World
EU lifts bans on Ukrainian grain but Poland and Hungary keep embargo

The European Commission has lifted the temporary bans on Ukrainian grain after Kyiv agreed to tighten control over its agricultural exports.
But the measure failed to satisfy Poland and Hungary, which swiftly announced they would impose their own nationwide prohibitions on a unilateral basis, the very chaotic scenario that Brussels wanted to avoid at all costs.
“We will extend this ban despite their disagreement, despite the European Commission’s disagreement,” Polish Prime Minister Mateusz Morawiecki told a rally on Friday. “We will do it because it is in the interest of the Polish farmer.”
Shortly after, Waldemar Buda, Poland’s minister of economic development, said he had signed a new “national regulation” to keep the trade embargo in place.
“The regulation is indefinite and will enter into force after publication at midnight on 16 September,” Buda said on X, formerly Twitter. “Polish farmers above all!”
Meanwhile, Hungary published a decree to block 24 Ukrainian agricultural products, including grains, vegetables, honey and several types of meat, Reuters reported. The products will be sealed at the border and allowed only transit to other countries.
“Hungary is taking matters into its own hands to safeguard its farmers, and will maintain and expand the import ban within its national jurisdiction,” said a government spokesperson, quoting the agriculture minister.
“Concerns arise that an influx of cheap Ukrainian imports could overwhelm neighbouring EU markets, leaving inadequate storage capacity for the upcoming autumn harvest.”
Speaking from Santiago de Compostela, in northern Spain, European Commission Executive Vice-President Valdis Dombrovskis, who is in charge of trade relations and has been personally involved in the negotiations, urged member states to “work along the lines” of the new agreement and “refrain from unliteral measures.”
“What’s important right now is that all countries work in a spirit of compromise and engage constructively,” Dombrovskis said when asked about the Polish reaction.
End-of-week deadline
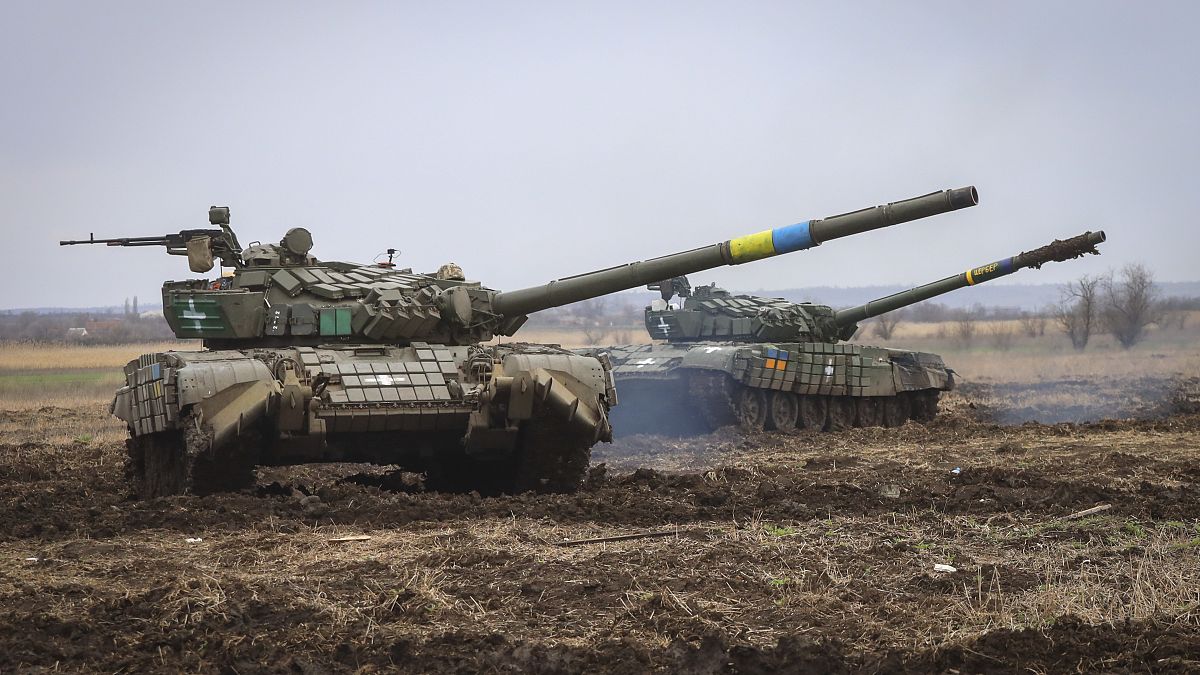
The temporary prohibitions lifted on Friday were first enacted on 2 May and applied to five European Union states located in Ukraine’s periphery: Poland, Hungary, Slovakia, Romania and Bulgaria.
