World
Old ways survive in Bali despite mass tourism, but for how long?

Bali, Indonesia – At dawn, as the first shards of light dance over the rice fields in the seaside village of Seseh on Bali’s west coast, Putu and her husband Made, who like many Indonesians go by one name only, spend an hour reciting prayers and distributing small palm leaf baskets containing offerings to ensure the health of the coming harvest.
Later in the day, their 11-year-old daughter will attend a class for “sanghyang dedari”, a sacred trance dance for girls that is designed to counteract negative supernatural forces.
Meanwhile, her two older brothers will hone their skills on wooden xylophones and hand drums as part of a traditional “gamelan” orchestra in preparation for a ceremony celebrating the completion of a new Hindu temple, one of more than 10,000 on the island.
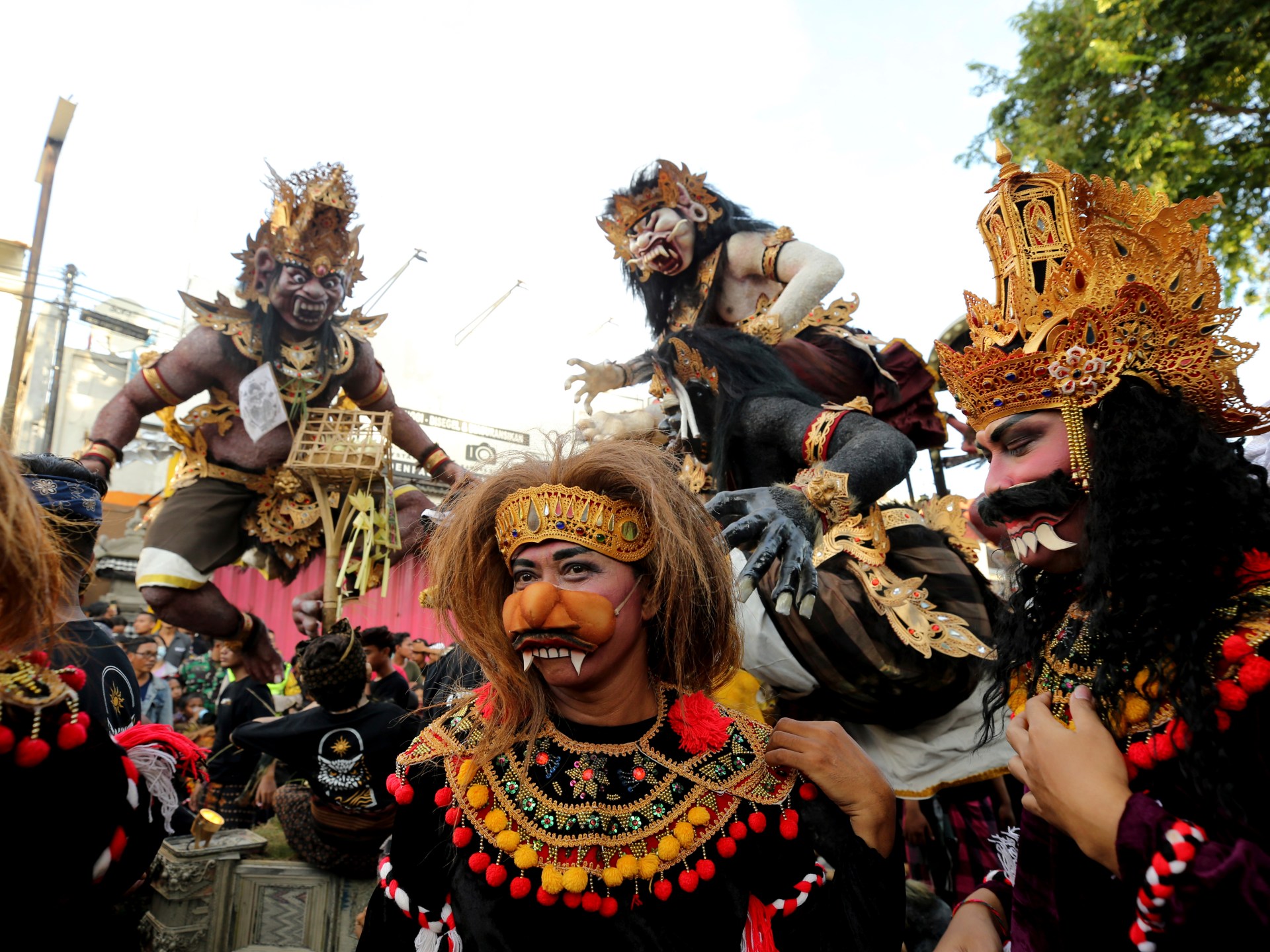
In the coming weeks, Made and his children will help their neighbours create giant “ogoh-ogoh” dolls, representations of evil mythological creatures fashioned from wood, bamboo, paper and styrofoam, that will be paraded through the streets and set alight the night before Nyepi, the Balinese Hindu new year.
