Politics
Congress Approves Legislation to Return the Postal Service to Solvency

WASHINGTON — Congress gave last approval on Tuesday to probably the most sprawling overhaul of the Postal Service in practically twenty years, sending President Biden laws meant to return the beleaguered company to solvency and deal with pandemic-era mail delays.
The Senate voted 79 to 19 to approve the measure, which handed the Home final month with overwhelming bipartisan assist. Mr. Biden was anticipated to signal the invoice, which the company’s management and an array of curiosity teams assist.
“With the legislative monetary reforms achieved immediately, mixed with our personal self-led operational reforms, we will self-fund our operations and proceed to ship to 161 million addresses six days per week for a lot of many years to come back,” Louis DeJoy, the postmaster normal, stated in a press release.
The Postal Service, arguably one of the beloved federal businesses, has been getting ready to insolvency for years, largely due to a 2006 regulation that requires the company to fund retiree well being care advantages for its staff prematurely. In 2020, a slowdown of mail supply and a collection of operational modifications earlier than the election prompted renewed scrutiny, and Congress doubled down on efforts to reform the company’s construction and deal with its monetary woes.
The laws removes the retirement mandate and as an alternative requires retired Postal Service staff to enroll in Medicare when they’re eligible, a change that lawmakers and company officers estimated would save $50 billion over a decade.
“The submit workplace often delivers for us, however immediately we’re going to ship for them,” stated Senator Chuck Schumer of New York, the bulk chief. “For the previous few months, Democrats and Republicans have been working collectively in good religion to reform among the most troubled components of the Postal Service.”
The company confronted renewed scrutiny partly due to a collection of reported mail delays forward of the 2020 election, during which a document variety of votes have been forged by mail. That yr, Democrats sparred with Mr. DeJoy, a megadonor who supported former President Donald J. Trump, over a collection of cost-cutting measures, which have been later postponed till after the election.
“Our nation is fairly divided proper now, let’s be sincere,” Senator Rob Portman, Republican of Ohio and a key sponsor of the invoice, stated in a latest ground speech. “However one enduring actuality about our nation is that now we have a submit workplace that ties us all collectively, and everyone depends upon that submit workplace.”
The laws additionally strikes to handle issues in regards to the company’s continued service, after Democrats pushed again when the Postal Service issued a 10-year strategic plan final yr that proposed lowering hours and lengthening supply instances. As an alternative, the measure that handed the Senate on Tuesday mandates a supply customary of a minimum of six days per week.
The invoice would additionally impose new transparency requirements for the company, requiring common stories to Congress in regards to the Postal Service’s monetary state and the publication of supply knowledge, which clients may search utilizing a road deal with, a ZIP code or a submit workplace field. It could additionally present for expanded particular charges for native newspaper distribution.
Some Republicans on Tuesday objected to the measure, calling it fiscally shortsighted and unsuccessfully pushing for last-minute modifications to the invoice.
“This invoice doesn’t cut back prices — it simply shifts them from one unfunded authorities program to a different unfunded authorities program,” stated Senator Rick Scott, Republican of Florida.
However a number of lawmakers hailed the bipartisan approval of the invoice as crucial assist for an company that gives an important lifeline to their states.
“There’s rising realization that the Postal Service is completely important for our nation — it’s the solely group that delivers to each single deal with in America,” Senator Gary Peters, Democrat of Michigan and one of many lawmakers who helped spearhead the measure’s consideration within the Senate, stated earlier than its passage. “It’s really written into the U.S. Structure as one thing that helps hold the nation certain collectively.”

Politics
Why Does Trump Want Greenland?

President-elect Donald J. Trump’s attention returned Tuesday to an idea that has fascinated him for years: acquiring Greenland for the United States. In a news conference on Tuesday, he refused to rule out using military or economic force to take the territory from Denmark, a U.S. ally.
“We need Greenland for national security purposes,” he said, arguing that Denmark should give it up to “protect the free world.” He threatened to impose tariffs on Denmark if it did not.
Earlier in the day, Mr. Trump wrote on social media that the potential American acquisition of the Arctic territory “is a deal that must happen” and uploaded photos of his eldest son, Donald Trump Jr., who was visiting Greenland.
“MAKE GREENLAND GREAT AGAIN,” the president-elect added.
