symptoms that include cough, fever, nasal congestion and sore throat.
HMPV infection can progress to:
- An asthma attack and reactive airway disease (wheezing and difficulty breathing)
- Middle ear infections behind the ear drum
- Croup, also known as “barking” cough — an infection of the vocal cords, windpipe and sometimes the larger airways in the lungs
- Bronchitis
- Fever
Anyone can contract human metapneumovirus, but those who are immunocompromised or have other underlying medical conditions are at particular risk of developing severe disease — including pneumonia. Young children and older adults are also considered higher-risk groups, Nanda said.
What is the treatment for HMPV?
There is no specified treatment protocol or antiviral medication for HMPV. However, it’s common for an infection to clear up on its own and treatment is mostly geared toward soothing symptoms, according to the American Lung Assn.
A doctor will likely send you home and tell you to rest and drink plenty of fluids, Nanda said.
If symptoms worsen, experts say you should contact your healthcare provider.
How to avoid contracting HMPV
Infectious-disease experts said the best way to avoid contracting HMPV is similar to preventing other respiratory illnesses.
The American Lung Assn.’s recommendations include:
- Wash your hands often with soap and water. If that’s not available, clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Clean frequently touched surfaces.
- Crack open a window to improve air flow in crowded spaces.
- Avoid being around sick people if you can.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth.
Assistant data and graphics editor Vanessa Martínez contributed to this report.
Science
After rash of overdose deaths, L.A. banned sales of kratom. Some say they lost lifeline for pain and opioid withdrawal

Nearly four months ago, Los Angeles County banned the sale of kratom, as well as 7-OH, the synthetic version of the alkaloid that is its active ingredient. The idea was to put an end to what at the time seemed like a rash of overdose deaths related to the drug.
It’s too soon to tell whether kratom-related deaths have dissipated as a result — or, really, whether there was ever actually an epidemic to begin with. But many L.A. residents had become reliant on kratom as something of a panacea for debilitating pain and opioid withdrawal symptoms, and the new rules have made it harder for them to find what they say has been a lifesaving drug.
Robert Wallace started using kratom a few years ago for his knees. For decades he had been in pain, which he says stems from his days as a physical education teacher for the Glendale Unified School District between 1989 and 1998, when he and his students primarily exercised on asphalt.
In 2004, he had arthroscopic surgery on his right knee, followed by varicose vein surgery on both legs. Over the next couple of decades, he saw pain-management specialists regularly. But the primary outcome was a growing dependence on opioid-based painkillers. “I found myself seeking doctors who would prescribe it,” he said.
He leaned on opioids when he could get them and alcohol when he couldn’t, resulting in a strain on his marriage.
When Wallace was scheduled for his first knee replacement in 2021 (he had his other knee replaced a few years later), his brother recommended he take kratom for the post-surgery pain.
It seemed to work: Wallace said he takes a quarter of a teaspoon of powdered kratom twice a day, and it lets him take charge of managing his pain without prescription painkillers and eases harsh opiate-withdrawal symptoms.
He’s one of many Angelenos frustrated by recent efforts by the county health department to limit access to the drug. “Kratom has impacted my life in only positive ways,” Wallace told The Times.
For now, Wallace is still able to get his kratom powder, called Red Bali, by ordering from a company in Florida.
However, advocates say that the county crackdown on kratom could significantly affect the ability of many Angelenos to access what they say is an affordable, safer alternative to prescription painkillers.
Kratom comes from the leaves of a tree native to Southeast Asia called Mitragyna speciosa. It has been used for hundreds of years to treat chronic pain, coughing and diarrhea as well as to boost energy — in low doses, kratom appears to act as a stimulant, though in higher doses, it can have effects more like opioids.
Though advocates note that kratom has been used in the U.S. for more than 50 years for all sorts of health applications, there is limited research that suggests kratom could have therapeutic value, and there is no scientific consensus.
Then there’s 7-OH, or 7-Hydroxymitragynine, a synthetic alkaloid derived from kratom that has similar effects and has been on the U.S. market for only about three years. However, because of its ability to bind to opioid receptors in the body, it has a higher potential for abuse than kratom.
Public health officials and advocates are divided on kratom. Some say it should be heavily regulated — and 7-OH banned altogether — while others say both should be accessible, as long as there are age limitations and proper labeling, such as with alcohol or cannabis.
In the U.S., kratom and 7-OH can be found in all sorts of forms, including powder, capsules and liquids — though it depends on exactly where you are in the country. Though the Food and Drug Administration has recommended that 7-OH be included as a Schedule 1 controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act, that hasn’t been made official. And the plant itself remains unscheduled on the federal level.