Taking place this year on March 11, Nyepi, or the “day of silence”, will see every light on the island turned off, transport come to a halt and the airport close. Everyone, Balinese or not, will stay at home to give evil spirits the impression there is nothing to be found on the island.
“Every day I lay offerings, attend a ceremony or go to a temple,” Putu told Al Jazeera. “I do this because I am Hindu, because I believe. My children do the same and when they have children, they will do the same also.”
The Balinese anomaly
Putu’s hopes for the future are shared with the vast majority of Balinese, an island where a hybrid Hindu-Buddhist religion based on ancestor worship and animism dating back to the first century has survived and even thrived in the face of mass tourism.
By 1930, tourist numbers reached several hundred per year. Last year, 5.2 million foreigners along with 9.4 million domestic holidaymakers visited Bali, according to government data, and the island is developing at breakneck speed to cater to the demand.
The negative effects of such tremendous growth are illustrated in the murals of Balinese artist Slinat, who marries the iconic photographs of Balinese dancers with contemporary emblems like gas masks and dollar bills.
“These old photos were the first images used to promote tourism in Bali and convey that it is an exotic place. They kick-started tourism in Bali,” Slinat told Al Jazeera. “But then we had too much tourism and it ruined the exoticness of Bali. So I created this parody to express how much things have changed here since those photos were taken.”
Nevertheless, Balinese traditional culture and religion have remained resilient in the face of the tourist onslaught, which is something of an anomaly compared with other tourist hot spots around the world.
“When local people entertain tourists, they adapt [to] tourists’ needs, attitudes and values and ultimately start to follow them. By following tourists’ lifestyle, young people bring changes in the material goods,” was the finding of a study on the impact of tourism on culture that was published in 2016 in the Journal of Tourism, Hospitality and Sports.
The study said the Pokhara-Ghandruk community in Nepal was a textbook example, where “the traditional fashion, behaviour and lifestyle of young Gurungs have been severely affected by tourism … [who] disobey their elders’ Kinship titles”. It said Indonesia was an exception – a country where “to attract distant tourists, children nurture local customs to create a strong and authentic base of cultural components without disrupting ancestors’ values”.

A lecturer in traditional architecture at Warmadewa University in Bali, I Nyoman Gede Maha Putra explains the roots of that approach.
“Colonial government policies dating back to the 1930s that promote how the Balinese should be Balinese, including school curriculums, production of traditional foods and beverages and unsparing investments in religious buildings have played a key role in preserving culture and religion on the so-called Island of the Gods,” he said, adding that construction codes formalised in the 1970s that required no new building to be no taller than a coconut tree had helped maintain “a sense of the place” on the island.
“Soon, all our young people will start making ogoh-ogoh paper statues for Nyepi. No one will be left out. They will enjoy the process, they will enjoy the parades, and feel proud when the tourists see what they’ve made. And our daily ceremonies will continue because we believe very strongly that our ancestors’ ghosts live around us and our ceremonies are the only way we can communicate with them,” Maha Putra said.
A facade
Others say it is the adaptability of Balinese culture that has made it resilient.
