World
Analysis: In the Red Sea, the US has no good options against the Houthis
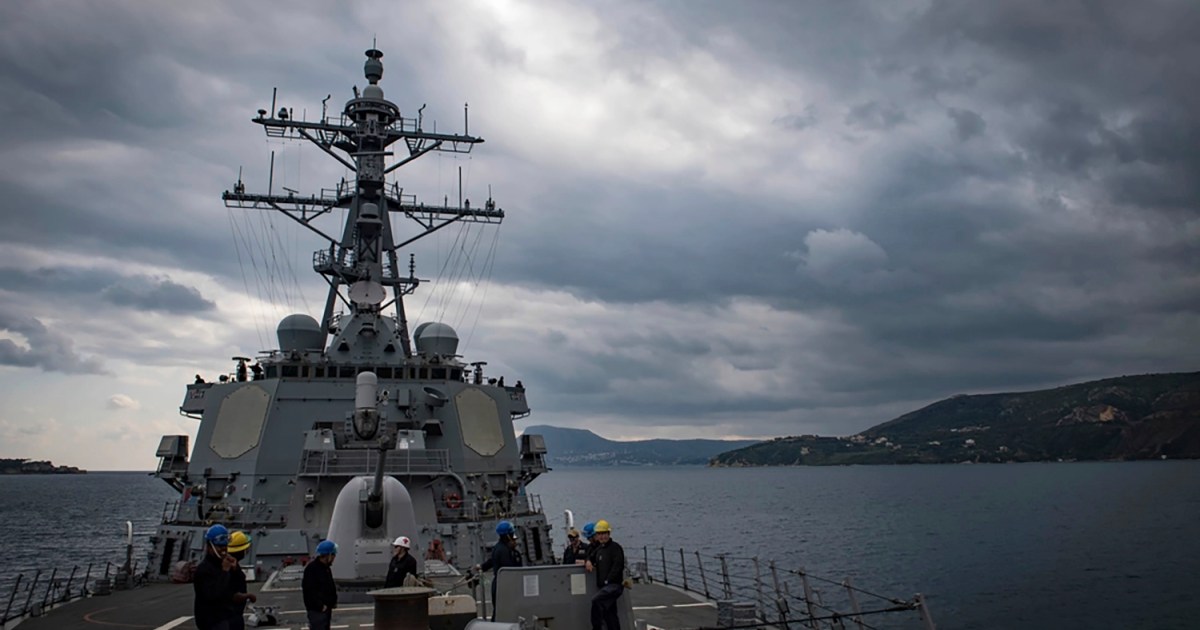

Operation Prosperity Guardian (OPG), the United States Navy-led coalition of the willing intended to allow international shipping to continue navigating safely through the Red Sea, is set to activate within days. Including allies from Europe and the Middle East, as well as Canada and Australia, the operation has been snubbed by three important NATO countries, France, Italy and Spain.
What is the exact task of OPG?
The official line, “to secure safe passage for the commercial ships”, is too vague for any naval flag officer to feel comfortable getting into. Admirals want politicians to give them precise tasks and clear mandates needed to achieve the desired results.
Defining the threat seems easy, for now: antiship missiles and drones of various types carrying explosive warheads have been targeting merchant ships on the way to and from the Suez Canal. All were fired from Yemen, by the Houthi group also known as Ansar Allah which now controls most of the country, including the longest section of its 450km-long Red Sea coast. All missiles were surface-launched, with warheads that can damage but hardly sink big cargo ships.
The Houthis at first announced that they would target Israeli-owned ships, then expanded that to include all those using Israeli ports, ultimately to those trading with Israel. After several attacks where the Israeli connection appeared very distant or vague, it is prudent to assume that any ship could be targeted.
All missiles neutralised by US and French warships so far were shot down by sophisticated shipborne surface-to-air missiles (SAM), proving that the modern vertical-launch systems guided by the latest generation phased array radars work as designed. Many nations earmarked to participate in OPG have ships with similar capabilities. Almost all also carry modern surface-to-surface missiles that can attack targets at sea or land.
If the task of OPG were to be defined narrowly, only to prevent hits on merchant ships, it could be performed using the centuries-old principle of sailing in convoys with the protection of warships.
