Business
Visa, Google, JetBlue: A Guide to a New Era of Antitrust Action
The Justice Department accuses Visa of unfairly stifling competition in debit cards, claiming the company has maintained a monopoly by imposing or threatening to impose higher fees on merchants that also use other payment networks.
Read more ›
President Biden’s top antitrust enforcers have promised to sue monopolies and block big mergers — a cornerstone of the administration’s economic agenda to restore competition to the economy.
Below are 15 major cases brought by the Justice Department and Federal Trade Commission since late 2020 (including cases against Google and Meta initially filed during the Trump administration just before Mr. Biden took office).
The government has won several but not all the cases. And with only a few months remaining for the current administration, the number of suits is climbing, as regulators go after dominant companies in tech, pharmaceuticals, finance and even groceries.
In a lawsuit, the D.O.J. said that more than 60 percent of debit transactions in the United States run on Visa’s network, allowing it to charge over $7 billion in fees each year for processing those transactions. Government lawyers argued that Visa penalizes its customers when they try to use competing services and that it has built a monopoly around payment processing.
The Justice Department accuses Visa of unfairly stifling competition in debit cards, claiming the company has maintained a monopoly by imposing or threatening to impose higher fees on merchants that also use other payment networks.
Read more › The F.T.C. accused three big prescription drug middlemen, known as pharmacy benefits managers, of artificially raising prices for insulin drugs and making it harder for individuals to obtain cheaper options. The legal action targeted CVS Health’s Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts and UnitedHealth’s Optum Rx and subsidiaries they’ve created to handle drug negotiations. The three companies collectively control 80 percent of prescriptions in the United States.
The F.T.C. files an administrative complaint, which is not yet public, that seeks to prohibit pharmacy benefit managers from steering patients to drugs that make them more money.
Read more › The F.T.C. sued to block Kroger’s $24.6 billion acquisiton of Albertsons, which, if allowed to proceed, would be the biggest supermarket merger in U.S. history. The companies said the merger would bolster their leverage with suppliers; the government contended that it would drive up prices for shoppers and suppress worker wages.
The hearing, a mini-trial, lasts just over three weeks. The judge in the case has yet to issue a decision.
The trial begins in Oregon, where both grocery companies have a significant presence. The case enters the spotlight as high food prices become a critical focus in the presidential race.
Read more ›
The F.T.C. and eight states, plus the District of Columbia, sue to block Kroger from acquiring rival supermarket chain Albertsons. They say the deal would most likely result in higher prices for groceries and weakened bargaining power for unionized workers.
Read more › The D.O.J. alleged Google harmed competition over the technology used to place advertising on web sites. The department and eight states said Google acquired rivals through anticompetitive mergers and bullied publishers and advertisers into using the company’s ad technology.
The trial is expected to take about a month. The government has asked for a breakup of the company, requiring Google to sell off some assets.
Read more › The Justice Department and a group of eight states accuse Google of abusing a monopoly over the technology that powers online advertising.
Read more › The D.O.J. and a group of states sued Google, saying its role in about 90 percent of all internet searches made it a monopoly. The lawsuit, which was filed in the final days of the Trump administration, alleged Google uses exclusive contracts with phone makers like Apple and other companies to feature Google search on their devices, making it harder for consumers to use rival search engines like Bing or DuckDuckGo.
In a 277-page ruling, a federal judge calls Google a monopolist and says it has acted illegally to maintain that monopoly. A trial to determine remedies is set to begin in 2025.
Read more › The chief executive of Google’s parent company, Sundar Pichai, counters the government’s narrative in testimony that describes Google’s deals with other tech companies as having been in the best interest of consumers.
Read more ›
As a trial begins, Satya Nadella, the chief executive of Microsoft, becomes the government’s highest-profile witness in the case when he testifies that even his company has found it difficult to compete with Google’s search products.
Read more › The Justice Department accuses Google of maintaining its monopoly over search and search advertising, crowding out competition through exclusive business contracts.
Read more › An F.T.C. lawsuit sought to block Tapestry’s $8.5 billion acquisition of Capri, a blockbuster fashion tie-up to bring together Coach, Kate Spade, Michael Kors and Versace. The suit was a rare move by the agency to block a fashion deal, given that the industry does not suffer from a lack of competition.