The countries had said the sudden increase in tariff-free, low-cost grain from Ukraine was depressing prices for local farmers after the EU suspended duties on all imports coming from the war-torn nation.
Under the restrictions, four products coming from Ukraine – wheat, maize, rapeseed and sunflower – were allowed to transit through the five Eastern countries but could not stay inside their markets for domestic consumption or storage.
The European Commission had committed to phasing out the bans by 15 September, even if Poland and Hungary had warned they would slap their own restrictions. Warsaw went as far as approving a resolution by the Council of Ministers and posting a video on social media featuring Prime Minister Morawiecki.
“Poland will not allow Ukrainian grain to flood us,” Morawiecki said on Tuesday. “Regardless of what Brussels officials decide, we will not open our borders.”
Under the decision announced on Friday, mere hours before the deadline expired, the temporary bans will be lifted. In return, Ukraine agrees to introduce “legal measures,” such a licensing system, within 30 days to avoid new surges in grain exports, the Commission said in a statement.
In the meantime, Ukraine will establish “effective measures” to tighten control over the four agricultural products previously blacklisted under the bans. These actions should prevent “any market distortions” in the neighbouring countries.
Kyiv has until Monday to submit a plan explaining what kind of steps it intends to take to keep their exports in check, the Commission added.
“The European Commission will refrain from imposing any restrictions as long as the effective measures by Ukraine are in place and fully working,” the statement said.
Dombrovskis said the market disturbances experienced in spring were no longer present and the prolongation of the bans was therefore not justified.
The restrictions were “exceptional safeguards” and “not something that should be there for an unlimited periods of time,” he said, noting the embargo could be re-instated as an “emergency option” if the situation deteriorates again.
“At the same time, to avoid these market distortions, those export control measures will be taken from the Ukrainian side,” he added.
A long-running saga
Since their introduction, the bans had been a point of deepening friction between Brussels and Kyiv, which considered them to be “unacceptable” and contrary to the spirit of solidarity shown towards the country after Russia launched the full-scale war.
Several member states, including Germany, France, the Netherlands and Belgium, had raised “serious concerns” about the detrimental impact the restrictions were having on the single market, which is supposed to function with equal rules for every country.
The European Commission committed to phasing out the embargo by 15 September and working on alternative solutions, such as improving infrastructure and boosting transport capacity through the Danube River, that could somehow alleviate the strain placed on road routes after the collapse of the Black Sea corridor.
But as the deadline approached, political pressure ratcheted up.
The five Eastern countries vocally pushed for the bans to be extended until the end of the year and possibly blacklist goods “other than cereals and oilseeds.”
Poland, the largest of the group, led the public campaign and adopted an uncompromising attitude, openly threatening the European Commission with imposing a unilateral, nationwide prohibition on Ukrainian cereals after 15 September.
The Polish opposition has been linked to the parliamentary elections of 15 October, as the ruling Law and Justice party (PiS) is aiming to attract conservative voters in the countryside. Slovakia is also heading to the polls on 30 September.
“We will extend this ban, this import ban, on a national basis, and this will become a serious fight in Brussels,” Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán said on Friday morning, denouncing traders for buying “cheaper” Ukrainian grain.
Bulgaria, however, broke ranks with the Eastern coalition and voted this week to remove the restrictions after the deadline, arguing the economic forecasts and indicators no longer predicted severe consequences for the country.
The clash between politics and agriculture has proven a formidable challenge for the European Commission to manage and has been described as a litmus test for the bloc’s steadfast support for Ukraine.
In the end, the executive chose a middle ground in which a considerable level of control will remain on Ukrainian cereals but under the direct supervision of Kyiv, injecting a sense of shared responsibility into the long-running dispute.
Ahead of the Friday deadline, President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and his officials have urged Brussels to keep it words and comply with the deadline.
“This is an example of Ukraine and the EU working together in true unity and trust. When rules are followed and agreements are kept, Europe always wins,” Zelenskyy said on Friday evening in reaction to the announcement.
The president then added a pointed warning against any unliteral move that the Eastern countries might make to stop Ukrainian cereals.
