World
Greece recovers hundreds of looted artefacts

Trove of 351 objects repatriated including a second-century bronze statue of Alexander the Great.
Greece said it has recovered hundreds of looted Neolithic to Byzantine artefacts including a second-century bronze statue of Alexander the Great from a notorious British antiquities dealer after a 17-year legal battle.
The fight to repatriate the trove of 351 objects began in 2006 with authorities investigating the eponymous company of Robin Symes in the country and abroad, Greece’s Culture Minister Lina Medoni said in a statement late on Friday.
The recovery came years after Italian and Swiss police in 2016 recovered a haul of archaeological artefacts stolen from Italy and stored by Symes, a key figure in the illegal antiquities trade with ties to Italian tomb raiders.
The Italian artefacts were found in a storage unit at the Geneva Freeport but Greece’s culture ministry did not specify if its recovery was linked to the Italian haul.
The extensive collection repatriated to Greece includes notable pieces such as a Neolithic-era statuette carved from white stone, dating back to the fourth millennium BCE.
Other significant finds include an Early Cycladic figurine dating to between 3200 and 2700 BCE, a damaged marble statue of an Archaic period kore from 550-500 BCE and an Archaic marble head of either a kore or a sphinx from 550-500 BCE.
Greece has been fighting to repatriate looted artefacts from museums and private collections around the world.
Three fragments of Athens’s Parthenon temple, kept by the Vatican for centuries, were returned to Greece in March in what Pope Francis has called a gesture of friendship.
The monument’s fragments are scattered throughout many renowned museums.
Earlier this year, reports also emerged that the Greek government and the British Museum are in advanced talks for the return of the Parthenon Marbles.
The ancient sculptures, also known as the Elgin Marbles, were taken from the Parthenon temple in Athens in the early 19th century by British diplomat Lord Elgin and have been held by the British Museum ever since.

World
Reacher Gets Early Season 4 Renewal Ahead of Amazon Hit’s 2025 Return

ad
World
The history of the Hoxne Hoard, the largest collection of Roman treasure found in Britain
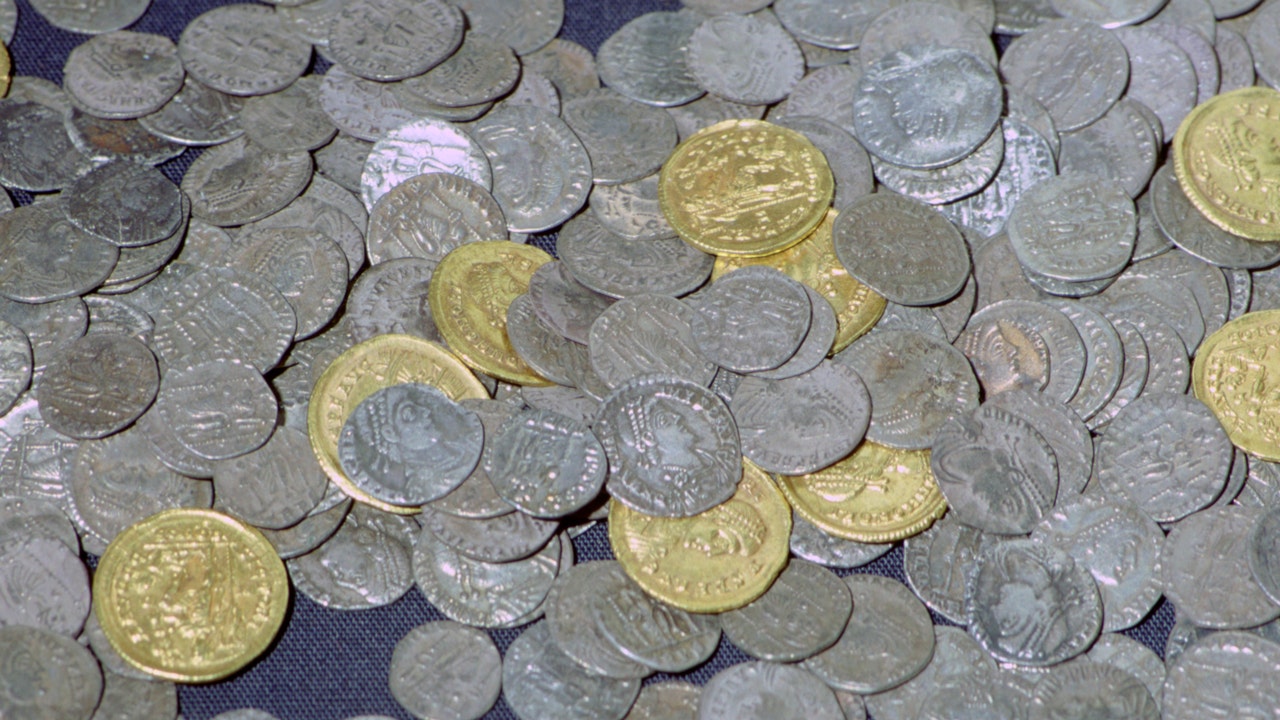

