World
What’s next after Brussels triggers rule of law mechanism on Hungary?

After months going through accusations of procrastination and unjustified delays, the European Fee has confirmed it can set off a novel mechanism in opposition to Hungary that, for the primary time within the EU’s historical past, will make the reception of widespread funds conditional on a rustic’s respect for the rule of regulation.
The budgetary instrument has by no means been used since its entry into power regardless of continued pleas from the European Parliament, whose members resorted to authorized motion in a bid for power the Fee’s hand.
In response, the manager led by President Ursula von der Leyen argued it wanted extra time to draft sensible pointers and look forward to a ruling from the European Court docket of Justice (ECJ) that was supposed to find out whether or not the mechanism was legally sound.
Ultimately, the 2 causes have been happy: the ECJ dominated in favour of the instrument in mid-February and the Fee printed its pointers in early March.
Then, the Hungarian parliamentary elections occurred and Prime Minister Viktor Orbán was as soon as once more given a clear majority to manipulate.
“We received a victory so large you could see it from the moon, and you may definitely see it from Brussels,” stated Orbán whereas celebrating his victory.
Two days after the poll, President von der Leyen appeared earlier than the European Parliament and gave MEPs the information most of them have been impatiently awaiting.
“The Fee has immediately spoken to the Hungarian authorities and knowledgeable them that we’ll now ship a proper letter to begin the conditionality mechanism,” von der Leyen stated.
The letter is anticipated to be formally despatched within the coming days, marking the beginning of a prolonged and sophisticated process that might find yourself freezing Budapest’s €6.14 billion yearly share from the EU funds.
However given the instrument’s novel and unprecedented nature, many doubts stay over its precise power and effectivity.
What precisely is the conditionality mechanism?
The mechanism is a brand new software meant to guard the EU’s monetary pursuits in opposition to breaches of rule of regulation happening inside a member state.
It was designed in a really explicit context: the COVID-19 pandemic had inflicted great ache to the bloc’s financial system and a €750 billion fund was set as much as speed up the restoration. The bottom-breaking fund, financed by widespread debt, was negotiated in parallel to the €1.1 trillion seven-year EU funds.
The substantial enhance in monetary energy fuelled calls to make sure offending governments don’t revenue from the EU taxpayers’ cash, a debate that had been raging for years.
Nations like Poland and Hungary are suspected of democratic backsliding and are at present below the Article 7 process, which stays stalled as the 2 nations have vowed to dam one another’s file.
Following tense negotiations in late 2020, which noticed failed makes an attempt to veto the textual content, the disciplinary system entered into power in January 2021.
The Fee has rejected its characterisations as a sanctioning mechanism, saying the suspension of funds is a reliable compensation for the harm attributable to the transgressions.
What circumstances can set off the mechanism?
The regulation defines rule of regulation as a set of elementary values, together with authorized certainty, efficient judicial safety, unbiased and neutral courts, separation of energy and non-discrimination.
“Compliance with these values can’t be decreased to an obligation which a candidate state should meet in an effort to accede to the European Union and which it might disregard after accession,” the ECJ stated in its ruling.
In follow, nevertheless, the instrument’s scope is relatively restricted: it doesn’t goal common breaches of EU regulation, however solely those who have an effect on or pose a critical menace to the EU’s monetary administration, specifically the widespread funds.
Conditions that may doubtlessly fall below the mechanism are lack of judicial independence, failure to forestall or appropriate illegal selections taken by public authorities and the presence of obstacles to hold out investigations, prosecute crimes and implement rulings.
In keeping with the regulation, these violations can have a unfavorable impression on the execution, management and audit of EU funds, the prevention of fraud and corruption, and the cooperation with related EU businesses.
The Fee has long-standing issues relating to Hungary’s judicial independence, conflicts of pursuits and systemic corruption. OLAF, the EU’s anti-fraud company, has put the nation on the high of its listing of irregularities involving EU funds, with public initiatives thought of to be over-budgeted and overpriced.
These concerns have prevented the approval of Hungary’s nationwide restoration fund, amounting to €7.2 billion in grants. The Fee argues essential points stay unaddressed however Orbán has criticised the coverage as “unprincipled, partial and professionally flawed.”