That has left states, counties and cities to decide how to regulate the substances.
California failed to approve an Assembly bill in 2024 that would have required kratom products to be registered with the state, have labeling and warnings, and be prohibited from being sold to anyone younger than 21.
It would also have banned products containing synthetic versions of kratom alkaloids. The state Legislature is now considering another bill that basically does the same without banning 7-OH — while also limiting the amount of synthetic alkaloids in kratom and 7-OH products sold in the state.
“Until kratom and its pharmacologically active key ingredients mitragynine and 7-OH are approved for use, they will remain classified as adulterants in drugs, dietary supplements and foods,” a California Department of Public Health spokesperson previously told The Times.
On Tuesday, California Gov. Gavin Newsom announced that the state’s efforts to crack down on kratom products has resulted in the removal of more than 3,300 kratom and 7-OH products from retail stores. According to a news release from the governor’s office, there has been a 95% compliance rate from businesses in removing the products.
(Los Angeles Times photo illustration; source photos by Getty Images)
Newsom has equated these actions to the state’s efforts in 2024 to quash the sale of hemp products containing cannabinoids such as THC. Under emergency state regulations two years ago, California banned these specific hemp products and agents with the state Department of Alcoholic Beverage Control seized thousands of products statewide.
Since the beginning of 2026, there have been no reported violations of the ban on sales of such products.
“We’ve shown with illegal hemp products that when the state sets clear expectations and partners with businesses, compliance follows,” Newsom said in a statement. “This effort builds on that model — education first, enforcement where necessary — to protect Californians.”
Despite the state’s actions, the Los Angeles County Board of Supervisors is still considering whether to regulate kratom, or ban it altogether.
The county Public Health Department’s decision to ban the sale of kratom didn’t come out of nowhere. As Maral Farsi, deputy director of the California Department of Public Health, noted during a Feb. 18 state Senate hearing, the agency “identified 362 kratom-related overdose deaths in California between 2019 and 2023, with a steady increase from 38 in 2019 up to 92 in 2023.”
However, some experts say those numbers aren’t as clear-cut as they seem.
For example, a Los Angeles Times investigation found that in a number of recent L.A. County deaths that were initially thought to be caused by kratom or 7-OH, there wasn’t enough evidence to say those drugs alone caused the deaths; it might be the case that the danger is in mixing them with other substances.
Meanwhile, the actual application of this new policy seems to be piecemeal at best.
The county Public Health Department told The Times it conducted 2,696 kratom-related inspections between Nov. 10 and Jan. 27, and found 352 locations selling kratom products. The health department said the majority stopped selling kratom after those inspections; there were nine locations that ignored the warnings, and in those cases, inspectors impounded their kratom products.
But the reality is that people who need kratom will buy it on the black market, drive far enough so they get to where it’s sold legally or, like Wallace, order it online from a different state.
For now, retailers who sell kratom products are simply carrying on until they’re investigated by county health inspectors.
Ari Agalopol, a decorated pianist and piano teacher, saw her performances and classes abruptly come to a halt in 2012 after a car accident resulted in severe spinal and knee injuries.
“I tried my best to do traditional acupuncture, physical therapy and hydrocortisone shots in my spine and everything,” she said. “Finally, after nothing was working, I relegated myself to being a pain-management patient.”
She was prescribed oxycodone, and while on the medication, battled depression, anhedonia and suicidal ideation. She felt as though she were in a fog when taking oxycodone, and when it ran out, ”the pain would rear its ugly head.” Agalopol struggled to get out of bed daily and could manage teaching only five students a week.
Then, looking for alternatives to opioids, she found a Reddit thread in which people were talking up the benefits of kratom.
“I was kind of hesitant at first because there’re so many horror stories about 7-OH, but then I researched and I realized that the natural plant is not the same as 7-OH,” she said.
She went to a local shop, Authentic Kratom in Woodland Hills, and spoke to a sales associate who helped her decide which of the 47 strains of kratom it sold would best suit her needs.
Agalopol currently takes a 75-milligram dose of mitragynine, the primary alkaloid in kratom, when necessary. It has enabled her to get back to where she was before her injury: teaching 40 students a week and performing every weekend.
Agalopol believes the county hasn’t done its homework on kratom. “They’re just taking these actions because of public pressure, and public pressure is happening because of ignorance,” she said.
During the course of reporting this story, Authentic Kratom has shut down its three locations; it’s unclear if the closures are temporary. The owner of the business declined to comment on the matter.