The Hoxne Hoard is one of Britain’s unique archaeological finds, not just by its value, but also by how it was found.
Various sources note the Hoxne Hoard as the largest hoard of Roman treasure ever found in Britain. The collection of treasures is heavily made up of gold and silver coins, though there are other objects, such as tableware and jewelry that were also found.
How this collection of ancient treasures was found adds to its uniqueness.
The Hoxne Hoard is primarily made up of coins. (CM Dixon/Print Collector/Getty Images)
SANXINGDUI RUINS WERE DISCOVERED ACCIDENTALLY BY A FARMER; HAS SINCE BEEN THE SITE OF OVER 60K RELICS
On Nov. 16, 1992, Eric Lawes was scouring a field in Hoxne village in Suffolk, not on the hunt for hidden treasure, but simply looking for a hammer that had been lost on the land.
Lawes was scanning the area with his metal detector, when he came across a small portion of the treasures within what would become the Hoxne Hoard.
After shoveling up some of the silver spoons and gold coins he found, he quickly reported his find to be properly excavated.
Lawes was awarded £1.75 million for his find, which he shared with the farmer who owned the land the treasures were discovered on, according to the Smithsonian Magazine.
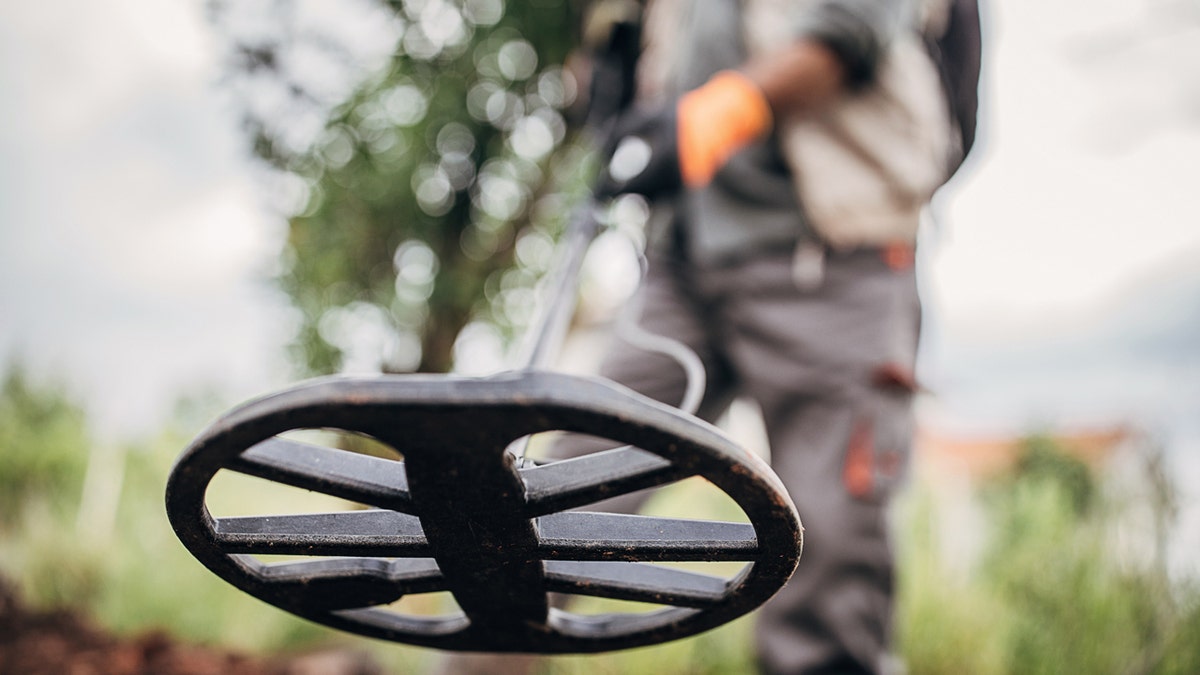

