Science
Shaking Ordinary Ice (Very Hard) Transformed It Into Something Never Seen Before

So Alexander Rosu-Finsen, a postdoctoral scientist in Dr. Salzmann’s analysis group and the lead creator of the Science paper, began smashing up ice. The water ice was first chilled in liquid nitrogen to minus 320 levels Fahrenheit after which positioned in a container together with metal balls. A machine then shook the ice and metal balls, nonetheless chilled at ultracold temperatures, forwards and backwards at 20 instances per second, pulverizing the ice into tiny bits, a course of often known as ball milling.
Consider it as a high-tech cocktail shaker.
Dr. Rosu-Finsen then opened the container.
“Lo and behold, one thing utterly surprising occurred,” stated Dr. Rosu-Finsen, who’s now an affiliate editor on the journal Nature Critiques Chemistry.
The white materials inside regarded like what one would anticipate smashed-up ice to appear like, but it surely had been reworked.
The fabric was now denser, and far of the crystalline construction had been destroyed, producing an amorphous materials. The density, nonetheless, didn’t match the already identified high- and low-density amorphous ices. Intriguingly, it fell in between; certainly, it was nearly precisely the identical density as liquid water. Till now, all the strong types of ice, crystalline or amorphous, had been both considerably denser or much less dense than liquid water.
The researchers named it medium-density amorphous ice, or MDA.
The banging of the metal balls utilized a shearing pressure on the ice crystals, sufficient to knock the water molecules out of their crystal positions, permitting them to be packed extra tightly.
“It’s actually cool,” stated Marius Millot, a physicist at Lawrence Livermore Nationwide Laboratory in California who led the experiment that created superionic water. “What it tells us is that there’s nonetheless loads of issues that we don’t perceive.”

Science
Second human case of bird flu detected in Michigan dairy worker
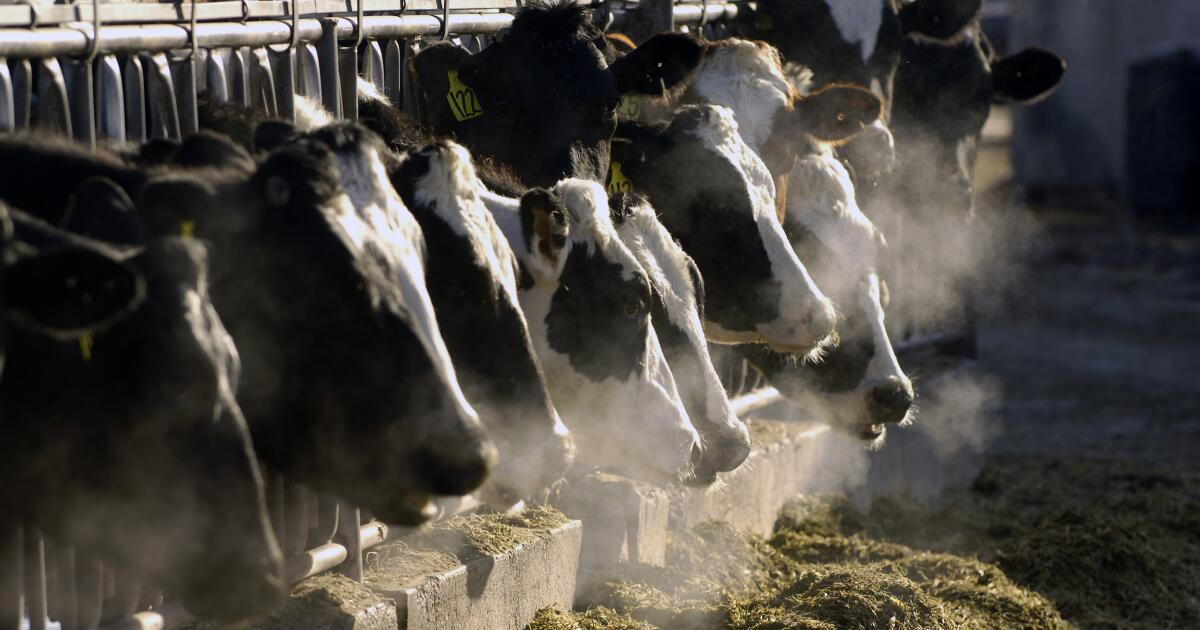

A second human case of bird flu in a diary worker has been confirmed in Michigan, state and federal health officials announced Wednesday.
