Massachusetts
Massachusetts will stop daily COVID case count report, switch to weekly
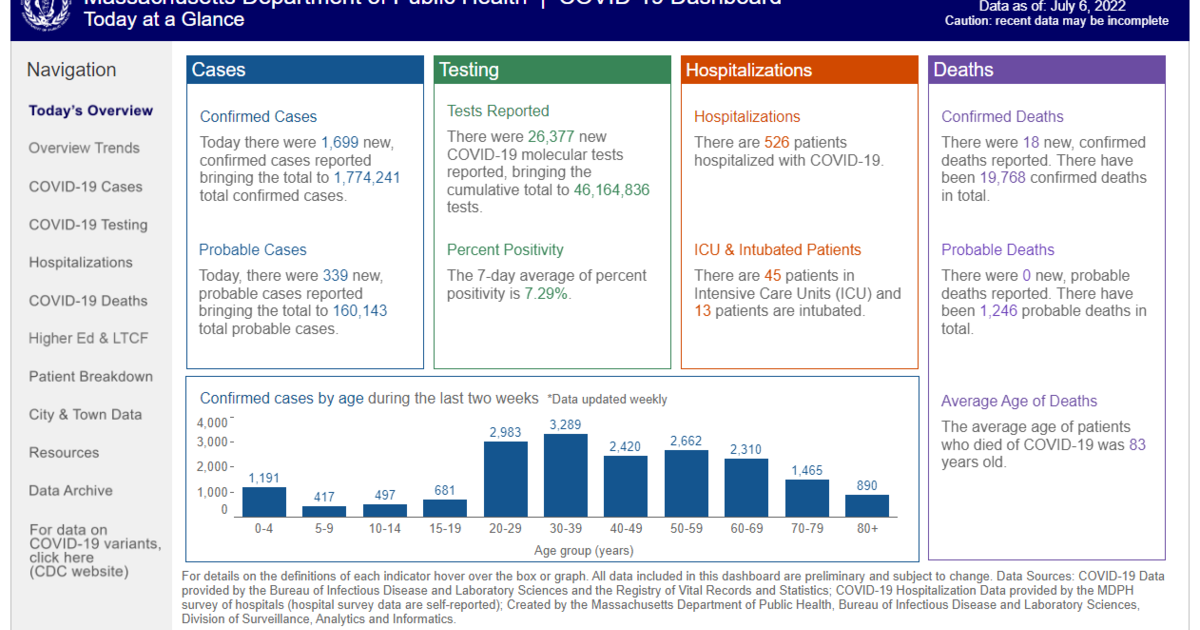
BOSTON — The Massachusetts Division of Public Well being will not launch coronavirus case numbers 5 days every week, they introduced Friday. As a substitute, they will put up COVID-19 knowledge on a weekly foundation.
“The adjustments taking impact subsequent week are a part of our ongoing efforts to adapt to the pandemic and deal with the metrics most helpful at a given time. The up to date reporting displays the present standing of COVID-19 and its affect,” mentioned State Epidemiologist Dr. Catherine Brown.
“Whereas all of us have turn into used to checking the numbers daily, monitoring traits over time is definitely essentially the most helpful technique to apply the COVID-19 knowledge,” mentioned Dr. Helen Boucher, Interim Dean of Tufts College College of Medication, Chief Tutorial Officer at Tufts Medication, and member of the Governor’s Medical Advisory Board. “Provided that Massachusetts has probably the greatest vaccination and booster percentages within the nation, these adjustments make sense at this stage in our COVID-19 response.”
Beginning subsequent week, knowledge can be launched on Thursdays. The inhabitants can be up to date to mirror more moderen census numbers going ahead, the state mentioned.
Within the Interactive Knowledge Dashboard, the Contact Tracing and Clusters tabs can be faraway from the COVID-19 Circumstances part. Greater training knowledge will even not be obtainable.
The vaccination report will now be launched on Wednesday as an alternative of Thursday.
Final yr, the dashboard went down from updates seven-days every week to 5.

