Business
Five animated shows based on Dr. Seuss books are headed to Netflix.

Constructing on a partnership began in 2019, Netflix and the Dr. Seuss property introduced Tuesday that they have been creating 5 new animated collection and specials for preschoolers primarily based on the work of the famed youngsters’s writer.
The exhibits embody “Horton Hears a Who!,” “The Sneetches,” “One Fish, Two Fish, Purple Fish, Blue Fish,” “Wacky Wednesday” and “Thidwick the Large-Hearted Moose.” The screenwriter and producer Dustin Ferrer (the creator of “Esme & Roy”) would be the showrunner for all of them.
“One Fish, Two Fish,” “Wacky Wednesday” and “Horton Hears a Who!” will likely be collection of assorted lengths. “The Sneetches” and “Thidwick” will each be 45-minute specials. The streaming service didn’t announce launch dates for the exhibits.
Netflix hopes the gathering of Dr. Seuss exhibits will function an anchor for the service because it expands extra aggressively into the preschool house. Netflix mentioned it has had sturdy viewership for different preschool content material, like “Cocomelon,” which started as a YouTube channel; “Gabby’s Dollhouse” from DreamWorks Animation; and “Sharkdog,” created by the Singaporean artist Jacinth Tan Yi Ting.
The primary collaboration between the Seuss property and Netflix got here in 2019, with the creation of the animated collection “Inexperienced Eggs and Ham.” The second season of that collection will grow to be obtainable on April 8.
“We’re at all times on the lookout for new and interesting methods to share our tales, characters and messages with the subsequent era of followers, and Netflix has a singular potential to create unique, pleasant diversifications of our timeless classics with an emphasis on creativeness, enjoyable, and schooling,” Susan Brandt, the president and chief govt of Dr. Seuss Enterprises, mentioned in an announcement.

Business
Opinion: California ruled with great jobs and boom times. What happened?

Gov. Gavin Newsom’s constant reminders that California’s economy ”leads the nation” as well as being a model for social justice are delusional. To be sure, California has a huge GDP, paced largely by high real estate prices and the stock value of a handful of tech companies, but it is not widely seen as a place for class mobility, and it is slowly ceding its dominance, even in tech-related industries.
In contemporary California, home to four of the world’s seven most valued tech firms, tech bros and real estate speculators occupy what Lenin called “the commanding heights,” while the reality on the ground is far less ethereal. The view from where most Californians reside is revealed in a new study sponsored by Chapman University: “Is California Losing Its Mojo?,” by business professors Marshall Toplansky (Chapman) and Kenneth Murphy (UC Irvine).
Historically, the report notes, California has outpaced the rest of the country in terms of the growth of its goods and services. However, that pace of GDP growth in the state has dropped significantly since 2022, with the measure now lagging when compared with other states. The distribution of jobs and wealth is even more worrisome.
California has been a particularly poor bet for blue-collar professions, such as manufacturing, the traditional path to upward mobility for minorities and non-college educated people. Bureau of Labor Statistics data, analyzed by Lightcast, shows California has lagged far behind places like Utah, Nevada, Texas and Arizona over a decade.
The Chapman paper acknowledges that the state has experienced enough job growth to keep unemployment levels low, but as the report details, most new jobs in California aren’t concentrated in high-wage sectors. Over the last 10 years, 62% of jobs added in California were in lower-than-average paying industries, versus 51.6% for the nation as a whole. In the last three years, the situation worsened, with 78.1% of all jobs added in California coming from lower-than-average paying industries, versus 61% for the nation as a whole.
In a state with high living costs, a dearth of well-paying jobs seems likely to bear responsibility for the state’s out-migration rate and its poverty rate, which the Census Bureau calculates, in its most comprehensive estimate, as 15.4%, one of the highest in the nation. California may be home to a lot of billionaires, but it also is home to nearly 30% of the country’s homeless.
Of course, not everyone has suffered. Besides tech billionaires, who is doing well in California? Older homeowners, for one, whose bottom line has risen as home values increased dramatically. Government workers have also thrived.