In a convoy, slow, defenceless commercial cargos sail in several columns at precisely defined distances from each other — led, flanked and tailed by fast warships that can take on any threat. The system is effective, as the United Kingdom, Russia, Malta, and many other countries saved by convoys in World War II can attest.
But every strategy has its limitations. A convoy is big and cumbersome, extending for miles to give behemoth ships a safe distance from each other and to enable them to manoeuvre if needed. Whatever the protective measures taken, huge tankers and container carriers – longer than 300 metres (984 feet) – still present big targets. Captains of commercial ships are generally not trained in convoy operations, and most have no experience operating in large groups or under military command.
Their escorts, even if well-armed, carry a limited number of missiles and must plan their use carefully, allowing for further attacks down the shipping lane and ultimately leaving a war reserve for the defence of the ship itself. Once they expend some of the missiles, they need to replenish them – a task that is possible at sea but done much more quickly and safely in a friendly port out of reach of Houthi missiles.
To clear the critical 250 nautical miles (463km) along the Yemeni coast leading to or from the Bab al-Mandeb strait, advancing at assumed 15 knots (28kmph) — as convoys always sail at the speed of the slowest units — ships would be exposed to even the shortest-ranged Houthi missiles and drones for at least 16 hours.
And before even trying to make the dash, they would be particularly vulnerable in the staging areas in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden where ships would spend some time gathering, forming the convoy and setting under way.
The Houthi missile threat is now known to be high, and their arsenal is substantial. Naval planners must be worried by their ability to mount concentrated prolonged attacks simultaneously from several directions.
This was demonstrated in the very first attack, on October 19, when the Houthi launched four cruise missiles and 15 drones at USS Carney, a destroyer that is still operating in the Red Sea and will be part of OPG. The attack, probably planned to test the Houthis’ attack doctrine and enemy response, lasted nine hours, forcing the crew of the target ship to maintain full readiness and concentration for a prolonged period to intercept all incoming missiles.
Every admiral would tell his political superiors that military necessity would call for attacks on Houthi missile infrastructure on the ground in Yemen: fixed and mobile launch sites, production and storage facilities, command centres and whatever little radar infrastructure there exists. A proactive response to the missile threat, in other words, to destroy the Houthi ship-targeting capability, rather than the reactive one limited to shooting missiles down as they come in.
In theory, attacks against Houthi missile infrastructure could be based on satellite and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) reconnaissance and carried out by missiles launched from the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean and armed drones from distant land bases. But the only realistic chance at meaningful success would require the use of combat aircraft, bombers based on the two US Navy nuclear carriers in the region.
Attacks against targets in Yemen would have a clear military justification. But they would also carry a clear political risk: that of the West, particularly the US, being seen in the Arab and Islamic world as actually entering the Gaza war on the side of Israel. After all, the Houthis say their attacks on Red Sea ships are aimed at getting Israel to end the war.
Aware of the perils of such a development that could easily cause the conflict to spread, the US has tried to tread carefully, engaging with regional powers, and sending messages that it wants no escalation. It even openly demanded of its ally Israel that it limit civilian suffering and end the conflict as quickly as possible — to no avail.
The White House and the Pentagon are now walking on hot coals. If they do nothing, the Red Sea route will quickly close, causing US, European and Asian economies significant damage. If the half measures they currently propose, just escorting convoys without attacking missile sites on land, fail to secure safe passage, they will have lost face and failed in preventing an economic downturn. And if the US is eventually forced to attack, it will have directly contributed to a dangerous escalation that may be difficult to contain.
Mindful of all these dilemmas, France, Italy and Spain are playing it safe: they will “unilaterally” deploy their frigates to the Red Sea to “protect the ships of their respective nations”. Should the US Navy ultimately attack Yemen, the Europeans will be able to claim that they did not contribute to the intensification of the war, shoving all the responsibility to the US.

World
The Apartment to Produce ‘Rosebushpruning,’ Starring Kristen Stewart, Josh O’Connor and Elle Fanning

Fremantle’s The Apartment will partner with The Match Factory, Mubi, Kavac Film and Rai Cinema to produce Karim Aïnouz’s next feature film “Rosebushpruning.”