“Balinese culture is not static,” I Ketut Putra Erawan, a lecturer in political science at Bali’s Udayana University, told Al Jazeera. “Time and time again it has shown it has the power to reinvent itself through the problems and opportunities we face; things like tourism, social media, individualism, capitalism and mass culture. It finds new ways to make itself relevant to young people in new times.”
But these new shapes and expressions are not as solid as those of the past, he cautions.
“Today we are flooded with so much information and misinformation, and what that tends to do is promote the skin of the culture, the outside element of the culture, things like consumerism and fashion, but not the core of the culture,” Erawan said. “Many people prioritise the wrong things in their cultural expressions. They are much more interested in dressing like Balinese and telling everyone on social media they are Balinese instead of obtaining the high level of knowledge needed to understand our complex culture and religion.”
Rio Helmi, an Indonesian photographer whose work focuses on the interaction between Indigenous peoples and their environment, agrees.
He fears time is working against Balinese culture.
“As to the strength of the culture, I think there is some truth to that,” he told Al Jazeera. “But a lot of it is about identity rather than involvement in the deeper side of the culture and its values. What I am seeing now feels more like form over function. People always repeat the phrase ‘tri hita karana’ – maintaining a good relationship between man and God, man and nature, man and the environment – but often it feels like a slogan, a bandage to cover up bad things like people building on sacred land. We have to be careful about making generalisations as there are still many people who live traditionally. But the power of money is everywhere.”
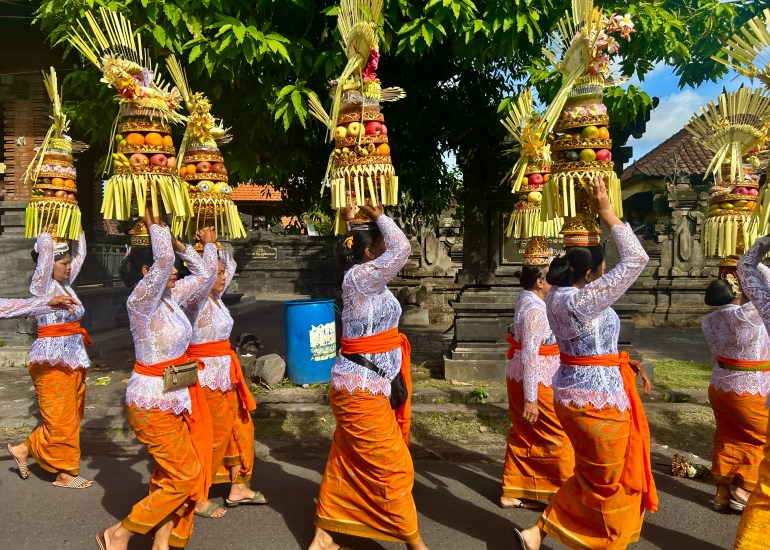

Today, multi-storey hotels and condominiums many times taller than coconut trees are popping up across the island’s traditional rice fields. However the biggest display of the disparity between form and function, Helmi says, will be on display during the ogah-ogah procession in Ubud, the spiritual heart of Bali that has expanded from a sleepy cultural village into a bustling tourist hotspot, where there will be loudspeakers, souvenir vendors and bandstands.
“It will be a real show put on for tourists, whereas in the villages the events will be about introspection, the sense of the year coming to an end and chasing the demons out. It is their moment, their culture. It is not a show,” Helmi said.