The symptoms were mild, consisting of conjunctivitis. The Texas dairy worker who contracted the virus in March also came down with pink eye.
At a press call on Wednesday, Nirav Shah, principal deputy director of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said the finding was “not unexpected” and that it was a scenario “that we had been preparing for.”
He said that since the discovery of H5N1 in dairy cattle, state and federal health officials have been closely monitoring farmworkers and slaughterhouse workers and urging farmers and farmworker organizations to “be alert, not alarmed.”
Federal officials say they still believe the human health risk of bird flu is low; however, it underscores the need for people who are interacting with infected or potentially infected farm animals or birds to take precautions, including avoiding dead animals and wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) if there’s a need to be in close contact.
Though a nasal swab from the person in Michigan tested negative for influenza, an eye swab from the patient was shipped to the CDC and tested positive for influenza A(H5N1) virus.
This is the third case of H5N1 reported in the United States. A poultry worker in Colorado was identified in 2022.
Although the symptoms in the three farmworkers in the U.S. have been mild, people elsewhere in the world have suffered more severe illness, including death. According to the World Health Organization, between Jan. 1, 2003, and March 28, 2024, there have been 888 cases of human infection from 23 countries; 463 were fatal.
In preparation for a more widespread outbreak, the CDC updated its guidance for PPE in dairies and issued a nationwide order for healthcare providers to be on the lookout for novel influenza.
On Tuesday, the CDC asked clinical laboratories and health departments to increase the number of influenza samples being analyzed “to maximize the likelihood of catching a case of H5N1 in the community,” Shah said.
The US Department of Agriculture is also expanding its surveillance and support by providing $1500 to non-infected farms to beef up biosecurity, and $100 to producers who want to buy inline samplers to test their milk. The agency will also provide $2000 per farm to cover veterinary fees for testing, as well as shipping costs to send those tests to laboratories for analysis.
There have been no cases of H5N1 detected in California’s dairy herds.
Officials said ongoing analysis of the nation’s dairy supply suggests it is safe to consume, Despite the risk to human health being low, an official with the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response said it will make Tamiflu available upon request “to jurisdictions that do not have their own stockpile and are responding to pre-symptomatic persons with exposure to confirmed or suspected infected birds, cattle or other animal exposures.”
Dawn O’Connell, assistant secretary of the preparedness agency, said it started the “fill and finish” process for approximately 4.8 million doses of vaccine “that is well matched to the currently circulating strain of H5N1 through the national pre-pandemic influenza vaccine stockpile program.”
She said the decision to get started on H5N1 vaccines was not a response to any heightened concern, but since it takes several months to fill and finish vaccine doses, the agency “thought it made sense given what we were seeing.”
Science
Gas stoves may contribute to early deaths and childhood asthma, new Stanford study finds
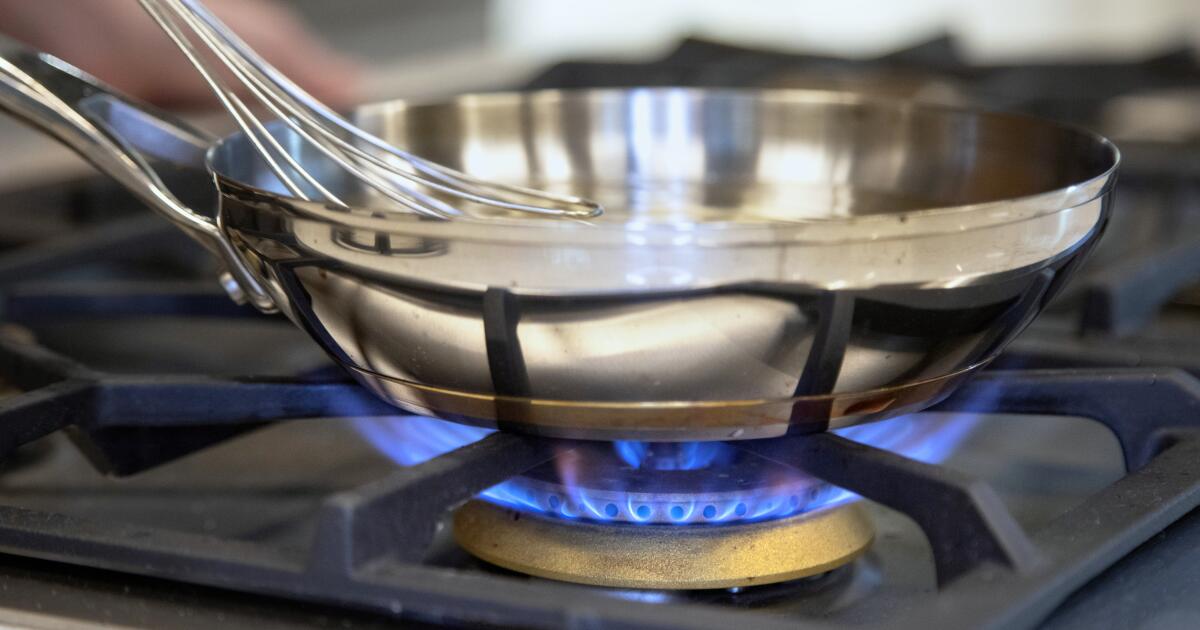

Lung-irritating pollution created by cooking with gas stoves may be contributing to tens of thousands of premature deaths and cases of childhood asthma in the United States, according to a new study published in the journal Science Advances.