While looking for a lost hammer with a metal detector, a man came across a find far bigger. This discovery later became known as the Hoxne Hoard. (iStock)
THE 4,000 ITEMS IN THE STAFFORDSHIRE HOARD MAKE IT THE LARGEST COLLECTION IN HISTORY OF ITS KIND
The very next day, the Suffolk County Council Archaeology Service (SCCAS) was on the scene, according to the World History Encyclopedia.
The gold and silver artifacts part of the Hoxne Hoard weigh around 60 pounds in total, according to Ancient Origins. There are around 15,000 Roman coins as part of the collection, per The British Museum, where many of the items are displayed today. The items were buried in the 5th century A.D.
Other unique finds include pieces of jewelry, like a body chain, six necklaces, three finger rings and gold bracelets, according to the source.

There were many pieces of jewelry found as part of the Hoxne Hoard, including gold bracelets. (CM Dixon/Print Collector/Getty Images)
MOM, SON DIG UP ANCIENT OBJECT OFTEN FOUND NEAR BURIAL GROUNDS WHILE GARDENING
Even though the Hoxne Hoard is heavily made up of coins, one of the best-known treasures that was found was the “Empress” pepper pot. This pot was one of four that were excavated from the site, according to The British Museum. The pepper pot is intricately formed to represent a woman.
Additionally, there were many tableware items that were part of the hoard, including a set of 19 spoons, in good condition, that were decorated with marine themes, according to The British Museum.
Archaeologists believe that the Hoxne Hoard was buried no later than 450 A.D., according to Ancient Origins.
At the end of the 4th century A.D., the western Roman Empire was in a place of uncertainty, with Roman soldiers exiting Britain, leaving citizens to fend for themselves.
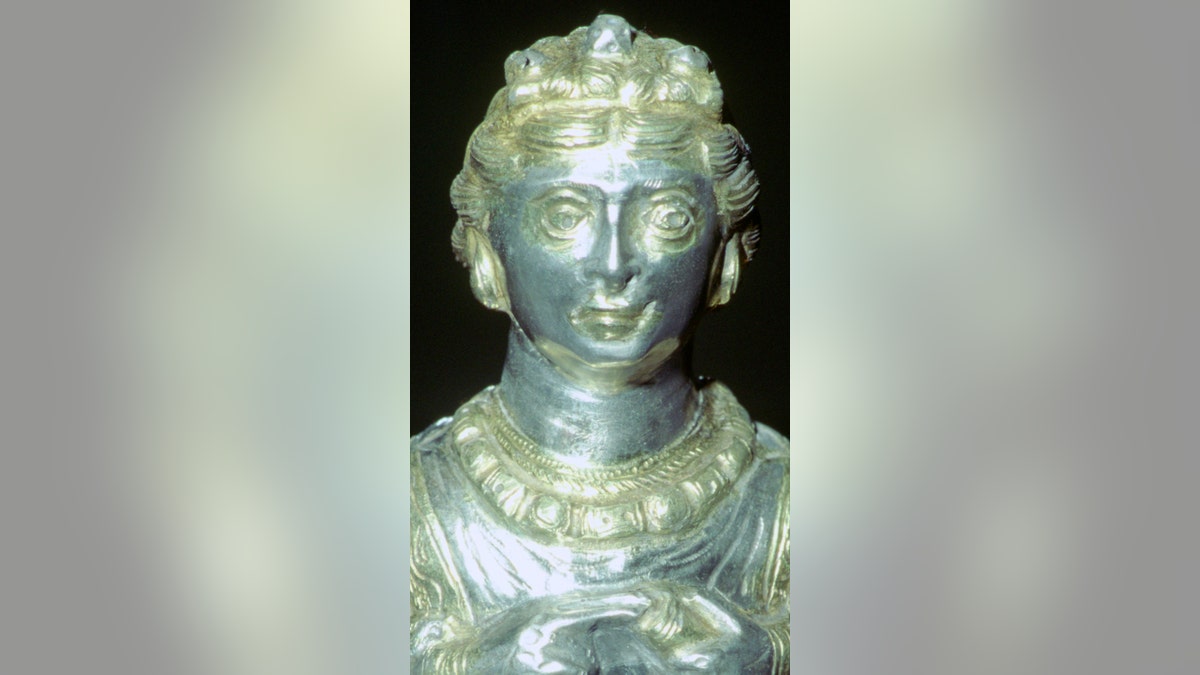

