Science
Immune amnesia: Why even mild measles infections can lead to serious disease later
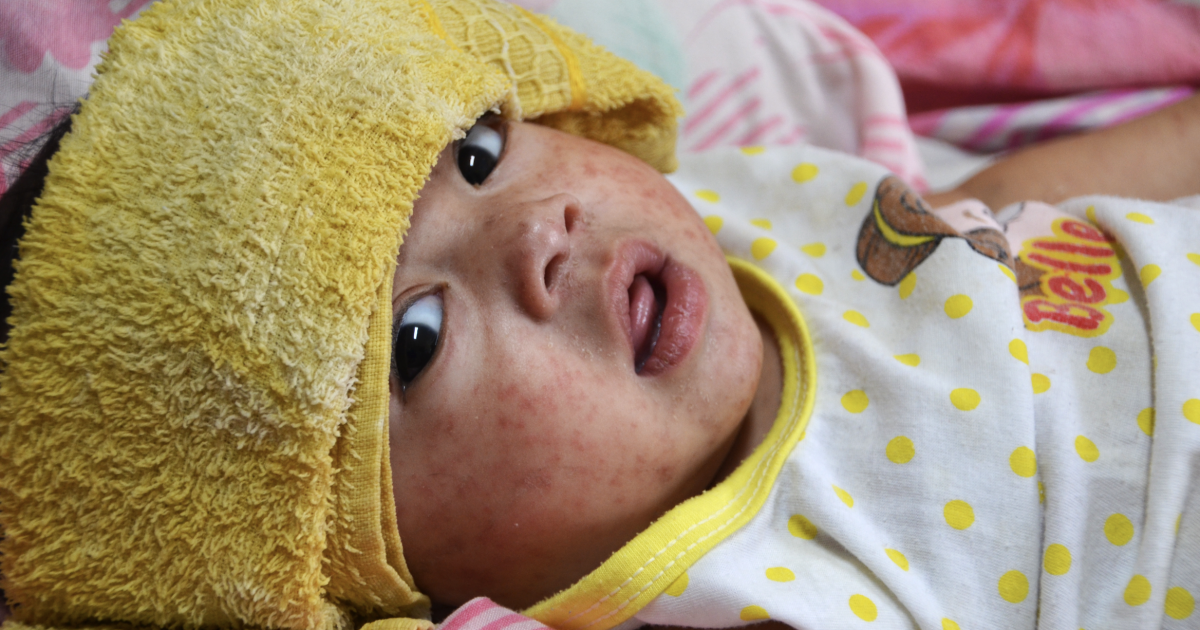
Dr. Adam Ratner has heard a lot of myths and misunderstandings about measles in his decades as a New York City pediatric infectious disease specialist.
A troubling untruth he’s seen circulating on social media during the current outbreak is that being infected with the virus instead of getting vaccinated confers benefits on the immune system — a strength-training program of sorts for the cells.
The truth, Ratner said, “is exactly the opposite.”
Measles is a highly contagious virus that presents as a rash and cold-like symptoms for many patients, and can lead to serious or fatal complications for others. An outbreak that began in west Texas in January has since infected nearly 500 people across 19 states, including eight people in California.
An insidious but lesser-known consequence of even a mild measles infection is that it kills the very cells that remember which pathogens the patient has previously fought and how those battles were won. As a result, recurring bugs that might have caused only minor symptoms make patients as sick as if they’d never encountered them before.
Measles destroys lymphocytes that defend against other bugs to make way for ones that defend against measles, an immunity won at the cost of other protections.
This “immune amnesia,” physicians say, leaves patients vulnerable to reccurrences of diseases their immune cells were previously able to resist.
If a child gets sick with measles, “for the next two or three years, you kind of have to be looking over your kid’s shoulder, wondering if some otherwise routine virus or bacteria that they should be very well protected against is potentially going to land them in the hospital,” said Dr. Michael Mina, an epidemiologist who was previously an assistant professor of immunology and infectious diseases at Harvard Medical School.
“Even if your measles virus infection seemed mild and you kind of blew through it, it doesn’t mean that it was mild on your immune system,” Mina added.
Take rotavirus, Ratner said, which causes severe diarrhea that can be life-threatening for children if untreated. A child who has rotavirus once will have antibodies that offer protection against future infections.
But a measles infection, said Ratner, author of the recent book “Booster Shots: The Urgent Lessons of Measles and the Uncertain Future of Children’s Health,“ “could wipe out that immunity and they could be just as vulnerable to rotavirus as if they had never seen it before.”
Immune amnesia results from the measles virus’ plan of attack. Viral particles travel via airborne droplets of saliva, mucus and cells that make their way into a new body when their unsuspecting host breathes them in.
From there, they sneak past the protective barrier lining the respiratory system and head to the lymph nodes in search of cells that express a particular protein called signaling lymphocytic activation molecule, or SLAM.
The virus then rides around the bloodstream on these hijacked SLAM-expressing cells, further infecting and destroying other SLAM expressers it meets on the way.
Among the SLAM-expressing cells that measles wrecks are memory B and T cells, two crucial players in a functioning immune system. Memory B cells manufacture the right antibodies quickly when a familiar microbe appears. Memory T cells recognize and kill viruses that your cells have encountered in the past.
A measles infection feeds on these memory cells. Vaccines, in contrast, stimulate the production of memory B and T cells without consuming others in the process.
This was not yet understood in the decades before the measles, mumps and rubella vaccine’s approval in 1963, when measles was a common childhood disease that killed some 400 children in the U.S. each year.
“For 100 years or more, we’ve known that measles does cause an acute susceptibility to other infections,” Mina said.
A measles infection temporarily suppresses the immune system, Mina said, and it was long assumed that opportunistic infections around the time of the illness were the result of that short-term suppression.
In 2015, Mina and colleagues published a paper that looked at mortality data in the U.S., the United Kingdom and Denmark before and after measles vaccines were introduced. They found that whenever there were measles outbreaks, childhood deaths from all other infectious diseases remained significantly higher for two to three years in outbreak locations, an increase that accounted for up to half of all childhood deaths from infectious disease.
Once those countries rolled out the MMR vaccine, measles cases fell, as expected. But so did childhood deaths from other infectious diseases, by about half.
Three years later, Mina and his collaborators took blood samples from 77 unvaccinated children in a community in the Netherlands before and then two to six months after the children contracted measles. They found that the virus wiped out 11% to 73% of the children’s preexisting antibodies to a host of pathogens.
Just as children in preschool fall ill constantly with common diseases they’re encountering for the first time, unvaccinated children who contract measles are at higher risk in the ensuing years for common early childhood sicknesses such as respiratory infections, earaches and viruses that cause diarrhea, said Shelly Bolotin, a scientist at Public Health Ontario in Canada and director of the Center for Vaccine Preventable Diseases at the University of Toronto.
“In order to correct that depletion [of B and T cells], you need to be reexposed to everything you were immune to before, and this can take years,” she said.
As of late March, 97% of the people sickened in the current outbreak were unvaccinated or didn’t disclose their vaccine status. The measles virus is attenuated in the MMR vaccine, meaning that it has been altered to produce the appropriate immune response without triggering the disease itself. In the case of measles, that means no mass destruction of the cells that hold the immune system’s memory.
“It doesn’t have this very, very damaging effect, which is why we recommend vaccination, because we get all of the immunity with none of the adverse consequences,” Bolotin said.

