Health
Could the Next Blockbuster Drug Be Lab-Rat Free?

In 1937, an American drug firm launched a brand new elixir to deal with strep throat — and unwittingly set off a public well being catastrophe. The product, which had not been examined in people or animals, contained a solvent that turned out to be poisonous. Greater than 100 folks died.
The next yr, Congress handed the Federal Meals, Drug and Beauty Security Act, requiring pharmaceutical corporations to submit security knowledge to the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration earlier than promoting new medicines, serving to to usher in an period of animal toxicity testing.
Now, a brand new chapter in drug improvement could also be starting. The F.D.A. Modernization Act 2.0, signed into regulation late final yr, permits drug makers to gather preliminary security and efficacy knowledge utilizing high-tech new instruments, akin to bioengineered organs, organs on chips and even laptop fashions, as a substitute of reside animals. Congress additionally allotted $5 million to the F.D.A. to speed up the event of options to animal testing.
Different companies and international locations are making comparable shifts. In 2019, the U.S. Environmental Safety Company introduced that it could cut back, and finally purpose to eradicate, testing on mammals. In 2021, the European Parliament known as for a plan to part out animal testing.
These strikes have been pushed by a confluence of things, together with evolving views of animals and a want to make drug improvement cheaper and quicker, specialists stated. However what’s lastly making them possible is the event of refined options to animal testing.
It’s nonetheless early for these applied sciences, lots of which nonetheless have to be refined, standardized and validated earlier than they can be utilized routinely in drug improvement. And even advocates for these options acknowledge that animal testing just isn’t prone to disappear anytime quickly.
However momentum is constructing for non-animal approaches, which might in the end assist pace drug improvement, enhance affected person outcomes and cut back the burdens borne by lab animals, specialists stated.
“Animals are merely a surrogate for predicting what’s going to occur in a human,” stated Nicole Kleinstreuer, director of the Nationwide Toxicology Program Interagency Middle for the Analysis of Different Toxicological Strategies.
“If we are able to get to a spot the place we even have a completely human-relevant mannequin,” she added, “then we don’t want the black field of animals anymore.”
Animal Attitudes
Animal rights teams have been lobbying for a discount in animal testing for many years, and so they have discovered an more and more receptive public. In a 2022 Gallup ballot, 43 p.c of People stated that medical testing on animals was “morally unsuitable,” up from 26 p.c in 2001.
Decreasing animal testing “issues to so many individuals for thus many various causes,” stated Elizabeth Baker, the director of analysis coverage on the Physicians Committee for Accountable Medication, a nonprofit group that advocates for options to animal testing. “Animal ethics is definitely fairly a giant driver.”
However it isn’t the one one. Animal testing can be time-consuming, costly and weak to shortages. Drug improvement, particularly, is rife with failures, and lots of medicines that seem promising in animals don’t pan out in people. “We’re not 70-kilogram rats,” stated Dr. Thomas Hartung, who directs the Johns Hopkins Middle for Options to Animal Testing.
Furthermore, some cutting-edge new remedies are based mostly on organic merchandise, akin to antibodies or fragments of DNA, which can have targets which might be particular to people.
“There’s a number of strain, not only for moral causes, but additionally for these economical causes and for actually closing security gaps, to adapt to issues that are extra trendy and human related,” Dr. Hartung stated.
(Dr. Hartung is the named inventor on a Johns Hopkins College patent on the manufacturing of mind organoids. He receives royalty shares from, and consults for, the corporate that has licensed the know-how.)
Lately, scientists have developed extra refined methods to copy human physiology within the laboratory.
They’ve realized the best way to coax human stem cells to assemble themselves right into a small, three-dimensional clump, generally known as an organoid, that shows a few of the identical fundamental traits as a particular human organ, akin to a mind, a lung or a kidney.
Scientists can use these mini-organs to review the underpinnings of illness or to check remedies, even on particular person sufferers. In a 2016 examine, researchers made mini-guts from cell samples from sufferers with cystic fibrosis after which used the organoids to foretell which sufferers would reply to new medicine.