“It is critical that European solidarity now work on a bilateral level. For our neighbors to support Ukraine during times of war,” Zelenskyy said. “Should their decisions violate EU legislation, Ukraine will respond in a civilized manner.”
The Ukrainian government had previously raised the prospect of taking legal action before the World Trade Organization if the prohibitions continued to drag on.
This piece has been updated to include new details and reactions.

World
EU preparing sanctions on Russia's 'shadow fleet' after cable damage
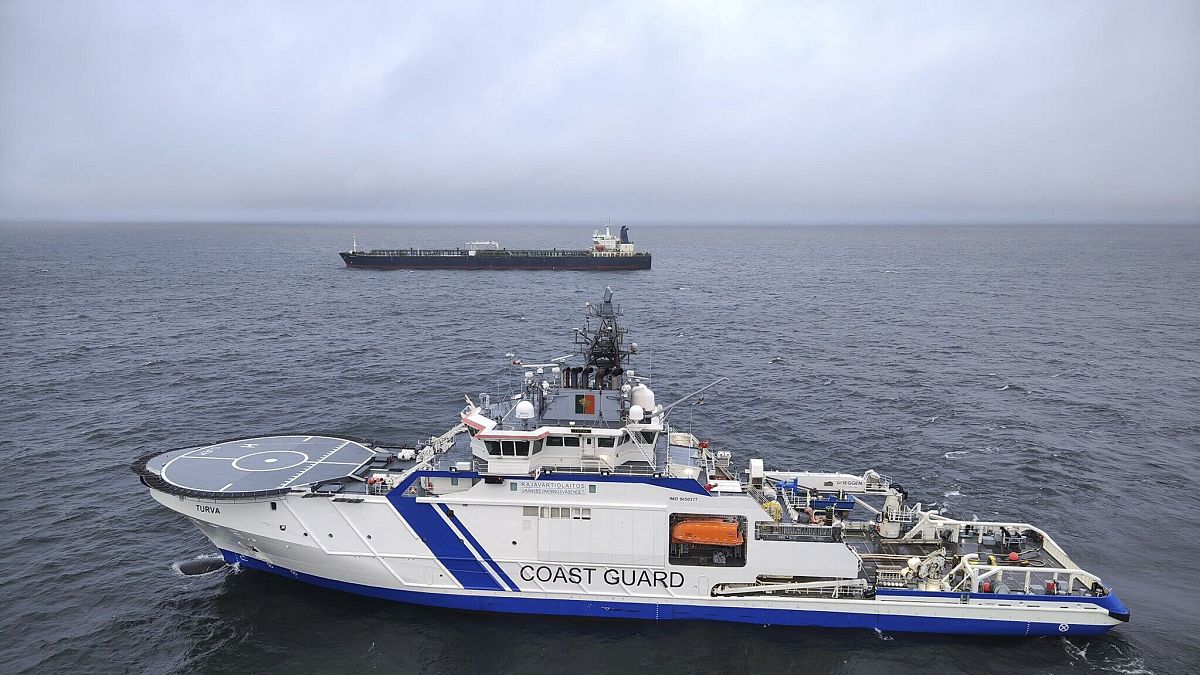

Countries in the region have been on alert following a string of incidents involving undersea cables and gas pipelines in the Baltic Sea since 2022.
The EU Foreign Policy chief has said the bloc is preparing sanctions on what it calls Russia’s ‘shadow fleet’ after an undersea power cable connecting Finland and Estonia was damaged in the Baltic Sea.
Kaja Kallas posted the joint statement from the EU Commission and the High Representative leading the investigation on X, saying the “suspected vessel is part of Russia’s shadow fleet, which threatens security and the environment, while funding Russia’s war budget.”
Kallas also said the EU was strengthening efforts to protect undersea cables, adding that there was no risk to regional electricity supplies.
That comes after Finnish authorities detained a Russian ship as part of an investigation into damage to the Estlink-2 power cable.
It carries electricity from Finland to Estonia across the Baltic Sea and went down on Wednesday.
Finnish police and border guards boarded the Eagle S vessel on Thursday and took over the command bridge, Helsinki Police Chief Jari Liukku said at a press conference.
The vessel was being held in Finnish territorial waters, police said.
The Eagle S is flagged in the Cook Islands but was described by Finnish customs officials and the European Union’s executive commission as part of Russia’s shadow fleet of fuel tankers.