For decades, scientists have known the flames from a gas stovetop produce nitrogen dioxide, a pungent gas that can inflame a person’s lungs when inhaled. But for the first time, a team of researchers from Stanford University and Oakland-based research institute PSE Healthy Energy published a nationwide estimate of the long-term health consequences associated with cooking with natural gas and propane stoves.
Researchers concluded that exposure to nitrogen dioxide emissions alone may contribute to nearly 19,000 premature deaths in the United States each year. It has also resulted in as many as 200,000 current cases of pediatric asthma compared with cooking with electric stoves, which do not produce nitrogen dioxide.
Aggressive and impactful reporting on climate change, the environment, health and science.
Stanford researcher Yannai Kashtan noted higher levels of pollution were correlated with the amount of gas that was burned. But pollution also accumulated at higher levels inside smaller homes.
“If you live in a smaller house, you’re exposed to more pollution, and that can lead to income and racial disparities in exposure,” Kashtan said. “In general, folks living in neighborhoods with higher levels of outdoor pollution also tend to have higher indoor pollution. So this environmental injustice extends indoors as well.”
The American Gas Assn., a trade organization representing more than 200 local energy companies nationwide, dismissed the findings as “misleading and unsupported.”
“Despite the impressive names on this study, the data presented here clearly does not support any linkages between gas stoves and childhood asthma or adult mortality,” the association’s president and CEO, Karen Harbert said in a statement earlier this month.
The study is the latest examining the serious health effects associated with breathing fumes from gas stoves, which release planet-warming carbon emissions and a variety of air pollutants. In recent years, the popular household appliance has become a political hot-button issue as policymakers and regulators have weighed environmental impacts against consumer choice.
Many large cities in California, including Los Angeles, have moved toward phasing out gas stoves in newly constructed residences. Earlier this month, the California Assembly advanced a bill to the Senate that would require gas stoves to come with warning labels detailing the pollution and health effects that can arise from cooking with gas.
Gas stoves emit a variety of pollutants, including asphyxiating carbon monoxide, cancer-causing formaldehyde and benzene. The flame also creates nitrogen dioxide, a precursor to smog and a pollutant that can cause difficulty breathing.
Environmental groups say consumers should be notified about these pollutants and the potential harm they can cause.
“Gas stoves create pollution in our homes, increasing the risk of childhood asthma and other respiratory problems for our families,” said Jenn Engstrom, state director for California Public Interest Research Group. “However, this risk has largely been hidden from the public. Consumers deserve the truth when it comes to the danger of cooking with gas. Warning labels will give consumers what they need to make informed decisions when they purchase appliances for their homes.”
Kashtan and other researchers had previously discovered cooking with gas stoves presented a similar cancer risk as inhaling second-hand cigarette smoke. They also found some gas stoves leaked contaminants even when the burners were off.
The effects are especially devastating to children, whose smaller and still-developing lungs need to take more breaths than adults, Kashtan said. Older adults, especially those with cardiovascular or respiratory illness, are also more vulnerable to pollution from gas stoves.