Science
AI windfall helps California narrow projected $3-billion budget deficit

SACRAMENTO — California and its state-funded programs are heading into a period of volatile fiscal uncertainty, driven largely by events in Washington and on Wall Street.
Gov. Gavin Newsom’s budget chief warned Friday that surging revenues tied to the artificial intelligence boom are being offset by rising costs and federal funding cuts. The result: a projected $3-billion state deficit for the next fiscal year despite no major new spending initiatives.
The Newsom administration on Friday released its proposed $348.9-billion budget for the fiscal year that begins July 1, formally launching negotiations with the Legislature over spending priorities and policy goals.
“This budget reflects both confidence and caution,” Newsom said in a statement. “California’s economy is strong, revenues are outperforming expectations, and our fiscal position is stable because of years of prudent fiscal management — but we remain disciplined and focused on sustaining progress, not overextending it.”
Newsom’s proposed budget did not include funding to backfill the massive cuts to Medicaid and other public assistance programs by President Trump and the Republican-led Congress, changes expected to lead to millions of low-income Californians losing healthcare coverage and other benefits.
“If the state doesn’t step up, communities across California will crumble,” California State Assn. of Counties Chief Executive Graham Knaus said in a statement.
The governor is expected to revise the plan in May using updated revenue projections after the income tax filing deadline, with lawmakers required to approve a final budget by June 15.
Newsom did not attend the budget presentation Friday, which was out of the ordinary, instead opting to have California Director of Finance Joe Stephenshaw field questions about the governor’s spending plan.
“Without having significant increases of spending, there also are no significant reductions or cuts to programs in the budget,” Stephenshaw said, noting that the proposal is a work in progress.
California has an unusually volatile revenue system — one that relies heavily on personal income taxes from high-earning residents whose capital gains rise and fall sharply with the stock market.
Entering state budget negotiations, many expected to see significant belt tightening after the nonpartisan Legislative Analyst’s Office warned in November that California faces a nearly $18-billion budget shortfall. The governor’s office and Department of Finance do not always agree, or use the LAO’s estimates.
On Friday, the Newsom administration said it is projecting a much smaller deficit — about $3 billion — after assuming higher revenues over the next three fiscal years than were forecast last year. The gap between the governor’s estimate and the LAO’s projection largely reflects differing assumptions about risk: The LAO factored in the possibility of a major stock market downturn.
“We do not do that,” Stephenshaw said.
Among the key areas in the budget:
Science
California confirms first measles case for 2026 in San Mateo County as vaccination debates continue