What are the following steps?
First, the Fee has to construct a authorized case that establishes a real and evidence-based hyperlink between the EU regulation breach and the EU funds.
The chief beforehand despatched administrative letters to Hungary and Poland explaining its issues and asking for clarifications. In keeping with von der Leyen, Budapest’s reply was not convincing sufficient to shut the file and her workforce determined to “transfer on to the following step.”
Brussels will now ship a proper notification to the Hungarian authorities, formally kicking off a process that may see a protracted forwards and backwards between the capitals.
Hungary is entitled to make feedback concerning the Fee’s authorized findings, supply extra info and suggest options to deal with the alleged breaches.
If after the change of communications, which is anticipated to tug on for months, the manager believes the wrongdoing persists and the widespread funds remains to be below menace, it might concern a advice to freeze EU funds.
The advice is distributed to member states, who’ve one month to debate it and take a vote.
The Council has to approve it by certified majority: 55% of EU nations representing at the very least 65% of the full EU inhabitants. This represents an essential distinction from Article 7, the place unanimity is required.
What measures might be taken in opposition to the accused nation?
The EU can transfer to partially or completely droop, interrupt or cut back EU funds which have been allotted to the accused nation.
It will possibly additionally prohibit the nation from getting into new monetary agreements with the bloc and power it to repay pending loans sooner than initially anticipated.
The scope and period of the response must be proportionate to the harm attributable to the authorized breaches. This implies a complete suspension of EU funds is extraordinarily unlikely to occur.
The measures will goal authorities our bodies at nationwide, regional and native degree.
The regulation stresses the ultimate recipients of EU funds, similar to NGOs and farmers, needs to be allowed to gather the cash that has been assigned below “pre-existing obligations”. The federal government can’t use the disciplinary transfer as an excuse to keep away from these funds, the Fee says.
Notably, the manager notes that if the ultimate beneficiaries have been personally concerned in breaching EU regulation, “similar to in instances of corruption, systemic fraud and conflicts of curiosity,” they are often in actual fact disadvantaged of funds.
The measures might be lifted at any time if the accused member state takes motion to appropriate the state of affairs and the Fee concludes the EU regulation breach, even when it persists, now not poses a menace to the EU funds.
How lengthy will the entire process take?
Given the untested nature of the conditionality mechanism, the timeline is unclear.
EU officers have estimated 5 to 9 months between the Fee’s formal notification and the vote by member states.

World
Fight for control of Yemen's banks between rebels, government threatens to further wreck economy
SANAA, Yemen (AP) — Yemen’s Houthi rebels and its internationally recognized government are locked in a fight for control of the country’s banks that experts warn is threatening to further wreck an economy already crippled by nearly a decade of war.
The rivalry over the banks is throwing Yemen’s financial system into deeper turmoil. Already, the Houthis who control the north and center of the country and the government running the south use different currency notes with different exchange rates. They also run rival central banks.
The escalating money divide is eroding the value of Yemen’s currency, the riyal, which had driven up prices for clothing and meat before the Islamic holiday of Eid al-Adha started on Sunday.
For weeks, Yemenis in Houthi-controlled areas have been unable to pull their money out of bank savings accounts, reportedly because the Houthi-run central bank, based in the capital, Sanaa, has stopped providing liquidity to commercial and government banks. Protests have broken out in front of some banks, dispersed by security forces.
Yemen has been torn by civil war ever since the Iranian-backed Houthi rebels took over Sanaa and much of Yemen’s north and center in 2015. The Saudi-backed internationally recognized government and its nominal ally the Southern Transitional Council, a group supported by the United Arab Emirates, govern the south and much of the east, centered in the southern port city of Aden.
Yemen was already the Arab world’s poorest country before the war began. Punitive actions by each side against the other’s banks over the past week now threaten to undermine merchants’ ability to import food and basic commodities and to disrupt the transfer of remittances from Yemenis abroad, on which many families depend, said Edem Wosornu, director of operations and advocacy for the U.N. humanitarian coordination office known as OCHA.