After the news conference, Denmark sharply rebuked the proposal, saying that the world’s largest island is not for sale.
During his first term, Mr. Trump urged his aides to explore ways to purchase Greenland, a semiautonomous territory known for its natural resources and strategical location for new shipping routes that can open up as the Arctic ice melts. A few weeks ago, Mr. Trump reignited the conversation through social media, asserting that “the ownership and control of Greenland is an absolute necessity.”
Greenland’s vast ice sheets and glaciers are quickly retreating as the Earth warms through accelerating climate change. That melting of ice could allow drilling for oil and mining for minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel and cobalt. Those mineral resources are essential to rapidly growing industries that make wind turbines, transmission lines, batteries and electric vehicles.
Because of higher temperatures, an estimated 11,000 square miles of Greenland’s ice sheets and glaciers have already melted in the past three decades, an area roughly the size of Massachusetts.
In 2023, the Danish government published a report that detailed Greenland’s potential as a rich deposit of valuable minerals. The Arctic island has “favorable conditions for the formations of ore deposition, including many of the critical raw minerals.”
The melting ice in the Arctic is also opening up a new strategic asset in geopolitics: shorter and more efficient shipping routes. Navigating through the Arctic Sea from Western Europe to East Asia, for example, is about 40 percent shorter compared to sailing through the Suez Canal. Ship traffic in the Arctic has already surged 37 percent over the past decade, according to a recent Arctic Council report.
China has shown significant interest in a new route through the Arctic, and in November, China and Russia agreed to work together to develop Arctic shipping routes.
Mr. Trump has repeatedly called climate change a “hoax.” But one of his former national security advisers, Robert C. O’Brien, suggested that its consequences are one of the reasons that Mr. Trump is interested in making Greenland a U.S. territory.
“Greenland is a highway from the Arctic all the way to North America, to the United States,” he told Fox News. “It’s strategically very important to the Arctic, which is going to be the critical battleground of the future because as the climate gets warmer, the Arctic is going to be a pathway that maybe cuts down on the usage of the Panama Canal.”
Politics
Outgoing WH official calls for US to bolster cybersecurity workforce by hiring non-degree holders
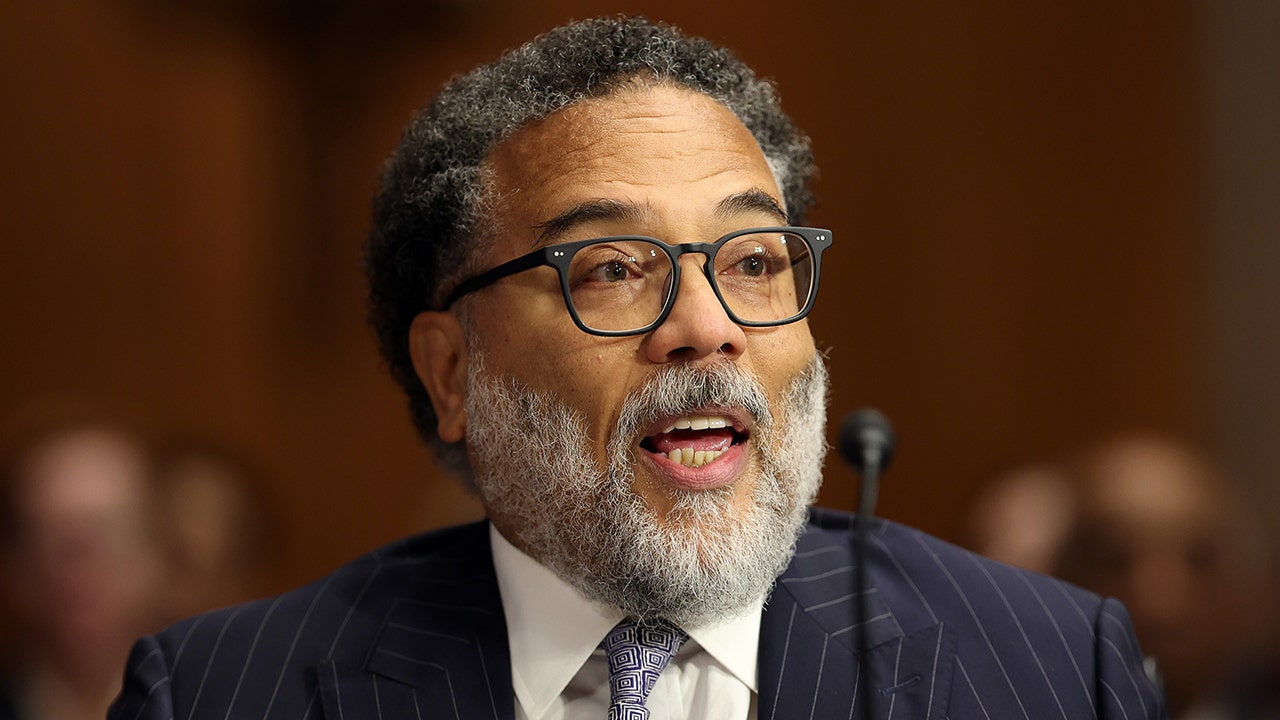

The White House’s outgoing cyber czar, Harry Coker, called for three key things to meet the growing threat of digital attacks: more funding, deregulation and opening up cyber jobs to those without college degrees.