To alleviate indoor air pollution, experts recommend using ventilation hoods and opening windows while cooking,
Starting in 2008, California required new and redeveloped homes to have ventilation that could prevent pollution from building up indoors. But during their research, measuring emissions in more than 100 households across the country, Yannai said they found many kitchens didn’t have ventilation hoods at all.
Although the health effects of breathing these pollutants are clear, researchers still wonder to what degree these conditions could be reversible. As communities take steps to mitigate their exposure or transition away, he said we could soon see the results.
“It’s never too late to stop breathing in pollution,” he said.
Science
Microplastics discovered in human and dog testes

Researchers have located one more anatomical organ where microplastics — of all shapes and constituents — are found: human testes.
And although they can’t say for sure, they suspect the presence of these jagged bits and strands of polymers such as polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride and polystyrene could be — in part — behind a global trend in diminishing sperm quality and quantity.
Aggressive and impactful reporting on climate change, the environment, health and science.
In 2022, a team of researchers published a paper showing that global sperm counts fell about 1.2% per year between 1973 and 2018. From the year 2000, that rate accelerated to more than 2.6% per year.
“What I think will grab people’s attention with this study is the fact that plastic is in the testicles and potentially contributing to disarray in the function of the testicles,” said Leonardo Trasande, a pediatrician and public policy expert at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine and Wagner School of Public Service.
“What should have gotten people excited all along is the fact that we’ve known that the invisible chemicals — the phthalates, the bisphenols and the PFAS that are used in plastic materials — are already known to be problems,” he said. “And so if this is what it takes to get people’s attention, I’m a bit sad. Because we already had enough evidence that plastics were bad for testicular function.”
Others, including Philip Landrigan, director of the Program for Global Public Health and the Common Good at Boston College, said the study was “consistent with a whole series of papers that have come out now in the last few years” showing these particles in a variety of organs, including the heart, liver, lungs and brain.
“It’s no surprise that microplastics are in the testes. The plastic is ubiquitous in today’s world, the stuff breaks down, and the smaller the particle, the more easily it can move into and throughout the human body,” he said.
Xiaozhong Yu, a professor of environmental health at the University of New Mexico — and an author on this latest research — said he’d been researching the effects of different chemicals on sperm production for years, and it was only recently that a colleague suggested he look for microplastics in testes.
“I said, ‘Are you joking?’,” he said, recalling the conversation, explaining he was pretty certain he wouldn’t find microplastics in tests because — like the brain — these sperm-generating factories are insulated by a protective barrier.
Nevertheless, they gave it a go.
They started by trying it out in dog testes. They were able to acquire 47 from neutering clinics. (The pet owners all provided permission.)
They found microplastics in small dogs, big dogs, young dogs and old dogs. The plastic bits were in every dog testis they examined. The number ranged from 2.36 micrograms per gram to 485.77 micrograms per gram. The average was 122.63 micrograms per gram, and 12 polymers were identified. The most abundant were polyethylene — the material found in plastic packaging, films and bottles — and polyvinyl chloride — a material found in most household water pipes.
He said he immediately went back to investigate their quality control. Maybe the testes had become contaminated at some point during the procedure or testing?
He and his team were able to rule that out, although Landrigan noted that contamination was still possible — unless everything, from procurement to analysis had been done in a “clean” room devoid of all plastic.
Yu and his team then decided to look at human samples. In the end, they were able to examine 23 testes from men ages 16 to 88. The tissue was acquired from males who had died in accidents and whose testes had been preserved post-autopsy. He said all samples were from men who had died in 2016 — made available following a seven-year storage requirement, after which time such samples are usually discarded.
Once again, they found microplastics in every sample they examined, and as with the dog testes, there was wide variation — from 161.22 micrograms per gram to 695.94 micrograms per gram, with an average of 328.44 micrograms per gram — nearly three times greater than what they found in dogs.
The microplastics in human testes were also composed of a variety of polymers, with polyethylene being the most common, followed by ABS (acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene monomers — which is used to make a variety of products, including toys, automotive parts, medical equipment and consumer electronics), N66 (a kind of nylon), polyvinyl chloride and others.
The researchers also noted a correlation between the concentrations of PVC and polyethylene and testes weight: The higher the concentration, the lower the weight.
“Generally, a decreased testis weight is indicative of reduced spermatogenesis,” wrote the authors in the paper.