“All these factors will likely deepen poverty, worsen food insecurity and malnutrition, and increase reliance on humanitarian assistance,” she told a U.N. Security Council briefing on Thursday. The dispute could escalate to the point that banks in Houthi-run areas are barred completely from international financial transactions, which she said would have “catastrophic ramifications.”
The internationally recognized government moved the central bank to Aden in 2016, and since then began issuing new banknotes to replace worn-out riyals. Houthi authorities, which set up their own central bank in Sanaa, banned the use of the new money in areas under their control.
In March, the Houthi-controlled central bank announced it was rolling out its own new 100-riyal coins. The international community and Yemen’s recognized government denounced the move, saying the Houthis were trying to set up their own financial system and warning it will deepen Yemen’s economic divide.
Adding to the confusion, the bills have different exchange rates — riyals issued in Sanaa go for about 530 to the dollar, while those from Aden are around 1,800 to the dollar.
In response, the Aden-based central bank gave banks 60 days to relocate their headquarters to the southern city and stop operating under Houthi policies, or else risk facing sanctions related to money laundering and anti-terrorism laws.
The central bank was “forced to make these decisions, especially after the Houthi group issued their own currency and took unilateral steps towards complete independence from the internationally recognized Central Bank in Aden,” said Mustafa Nasr, an economic expert and head of the Studies and Economic Media Center SEMC.
No banks met the deadline — either because they needed more time or because they feared Houthi sanctions if they moved, Nasr said.
When the deadline ran out last week, the central bank in Aden banned dealing with six banks headquartered in Sanaa, meaning currency exchange offices, money transfer agencies and banks in the south could no longer work with them.
In retaliation, the Houthi-run central bank in Sanaa banned all dealings with 13 banks headquartered in Aden. That means people in Houthi-controlled areas can’t deposit or withdraw funds through those banks or receive wire transfers made through them.
Even as the fight for control is going on, both sides are facing a cash crunch. The Houthi government has few sources of foreign currency and its new coins aren’t recognized outside its territory.
In January, the United States designated the Houthis as a global terror group in response to the rebels’ attacks on shipping in the Red Sea and Arabian Sea. The Houthis say the attacks are in retaliation for the Israel-Hamas war in the Gaza Strip. Because of the U.S. decision, banks around the world might be concerned and reluctant to continue any financial dealings with banks that have headquarters under Houthi control, said Youssef Saeed, a University of Aden economic professor.
The economy in Aden isn’t significantly better. The government’s revenues have been hit hard ever since Houthi attacks on oil ports in late 2022 forced a halt in oil exports, the main earner of foreign currency.
Since March, depositors in Houthi-run areas have been unable to pull money out of their accounts. The central bank in Sanaa hasn’t announced any formal restrictions, but several economists told The Associated Press that it has informally stopped releasing funds that individual banks have put in its coffers — in part because of a lack of liquidity.
At one bank that saw protests by depositors last month, the International Bank of Yemen, a note hung in the lobby said, “In coordination with the Central Bank, withdrawals from old accounts have been suspended until further notice.”
Um Ahmed, a 65-year-old woman who was among those protesting outside the bank, said that she was trying to withdraw money to help her son buy a motor scooter for work, but the bank refused.
“I served this country as a teacher for 35 years and saved every penny and deposited my money at the bank, but they took it all,” she said. “This money belongs to my husband and me and our children.”
___
Fatma Khaled reported from Cairo.
World
At 28, Jordan Bardella shakes up French politics: 'People across France have woken up'

FRANCE — Jordan Bardella is shaking things up in French politics. He’s young. He’s handsome like a male fashion model, and since 2022, he’s been president of the National Rally, the new name for the National Front party founded in 1972 by controversial far-right politician Jean-Marie Le Pen. The party has moved on from its far-right roots, becoming more of a populist party under Le Pen’s daughter, Marine.
“Jordan Bardella, the right-wing 28-year-old without a college degree, could be the French prime minister in a few weeks,” says Thomas Corbett-Dillon, a former adviser to former U.K. Prime Minister Boris Johnson and adviser to other European politicians. “This is great news for the French people that have suffered relentless attacks on their culture by left-wing Macron and the millions of migrants he imported.”