World
Temporary floating pier for Gaza aid completed, will move into position once weather lets up: Pentagon
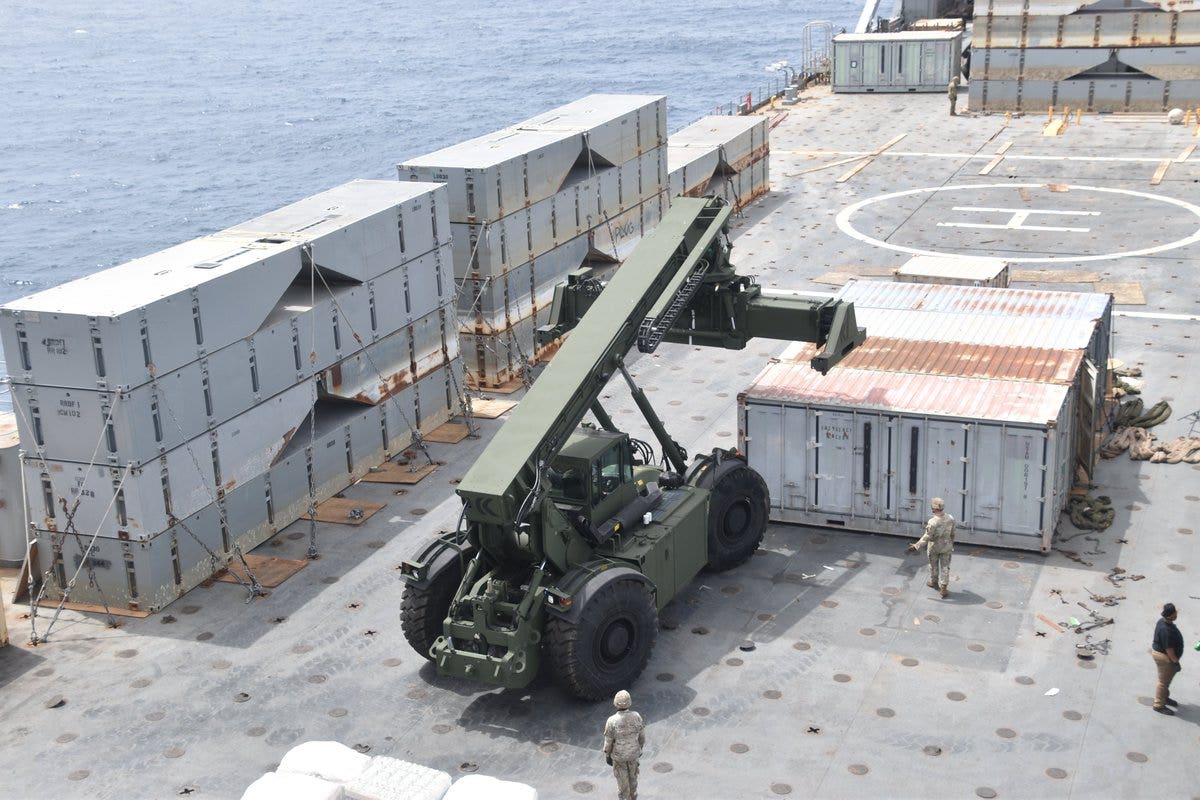

Both sections of the temporary floating pier intended to be placed off the coast of Gaza Strip for the delivery of humanitarian aid have been completed, though weather and sea conditions are preventing delivery of the parts to the embattled region, Pentagon officials tell Fox News.
Pentagon Deputy Press Secretary Sabrina Singh said during a press briefing on Tuesday that the U.S. Military completed the offshore construction of the Trident Pier section, or the causeway, which is the component that will eventually be anchored to the Gaza shore.
The second element of the project, the floating pier section, has also been completed.
“So, as of today, the construction of the two portions of the JLOTS [Joint Logistics Over-the-Shore], the floating pier and the Trident pier are complete and awaiting final movement offshore,” Singh said. “As you know, late last week, CENTCOM [U.S. Central Command] temporarily paused moving the floating pier and Trident pier toward the vicinity of Gaza due to sea state conditions. Today, there are still forecasted high winds and high sea swells, which are causing unsafe conditions for the JLOTS [Joint Logistics Over-The-Shore] components to be moved.”
MORE AID IS SUPPOSED TO BE ENTERING THE GAZA STRIP. WHY ISN’T IT HELPING?
U.S. Central Command tweeted that the construction of the floating Joint Logistics Over-The-Shore pier in the Mediterranean is underway. (CENTCOM)
The components are still sitting at the Port of Ashdod, and CENTCOM “stands by” to relocate the pier sections to Gaza, Singh added.
Once off the coast of Gaza, the U.S. military and USAID will work together to deliver humanitarian assistance using military support vessels and trucks.