Census Bureau data highlighted in the Chapman report show that California public sector job growth over the last decade has been growing at about the same pace as jobs overall in California, but the average annual pay for those government jobs was almost double that of private sector jobs. In other words, the road to the middle class comes not from private employment but from jobs that are funded by taxpayers.
In the past, California cities including San Francisco, San Jose and San Diego all ranked in the top 10 among hubs for “advanced industry” employment — where there’s high investment in R&D and a high percentage of STEM roles. But since 2020, only San Jose remains in the top 25 metro areas for growth in such employment. Today the emerging hot spots are often east of the Sierra: Austin, Texas; Nashville; Indianapolis; Salt Lake City; and Phoenix.
Can California get its mojo back? After all, many of the state’s assets — research universities, leading tech firms and the lifestyle appeal — have not disappeared.
First, Newsom and other state cheerleaders have to stop using the size of the economy as a cover for real problems. Whatever the state’s strengths, as the Chapman report puts it, low-wage jobs overtaking advanced industry work is not sustainable.
The Biden administration emphasized bringing manufacturing back to the U.S., and President-elect Donald Trump promises to do the same, but California misses out on opportunities due to the costs associated with its regulatory regimes.
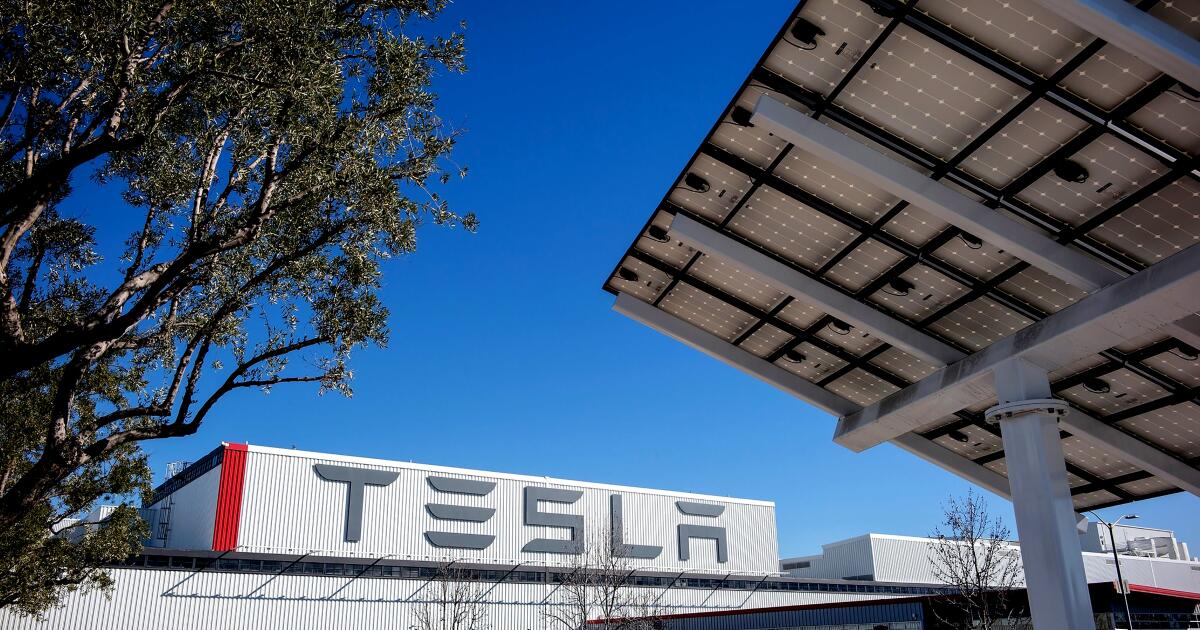
Consider technologies largely developed and embraced by California, such as EVs and the batteries that run them. Jobs in those manufacturing industries overwhelmingly fall to red states, largely a reflection of such things as easier permitting rules, lower energy costs and less intrusive labor regulations.