Bardella was born into a family of Italian immigrants and excelled in school before attending the country’s top university, the Sorbonne. However, he dropped out before earning a degree to pursue a career in politics. His parents divorced at an early age, and he was largely brought up by his mother in a working-class neighborhood in the Paris suburbs.
EUROPEAN VOTERS REJECT SOCIALISM, FAR-LEFT POLICIES IN EU PARLIAMENT ELECTIONS: ‘POLITICAL EARTHQUAKE’
Rassemblement National President and electoral list leader Jordan Bardella poses for a selfie with supporters during a campaign rally for the upcoming European elections in Montbeliard, eastern France, March 22, 2024. (Patrick Hertzog/AFP via Getty Images)
The reason Bardella has a chance at being the next French prime minister is due to the country’s electorate swing to the populist right in the European Union elections at the beginning of the month. France led the way with the National Rally snagging 31.5% of the votes, making it the most popular French political block in the election.
That led President Emmanuel Macron to call a snap parliamentary election for the end of the month.
“[Macron] called an urgent election to try and surprise the National Rally party before they were ready,” Corbett-Dillon says. “The people across France have woken up and are sick of the left-wing policies.”
Still, there are other changes that might seem to make Bardella and National Rally more popular to the French. Specifically, Bardella and Marine Le Pen, daughter of Jean-Marie, have a different way of doing things compared to Marine’s father, says French-born Veronique de Rugy, a senior research fellow at the Mercatus Center at George Mason University in Virginia.
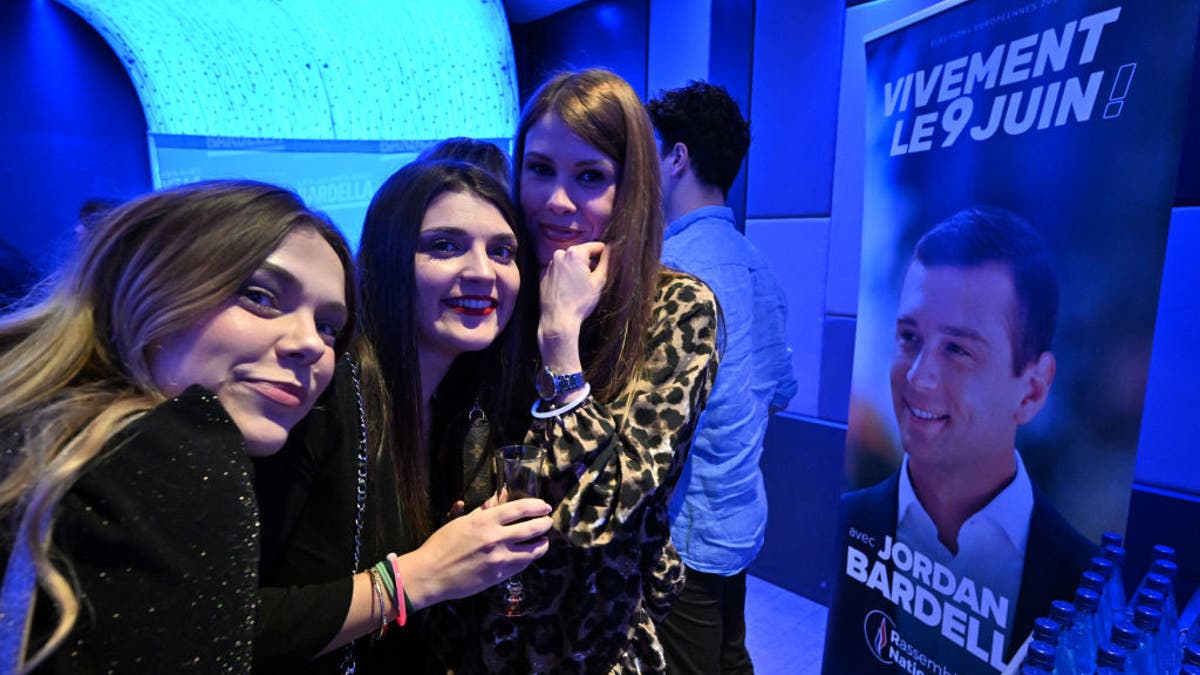

Women pose in front of a poster of the head of the Rassemblement National far-right party, Jordan Bardella, during the launching event of the movement “Les Jeunes avec Bardella” (Youth with Bardella) in Paris, Jan. 27, 2024. (Miguel Medina/AFP via Getty Images)
“Jean-Marie’s demeanor was not fitting in with the French elite,” de Rugy says. “When I see Marine and Jordan, they fit very well.”