A hearing, which effectively serves as a mini-trial, begins over whether the government should put a halt to the deal while the F.T.C. can mount a case against the merger.
The F.T.C. sues to block a merger of two fashion companies, Tapestry and Capri Holdings, that would bring together brands like Coach, Michael Kors and Kate Spade. The agency says the deal could force millions of consumers to pay more for “accessible luxury” accessories — less expensive goods sold by high-end firms — because the combined company would no longer have the incentive to compete on price.
Read more › An antitrust lawsuit filed by the D.O.J. and several states against RealPage, a real estate software company, said its technology enabled landlords to collude to raise rents across the country. It was the first major civil antitrust lawsuit to centrally feature the role of an algorithm in pricing manipulation, D.O.J. officials said.
In its complaint, the Justice Department accuses RealPage of enabling a price-fixing conspiracy that artificially raised rents for millions of people.
Read more › The D.O.J. accused Apple of using a monopoly in the smartphone market to stifle competition and inflate prices for consumers. In its suit, the department said Apple blocked companies from offering apps that competed with Apple versions, including Messages and Wallet.
Apple files a motion to dismiss the case, saying its business decisions didn’t violate antitrust laws. It has argued that those decisions make the iPhone a better experience.
The Justice Department and 16 states, plus the District of Columbia, file a challenge to the reach and influence of Apple, arguing that the company has used anticompetitive tactics to keep customers reliant on their iPhones.
Read more › Live Nation Entertainment, the concert giant that owns Ticketmaster, stands accused of illegally maintaining a monopoly in the live entertainment industry. The D.O.J. said Ticketmaster provided exclusive ticketing contracts with concert venues, which helped Live Nation shore up its dominance, depriving consumers of better prices and options.
The Justice Department, joined by 29 states and the District of Columbia, accuses Live Nation of leveraging its sprawling empire to dominate the live music industry by locking venues into exclusive ticketing contracts, pressuring artists to use its services and threatening its rivals with financial retribution.
Read more › A merger between JetBlue and Spirit, which would have created the fifth-largest airline in the United States, was blocked by a federal judge after a D.O.J. challenge. Government lawyers argued that smaller, low-cost airlines like Spirit helped reduce fares and that allowing the company to be acquired by JetBlue, which tends to charge higher prices than Spirit, would have hurt consumers.
JetBlue and Spirit announce that they will not seek to overturn a court ruling that blocked their planned $3.8 billion merger.
Read more › In a 109-page ruling siding with the government, the judge in the case says the merger would “likely incentivize JetBlue further to abandon its roots as a maverick, low-cost carrier.”
Read more ›
The Justice Department files a lawsuit seeking to stop JetBlue Airways from buying Spirit Airlines, arguing that the $3.8 billion deal would reduce competition.
Read more › A lawsuit filed by the F.T.C. and 17 states against Amazon accused the retail behemoth of squeezing merchants and favoring its own competing brands and services over third-party sellers. A trial date is set for 2026.
Amazon asks the court to dismiss the suit, arguing that the F.T.C. failed to identify the harm consumers were experiencing. It says the agency confused “common retail practices” with monopolistic behavior.
The F.T.C. and 17 states sue Amazon, contending its online store and merchant services illegally stifle competition. The lawsuit that raises the possibility of altering the company’s structure.
Read more › The F.T.C. sued to block Microsoft’s $69 billion acquisition of Activision Blizzard, which, if allowed to proceed, would be the largest consumer tech acquisition since AOL bought Time Warner more than two decades ago. The case follows scrutiny of the deal by regulators in Europe. Microsoft makes the consoles and platforms on which Activision’s games are played, and the merger of two companies that don’t directly compete is known as a vertical merger. Cases against vertical mergers have traditionally been difficult to win.
Microsoft says it has closed its deal with Activision Blizzard, signaling that the tech industry’s giants are still free to use their cash hoards to get even bigger.
Read more › In a 53-page decision, a judge says the F.T.C. has failed to show the merger would result in a substantial reduction in competition that would harm consumers.