As adversaries like Iran, China and Russia lob near-constant attacks on the U.S. digital infrastructure, “we have to prioritize cybersecurity within federal budgets” President Joe Biden’s national cyber director said at an event with the Foundation for Defense of Democracies in Washington, D.C.
“I would love for the incoming administration, or any administration, to recognize the priority of cybersecurity,” Coker said.
He added that he understands the U.S. is in a “tough budget situation.”
“I get that, and I support making progress towards reducing the deficit, but we have to prioritize cybersecurity within our current budgets,” he said.
“I would love for the incoming administration, or any administration, to recognize the priority of cybersecurity,” Coker said. (Kevin Dietsch/Getty Images)
At the same time, the Biden appointee railed against “duplicative federal regulation” and said he’d heard from those working to protect the nation’s online infrastructure that they spend “a staggering 30 to 50%” of their time working to comply with regulation, rather than ensuring protection from hacks.
“Armed with the industry’s call to streamline, we worked with Congress to write bipartisan legislation that would bring all stakeholders, including independent regulators, to the table to advance the regulatory harmonization,” he went on.
TOP REPUBLICAN DEMANDS ‘COSTS’ FOR CHINA AFTER IT HACKED TREASURY DEPT IN YEAR MARKED BY CCP ESPIONAGE
“Many of us were disappointed that this has not become law yet, but we have laid the groundwork for the next administration in Congress to do the right thing for our partners in the private sector.”
His urging comes as the U.S. is grappling with the fallout of one of China’s biggest attacks on American infrastructure in history, dubbed Salt Typhoon.
A Chinese intelligence group infiltrated nine U.S. telecommunications giants and gained access to the private text messages and phone calls of Americans, including senior government officials and prominent political figures.
China was behind a slew of major cyberattacks on the U.S. this year. (PHILIPPE HUGUEN/AFP via Getty Images)

A Chinese intelligence group infiltrated nine U.S. telecommunications giants recently. (REUTERS/Adriano Machado)
The Salt Typhoon hackers also gained access to an exhaustive list of phone numbers the Justice Department had wiretapped to monitor people suspected of espionage, granting them insight into which Chinese spies the U.S. had caught onto and which they had missed.
FBI’S NEW WARNING ABOUT AI-DRIVEN SCAMS THAT ARE AFTER YOUR CASH
China was also behind a “major” hack of the Treasury Department in December, gaining access to unclassified documents and the workstations of government employees.
And earlier this year, Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo’s communications were intercepted by Chinese intelligence, just as she was making determinations about new export controls on semiconductors and other key technologies. The same hacking group also targeted officials at the State Department and members of Congress.
Amid this onslaught of attacks, Coker said the cyber industry is suffering a recruitment issue.
CLICK TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
“Today there are nearly 500,000 open cyber jobs in this great nation,” he said.
“The federal government is leading by example… removing federal employee and contractor hiring from a focus on college degrees to a focus on what we’re really after: skills.
“When we do away with the four-year college degree requirement, we expand our talent pool,” Coker went on. “Many Americans don’t have the time or the means to go to college for four years, but they can do it for two years or less.”