Directed by Aïnouz, the film’s lead cast includes Kristen Stewart (“Love Lies Bleeding,” “Spencer”), Josh O’Connor (“Challengers,” “God’s Own Country”) and Elle Fanning (“Teen Spirit,” “The Great”). Aïnouz is directing from a script written by Efthimis Filippou (Kinds of Kindness, Dogtooth, The Lobster), which is an adaptation from Marco Bellocchio’s debut feature Fists in the Pocket.
Viola Fügen and Michael Weber are producing “Rosebushpruning” for The Match Factory, who are also handling worldwide sales for the film. The adaptation rights have been acquired from Kavac Film also attached at the production team with Simone Gattoni. The Apartment, a Fremantle Company, is co-producing, with Annamaria Morelli as executive producer. Rachel Dargavel for Crybaby Films is co-producing in the UK. Mubi is financing production alongside Catherine Boily and Mitch Oliver’s Metafilms and Anna Films in association with Fremantle. Film und Medienstiftung NRW, Medienboard and the German Federal Film Board also funded the film.
“We are extremely happy to be part of this important film together with exceptional partners such as The Match Factory, MUBI, Kavac and Rai Cinema,” said Annamaria Morelli, CEO, The Apartment. “We deeply appreciate Karim Aïnouz’s films and are enthusiastic of the way he and Efthymis Filippou adapted Bellocchio’s masterpiece, revisited with a strikingly bold and original vision.”
Commenting on “Rosebushpruning,” Aïnouz said: “Marco Bellocchio’s astonishing debut, ‘Fists in the Pocket,’ was released over 50 years ago and had a huge impact on Italian cinema and storytelling at the time. I’m excited to be collaborating with Efthimis Filippou to revisit this iconic work to create a contemporary parable about the explosion of the traditional patriarchal family — which I hope will be touching and provocative in equal measure. It’s a dream come true to be working with such a dynamic ensemble of actors that I have long admired to bring this explosive adaptation to audiences today.”
The film will begin production later this year.
Aïnouz is represented by Lark Management, CAA and Andre des Rochers.
World
Thailand's new Senate selection process unfolds as candidates begin 'complicated' registration
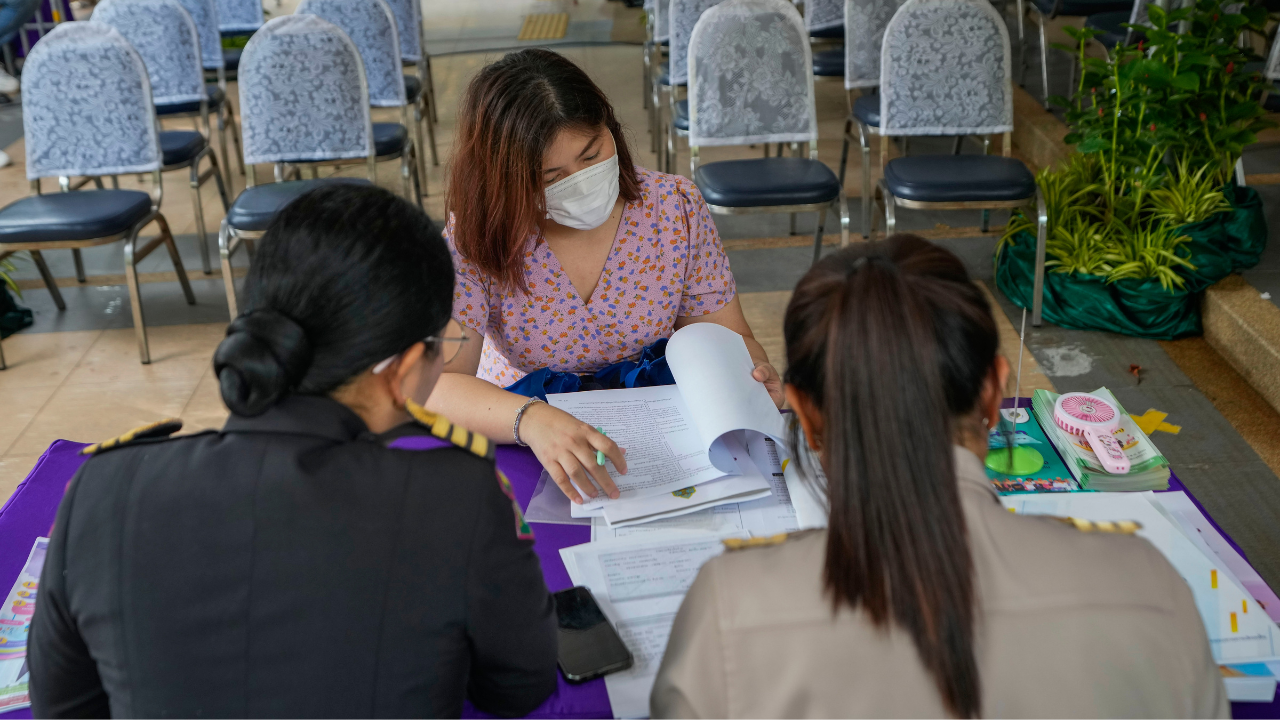

- Thailand has started the selection of new senators, marking the start of a contentious battle between progressives and conservatives.