Read more › The F.T.C. seeks a preliminary injunction to bar Microsoft from completing the deal before the F.T.C. has the chance to argue the case in its internal court. Microsoft argues a delay would essentially be killing the deal anyway.
Read more › In its suit, the F.T.C. says Microsoft’s proposed acquisition of Activision Blizzard would harm consumers because Microsoft could use Activision’s blockbuster games like Call of Duty to lure gamers from rivals.
Read more › The Justice Department sought to block a proposed merger between the largest publisher in the United States and a key rival.
In an order, a judge says that the government has demonstrated that the merger might “substantially” harm competition in the market for U.S. publishing rights to anticipated top-selling books.
Read more › The D.O.J. sued to block UnitedHealth Group’s $13 billion acquisition of health technology company Change Healthcare, arguing that a deal would give UnitedHealth sensitive data that it could wield against its competitors in the insurance business.
After a trial over the summer, a judge says in a 58-page memo that UnitedHealth’s incentives to protect customer data as it grows its businesses outweigh motivations to misuse the information.
In a lawsuit, the Justice Department argues UnitedHealth Group’s deal to acquire Change Healthcare, a health technology company, would give the giant insurer access to sensitive data that it could wield against its competitors.
Read more ›

Business
Commentary: How Trump helped foreign markets outperform U.S. stocks during his first year in office
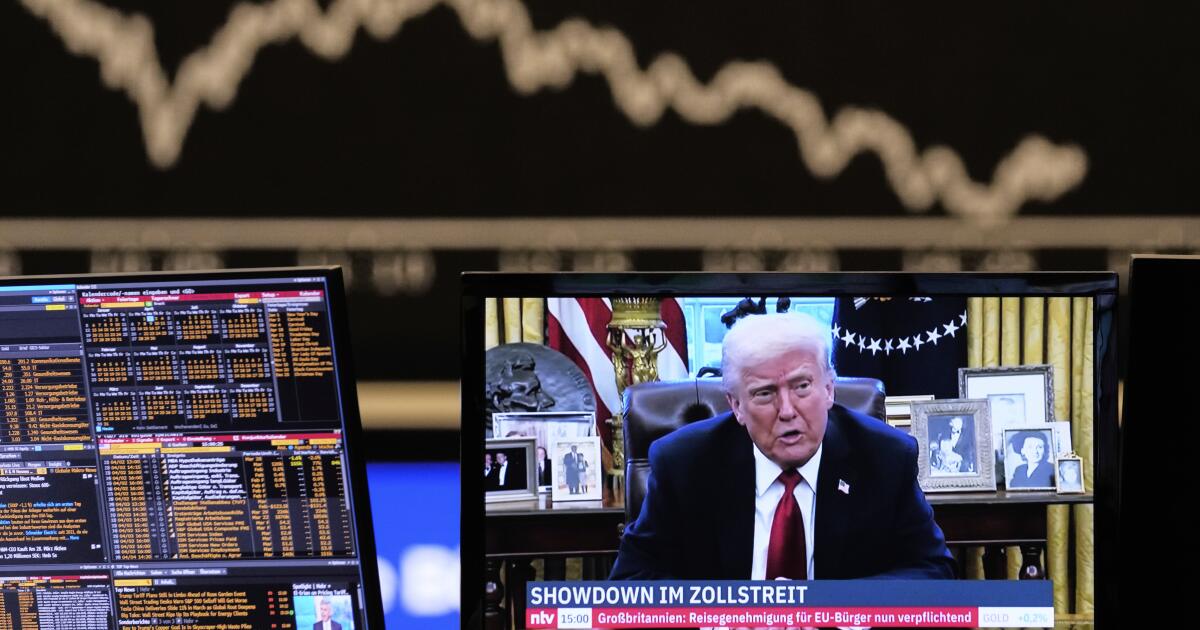
Trump has crowed about the gains in the U.S. stock market during his term, but in 2025 investors saw more opportunity in the rest of the world.
If you’re a stock market investor you might be feeling pretty good about how your portfolio of U.S. equities fared in the first year of President Trump’s term.
All the major market indices seemed to be firing on all cylinders, with the Standard & Poor’s 500 index gaining 17.9% through the full year.