Barely more than a week into the new year, the California Department of Public Health confirmed its first measles case of 2026.
The diagnosis came from San Mateo County, where an unvaccinated adult likely contracted the virus from recent international travel, according to Preston Merchant, a San Mateo County Health spokesperson.
Measles is one of the most infectious viruses in the world, and can remain in the air for two hours after an infected person leaves, according to the CDPH. Although the U.S. announced it had eliminated measles in 2000, meaning there had been no reported infections of the disease in 12 months, measles have since returned.
Last year, the U.S. reported about 2,000 cases, the highest reported count since 1992, according to CDC data.
“Right now, our best strategy to avoid spread is contact tracing, so reaching out to everybody that came in contact with this person,” Merchant said. “So far, they have no reported symptoms. We’re assuming that this is the first [California] measles case of the year.”
San Mateo County also reported an unvaccinated child’s death from influenza this week.
Across the country, measles outbreaks are spreading. Today, the South Carolina State Department of Public Health confirmed the state’s outbreak had reached 310 cases. The number has been steadily rising since an initial infection in July spread across the state and is now reported to be connected with infections in North Carolina and Washington.
Similarly to San Mateo’s case, the first reported infection in South Carolina came from an unvaccinated person who was exposed to measles while traveling internationally.
At the border of Utah and Arizona, a separate measles outbreak has reached 390 cases, stemming from schools and pediatric centers, according to the Utah Department of Health and Human Services.
Canada, another long-standing “measles-free” nation, lost ground in its battle with measles in November. The Public Health Agency of Canada announced that the nation is battling a “large, multi-jurisdictional” measles outbreak that began in October 2024.
If American measles cases follow last year’s pattern, the United States is facing losing its measles elimination status next.
For a country to lose measles-free status, reported outbreaks must be of the same locally spread strain, as was the case in Canada. As many cases in the United States were initially connected to international travel, the U.S. has been able to hold on to the status. However, as outbreaks with American-origin cases continue, this pattern could lead the Pan American Health Organization to change the country’s status.
In the first year of the Trump administration, officials led by Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. have promoted lowering vaccine mandates and reducing funding for health research.
In December, Trump’s presidential memorandum led to this week’s reduced recommended childhood vaccines; in June, Kennedy fired an entire CDC vaccine advisory committee, replacing members with multiple vaccine skeptics.
Experts are concerned that recent debates over vaccine mandates in the White House will shake the public’s confidence in the effectiveness of vaccines.
“Viruses and bacteria that were under control are being set free on our most vulnerable,” Dr. James Alwine, a virologist and member of the nonprofit advocacy group Defend Public Health, said to The Times.
According to the CDPH, the measles vaccine provides 97% protection against measles in two doses.
Common symptoms of measles include cough, runny nose, pink eye and rash. The virus is spread through breathing, coughing or talking, according to the CDPH.
Measles often leads to hospitalization and, for some, can be fatal.
Science
Trump administration declares ‘war on sugar’ in overhaul of food guidelines

The Trump administration announced a major overhaul of American nutrition guidelines Wednesday, replacing the old, carbohydrate-heavy food pyramid with one that prioritizes protein, healthy fats and whole grains.
“Our government declares war on added sugar,” Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. said in a White House press conference announcing the changes. “We are ending the war on saturated fats.”
“If a foreign adversary sought to destroy the health of our children, to cripple our economy, to weaken our national security, there would be no better strategy than to addict us to ultra-processed foods,” Kennedy said.
Improving U.S. eating habits and the availability of nutritious foods is an issue with broad bipartisan support, and has been a long-standing goal of Kennedy’s Make America Healthy Again movement.
During the press conference, he acknowledged both the American Medical Association and the American Assn. of Pediatrics for partnering on the new guidelines — two organizations that earlier this week condemned the administration’s decision to slash the number of diseases that U.S. children are vaccinated against.
“The American Medical Association applauds the administration’s new Dietary Guidelines for spotlighting the highly processed foods, sugar-sweetened beverages, and excess sodium that fuel heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and other chronic illnesses,” AMA president Bobby Mukkamala said in a statement.
-

 Detroit, MI1 week ago
Detroit, MI1 week ago2 hospitalized after shooting on Lodge Freeway in Detroit
-

 Technology5 days ago
Technology5 days agoPower bank feature creep is out of control
-

 Dallas, TX2 days ago
Dallas, TX2 days agoAnti-ICE protest outside Dallas City Hall follows deadly shooting in Minneapolis
-

 Dallas, TX6 days ago
Dallas, TX6 days agoDefensive coordinator candidates who could improve Cowboys’ brutal secondary in 2026
-

 Delaware2 days ago
Delaware2 days agoMERR responds to dead humpback whale washed up near Bethany Beach
-

 Iowa5 days ago
Iowa5 days agoPat McAfee praises Audi Crooks, plays hype song for Iowa State star
-

 Health7 days ago
Health7 days agoViral New Year reset routine is helping people adopt healthier habits
-

 Nebraska4 days ago
Nebraska4 days agoOregon State LB transfer Dexter Foster commits to Nebraska



