Singh could not provide an exact date for when the pier would be maneuvered into place, mainly because of the weather and security conditions.
“As CENTCOM stands by to move the pier into position in the near future, and again, in partnership with USAID, we’re loading humanitarian aid onto the MV Sagamore, which is currently in Cyprus,” she said. “The Sagamore is a cargo vessel that will use the JLOTS system and will make trips between Cyprus and the offshore floating pier, as USAID and other partners collect aid from around the world.”
GROWING CONTROVERSY OVER BIDEN’S GAZA PIER FUELS CONCERNS OVER COST, SECURITY

Pentagon Deputy spokesperson Sabrina Singh holds a press briefing at the Pentagon in Arlington, Va. (Kevin Dietsch/Getty Images)
The unloading of the aid will be, as she called it, a “crawl, walk, run scenario.”
Once fully operational, 150 trucks will be available to move aid into Gaza. At first, though, a small number of trucks will be used to make sure the distribution system works.
BIDEN’S VISION FOR A PALESTINIAN STATE DOOMED, EXPERTS SAY: ‘AN EXPLICIT RECOGNITION OF HAMAS’
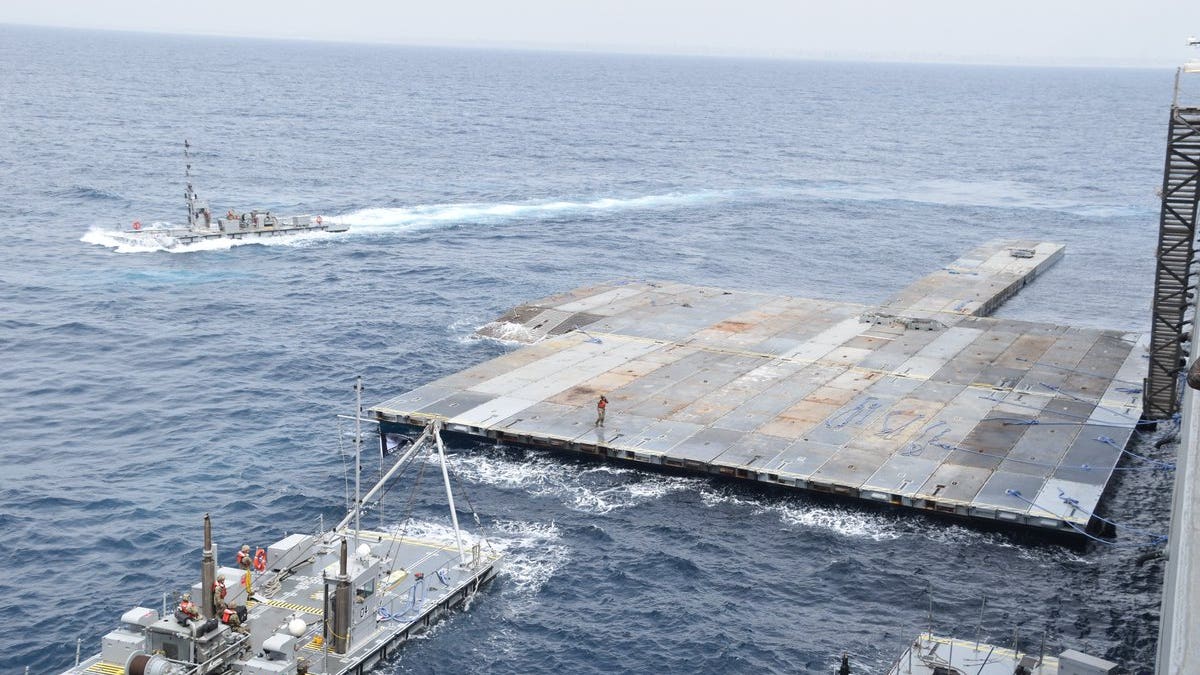

CENTCOM tweeted on X that, ‘The pier will support @USAID and humanitarian partners to receive and deliver humanitarian aid to the people of Gaza. @USTRANSCOM and @USEUCOM support the movement of #humanitarianaid. (CENTCOM)
Last week, U.S. Central Command posted photographs on X of the pier under construction by U.S. soldiers in the Mediterranean Sea, saying that the hulking metal platform “will support USAID and other humanitarian partners who will receive and deliver humanitarian aid to the people of Gaza.”