But if you’re the type of investor who looks for things to regret, pay no attention to the rest of the world’s stock markets. That’s because overseas markets did better than the U.S. market in 2025 — a lot better. The MSCI World ex-USA index — that is, all the stock markets except the U.S. — gained more than 32% last year, nearly double the percentage gains of U.S. markets.
That’s a major departure from recent trends. Since 2013, the MSCI US index had bested the non-U.S. index every year except 2017 and 2022, sometimes by a wide margin — in 2024, for instance, the U.S. index gained 24.6%, while non-U.S. markets gained only 4.7%.
The Trump trade is dead. Long live the anti-Trump trade.
— Katie Martin, Financial Times
Broken down into individual country markets (also by MSCI indices), in 2025 the U.S. ranked 21st out of 23 developed markets, with only New Zealand and Denmark doing worse. Leading the pack were Austria and Spain, with 86% gains, but superior records were turned in by Finland, Ireland and Hong Kong, with gains of 50% or more; and the Netherlands, Norway, Britain and Japan, with gains of 40% or more.
Investment analysts cite several factors to explain this trend. Judging by traditional metrics such as price/earnings multiples, the U.S. markets have been much more expensive than those in the rest of the world. Indeed, they’re historically expensive. The Standard & Poor’s 500 index traded in 2025 at about 23 times expected corporate earnings; the historical average is 18 times earnings.
Investment managers also have become nervous about the concentration of market gains within the U.S. technology sector, especially in companies associated with artificial intelligence R&D. Fears that AI is an investment bubble that could take down the S&P’s highest fliers have investors looking elsewhere for returns.
But one factor recurs in almost all the market analyses tracking relative performance by U.S. and non-U.S. markets: Donald Trump.
Investors started 2025 with optimism about Trump’s influence on trading opportunities, given his apparent commitment to deregulation and his braggadocio about America’s dominant position in the world and his determination to preserve, even increase it.
That hasn’t been the case for months.
”The Trump trade is dead. Long live the anti-Trump trade,” Katie Martin of the Financial Times wrote this week. “Wherever you look in financial markets, you see signs that global investors are going out of their way to avoid Donald Trump’s America.”
Two Trump policy initiatives are commonly cited by wary investment experts. One, of course, is Trump’s on-and-off tariffs, which have left investors with little ability to assess international trade flows. The Supreme Court’s invalidation of most Trump tariffs and the bellicosity of his response, which included the immediate imposition of new 10% tariffs across the board and the threat to increase them to 15%, have done nothing to settle investors’ nerves.
Then there’s Trump’s driving down the value of the dollar through his agitation for lower interest rates, among other policies. For overseas investors, a weaker dollar makes U.S. assets more expensive relative to the outside world.
It would be one thing if trade flows and the dollar’s value reflected economic conditions that investors could themselves parse in creating a picture of investment opportunities. That’s not the case just now. “The current uncertainty is entirely man-made (largely by one orange-hued man in particular) but could well continue at least until the US mid-term elections in November,” Sam Burns of Mill Street Research wrote on Dec. 29.
Trump hasn’t been shy about trumpeting U.S. stock market gains as emblems of his policy wisdom. “The stock market has set 53 all-time record highs since the election,” he said in his State of the Union address Tuesday. “Think of that, one year, boosting pensions, 401(k)s and retirement accounts for the millions and the millions of Americans.”
Trump asserted: “Since I took office, the typical 401(k) balance is up by at least $30,000. That’s a lot of money. … Because the stock market has done so well, setting all those records, your 401(k)s are way up.”
Trump’s figure doesn’t conform to findings by retirement professionals such as the 401(k) overseers at Bank of America. They reported that the average account balance grew by only about $13,000 in 2025. I asked the White House for the source of Trump’s claim, but haven’t heard back.
Interpreting stock market returns as snapshots of the economy is a mug’s game. Despite that, at her recent appearance before a House committee, Atty. Gen. Pam Bondi tried to deflect questions about her handling of the Jeffrey Epstein records by crowing about it.
“The Dow is over 50,000 right now, she declared. “Americans’ 401(k)s and retirement savings are booming. That’s what we should be talking about.”