Yu said the difference in humans and dogs between polymer types — with dogs showing higher concentrations of PVC than men — likely has to do with lifestyle differences. He said consumer trends show a general aversion to eating or drinking out of bottles and foodware made from PVC, which contains bisphenol A — an additive that has been associated with health and developmental harm.
However, he began looking at dog toys, and noticed many of them are made from this kind of plastic.
“People are choosing to avoid it,” he said. But the market hasn’t budged in the same way for dogs.
Asked what the major route of exposure was for dogs and people, he said “microplastics are everywhere — in the air, in the drinking water, in the food, in our clothes. We don’t exactly know what is the most probable route. But they are everywhere.”
He also noticed variation within the groups. Dog testes acquired from public veterinary clinics showed higher levels of microplastics than those from private clinics, “potentially reflecting the influence of socioeconomic differences on the living environments and lifestyles of dogs.”
The researchers were also not able to find a correlation between age and microplastic concentration — a finding that surprised them. (Although men over the age of 55 had the least amount).
“The absence of a distinct age-dependent accumulation of microplastics in human testes may be due to unique physiological and biological processes of spermatogenesis,” they wrote, noting the continual renewal and release of sperm, which could “help mitigate the buildup of microplastics over time.”
That hypothesis, they noted, was supported by the presence of microplastics in human seminal fluid.
“The reality is that the petrochemical industry has gotten a pass all these years,” said Trasande, the NYU professor. “We know that plastics come from the petrochemical industry … and it’s no secret that we have paid as a society by letting the petrochemical industry pollute us. Now we’re paying the consequences. And if we don’t reverse course fairly quickly, we will have an even bigger problems before us because plastic consumption is growing, not slowing down.”