- Hopeful candidates registered at district offices nationwide, competing for one of the 200 seats in the upper house of Parliament.
- The Senate, though less powerful than the House of Representatives, played a large role in blocking the formation of a new government.
Thailand on Monday officially began the selection of new senators, a process that has become part of an ongoing war between progressive forces hoping for democratic political reforms and conservatives seeking to keep the status quo.
Hopeful candidates headed to district offices across the country on the first day of registration to compete for one of the 200 seats in Parliament’s upper house.
The power of the Senate — although limited compared to the House of Representatives, which is tasked with law-making responsibilities — was demonstrated dramatically when it blocked the progressive party that won the most seats in last year’s election from forming a new government.
HUMAN RIGHTS GROUP URGES THAI GOVERNMENT TO HALT FORCED REPATRIATION OF POLITICAL DISSIDENTS
The senators were able to do so because of the 2017 Constitution, passed under a military government, which requires the prime minister to be approved by a joint vote of the elected House and the Senate, which was appointed by the military regime.
Potential candidates to become members of Thailand’s next Senate arrive at the Phaya Thai district office in Bangkok on May 20, 2024. Thailand on Monday officially began the selection of new senators, a process that has become part of an ongoing war between progressive forces hoping for democratic political reforms and conservatives seeking to keep the status quo. (AP Photo/Sakchai Lalit)
The Move Forward Party was opposed by senators who disapproved of its vow to seek reforms of Thailand’s monarchy.
The process of selecting the new senators will include three rounds of voting: district, provincial and national.
Unlike the elected lower house legislators, the senators will be chosen by their fellow applicants, competing in 20 categories such as occupation or social position, including women, the elderly and the disabled.
THAI PRO-CANNABIS ADVOCATES RALLY AS GOVERNMENT MOVES TO RECRIMINALIZE
The final results are expected to be announced in July.
The selection process in the Constitution is so complicated and unclear that critics say it was deliberately designed to discourage public participation. Critics say the Constitution also allows the state bureaucracy to hold more power than directly elected political officeholders.
The new senators will no longer be able to take part in selecting a prime minister but will retain the power to approve legislation passed by the House.
They also have the power to select members of nominally independent regulatory bodies such as the Election Commission and the Constitutional Court, whose work has been widely seen as impeding efforts at political reform and crippling proponents with legal penalties, including prison.
The Senate’s votes are also required to amend the Constitution. The governing Pheu Thai party is pushing for a new charter to replace the 2017 one to facilitate certain reform efforts promised during the campaign.
Civil society groups have campaigned to raise public awareness and encourage those favoring democratic reforms to enter the Senate selection process.
Law reform advocate Yingcheep Atchanont of the group iLaw has been organizing public discussions on the importance of the Senate and workshops to help would-be applicants understand how the selection process works.
“We are telling people what to do if they want change. There have been calls in recent years to reduce the power of the Senate, to get rid of the Senate,” he said. “All of this can only happen if we can amend the Constitution, and we need enough votes from the senators for that.”