When she heard the news of the recent closures, Agalopol was seething. She told The Times she has enough capsules of kratom for now, but when she runs out, her option will have to be Tylenol and ibuprofen, “which will slowly kill my liver.”
“Prohibition is not a public health strategy,” said Jackie Subeck, executive director of 7-Hope Alliance, a nonprofit that promotes safe and responsible access to 7-OH for consumers, at the Feb. 18 Senate hearing. “[It’s] only going to make things worse, likely resulting in an entirely new health crisis for Californians.”
Science
There were 13 full-service public health clinics in L.A. County. Now there are 6

Because of budget cuts, the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health has ended clinical services at seven of its public health clinic sites.
As of Feb. 27, the county is no longer providing services such as vaccinations, sexually transmitted infection testing and treatment, or tuberculosis diagnosis and specialty TB care at the affected locations, according to county officials and a department fact sheet.
The sites losing clinical services are Antelope Valley in Lancaster; the Center for Community Health (Leavy) in San Pedro, Curtis R. Tucker in Inglewood, Hollywood-Wilshire, Pomona, Dr. Ruth Temple in South Los Angeles, and Torrance. Services will continue to be provided by the six remaining public health clinics, and through nearby community clinics.
The changes are the result of about $50 million in funding losses, according to official county statements.
“That pushed us to make the very difficult decision to end clinical services at seven of our sites,” said Dr. Anish Mahajan, chief deputy director of the L.A. County Department of Public Health.
Mahajan said the department selected clinics with relatively lower patient volumes. Over the last month, he said, the department has sent letters to patients about the changes, and referred them to unaffected county clinics, nearby federally qualified health centers or other community providers. According to Mahajan, for tuberculosis patients, particularly those requiring directly observed therapy, public health nurses will continue visiting patients.
Public health clinics form part of the county’s healthcare safety net, serving low-income residents and those with limited access to care. Officials said that about half of the patients the county currently sees across its clinics are uninsured.
Mahajan noted that the clinics were established decades ago, before the Affordable Care Act expanded Medi-Cal coverage and increased the number of federally qualified health centers. He said that as more residents gained access to primary care, utilization at some county-run clinics declined.
“Now that we have a more sophisticated safety net, people often have another place to go for their full range of care,” he said.
Still, the closures have unsettled providers who work closely with local vulnerable populations.
“I hate to see any services that serve our at-risk and homeless community shut down,” said Mark Hood, chief executive of Union Rescue Mission in downtown Los Angeles. “There’s so much need out there, so it always is going to create hardship for the people that actually need the help the most.”
Union Rescue Mission does not receive government funding for its healthcare services, Hood said. The mission’s clinics are open not only to shelter guests, up to 1,000 people nightly, but also to people living on the streets who walk in seeking care.
Its dental clinic alone sees nearly 9,000 patients a year, Hood said.
“We haven’t seen it yet, but I expect in the coming days and weeks we’ll see more people coming through our doors looking for help,” he said. “They’re going to have to find help somewhere.” Hood said women experiencing homelessness are especially vulnerable when preventive care, including sexual and reproductive health services, becomes harder to access.
County officials said staffing impacts so far have been managed through reassignment rather than layoffs. Roughly 200 to 300 positions across the department have been eliminated amid funding cuts, officials said, though many were vacant. About 120 employees whose positions were affected have been reassigned; according to Mahajan, no one has been laid off.
The clinic closures come amid broader fiscal uncertainty. Mahajan said that due to the Trump administration’s “Big Beautiful Bill,” Los Angeles County could lose $2.4 billion over the next several years. That funding, he said, supports clinics, hospitals and community clinic partners now absorbing patients who previously went to the clinics that closed on Feb. 27.
In response, the L.A. County Board of Supervisors has backed a proposed half-cent sales tax measure that would generate hundreds of millions of dollars annually for healthcare and public health services. Voters are expected to consider the measure in June.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts1 week ago
Massachusetts1 week agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Wisconsin4 days ago
Wisconsin4 days agoSetting sail on iceboats across a frozen lake in Wisconsin
-

 Maryland4 days ago
Maryland4 days agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Florida4 days ago
Florida4 days agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Denver, CO1 week ago
Denver, CO1 week ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Massachusetts2 days ago
Massachusetts2 days agoMassachusetts man awaits word from family in Iran after attacks
-

 Oregon6 days ago
Oregon6 days ago2026 OSAA Oregon Wrestling State Championship Results And Brackets – FloWrestling
