Landrigan agreed and noted that nations were currently in negotiations to sign a treaty that would curb the use of plastic and cap production.
“Plastic production is increasing exponentially,” he said noting that it’s increased more than 200-fold since the 1950s. He said plastic production is on a trajectory to double by 2040 and triple by 2060. There have been a total of about 8 billion tons of plastic produced since 1950, he said, and about 6 billion tons is “floating around us, most of it in the form of microplastics.”
He said the anatomical location of this latest microplastic discovery may hit close to home for lawmakers, who until this time, have not been too concerned.
He said he’d had to testify in the Senate several years ago about endocrine disruptors, and mentioned that sperm quantity was reduced in men who’d been exposed.
“Two senators sat back and unconsciously crossed their legs,” he said. “The body language was amazing.”

-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoNevada Cross-Tabs: May 2024 Times/Siena Poll
-
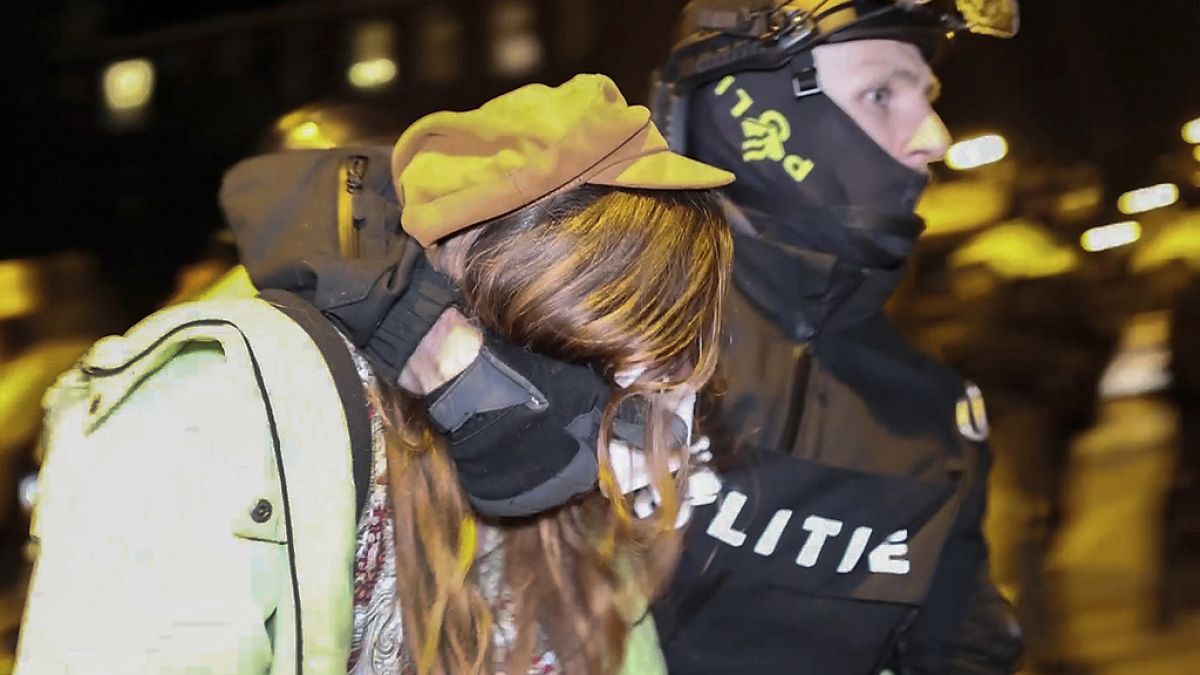
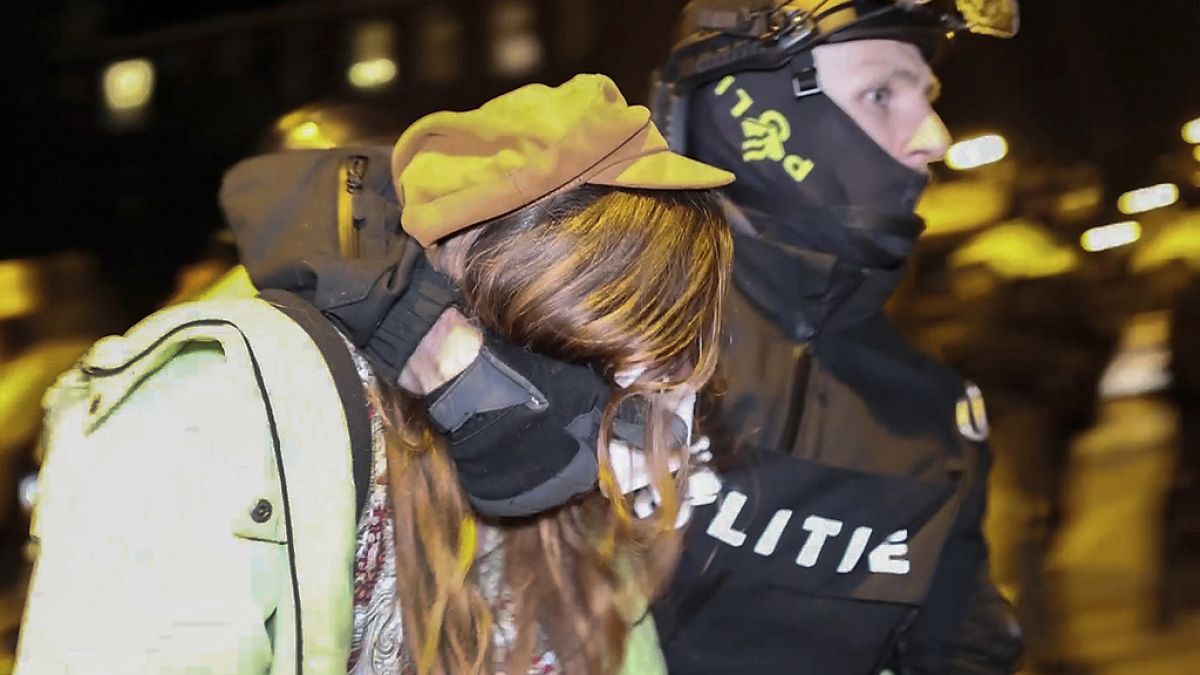 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPro-Palestinian university students in the Netherlands uphold protest
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoReports of Biden White House keeping 'sensitive' Hamas intel from Israel draws outrage
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoSouthern border migrant encounters decrease slightly but gotaways still surge under Biden
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoWhite House walks diplomatic tightrope on Israel amid contradictory messaging: 'You can't have it both ways'
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDem newcomer aims for history with primary win over wealthy controversial congressman
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSlovakia PM Robert Fico in ‘very serious’ condition after being shot
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNY v. Trump trial resumes with 'star witness' Michael Cohen expected to take the stand