One of the significant finds of the Hoxne Hoard is the pepper pot pictured above. (CM Dixon/Print Collector/Getty Images)
While experts have posed varying hypotheses as to why the hoard was buried, one common suggestion is that it was done for protection, with the intent of the owners collecting their precious items once again. In the case of the Hoxne Hoard, the items were never retrieved by their owners.
Today, the Hoxne Hoard is on display at the British Museum in London. The display contains many of the coins, jewelry and tableware, as well as Lawes’ hammer, which he was originally looking for when he stumbled upon the far more significant discovery.
World
Greece confronts disastrously low birth rate in Aegean Islands

At 1.3 babies per woman, Greece’s fertility rate is among Europe’s lowest — and well below the threshold for population growth.
Authorities in the Aegean Islands have warned that low birth rates spell disaster for their region.
Mayors from the islands expressed serious concerns during the 15th Congress of Small Islands in Milos, where they lamented the continuous downward trend of Greece’s births-to-deaths ratio and said the consequences were already visible in their communities.
A case in point is Agios Efstratios, a small island in the north Aegean with no more than 250 inhabitants.
‘’There are no girls on the island. Or at least there are no more than 2 women under 30 years old,” said Kostas Sinanis, the local mayor.
“The same goes for the boys. We need to search for the incentives that will bring the young boys and girls back to the island, the place where they were born and raised, to create their families. Unfortunately, we had one birth last year and another one three years ago.”
In 2022, Greece recorded its lowest number of births in 92 years — and this year, the country posted the second-largest population decrease in the EU.
Greece’s fertility rate is among the continent’s lowest at 1.3 babies per woman, well below the 2.5 needed for population growth. Economic forecasts indicate its workforce will fall by 50% by 2100, with its output shrinking by 31% over the same period.
Michalis Vlastarakis of the Eurobank Group warned that if nothing is done, disaster will follow.
‘’If we don’t do something, in about 25 years from now, in two decades, one-third of the population will be over 65 years old, and in 2050 we will be 2.5 million less”, said Vlastakaris.
“You don’t need to have studied finance to understand the consequences of these projections on economic indicators, GDP, the workforce, the insurance system, pensions, health, and education, even since there’re going to be fewer schools.’’
Greece’s family ministry said a few days ago that it plans to spend €20 billion through 2035 on incentives to halt the decline, including cash benefits and tax breaks.
The government already spends around €1 billion a year on pro-child measures — but like other European countries doing the same, it has seen little impact.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25439572/VRG_TEC_Textless.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25439572/VRG_TEC_Textless.jpg) Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoCharter will offer Peacock for free with some cable subscriptions next year
-

 World6 days ago
World6 days agoUkrainian stronghold Vuhledar falls to Russian offensive after two years of bombardment
-

 World6 days ago
World6 days agoWikiLeaks’ Julian Assange says he pleaded ‘guilty to journalism’ in order to be freed
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoBeware of fraudsters posing as government officials trying to steal your cash
-

 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoHealth, happiness and helping others are vital parts of free and responsible society, Founding Fathers taught
-

 Virginia1 week ago
Virginia1 week agoStatus for Daniels and Green still uncertain for this week against Virginia Tech; Reuben done for season
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoFreddie Freeman says his ankle sprain is worst injury he's ever tried to play through
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoLebanon says 50 medics killed in past three days as Israel extends its bombardment







/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22259288/Apple_dan_riccio_begins_a_new_chapter_at_apple_01252020_big.jpg.large_2x.jpg)