Remarkably, Newsom, who feuds with Elon Musk and has taken on the role of the national anti-Trump, has promised that if the next administration in Washington eliminates the federal $7,500 buyer EV tax credits, California will step in with state rebates for the vehicles — with reportedly one exception, Teslas, which happen to be the dominant American brand and the only EVs made in California. The plant in Fremont employs thousands in good manufacturing jobs.
And that’s hardly the end of the self-destructive politicking.
One “advanced industry” where California, and in particular Southern California, still has a leg up is aerospace, and its corollary, defense. The state remains well in the lead in terms of aerospace-related employment, and innovative new firms, such as Anduril in Orange County, seem primed to take advantage of Trump’s emphasis on military spending. In his first term, he increased the defense budget to historic highs.
But is California’s Democratic leadership on board?
Once again, the state’s relations with Musk, Trump “first buddy” and the world’s preeminent space pioneer, would indicate just the opposite. Musk, upset at a California law that allows schools to keep parents in the dark when their children identify as LGBTQ+, decided to move SpaceX’s headquarters from Hawthorne to Texas this year. And just weeks ago, the California Coastal Commission denied SpaceX’s request to increase its rocket launches from Vandenberg Air Force Base; reportedly after commissioners discussed his political views before they voted on the issue. Even Newsom objected.
This is not the way to build a truly inclusive and healthy economy. Gavin Newsom can talk all he wants about California’s bounty, but the road the state’s Democrats have set for us has been profoundly regressive.
Joel Kotkin is a contributing writer to Opinion, the presidential fellow for urban futures at Chapman University and senior research fellow at the Civitas Institute at the University of Texas, Austin.
Business
Lyft says San Francisco overcharged it $100 million in taxes, according to lawsuit

The ride-hailing company Lyft accused San Francisco of overcharging it $100 million in taxes over the last five years in a lawsuit filed last week.
Lyft, which is headquartered in the city, said in the complaint that the fees paid by riders to drivers are not part of the company’s revenue and should not be taxed. The company considers its drivers as customers, not employees, the company said.
“Lyft does not treat drivers as employees for any purpose,” the complaint said. “Lyft serves a broker/middleman role in the transaction between drivers and riders, and as such, its taxable gross receipts must be limited to the amounts charged to drivers for use of its marketplace services.”
Lyft makes the bulk of its money from the fees it charges drivers. It also brings in some revenue from other sources, including subscriptions and advertising.
“Lyft recognizes revenue from rideshare as being comprised of fees paid to Lyft by drivers, not charges paid by riders to drivers,” said the complaint, filed in San Francisco Superior Court.
San Francisco wrongly included driver income as part of Lyft’s revenue when calculating taxes between 2019 and 2023, Lyft said. The company is now seeking refunds for overpaid taxes as well as interest and penalties.
“Lyft doesn’t take operating in San Francisco for granted and we love serving both riders and drivers in our hometown city,” the company said in a statement. “We believe the city is incorrect with how it calculated our gross receipts tax. … We filed this lawsuit to help correct this issue.”
Lyft called San Francisco’s tax methodology “distortive” and is waiting for a formal response from the city.
“We will review the complaint and respond accordingly,” said Jen Kwart, a spokesperson for the San Francisco city attorney.
This isn’t the first time a business has disputed a high tax bill from San Francisco. Last year, Detroit-based automaker General Motors sued the city, seeking to recoup more than $100 million in back taxes, claiming the taxes were improperly calculated.
The Lyft lawsuit comes amid debate over how rideshare drivers should be classified and how gig economy companies such as Lyft and Uber should be taxed. Lyft’s complaint notes that neither the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission nor federal tax authorities consider driver compensation as part of company revenue.
Ride-hailing companies classify their drivers as independent contractors in the United States instead of employees, meaning the companies don’t have to provide workers certain benefits such as sick leave and overtime pay.