Scientists are additionally utilizing 3-D printers to provide organoids at scale and to print strips of other forms of human tissue, akin to pores and skin.
One other method depends on “organs on a chip.” These units, that are roughly the dimensions of AA batteries, include tiny channels that may be lined with completely different sorts of human cells. Researchers can pump medicine by means of the channels to simulate how they may journey by means of a specific a part of the physique.
In a single current examine, the biotech firm Emulate, which makes organs on chips, used a liver-on-a-chip to display screen 27 well-studied medicine. All the medicine had handed preliminary animal testing, however some had later turned out to trigger liver toxicity in people. The liver-on-a-chip efficiently flagged as many as 87 p.c of the poisonous compounds, the researchers reported in Communications Medication final December.
Researchers may hyperlink completely different methods collectively, connecting a heart-on-a-chip to a lung-on-a-chip to a liver-on-a-chip, to review how a drug would possibly have an effect on all the interconnected system. “That’s the place I believe the long run lies,” Dr. Kleinstreuer stated.
Compound Computations
Not all the brand new instruments require actual cells. There are additionally computational fashions that may predict whether or not a compound with sure chemical traits is prone to be poisonous, how a lot of it is going to attain completely different organs and the way shortly it will likely be metabolized.
The fashions could be adjusted to signify various kinds of sufferers. As an example, a drug developer might check whether or not a drugs that works in younger adults could be protected and efficient in older adults, who usually have decreased kidney perform.
“When you can determine the issues as early as doable utilizing a computational mannequin that saves you happening the unsuitable route with these chemical compounds,” stated Judith Madden, an professional on “in silico,” or computer-based, chemical testing at Liverpool John Moores College. (Dr. Madden can be the editor in chief of the journal Options to Laboratory Animals.)
A few of the approaches have been round for years, however advances in computing know-how and synthetic intelligence are making them more and more highly effective and complicated, Dr. Madden stated.
Digital cells have additionally proven promise. As an example, researchers can mannequin particular person human coronary heart cells utilizing “a set of equations that describe all the pieces that’s happening within the cell,” stated Elisa Passini, this system supervisor for drug improvement on the Nationwide Middle for the Alternative, Refinement and Discount of Animals in Analysis, or NC3Rs, in Britain.
In a 2017 examine, Dr. Passini, then a researcher on the College of Oxford, and her colleagues concluded that these digital cells had been higher than animal fashions at predicting whether or not dozens of identified medicine would trigger coronary heart issues in people.
Scientists are actually constructing whole digital organs, which might finally be linked collectively right into a type of digital human, Dr. Passini added, although a few of the work stays in early phases.
Within the brief time period, a digital lab animal is likely to be extra achievable, stated Cathy Vickers, the top of innovation at NC3Rs, which is working with scientists and pharmaceutical corporations to develop a digital mannequin of a canine that may very well be used for drug toxicity testing.
“It’s nonetheless a giant push to develop a digital canine,” Dr. Vickers stated. “Nevertheless it’s about constructing that capability, constructing that momentum.”
Cut back or Substitute
Many potential animal options would require extra funding and improvement earlier than they can be utilized broadly, specialists stated. Additionally they have limitations of their very own. Laptop fashions, for example, are solely nearly as good as the information they’re constructed on, and extra knowledge is obtainable on sure sorts of compounds, cells and outcomes than others.
For now, these various strategies are higher at predicting comparatively easy, short-term outcomes, akin to acute toxicity, than difficult, long-term ones, akin to whether or not a chemical would possibly enhance the danger of most cancers when used over months or years, scientists stated.
And specialists disagreed on the extent to which these various approaches would possibly substitute animal fashions. “We’re completely working towards a future the place we wish to have the ability to absolutely substitute them,” Dr. Kleinstreuer stated, though she acknowledged that it’d take a long time, “if not centuries.”