Those are aging vessels with obscure ownership, acquired to skirt Western sanctions and operating without Western-regulated insurance.
Russia’s use of the vessels has raised environmental concerns about accidents given their age and uncertain insurance coverage.
The Eagle S’ anchor is suspected of causing damage to the cable, Yle television reported, citing police statements.
The Estonian government met in emergency session over the incident.
The shadow tankers “are helping Russia to earn funds that will aid Russian hybrid attacks,” Prime Minister Kristen Michal said at a news conference.
“We need to improve the monitoring and protection of critical infrastructure both on land and on sea.”
He said repairs to the cable could take as long as seven months.
“Repeated damage to Baltic Sea infrastructure signals a systemic threat, not mere accidents,” Estonia’s President Alar Karis said on X.
“Estonia will take action to counter this threat, together with Finland and other NATO allies.”
On high alert
Countries in the region have been on alert following a string of incidents involving undersea cables and gas pipelines in the Baltic Sea since 2022.
Two data cables — one running between Finland and Germany and the other between Lithuania and Sweden — were severed in November.
Germany’s defence minister said officials had to assume the incident was “sabotage,” but he didn’t provide evidence or say who might have been responsible.
And the Nord Stream pipelines that once brought natural gas from Russia to Germany were damaged by underwater explosions in September 2022.
Authorities have said the cause was sabotage and launched criminal investigations.
World
Saudi executions rose sharply in 2024

World
Israel launches strikes in Yemen on Houthi military targets, IDF says
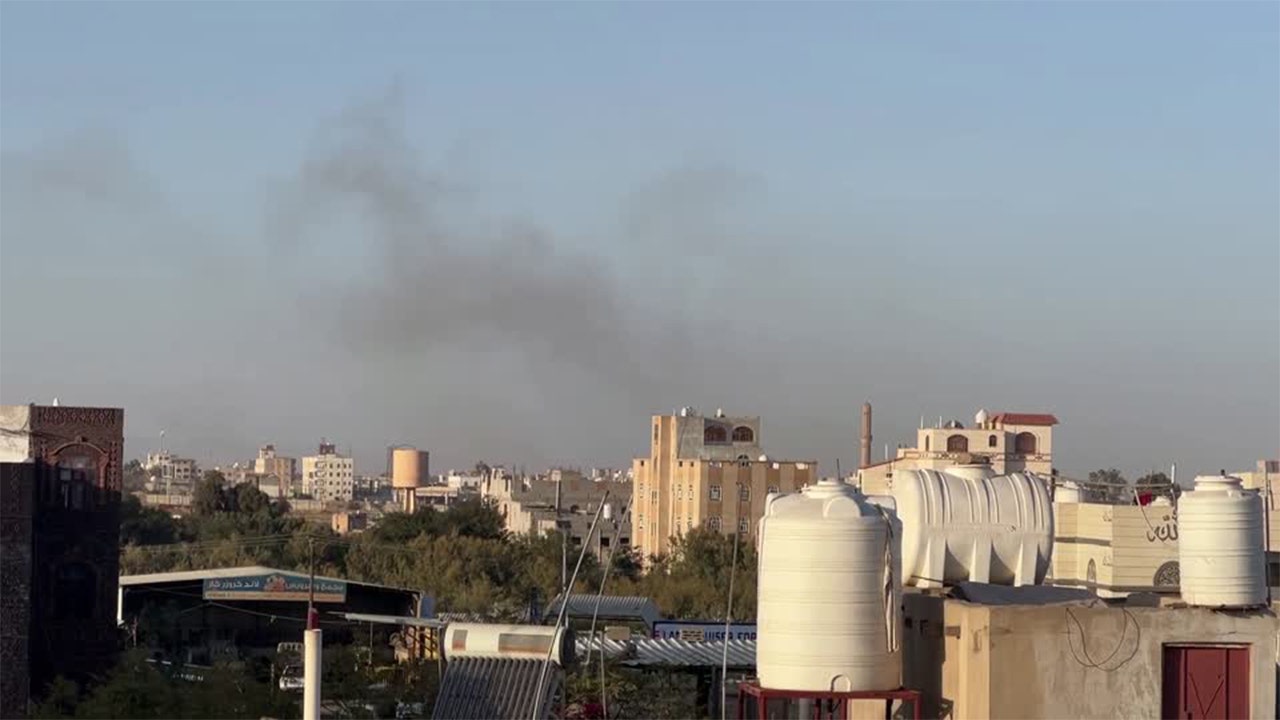

The Israeli military claimed responsibility for a series of airstrikes in Yemen on Thursday that hit Sana’a International Airport and other targets in the Houthi-controlled capital.