In addition, neither Bardella nor Madame Le Pen push antisemitic rhetoric as did Mr. Le Pen.
“They are not Jean-Marie,” de Rugy says. She also notes the usual “far right” description of the National Rally isn’t quite accurate. Yes, the party does have an anti-immigrant and protectionist stance on imported goods, which are both far right, she says. But on domestic issues, the party is quite different.
“These guys are more inclined to big government programs,” she says. Such things include the hefty cost of state-funded pensions and other social safety nets.
GERMANY’S CONSERVATIVES FINISH FIRST IN EU ELECTION, AS FAR-RIGHT MOMENTUM SENDS FRANCE’S LEADER SCRAMBLING
Another thing drawing voters to the National Rally is the high unemployment of young people between 15 and 24. Recent data shows that the so-called youth unemployment rate was running at 17.8%, according to data from April. That’s up from 16.8% at the beginning of last year.
That high youth unemployment rate may be due to a lack of education or skills, says Ivo Pezzuto, a Paris-based professor of global economics and competitiveness at the ISM Business School.
“There are a lot of jobs but only for the people with the new skills,” Pezzuto says. “Those most likely to get jobs would include people with digital know-how.”
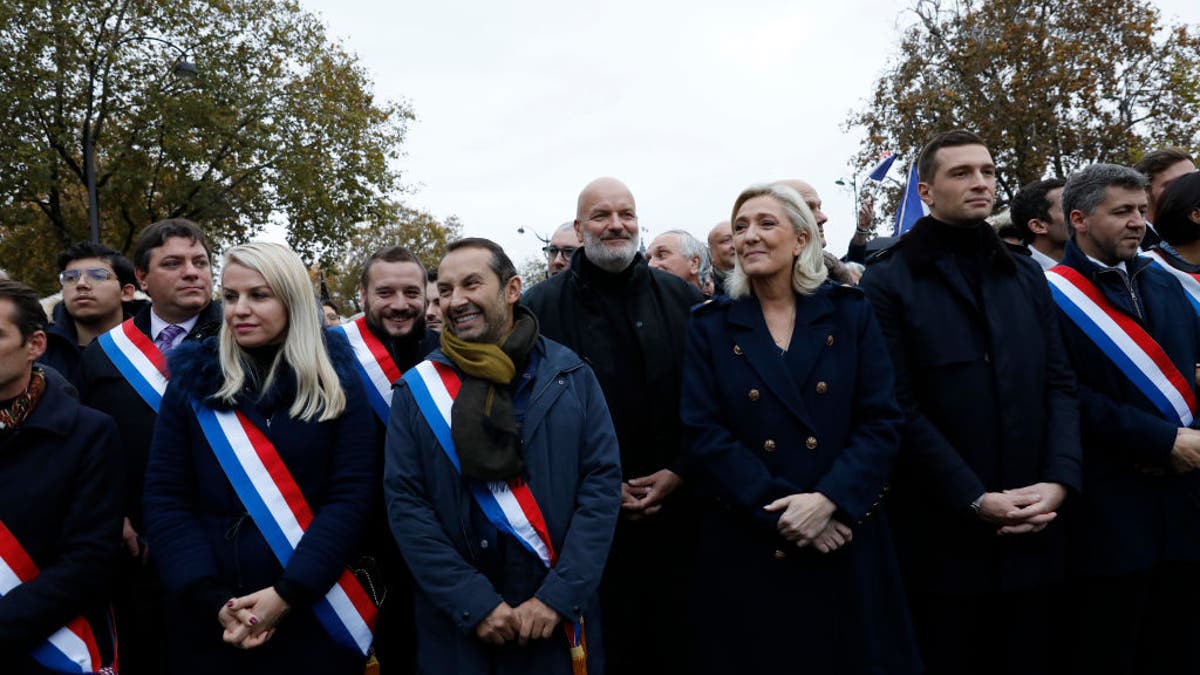

Marine Le Pen, center, and deputies, including Sebastien Chenu to her left and Jordan Bardella, president of the National Rally, to her right, participate in a march against antisemitism from the Esplanade des Invalides to the Senate Nov. 12, 2023, in Paris. (Antoine Gyori/Corbis/Corbis via Getty Images)
However, Bardella and the National Rally face some huge challenges. First, winning a majority in the French parliament isn’t the most likely outcome, says Mujtaba Rahman, Eurasia Group’s managing director for Europe. Instead, he says the likelihood of a victory is “non-negligible” with a 30% chance of the National Rally winning a majority of the parliamentary seats.