However others stated that these applied sciences needs to be considered as a complement to, relatively than a substitute for, animal testing. Medicine that show promising in organoids or laptop fashions ought to nonetheless be examined in animals, stated Matthew Bailey, president of the Nationwide Affiliation for Biomedical Analysis, a nonprofit group that advocates for the accountable use of animals in analysis.
“Researchers nonetheless want to have the ability to see all the pieces that occurs in a posh mammalian organism earlier than being allowed to maneuver to the human scientific trials,” he stated.
Nonetheless, even this extra conservative method might have advantages, stated Nicole zur Nieden, a developmental toxicologist on the College of California, Riverside, who stated that she thought the wholesale substitute of animal testing was unrealistic.
Particularly, she stated, the brand new approaches might assist scientists display screen out a better variety of ineffective and unsafe compounds earlier than they ever get to animal trials. That would cut back the variety of animal research researchers have to conduct and the restrict the chemical compounds lab animals are uncovered to, she stated, including, “We will cut back the struggling of check animals fairly tremendously.”

Health
How Yvette Nicole Brown Lost Weight and Got Her Diabetes Under Control

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
As bird flu spreads, CDC recommends faster 'subtyping' to catch more cases

As cases of H5N1, also known as avian flu or bird flu, continue to surface across the U.S., safety precautions are ramping up.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced on Thursday its recommendation to test hospitalized influenza A patients more quickly and thoroughly to distinguish between seasonal flu and bird flu.
The accelerated “subtyping” of flu A in hospitalized patients is in response to “sporadic human infections” of avian flu, the CDC wrote in a press release.
ONE STATE LEADS COUNTRY IN HUMAN BIRD FLU WITH NEARLY 40 CONFIRMED CASES
“CDC is recommending a shortened timeline for subtyping all influenza A specimens among hospitalized patients and increasing efforts at clinical laboratories to identify non-seasonal influenza,” the agency wrote.
The CDC now recommends accelerated subtyping of influenza A in response to “sporadic human infections” in the U.S. (iStock)
“Clinicians and laboratorians are reminded to test for influenza in patients with suspected influenza and, going forward, to now expedite the subtyping of influenza A-positive specimens from hospitalized patients, particularly those in an intensive care unit (ICU).”
LOUISIANA REPORTS FIRST BIRD FLU-RELATED HUMAN DEATH IN US
The goal is to prevent delays in identifying bird flu infections and promote better patient care, “timely infection control” and case investigation, the agency stated.
These delays are more likely to occur during the flu season due to high patient volumes, according to the CDC.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