Massachusetts
Thursday’s six biggest high school takeaways, including a Gatorade award and a new all-time leading scorer in Saugus – The Boston Globe

While Newton North claimed its third straight Division 1 championship in the fall, on Thursday Sasha Selivan became the first Tiger to be named Gatorade Massachusetts Volleyball Player of the Year.
“Sasha is in a league of her own as far as Massachusetts’ setters go,” said Bishop Feehan coach Heidi Bruschi. “No one else I’ve seen comes close.”
The 5-foot-9-inch sophomore led the Tigers to a 24-1 record with 673 assists, 133 digs, and 115 kills. In the Division 1 final, a 3-0 win over Brookline, she recorded 26 assists and four aces. Selivan is ranked as the nationals’ No. 128 player in the Class of 2027, according to PrepVolleyball, and was the Division 1 tournament MVP and a Division 1 All-State selection.
She maintains an A average in the classroom and volunteers locally as a youth volleyball coach and mentor.
2. DiBiasio keeps scoring for Saugus
While Saugus assistant coach Norma Waggett watched, junior Peyton DiBiasio broke her coach’s all-time program scoring record by netting 27 points to surpass the mark of 1,100 Waggett set in 2013. Saugus lost, 51-40, to Minuteman to fall to 5-2.
3. On to college
In Danvers, St. John’s Prep announced 18 college commitments across eight sports:
Football
Merrick Barlow (Newburyport) to Naval Academy
Graham Roberts (Swampscott) to Harvard
Baseball
Will Shaheen (Portsmouth, N.H.) to Harvard
Nic Lembo (Danvers) to High Point
Lacrosse
Charlie Angell (Winchester) to Pennsylvania
Ryan DeLucia (Winchester) to Georgetown
Luke Kelly (Marblehead) to Michigan
Cameron McCarthy (Marblehead) to Loyola Maryland
JP Sullivan (Swampscott) to Saint Anselm
Jack Weissenburger (Marblehead) to Harvard
Sam Wilmot (Topsfield) to Richmond

Golf
Tripp Hollister (Sudbury) to Bryant
Cross-country
Daniel Padley (South Hamilton) to Holy Cross
Swimming and diving
Kye McClory (Lynnfield) to Holy Cross
Greg Santosus (Marblehead) to Virginia Military Institute
Tennis
Luke Prokopis (Lynnfield) to Holy Cross
Jack Prokopis (Lynnfield) to Holy Cross
Track and field
Noah Kabel (Swampscott) to Sacred Heart
4. Western Mass shuffle
Lots of league movement in Western Mass, particularly in football and girls’ soccer. Check out the reporting from Jesse Koldokin at the Eagle Tribune and Gage Nutter at MassLive.
Here’s the Cliff’s notes version: Chicopee Comprehensive and Holyoke will leave the AA League and be replaced by West Springfield and East Longmeadow. The Tri-County loses Springfield International and gains Belchertown.
In the Suburban South, Wahconah is joined by Pittsfield, Putnam, and Chicopee Comprehensive. The Suburban North will feature Taconic and South Hadley, plus Hoosac Valley, Lee, Easthampton, and Holyoke.
The Intercounty South sees Chicopee, Ludlow, Springfield International, and Northampton join Commerce and Frontier. The Intercounty North remained unchanged.
In girls’ soccer, the Berkshire League’s Grieve division will be Drury, Wahconah, Pittsfield, Lenox, Monument Valley and Mount Greylock. McCann and Hoosac Valley move to the Pioneer South and Taconic, Lee, and Mt. Everett move to the Tri-County North.
5. Thursday’s leaderboard
The top scoring performance of the night came in a defeat as Jacob Klass dropped 35 points for Beverly in a 77-73 loss to Gloucester that saw Nick Deleon score 26 for the Fishermen.
Minuteman’s Muji Vader nabbed 11 steals and added 24 points in a 63-19 win over KIPP Academy, sophomore Divine Egbuta led Lynn Classical with 26 points in a 58-46 win over Somerville, and Notre Dame (Hingham) junior Elle Orlando packed the box score with 25 points, 9 rebounds, and 8 steals in a 72-35 win over Ursuline.
On the ice, Newburyport’s Olivia Wilson netted a hat trick in a 7-3 win over Stoneham/Wilmington and Justin Thibert delivered three goals for Shawsheen in a 9-1 win against Nashoba Tech/Greater Lowell.
Freshman netminder Suki ten Brinke saved all 18 shots she faced to record her first shutout of the season in Lincoln-Sudbury’s 3-0 win over Westford, and Central Catholic junior Sydney Foster made 21 saves in her first shutout of the season, a 7-0 defeat of Wayland.
6. Linked up
Before we bid adieu, a few things we’ve written recently, starting with Trevor Hass’s story on Bishop Feehan honoring the late local hoops legend Mike Babul by wearing black wristbands featuring his initials during a win over Bishop Fenwick.
Brendan Kurie can be reached at brendan.kurie@globe.com. Follow him on X @BrendanKurie.
Massachusetts
Massachusetts State Police release Body Camera footage of Nick Cocchi arrest