Politics
Opinion: What antiabortion activists want next

The state of Texas filed a major lawsuit on Dec. 12 against a New York doctor who mailed abortion pills to a Collin County, Texas, woman, arguing that the doctor was practicing medicine without a Texas license and violating the state’s abortion ban. The suit raises messy legal questions about whether one state can haul a doctor abiding by the law in another state into its courts, or enforce a judgment if it wins. More than that, however, the suit is a window into the next battlefield over abortion rights — and how abortion pills and telemedicine are reshaping the politics of abortion in America.
The antiabortion movement’s endgame is establishing fetal personhood — the idea that life and constitutional rights begin at the moment sperm fertilizes an egg. Fetal personhood was referenced in the 2024 GOP platform and embraced in a strategy endorsed by most leading antiabortion groups. It has been a focal point of the movement’s efforts for 50 years.
But with blue states and many red states reaffirming a right to abortion, fetal personhood doesn’t seem like it’s going to come to pass anytime soon. In the meantime, abortion opponents have set their sights on shutting down access to abortion pills — mifepristone and misoprostol. The Supreme Court rebuffed one Texas lawsuit targeting mifepristone in June (on the basis of standing), but as the new case indicates, that hasn’t discouraged the antiabortion movement.
Here’s why: Medication abortion, also called chemical abortion, has made it difficult to enforce abortion bans in the states where they exist — indeed, even with Roe vs. Wade reversed, studies show an increase in the number of abortions performed annually in the U.S. Abortion pills also make it harder to frighten doctors and harder to stigmatize the termination of pregnancy.
When all abortions were surgical, the procedure had to take place in bricks-and-mortar facilities. The clinics became targets for protest and sometimes violence and vandalism. Abortion pills, however, can be prescribed remotely, through a telehealth consultation, and they are taken at home very early in a pregnancy. Pills make abortion more private, distancing patients from clinic protests, and their effects may resemble miscarriage, which already occurs in up to 20% of known pregnancies — so much so that physicians have no reliable way of telling the symptoms apart. Along with backlash against the reversal of Roe, the nature of medication abortion seems to be reshaping how Americans think about terminating a pregnancy: The number of those who see abortion as a moral decision has increased in recent years.
The Texas lawsuit is part of a much broader antiabortion strategy that will unfold in the new year. Besides targeting telemedicine and pills, antiabortion groups plan to pursue anyone who aids or abets abortion — for example, internet service providers that allow websites to provide information about abortion pills and where to get them. Other proposals copy a Louisiana law that designates safe and effective drugs used in abortion as “controlled substances.”
In addition to these maneuvers, look for abortion opponents to lobby the Trump administration to reinterpret the Comstock Act, a 19th century obscenity law, to make it illegal to send anything used in abortions by mail. That could create the equivalent of a nationwide ban, which Congress so far won’t legislate and voters don’t want.
And there are other steps the Trump administration could take that would dramatically change abortion access. In 2023, the Food and Drug Administration made changes to the restrictions governing mifepristone and telemedicine abortion appointments. Ever since, antiabortion groups have developed a grab-bag of arguments against the FDA’s rules. They argue that the consensus of peer-reviewed studies is wrong and that mifepristone is extremely dangerous. They also have argued that mifepristone and fetal “remains” are an environmental hazard polluting groundwater.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr., who would have oversight of the FDA if he is confirmed as Trump’s pick to be secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services, said he was pro-choice on the campaign trail, but he also has signaled openness to the antiabortion movement. Claims about drug safety and environmental hazards might resonate with Kennedy, who is an opponent of Big Pharma and once worked in environmental law.
The Supreme Court decision overturning Roe has done nothing to end abortion battles; instead, it has given them new life. Fights over telemedicine consultations, mail-order access to abortion pills and FDA safety rules could make abortion bans far more effective, reshape the procedure in states that protect abortion rights and expand the power of one state to dictate policy in another.
Most important: If abortion opponents succeed in making abortion pills inaccessible, the stigma surrounding abortion may well increase, and access to the procedure decrease. That’s why antiabortion groups have been relentless in their pursuit of pills. Nothing less than Americans’ view of abortion itself is on the line.
Mary Ziegler is a law professor at UC Davis. Her latest book, “Personhood: The New Civil War over Reproduction,” is scheduled for publication in April.
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Culture7 days ago
Culture7 days agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoWho Are the Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom?
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoOzempic ‘microdosing’ is the new weight-loss trend: Should you try it?
-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoIvory Coast says French troops to leave country after decades