Health care systems are expected to use tests that identify seasonal influenza A as a subtype – so if a test comes back positive for influenza A but negative for seasonal influenza, that is an indicator that the detected virus might be novel.
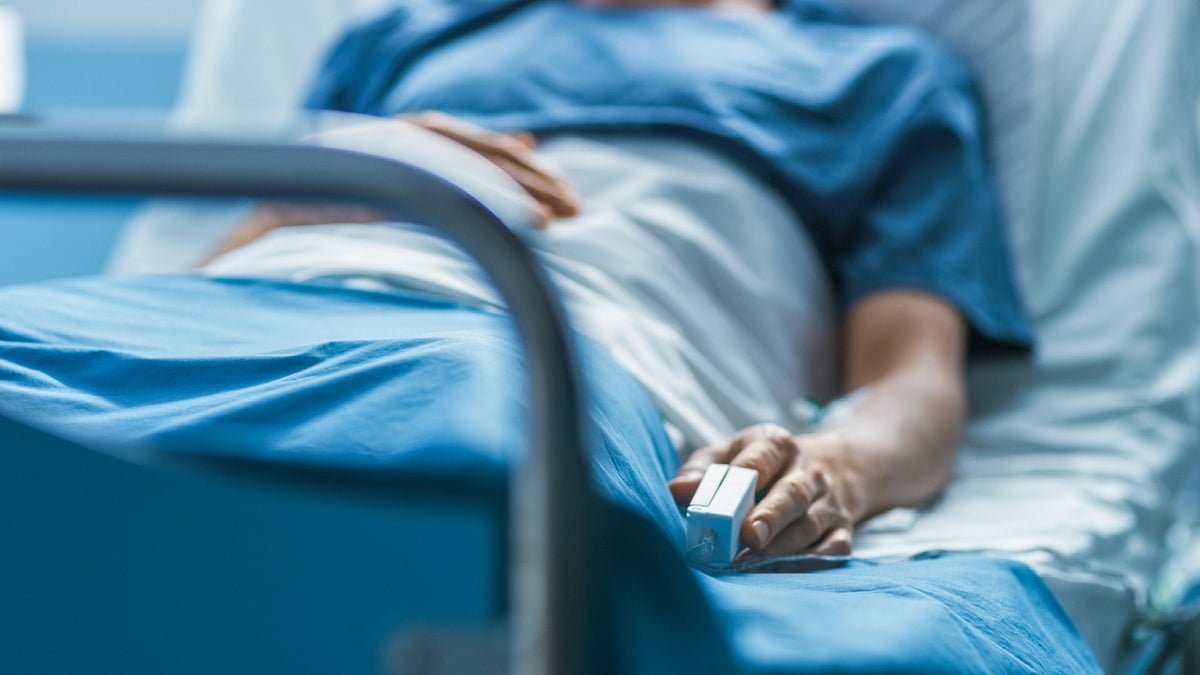
Identifying bird flu infections will support better patient care and infection control, the CDC says. (iStock)
“Subtyping is especially important in people who have a history of relevant exposure to wild or domestic animals [that are] infected or possibly infected with avian influenza A (H5N1) viruses,” the CDC wrote.
In an HHS media briefing on Thursday, the CDC confirmed that the public risk for avian flu is still low, but is being closely monitored.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
The agency spokesperson clarified that this accelerated testing is not due to bird flu cases being missed, as the CDC noted in its press release that those hospitalized with influenza A “probably have seasonal influenza.”
Niels Riedemann, MD, PhD, CEO and founder of InflaRx, a German biotechnology company, said that understanding these subtypes is an “important step” in better preparing for “any potential outbreak of concerning variants.”

The CDC recommends avoiding direct contact with wild birds or other animals that may be infected. (iStock)
“It will also be important to foster research and development of therapeutics, including those addressing the patient’s inflammatory immune response to these types of viruses – as this has been shown to cause organ injury and death during the COVID pandemic,” he told Fox News Digital.
Since 2022, there have been 67 total human cases of bird flu, according to the CDC, with 66 of those occurring in 2024.
The CDC recommends that people avoid direct contact with wild birds or other animals that are suspected to be infected. Those who work closely with animals should also wear the proper personal protective equipment (PPE).
Health
Sick Prisoners in New York Were Granted Parole but Remain Behind Bars

When the letter arrived at Westil Gonzalez’s prison cell saying that he had been granted parole, he couldn’t read it. Over the 33 years he had been locked up for murder, multiple sclerosis had taken much of his vision and left him reliant on a wheelchair.
He had a clear sense of what he would do once freed. “I want to give my testimony to a couple of young people who are out there, picking up guns,” Mr. Gonzalez, 57, said in a recent interview. “I want to save one person from what I’ve been through.”
But six months have passed, and Mr. Gonzalez is still incarcerated outside Buffalo, because the Department of Corrections has not found a nursing home that will accept him. Another New York inmate has been in the same limbo for 20 months. Others were released only after suing the state.
America’s elderly prison population is rising, partly because of more people serving long sentences for violent crimes. Nearly 16 percent of prisoners were over 55 in 2022, up from 5 percent in 2007. The share of prisoners over 65 quadrupled over the same time period, to about 4 percent.