If Bardella beats the odds and gets a parliamentary majority, it still won’t be easy to pursue new policy programs, Rahman says. Part of that block will likely be President Macron, who some say leans a tad to the left. That means there will likely be a clash of policy goals between the president and the prime minister.
“Never have we had a co-habitation of such big ideological differences,” Rahman says.
There’s also the potential for problems with government spending. Notably, as a European Union member, France is obliged to stick to limits on how much of a fiscal deficit it runs as a percentage of GDP. The issue that Rahman sees popping up is Macron trying to constrain spending by Bardella.
“It’s not clear [Macron would] be able to do that,” Rahman says. “I think there would be a period of experimentation and uncertainty resulting in the constitution being tested.”
The result could put France’s finances in the spotlight, and that may already be beginning.

National Rally lead candidate Jordan Bardella delivers a speech at the party election night headquarters June 9, 2024, in Paris. (AP Photo/Lewis Joly)
Investors have shown their concerns over the past few days since Macron called the snap vote. The Paris CAC index (roughly the French equivalent of the Dow Jones index) had subsequently dropped 4% last week. And its finances are stretched. The country had a debt of 111% of its GDP at the end of last year.
And the same year, its deficit rose to 5.5% of GDP. The EU requires member states to run deficits no higher than 3%.
“The new government will have a severe fiscal constraint,” says Marc Chandler, chief market strategist at currency specialist Bannockburn Global Forex. In other words, whoever gets a majority in the French parliament, there won’t be much wiggle room.
Chandler also sees an increased risk of France leaving the EU.
“It’s a tail risk, but the tail has gotten a bit bigger,” he said.
World
Swiss summit demands 'territorial integrity' of Ukraine
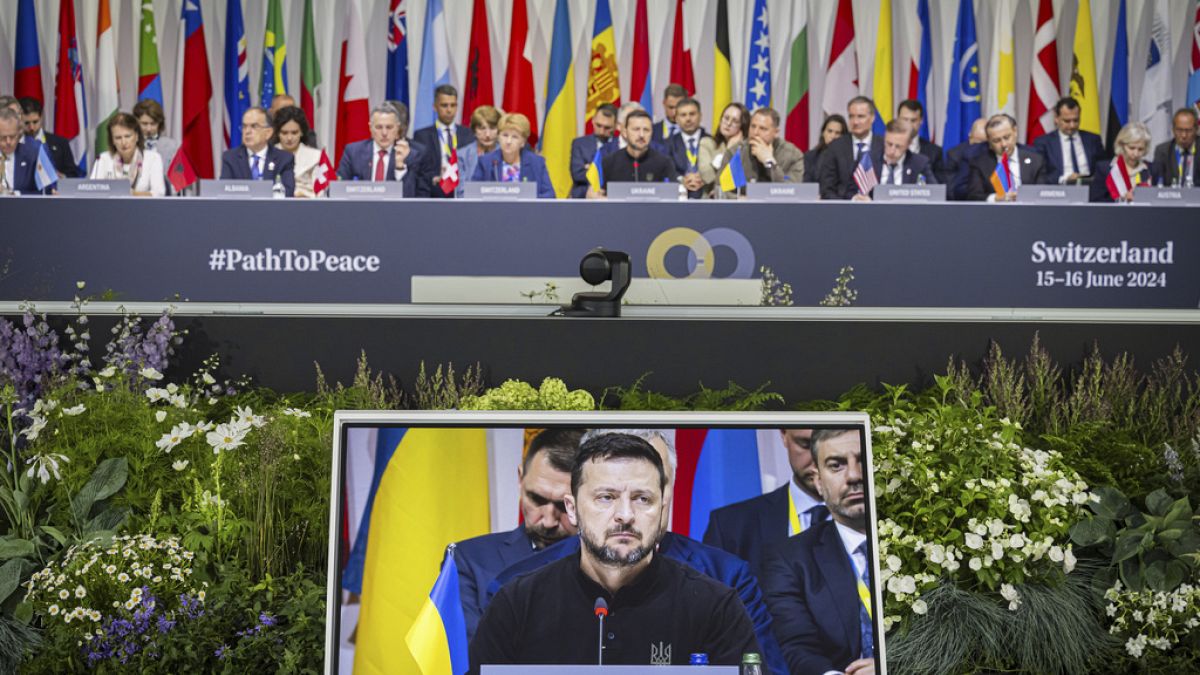

In joint communique 80 countries at the summit agree that the ‘territorial integrity’ of Ukraine must be the basis of any peace agreement.