Candidates must be more than 40 years old and have more than 10 years of experience in their chosen occupational group, the latter provision not applying for those competing in one of the social identity groups. They also cannot campaign or do anything that can be interpreted as campaigning.
Even the Election Commission has acknowledged how complicated the process is but says it will be able to carry it out smoothly and transparently.
Purawich Watanasukh, a political science lecturer at Bangkok’s Thammasat University, said he thinks the complicated rules were intentionally designed to reduce public participation.
“This is the contest of the people to debug not just the Senate itself, but the Constitution, which would lead to a new political landscape in Thailand,” he said, “”It will be the next battleground between the progressive movement and the establishment.”
World
Panic in Bishkek: Why were Pakistani students attacked in Kyrgyzstan?

Islamabad, Pakistan — More than 300 Pakistani students have rushed home from Kyrgyzstan after a mob attacked hostels occupied by international students, injuring several of them, in the Central Asian nation’s capital Bishkek last week.
The violence broke out in the late hours of May 17, lasting for more than six hours, when hundreds of Kyrgyz people targeted hostels of international students, leaving more than 30 injured.
In a news conference on Sunday, Pakistan’s Foreign Minister Ishaq Dar said Kyrgyz authorities had assured that the situation had been brought under control. He confirmed that “four or five” Pakistani students were injured in the violence but refuted online rumours of any deaths in the clashes.
Yet, Dar appeared to acknowledge the fears of the more than 11,000 Pakistani students in Kyrgyzstan, and their families, announcing that the government was arranging flights to bring back all students who wanted to return. The government, he said, would bear the expenses — though Pakistani students in Bishkek claimed they had to pay out of pocket for tickets back.
So what led to the violence, what happened on May 17, and what is the situation in Bishkek now?
What happened on the night of May 17?
Korish Malik, a 24-year-old Pakistani student pursuing a medical degree in Bishkek, recalled that he was in his hostel when, in the evening, student residents received a message from the hostel administration to stay indoors.
“The administration said there appears to be a threat to international students and they must refrain from leaving the premises of their hostels. But then we saw on TikTok that a large group of locals was gathering and marching towards our hostel,” he told Al Jazeera from Bishkek.
According to Kyrgyz media reports, a crowd of more than 700 people gathered outside the city’s VIP Hostel, which houses more than 800 international students, including Pakistanis, Indians, Egyptians and Bangladeshis.
Bilal Ishaq, a Pakistani medical student from Faisalabad who lives in a private apartment near the VIP Hostel, said he also received alerts on WhatsApp groups of fellow university students and the Pakistani student community, asking students to stay indoors. He saw a crowd chanting slogans pass his building, moving towards the hostel. The WhatsApp groups, he said, were buzzing with messages from terrified students.
Back at the VIP Hostel, Korish said, soon after students received the warning, police officials arrived and cordoned off the front gate of the building. But the crowd, he said, was large — too large, it turned out.
“While there were a lot of police officials there, they did not have any riot gear with them,” he said. “We were just asked to switch off lights, lock the doors, and put heavy objects in front of the doors of our room.”
Korish said the mob entered the hostel from the emergency exit at the back of the building and went on to indulge in vandalism.
Videos on social media show a huge number of people walking towards the hostel, hurling stones at the windows. Another video shows a door being broken, and glass shattered in the corridor of the hostel.
Korish said he and his three roommates hid in their room on the fourth floor of the five-storey building. They could hear loud noises from other floors, he said.
“The whole thing lasted for almost six to eight hours and when we eventually came out of the room, it was obvious that the mob was there to just cause chaos and spread terror,” Korish said.
What triggered the attack?
The May 17 violence followed a brawl between Kyrgyz locals and a group of international students four days earlier.
Hassan Aryani, a Pakistani student pursuing his degree in medicine, said the videos of the fight went viral among students in the city. Aryani, from Mardan in the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, said an “uneasy calm” hung over the student community in Bishkek after that clash.
On the night of May 17, that tension exploded in mob violence.
What were the international responses?
The embassies of India and Pakistan in Bishkek advised the students to stay indoors.
On the morning of May 18, Pakistan’s Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif posted on X that he was “deeply concerned over the situation of Pakistani students in Bishkek”.