Unions fighting for better working conditions say drivers are improperly labeled but lost a legal battle this year in California over the issue. The California Supreme Court upheld a voter initiative known as Proposition 22 that allowed companies such as Lyft to classify their workers as contractors, a law ride-hailing services say is vital to their business model.
Lyft has also faced scrutiny from the federal government over allegations that it made false and misleading statements about how much its drivers would earn. In November, Lyft agreed to pay $2.1 million in civil penalties to resolve the accusations.
Business
Sony Pictures CEO Tony Vinciquerra talks 'arms dealer' strategy, defends 'Spider-Man' spinoffs
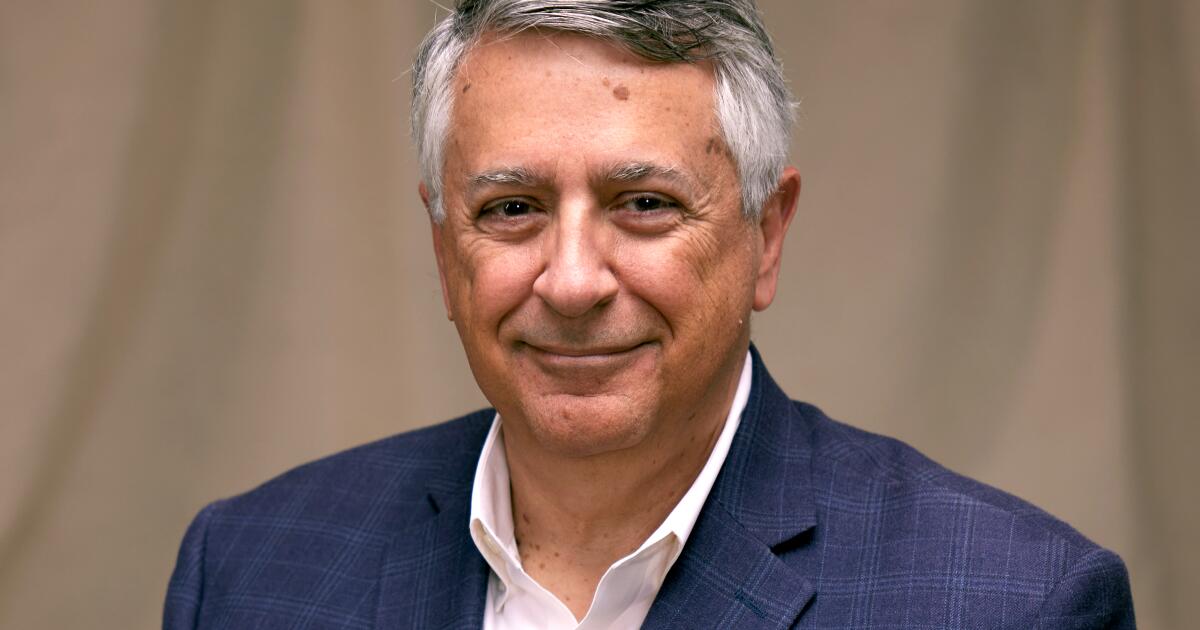

When Tony Vinciquerra arrived at Sony Pictures Entertainment in 2017, it was far from business as usual.
The Culver City studio was still reeling from a 2014 cyber attack that exposed employees’ personal information and revealed internal communications, damaging its reputation and leading to major financial losses. Its film studio was in such a slump that Tokyo parent company Sony Corp. took a nearly $1 billion write-down just months before Vinciquerra was announced as the new chief executive and chairman.
At the time, he was working at private equity firm TPG after a long career at Fox Networks.
“When people approached me about this job, I really wasn’t looking to go back to work full-time, be in the office every day,” said Vinciquerra, 70. “But what was really attractive was the potential.”
Under his leadership, Sony Pictures mounted a comeback.