I predicted that the administration would use the Dow industrial average’s break above 50,000 to assert that “the overall economy is firing on all cylinders, thanks to his policies.” The Dow reached that mark on Feb. 6. But Feb. 11, the day of Bondi’s testimony, was the last day the index closed above 50,000. On Thursday, it closed at 49,499.50, or about 1.4% below its Feb. 10 peak close of 50,188.14.
To use a metric suggested by economist Justin Wolfers of the University of Michigan, if you invested $48,488 in the Dow on the day Trump took office last year, when the Dow closed at 48,448 points, you would have had $50,000 on Feb. 6. That’s a gain of about 3.2%. But if you had invested the same amount in the global stock market not including the U.S. (based on the MSCI World ex-USA index), on that same day you would have had nearly $60,000. That’s a gain of nearly 24%.
Broader market indices tell essentially the same story. From Jan. 17, 2025, the last day before Trump’s inauguration, through Thursday’s close, the MSCI US stock index gained a cumulative 16.3%. But the world index minus the U.S. gained nearly 42%.
The gulf between U.S. and non-U.S. performance has continued into the current year. The S&P 500 has gained about 0.74% this year through Wednesday, while the MSCI World ex-USA index has gained about 8.9%. That’s “the best start for a calendar year for global stocks relative to the S&P 500 going back to at least 1996,” Morningstar reports.
It wouldn’t be unusual for the discrepancy between the U.S. and global markets to shrink or even reverse itself over the course of this year.
That’s what happened in 2017, when overseas markets as tracked by MSCI beat the U.S. by more than three percentage points, and 2022, when global markets lost money but U.S. markets underperformed the rest of the world by more than five percentage points.
Economic conditions change, and often the stock markets march to their own drummers. The one thing less likely to change is that Trump is set to remain president until Jan. 20, 2029. Make your investment bets accordingly.
Business
How the S&P 500 Stock Index Became So Skewed to Tech and A.I.

Nvidia, the chipmaker that became the world’s most valuable public company two years ago, was alone worth more than $4.75 trillion as of Thursday morning. Its value, or market capitalization, is more than double the combined worth of all the companies in the energy sector, including oil giants like Exxon Mobil and Chevron.
The chipmaker’s market cap has swelled so much recently, it is now 20 percent greater than the sum of all of the companies in the materials, utilities and real estate sectors combined.
What unifies these giant tech companies is artificial intelligence. Nvidia makes the hardware that powers it; Microsoft, Apple and others have been making big bets on products that people can use in their everyday lives.
But as worries grow over lavish spending on A.I., as well as the technology’s potential to disrupt large swaths of the economy, the outsize influence that these companies exert over markets has raised alarms. They can mask underlying risks in other parts of the index. And if a handful of these giants falter, it could mean widespread damage to investors’ portfolios and retirement funds in ways that could ripple more broadly across the economy.
The dynamic has drawn comparisons to past crises, notably the dot-com bubble. Tech companies also made up a large share of the stock index then — though not as much as today, and many were not nearly as profitable, if they made money at all.
How the current moment compares with past pre-crisis moments
To understand how abnormal and worrisome this moment might be, The New York Times analyzed data from S&P Dow Jones Indices that compiled the market values of the companies in the S&P 500 in December 1999 and August 2007. Each date was chosen roughly three months before a downturn to capture the weighted breakdown of the index before crises fully took hold and values fell.
The companies that make up the index have periodically cycled in and out, and the sectors were reclassified over the last two decades. But even after factoring in those changes, the picture that emerges is a market that is becoming increasingly one-sided.
In December 1999, the tech sector made up 26 percent of the total.
In August 2007, just before the Great Recession, it was only 14 percent.
Today, tech is worth a third of the market, as other vital sectors, such as energy and those that include manufacturing, have shrunk.
Since then, the huge growth of the internet, social media and other technologies propelled the economy.
Now, never has so much of the market been concentrated in so few companies. The top 10 make up almost 40 percent of the S&P 500.
How much of the S&P 500 is occupied by the top 10 companies
With greater concentration of wealth comes greater risk. When so much money has accumulated in just a handful of companies, stock trading can be more volatile and susceptible to large swings. One day after Nvidia posted a huge profit for its most recent quarter, its stock price paradoxically fell by 5.5 percent. So far in 2026, more than a fifth of the stocks in the S&P 500 have moved by 20 percent or more. Companies and industries that are seen as particularly prone to disruption by A.I. have been hard hit.