Eighty countries jointly called on Sunday for the “territorial integrity” of Ukraine to be the basis for any peace agreement to end Russia’s war, though some key developing nations did not join in.
The joint communique capped a two-day conference at the Burgenstock resort in Switzerland marked by the absence of Russia, which was not invited, but that many attendees hoped could join in on a roadmap to peace.
About 100 delegations, mostly Western countries but also some key developing nations, were on hand for the conference — and experts were on watch to see how and if at all they might line up behind the outcome document.
Participants India, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates were among those that did not sign onto the final document, which focused on issues of nuclear safety, food security and the exchange of prisoners.
The final document said the U.N. Charter and “respect for territorial integrity and sovereignty” can and will serve as a basis for achieving a comprehensive, just and lasting peace in Ukraine.”
Analysts say the two-day conference will likely have little concrete impact toward ending the war because the country leading and continuing it, Russia, was not invited — for now. Its key ally, China, which did not attend, and Brazil, which was on hand at the meeting as an observer, have jointly sought to plot alternative routes toward peace.
The meeting also endeavoured to return a spotlight to the war at a time when conflict in Gaza, national elections and other concerns have seized global attention.
The three themes of nuclear safety, food security and prisoner exchanges featured in the final statement. Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni said they amounted to “minimum conditions” for negotiations with Russia, alluding to how many other areas of disagreement between Kyiv and Moscow will be harder to overcome.
Qatar’s prime minister, Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulrahman Al Thani, noted a day earlier how his rich Gulf country hosted talks with both Ukrainian and Russian delegations on the reunification of Ukrainian children with their families that has so far resulted in 34 children being reunited.
White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan, speaking to reporters at the resort on Saturday, said it’s “going to take work” and countries stepping up to build on efforts by nations like Qatar.
“It’s going to take a spotlight from the international community, not just from only voices from the United States or Europe, but from unusual voices as well to say what Russia has done here is more than reprehensible and must be reversed,” he said.
The Ukrainian government believes that 19,546 children have been deported or forcibly displaced, and Russian Children’s Rights Commissioner Maria Lvova-Belova has previously confirmed that at least 2,000 were taken from Ukrainian orphanages.
Montenegro Prime Minister Milojko Spajic told the gathering Sunday: “As a father of three, I’m deeply concerned by thousands of Ukrainian kids forcibly transferred to Russia or Russia-occupied territories of Ukraine.”