The film studio revitalized several franchises, including “Jumanji” and “Bad Boys,” churned out its all-important “Spider-Man” movies and started to capitalize on its sister PlayStation video game division by making film and TV series based on that intellectual property. The studio continued to nurture its key shows “Jeopardy” and “Wheel of Fortune,” weathering host changes for both. And it branched out, making acquisitions in the anime market and in movie theaters.
But the studio also had its share of struggles. Like every studio, Sony’s business was hurt by the pandemic and last year’s dual strikes. The company mounted a failed bid for Paramount Global earlier this year. The film studio’s efforts to expand the “Spider-Man” universe into movies about characters other than the titular superhero have had middling box office results.
On Jan. 2, Vinciquerra will step down from his role and hand control to current Sony Pictures Chief Operating Officer Ravi Ahuja in a planned succession that was signaled for months.
Vinciquerra spoke with The Times ahead of his last day to reflect on his more than seven-year tenure at Sony Pictures and what’s to come for him. This conversation has been edited for clarity and length.
Describe the state of Sony Pictures when you arrived in 2017.
The environment of the studios and the business was still vibrating from the hack. There was so much damage done by that in terms of invasion of privacy and sharing of emails. It was palpable. You could feel it even in June of ’17 when I joined.
The financials showed a lot of room for improvement. The fact that Sony owned pictures, music, PlayStation and technology … there’s no other company in the business that had that combination of assets. I didn’t understand why the company wasn’t trading IP back and forth among its units, and they weren’t really working together. So I saw that as a great opportunity; it’s really why I decided to come here.
What were your main priorities when you started in the job?
All of our competitor companies either had started, or were about to start, general entertainment streaming services, and we were under some pressure to do that as well. But we realized pretty quickly that if everybody else is doing that — all seven or eight of our competitors were doing that — why should we? Knowing that they would be fighting tooth and nail to get subscribers, why wouldn’t we just be the arms dealer to supply the weapons for those streaming services to fight each other and thereby improve our business?
We also, at the time, had 110 cable networks. And it was pretty clear that that business was on the downslope. So we set a strategy to get out of that business for the most part, except in markets where cable networks are still doing really well, which is Latin America, Spain and India.
Looking back at what’s happened with all the streamers, the arms dealer decision looks pretty prescient now.
It was pretty obvious, and also the cable network decision was pretty obvious. And really, what’s going on in the business today, most of the streaming services will become profitable, but the cable networks are going in the wrong direction, and that’s not going to change. That’s really the issue for our colleague companies.
How do you feel about the future for anime?
We haven’t rolled Crunchyroll out in the entire world yet, so we still have quite a ways to go. The audience for anime is violently passionate — violent in a good way, not violent in a bad way. They are the most passionate audience ever. It’s got a great future. And unfortunately, others have noticed now and are starting to get into the business. Netflix and Hulu are starting to get in the business and raise the cost of product for us. But, you know, that comes with success.
Part of your tenure included the strikes, and you’ve commented before on how you feel the contract terms from the unions are increasing costs and forcing productions out of the U.S. Do you think the new California film tax credit proposal will change things?
I don’t think the California change will really impact [the situation] because it still doesn’t cover above-the-line actors, it doesn’t cover casting, and it’s still a very difficult process to get done in California.
Not only did the union deals raise costs, but California raises costs as well, just the regulations and the hoops that you have to jump through to get production done here. My suggestion would be, as I’m leaving this job, is that they take a real hard look at the program and the restrictions on the business and and try to figure that out.
How do you feel about the performance of the film studio during your tenure?
We’ve had mostly very, very good results. Unfortunately, [“Kraven the Hunter”] that we launched last weekend, and my last film launch, is probably the worst launch we had in the 7 1/2 years so that didn’t work out very well, which I still don’t understand, because the film is not a bad film.
But we’ve been very successful. We’ve beat our budgets every year I’ve been here, even through strikes and COVID, and max bonuses several of the years for all the employees. It was a good run, and the film studio was a big part of it.