Complex and costly medical conditions require more nursing care, both in prison and after an inmate’s release. Across the country, prison systems attempting to discharge inmates convicted of serious crimes often find themselves with few options. Nursing home beds can be hard to find even for those without criminal records.
Spending on inmates’ medical care is increasing — in New York, it has grown to just over $7,500 in 2021 from about $6,000 per person in 2012. Even so, those who work with the incarcerated say the money is often not enough to keep up with the growing share of older inmates who have chronic health problems.
“We see a lot of unfortunate gaps in care,” said Dr. William Weber, an emergency physician in Chicago and medical director of the Medical Justice Alliance, a nonprofit that trains doctors to work as expert witnesses in cases involving prison inmates. With inmates often struggling to get specialty care or even copies of their own medical records, “things fall through the cracks,” he said.
Dr. Weber said he was recently involved in two cases of seriously ill prisoners, one in Pennsylvania and the other in Illinois, who could not be released without a nursing home placement. The Pennsylvania inmate died in prison and the Illinois man remains incarcerated, he said.
Almost all states have programs that allow early release for inmates with serious or life-threatening medical conditions. New York’s program is one of the more expansive: While other states often limit the policy to those with less than six months to live, New York’s is open to anyone with a terminal or debilitating illness. Nearly 90 people were granted medical parole in New York between 2020 and 2023.
But the state’s nursing home occupancy rate hovers around 90 percent, one of the highest in the nation, making it especially hard to find spots for prisoners.
The prison system is “competing with hospital patients, rehabilitation patients and the general public that require skilled nursing for the limited number of beds available,” said Thomas Mailey, a spokesman for the New York Department of Corrections and Community Supervision. He declined to comment on Mr. Gonzalez’s case or on any other inmate’s medical conditions.
Parolees remain in the state’s custody until their original imprisonment term has expired. Courts have previously upheld the state’s right to place conditions on prisoner releases to safeguard the public, such as barring paroled sex offenders from living near schools.
But lawyers and medical ethicists contend that paroled patients should be allowed to choose how to get their care. And some noted that these prisoners’ medical needs are not necessarily met in prison. Mr. Gonzalez, for example, said he had not received glasses, despite repeated requests. His disease has made one of his hands curl inward, leaving his unclipped nails to dig into his palm.
“Although I’m sympathetic to the difficulty of finding placements, the default solution cannot be continued incarceration,” said Steven Zeidman, director of the criminal defense clinic at CUNY School of Law. In 2019, one of his clients died in prison weeks after being granted medical parole.
New York does not publish data on how many inmates are waiting for nursing home placements. One 2018 study found that, between 2013 and 2015, six of the 36 inmates granted medical parole died before a placement could be found. The medical parole process moves slowly, the study showed, sometimes taking years for a prisoner to even get an interview about their possible release.
Finding a nursing home can prove difficult even for a patient with no criminal record. Facilities have struggled to recruit staff, especially since the coronavirus pandemic. Nursing homes may also worry about the safety risk of someone with a prior conviction, or about the financial risk of losing residents who do not want to live in a facility that accepts former inmates.
“Nursing homes have concerns and, whether they are rational or not, it’s pretty easy not to pick up or return that phone call,” said Ruth Finkelstein, a professor at Hunter College who specializes in policies for older adults and reviewed legal filings at The Times’s request.
Some people involved in such cases said that New York prisons often perform little more than a cursory search for nursing care.
Jose Saldana, the director of a nonprofit called the Release Aging People in Prison Campaign, said that when he was incarcerated at Sullivan Correctional Facility from 2010 through 2016, he worked in a department that helped coordinate parolees’ releases. He said he often reminded his supervisor to call nursing homes that hadn’t picked up the first time.
“They would say they had too many other responsibilities to stay on the phone calling,” Mr. Saldana said.
Mr. Mailey, the spokesman for the New York corrections department, said that the agency had multiple discharge teams seeking placement options.