LUDLOW, Mass (WWLP) – Massachusetts State Police have released body camera footage from the arrest of Hampden County Sheriff Nick Cocchi back in September.
The public is now getting a glimpse into the night of September 21st, when Sheriff Nick Cocchi was arrested by Massachusetts State Police outside of MGM Springfield. The night his state issued white Ford Explorer was found without a front right tire in the valet section of the garage.
The video shows the interaction with Cocchi and law enforcement as they are trying to piece together what happened.
“Yeah, ok, wanna go down that road, huh? ok,” says Sheriff Cocchi. The state trooper responds, “I want to take everything right by the numbers and by the books, sir.”
At first when asked who was driving, Cocchi said a friend, then later admitting it was him behind the wheel. The trooper also saying he can smell alcohol, asking Cocchi how much he had to drink. To which he responds he had “a couple beers” when he was at the Springfield Country Club, but nothing at MGM Springfield.
Cocchi also declined a field sobriety test, multiple times.
Since the incident, Cocchi says he has taken full responsibility for his behavior.
“I’m not looking for empathy or sympathy. I’m not looking for people to give me a pass. All I’m asking for people to do and all I’ve said that I am is human, and I have integrity, I have honesty, and I have character. And I will always try to be the best version of myself, and that night I wasn’t,” said Sheriff Cocchi in response to the video release.
In regards to that night, Cocchi praises the troopers, saying throughout this process, he should not be treated differently from anyone else.
Cocchi also said quote “Since the incident, I have done everything possible to show the public that I believe in transparency and accountability, especially in myself.”
He said at the Sheriff’s Department, they believe people are not defined by moments like these, but rather how they handle those moments.
Massachusetts
2 of the largest fairs in North America are in Massachusetts

Travel
One saw record-breaking attendance in 2024.
If you attended The Big E or the Topsfield Fair this past fall, you were in good company.
-
These New England hotels, restaurants, and more are ‘must visit spots’ in 2025, according to USA Today readers
Both Massachusetts fairs ranked among the top 50 fairs in the U.S. and Canada in 2024, according to Carnival Warehouse. The list was ranked by attendance.
“2024 contained very positive indicators that North Americans have rekindled their romance for midways, outdoor shows, agricultural programming and food-on-a-stick,” wrote Carnival Warehouse on its website. “Most fairs saw increases over last year’s attendance, only 12 top-50 fairs saw decreases, most of which were nominal and all of which were due to weather.”
The Big E (the Eastern States Exposition) in Springfield ranked No. 4 with an all-time total attendance record of more than 1.6 million visitors. Seven other daily attendance records were also set this year at The Big E, including an all-time single day attendance record of 178,608 visitors on Sept. 21. The Topsfield Fair, at No. 40, saw 418,170 visitors.
Running since 1916, The Big E is New England’s biggest fair. The fair brought live musical acts, carnival rides, agricultural competitions, and food vendors this past September. All six New England states are famously represented on its grounds.
The Topsfield Fair, America’s oldest agricultural fair (running for more than 200 years), featured carnival rides, food, live music, rodeos, art shows, exhibits, and nearly 300 vendors this past October.
For those looking to help boost attendance in 2025, this year’s fair dates are Sept. 12-28 for The Big E and Oct. 3-13 for the Topsfield Fair.
North America’s No. 1 fair in 2024 is the Houston Livestock Show and Rodeo, which saw 2.5 million visitors.
Check out the top 50 fairs in the U.S. and Canada in 2024.
Sign up for Scenic Six
Navigate the endless possibilities of New England travel with Boston.com.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoWho Are the Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom?
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoOzempic ‘microdosing’ is the new weight-loss trend: Should you try it?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIvory Coast says French troops to leave country after decades