“We all at this table need to do more so that children of Ukraine are back in Ukraine,” he added.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIsrael used a U.S.-made bomb in a deadly U.N. school strike in Gaza
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 833
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoGeorge Clooney called White House to complain about Biden’s criticism of ICC and defend wife’s work: report
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNewson, Dem leaders try to negotiate Prop 47 reform off California ballots, as GOP wants to let voters decide
-
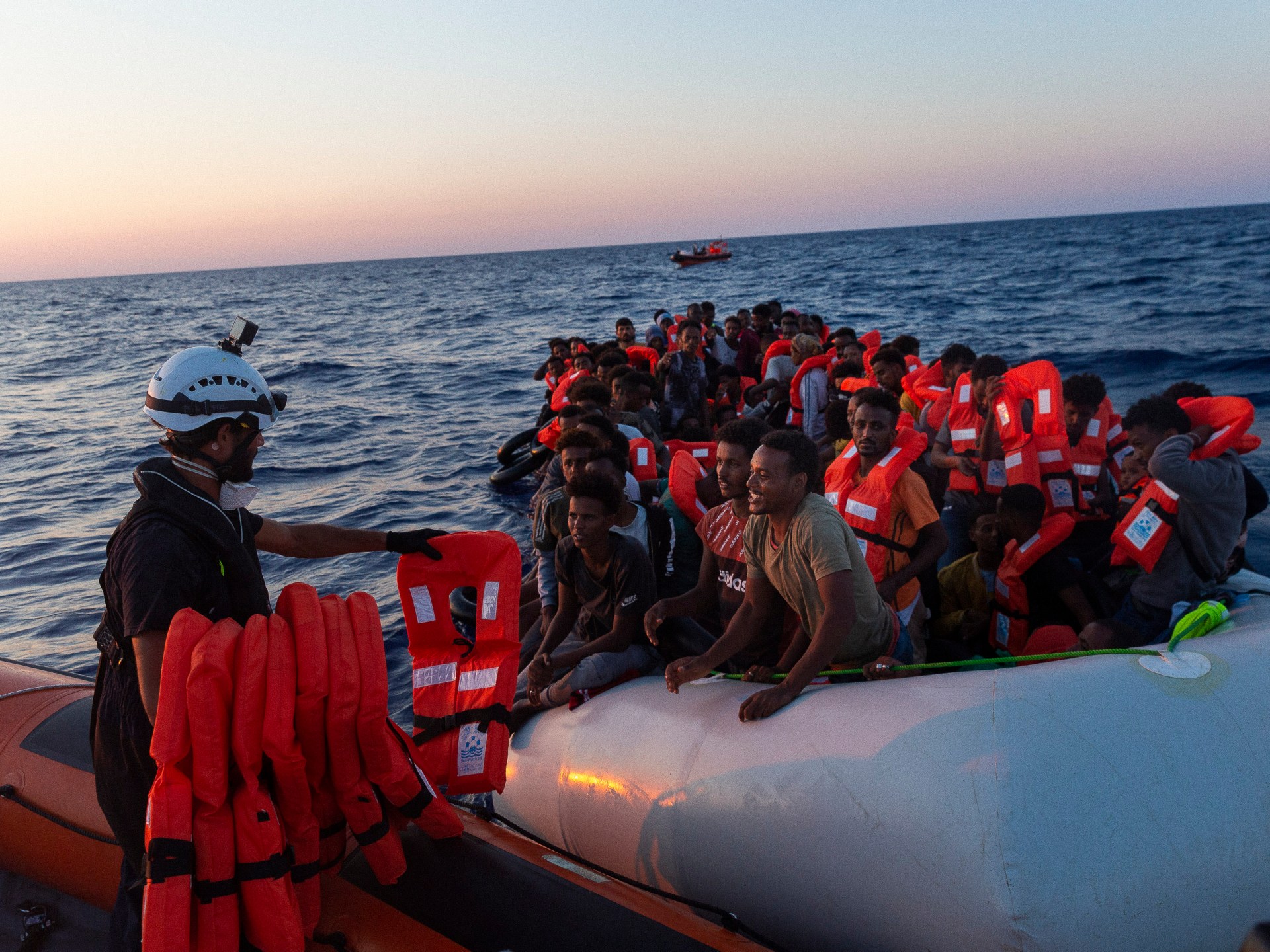

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago‘Bloody policies’: Bodies of 11 refugees and migrants recovered off Libya
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoEmbattled Biden border order loaded with loopholes 'to drive a truck through': critics
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoDozens killed near Sudan’s capital as UN warns of soaring displacement
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoVideo: U.S. Official Responds to Israeli Strike on a U.N. School in Gaza