In 2023, Arthur Green, a 73-year-old patient on kidney dialysis, sued the state for release four months after being granted medical parole. In his lawsuit, Mr. Green’s attorneys said that they had secured a nursing home placement for him, but that it lapsed because the Department of Corrections submitted an incomplete application to a nearby dialysis center.
The state found a placement for Mr. Green a year after his parole date, according to Martha Rayner, an attorney who specializes in prisoner release cases.
John Teixeira was granted medical parole in 2020, at age 56, but remained incarcerated for two and a half years, as the state searched for a nursing home. He had a history of heart attacks and took daily medications, including one delivered through an intravenous port. But an assessment from an independent cardiologist concluded that Mr. Teixeira did not need nursing care.
Lawyers with the Legal Aid Society in New York sued the state for his release, noting that during his wait, his port repeatedly became infected and his diagnosis progressed from “advanced” to “end-stage” heart failure.
The Department of Corrections responded that 16 nursing homes had declined to accept Mr. Teixeira because they could not manage his medical needs. The case resolved three months after the suit was filed, when “the judge put significant pressure” on the state to find an appropriate placement, according to Stefen Short, one of Mr. Teixeira’s lawyers.
Some sick prisoners awaiting release have found it difficult to get medical care on the inside.
Steve Coleman, 67, has trouble walking and spends most of the day sitting down. After 43 years locked up for murder, he was granted parole in April 2023 and has remained incarcerated, as the state looks for a nursing home that could coordinate with a kidney dialysis center three times each week.
But Mr. Coleman has not had dialysis treatment since March, when the state ended a contract with its provider. The prison has offered to take Mr. Coleman to a nearby clinic for treatment, but he has declined because he finds the transportation protocol — which involves a strip search and shackles — painful and invasive.
“They say you’ve got to go through a strip search,” he said in a recent interview. “If I’m being paroled, I can’t walk and I’m going to a hospital, who could I be hurting?”
Volunteers at the nonprofit Parole Prep Project, which assisted Mr. Coleman with his parole application, obtained a letter from Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City in June offering to give him medical care and help him transition back into the community.
Still incarcerated two months later, Mr. Coleman sued for his release.
In court filings, the state argued that it would be “unsafe and irresponsible” to release Mr. Coleman without plans to meet his medical needs. The state also said that it had contacted Mount Sinai, as well as hundreds of nursing homes, about Mr. Coleman’s placement and had never heard back.
In October, a court ruled in the prison system’s favor. Describing Mr. Coleman’s situation as “very sad and frustrating,” Justice Debra Givens of New York State Supreme Court concluded that the state had a rational reason to hold Mr. Coleman past his parole date. Ms. Rayner, Mr. Coleman’s lawyer, and the New York Civil Liberties Union appealed the ruling on Wednesday.
Fourteen medical ethicists have sent a letter to the prison supporting Mr. Coleman’s release. “Forcing continued incarceration under the guise of ‘best interests,’ even if doing so is well-intentioned, disregards his autonomy,” they wrote.
Several other states have come up with a different solution for people on medical parole: soliciting the business of nursing homes that specialize in housing patients rejected elsewhere.
A private company called iCare in 2013 opened the first such facility in Connecticut, which now houses 95 residents. The company runs similar nursing homes in Vermont and Massachusetts.
David Skoczulek, iCare’s vice president of business development, said that these facilities tend to save states money because the federal government covers some of the costs through Medicaid.
“It’s more humane, less restrictive and cost-effective,” he said. “There is no reason for these people to remain in a corrections environment.”
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science6 days ago
Science6 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLas Vegas police release ChatGPT logs from the suspect in the Cybertruck explosion
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPhotos: Pacific Palisades Wildfire Engulfs Homes in an L.A. Neighborhood
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoFour Fraternity Members Charged After a Pledge Is Set on Fire
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump trolls Canada again, shares map with country as part of US: 'Oh Canada!'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoAmazon Prime will shut down its clothing try-on program
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoMapping the Damage From the Palisades Fire