Deeply concerned over the situation of Pakistani students in Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan. I have directed Pakistan’s Ambassador to provide all necessary help and assistance. My office is also in touch with the Embassy and constantly monitoring the situation.
— Shehbaz Sharif (@CMShehbaz) May 18, 2024
Indian Foreign Minister S Jaishankar also wrote on the social media platform that he was monitoring events in Bishkek, urging Indian students to stay in contact with the country’s embassy.
The Kyrgyz government said on the morning of May 18 that calm had returned to the capital.
![Pakistanis protest against the attacks on international students, including Pakistanis, in Kyrgyz capital of Bishkek last week. [Sohail Shahzad/EPA]](https://www.aljazeera.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/sohail-shahzad-1716194557.jpg?w=770&resize=770%2C505)
How is the situation in Bishkek now?
Aryani, who is in his final year of college, said while Bishkek appears to be returning to a state of normalcy, he was not willing to stick around in the Kyrgyz capital at the moment.
He said he planned to get a ticket and fly back to Pakistan as soon as he could.
Korish, the third-year student, said he managed to step out of his hostel on Monday morning and could move around the city. But he also said he would travel back to Pakistan to allay his parents’ concerns.
Meanwhile, Kyrgyz authorities also do not want to take chances.
Rasul Abazbek uulu, the country’s deputy minister for education and science, announced in a news conference on Monday that foreign students had been allowed to attend classes online for a week.
The latest announcement helped students like Korish make up their minds about the decision to return home.
“My family is naturally very worried about the situation. But now since our college has said that classes will take place online, and the semester was to end anyway at the end of May, I have bought a ticket to go back tomorrow,” Korish said.
While the Pakistani embassy in Kyrgyzstan says it is in close contact with the local authorities to facilitate the students, several students in Bishkek accused the government of abandoning them. Though Dar, Pakistan’s foreign minister, has said the government would bear the cost of transporting students back, the three students Al Jazeera spoke to all said they had to pay themselves for their tickets. It is unclear if the government plans to subsequently reimburse students.
The Kyrgyz government said those involved in the violence had been arrested and it was in touch with different foreign governments whose nationals were affected by the incident.
“There are no seriously injured people among participants of the incident. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Kyrgyz Republic did not receive any messages regarding injured foreign citizens. At the same time, the ministry urges representatives of the media and foreign diplomatic missions not to disseminate false and unverified information,” the Kyrgyz government said in a statement on May 18.
How many Pakistanis and Indians study in Kyrgyzstan and where?
More than 11,000 Pakistani students and 15,000 Indian students are pursuing degrees in medicine in Kyrgyzstan.
The attraction: a combination of reasonably high standards at Soviet-era medical colleges combined with tuition fees that are lower than most educational destinations in the West and even in their home countries. Kyrgyzstan medical colleges are also popular among students from several Arab and African nations.
![Kyrgyz media reports that more than 700 people were part of the mob that attacked international students in Bishkek. [Courtesy Korish Malik]](https://www.aljazeera.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Courtesy-Korish-Malik-1716194805.jpeg?w=770&resize=770%2C1027)
Ishaq, the student from Faisalabad, said while his medical degree in Pakistan could cost him nearly eight to nine million rupees ($28,000 to $32,000), the corresponding amount in Kyrgyzstan was closer to four to five million rupees ($14,000 to $18,000).
“It was a lot more feasible to study here money-wise. But now, with the Pakistani currency devaluation, the cost for studies even here is increasing,” he added. The Pakistani rupee, which stood at 160 against the US dollar in December 2020, has since slipped by more than 70 percent to 278 rupees a dollar.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSkeletal remains found almost 40 years ago identified as woman who disappeared in 1968
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIndia Lok Sabha election 2024 Phase 4: Who votes and what’s at stake?
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago“Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes”: Disney's New Kingdom is Far From Magical (Movie Review)
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUkraine’s military chief admits ‘difficult situation’ in Kharkiv region
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTales from the trail: The blue states Trump eyes to turn red in November
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoBorrell: Spain, Ireland and others could recognise Palestine on 21 May
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCatalans vote in crucial regional election for the separatist movement
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNorth Dakota gov, former presidential candidate Doug Burgum front and center at Trump New Jersey rally