The Pentagon has said the estimated cost would nearly double the original estimate of $180 million. It also said the project will only be in use temporarily, for a period of three months.
The pier will be able to process up to two million meals a day for the people in Gaza, U.S. Central Command said.
Ruth Marks Eglash of Fox News contributed to this report.
World
‘Bleak milestone’: UN says 3 million forced to flee in Myanmar conflict

United Nations says the number displaced has jumped by 50 percent in last six months as fighting has intensified.
The number of people in Myanmar forced from their homes by conflict now exceeds more than 3 million in what the United Nations has described as a “bleak milestone” for the country.
The UN said the number displaced had surged by 50 percent in the last six months as fighting escalated between the military and armed groups trying to remove the generals who seized power in a coup in February 2021.
“Myanmar has this week marked a bleak milestone with more than 3 million civilians now displaced nationwide amid intensifying conflict,” the office of the UN Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for Myanmar said in a statement on Monday.
“Myanmar stands at the precipice in 2024 with a deepening humanitarian crisis that has spiraled since the military takeover in February 2021 and the consequent conflicts in many parts of the country, driving record numbers of people to abandon their homes seeking safety.”
Of the 3 million internally displaced people, more than 90 percent fled as a result of the conflict triggered by the coup, the UN added.
About half of the displaced are in the northwestern regions of Chin, Magway and Sagaing, with more than 900,000 in the southeast. About 356,000 people live in the western state of Rakhine where a brutal military crackdown in 2017 prompted more than 750,000 mostly Muslim Rohingya to flee into neighbouring Bangladesh.
Myanmar was plunged into crisis when Senior General Min Aung Hlaing seized power from the elected government of Aung San Suu Kyi, which led to mass protests that evolved into an armed uprising when the military responded with brutal force.
Fighting has intensified since the end of October last year when ethnic armed groups allied with anti-coup fighters launched a major offensive in northern Shan and western Rakhine states overrunning dozens of military outposts and taking control of several key towns near the border with China.
In recent weeks, the military has also been battling with ethnic Karen groups for control of Myawaddy, a major trade hub on the border with Thailand.
The UN said the deepening conflict meant that some 18.6 million people in Myanmar were now in need of humanitarian assistance, 1 million more than in 2023.
But it said efforts to reach those in need were being hampered by “gross underfunding”. It said it had so far received less than 5 percent of the funds it needed for humanitarian operations.
“With cyclone season fast approaching, additional resources are needed now to protect the most vulnerable and save lives,” the statement said.
Last year, UN human rights chief Volker Turk accused the military of preventing life-saving humanitarian aid from reaching people in need by creating a web of legal, bureaucratic and financial hurdles.
The generals, who have been accused of launching air attacks on civilians and burning villages to the ground, have ignored a five-point peace plan that it agreed to with fellow members of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in April 2021, under which it was supposed to end the violence.
Nearly 5,000 people have been killed by the military since the coup, according to the Assistance Association for Political Prisoners, which has been tracking the situation. More than 20,000 people are in detention, while Aung San Suu Kyi is serving a combined 27-year sentence after a secret trial in a military court.
World
Extreme Makeover: Home Edition, Now Hosted by Home Edit Duo, Ordered to Series at ABC

ad
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussian forces gained partial control of Donetsk's Ocheretyne town
-
Movie Reviews1 week ago
Challengers Movie Review
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDems disagree on whether party has antisemitism problem
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoHouse Republicans brace for spring legislative sprint with one less GOP vote
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoAt least four dead in US after dozens of tornadoes rip through Oklahoma
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoAnti-Trump DA's no-show at debate leaves challenger facing off against empty podium
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoStefanik hits special counsel Jack Smith with ethics complaint, accuses him of election meddling
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAs student protesters get arrested, they risk being banned from campus too








/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25437025/ipad_air_larger.png)