The volatility can be compounded as everyone reorients their businesses around A.I, or in response to it.
The artificial intelligence boom has touched every corner of the economy. As data centers proliferate to support massive computation, the utilities sector has seen huge growth, fueled by the energy demands of the grid. In 2025, companies like NextEra and Exelon saw their valuations surge.
The industrials sector, too, has undergone a notable shift. General Electric was its undisputed heavyweight in 1999 and 2007, but the recent explosion in data center construction has evened out growth in the sector. GE still leads today, but Caterpillar is a very close second. Caterpillar, which is often associated with construction, has seen a spike in sales of its turbines and power-generation equipment, which are used in data centers.
One large difference between the big tech companies now and their counterparts during the dot-com boom is that many now earn money. A lot of the well-known names in the late 1990s, including Pets.com, had soaring valuations and little revenue, which meant that when the bubble popped, many companies quickly collapsed.
Nvidia, Apple, Alphabet and others generate hundreds of billions of dollars in revenue each year.
And many of the biggest players in artificial intelligence these days are private companies. OpenAI, Anthropic and SpaceX are expected to go public later this year, which could further tilt the market dynamic toward tech and A.I.
Methodology
Sector values reflect the GICS code classification system of companies in the S&P 500. As changes to the GICS system took place from 1999 to now, The New York Times reclassified all companies in the index in 1999 and 2007 with current sector values. All monetary figures from 1999 and 2007 have been adjusted for inflation.
Business
Coming soon: L.A. Metro stops that connect downtown to Beverly Hills, Miracle Mile

Metro has announced it will open three new stations connecting downtown Los Angeles to Beverly Hills in May.
The new stations mark the first phase of a rail extension project on the Metro D line, also known as the Purple Line, beneath Wilshire Boulevard. The extension will open to the public on May 8.
It’s part of a broader plan to enhance the region’s transit infrastructure in time for the 2028 Olympic and Paralympic Games.
The new stations will take riders west, past the existing Wilshire/Western station in Koreatown, and stopping along the Miracle Mile before arriving at Beverly Hills. The 3.92-mile addition winds through Hancock Park, Windsor Square, the Fairfax District and Carthay Circle. The stations will be located at Wilshire/La Brea, Wilshire/Fairfax and Wilshire/La Cienega.
This is the first of three phases in the D Line extension project. The completion of the this phase, budgeted at $3.7 billion, comes months later than earlier projections. Metro said in 2025 it expected to wrap up the phase by the end of the year.
The route between downtown Los Angeles and Koreatown is one of Metro’s most heavily used rail lines, with an average of around 65,000 daily boardings. The Purple Line extension project — with the goal of adding seven stations and expanding service on the line to Hancock Park, Century City, Beverly Hills and Westwood — broke ground more than a decade ago. Metro’s goal is to finish by the 2028 Summer Olympics.
In a news release on Thursday, Metro described its D Line expansion as “one of the highest-priority” transit projects in its portfolio and “a historic milestone.”
“Traveling through Mid-Wilshire to experience the culture, cuisine and commerce across diverse neighborhoods will be easier, faster and more accessible,” said Fernando Dutra, Metro board chair and Whittier City Council member, in the release. “That connectivity from Downtown LA to the westside will serve as a lasting legacy for all Angelenos.”
The D line was closed for more than two months last year for construction under Wilshire Boulevard, contributing to a 13.5% drop in ridership that was exacerbated by immigration raids in the area.
“I can’t wait for everyone to enjoy and discover the vibrance of mid-Wilshire without the traffic,” Metro CEO Stephanie Wiggins said in a statement.
-

 World1 day ago
World1 day agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts2 days ago
Massachusetts2 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Montana1 week ago
Montana1 week ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Oklahoma1 week ago
Oklahoma1 week agoWildfires rage in Oklahoma as thousands urged to evacuate a small city
-

 Louisiana4 days ago
Louisiana4 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Denver, CO2 days ago
Denver, CO2 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making


