Going back to “Kraven the Hunter,” and Sony had “Madame Web” earlier this year, which also underperformed …
Let’s just touch on “Madame Web” for a moment. “Madame Web” underperformed in the theaters because the press just crucified it. It was not a bad film, and it did great on Netflix. For some reason, the press decided that they didn’t want us making these films out of “Kraven” and “Madame Web,” and the critics just destroyed them. They also did it with “Venom,” but the audience loved “Venom” and made “Venom” a massive hit. These are not terrible films. They were just destroyed by the critics in the press, for some reason.
Do you think that the “Spider-Man” universe strategy needs to be rethought?
I do think we need to rethink it, just because it’s snake-bitten. If we put another one out, it’s going to get destroyed, no matter how good or bad it is.
How do you feel about the state of the industry going into 2025?
There’s a period of asset readjustment coming. It’s going to be for the next year and a half to two. I think it’s going to be a little bit chaotic. The one thing we do know for sure is that the demand for entertainment is not going down. It’s becoming slightly different. But once all of these companies get to the point where they’re stable, they’ll have a great run ahead of them.
2026 is going to be a great year in the film business. And the television business is still perking along, and our market share keeps going up, so we’re very content there. And then we’re looking at other businesses. The film and TV business are probably not going to be great growth businesses, but we’re looking at other things. We have Crunchyroll, we have Alamo Drafthouse and we’re looking at location-based entertainment projects. I’m pretty comfortable with where the company is right now. It’s very stable, relative to the rest of the business.
What made Sony interested in the Alamo Drafthouse deal?
It’s a very different, very unique concept for viewing a film. It’s a very small business. So we have to grow into the markets that are important to domestic box office.
Alamo, even though it only has 41 locations, has 4.5 million loyalty program members, so we have a built-in way to talk to their customers. That’s going to be a very, very big advantage of it for us in the future. And secondly, the customer profile of Alamo Drafthouse is not terribly dissimilar to Crunchyroll. So we’ll use it to promote Crunchyroll, and we’ll also use it in a lot of other ways. It was not a big cash outlay, but the results of what we’re going to gain from this by having a view of our customers’ likes and dislikes will benefit us greatly in the long run.
After you step down, you’ll be moving into an advisor role for 2025. What does that role look like?
I’m here to answer questions, and I’ll be doing some work with Sony Tokyo, but I’ll be in a different office, hidden away so nobody can find me. I don’t know. We’ll see how it works out.
What are your plans for the future?
I don’t know yet. I’ve had a lot of outreach from private equity firms and and other investment-oriented companies. I’m not going to think about it until after the holidays. But most likely will involve some return to private equity or investment companies, but not for sure.
How would you describe your legacy at Sony Pictures?
Where I get my psychic reward is helping people to do their jobs better and get better in their careers, and that’s really how I judge how well I do. The second part of that corollary is to leave a place better than I found it. And I think I’ve done that most every place I’ve been at. I like to fix things and that’s really how it all comes together.
I think I’m leaving the place in a better place, but time will tell. It feels like it’s a very stable business, and I think that’s the legacy.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24924653/236780_Google_AntiTrust_Trial_Custom_Art_CVirginia__0003_1.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24924653/236780_Google_AntiTrust_Trial_Custom_Art_CVirginia__0003_1.png) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoGoogle’s counteroffer to the government trying to break it up is unbundling Android apps
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoNovo Nordisk shares tumble as weight-loss drug trial data disappoints
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoIllegal immigrant sexually abused child in the U.S. after being removed from the country five times
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week ago'It's a little holiday gift': Inside the Weeknd's free Santa Monica show for his biggest fans
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoThink you can't dance? Get up and try these tips in our comic. We dare you!
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25672934/Metaphor_Key_Art_Horizontal.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25672934/Metaphor_Key_Art_Horizontal.png) Technology2 days ago
Technology2 days agoThere’s a reason Metaphor: ReFantanzio’s battle music sounds as cool as it does
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoFox News AI Newsletter: OpenAI responds to Elon Musk's lawsuit
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoFrance’s new premier selects Eric Lombard as finance minister