The Israel Defense Forces said the strikes targeted military infrastructure used by the Houthis to conduct acts of terrorism.
“The Houthi terrorist regime has repeatedly attacked the State of Israel and its citizens, including in UAV and surface-to-surface missile attacks on Israeli territory,” the IDF said in a statement.
“The targets that were struck by the IDF include military infrastructure used by the Houthi terrorist regime for its military activities in both the Sana’a International Airport and the Hezyaz and Ras Kanatib power stations. In addition, the IDF struck military infrastructure in the Al-Hudaydah, Salif, and Ras Kanatib ports on the western coast.”
PROJECTILE FROM YEMEN STRIKES NEAR TEL AVIV, INJURING MORE THAN A DOZEN: OFFICIALS
Black smoke rises near Sana’a International Airport in Yemen after reported Israeli airstrikes. (Reuters)
The strikes come days after Israel’s defense minister promised retaliation against Houthi leaders for missile strikes launched at Israel from Yemen.
Houthi rebels, who control most of northern Yemen, have fired upon Israel for more than a year to support Hamas terrorists at war with the Jewish State. The Houthis have attempted to enforce an embargo on Israel by launching missiles and drones at cargo vessels crossing the Red Sea – a major shipping lane for international trade.
US NAVY SHIPS REPEL ATTACK FROM HOUTHIS IN GULF OF ADEN
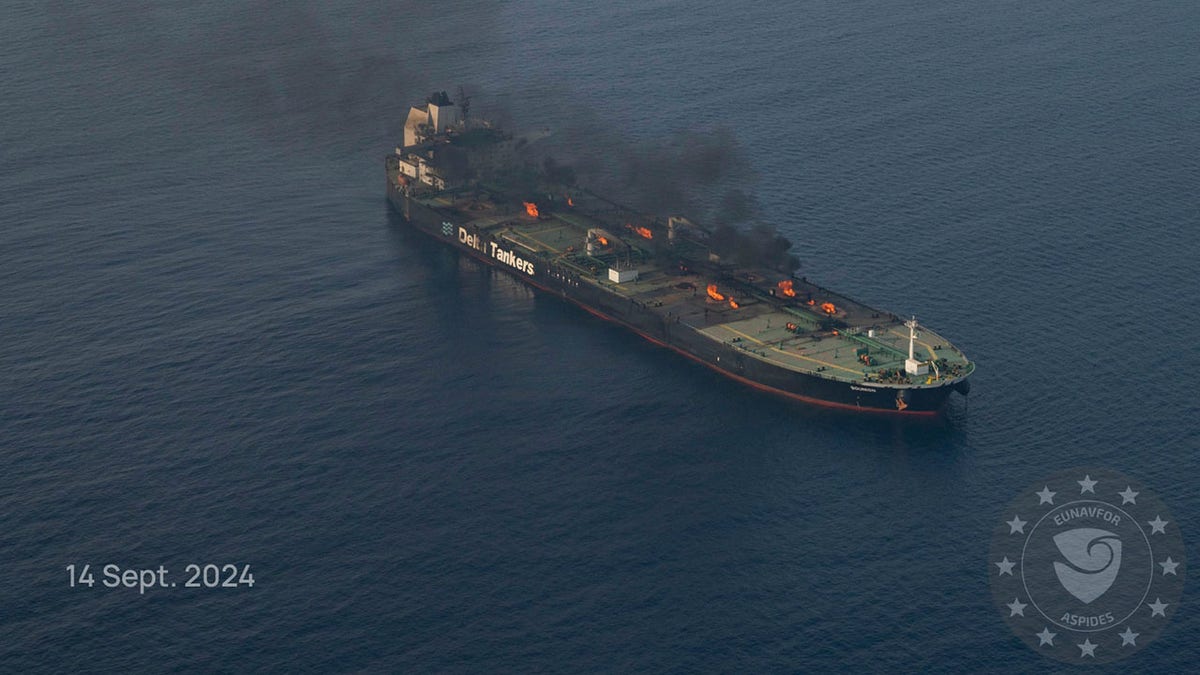

This photo released by the European Union’s Operation Aspides naval force shows the oil tanker Sounion burning in the Red Sea following a series of attacks by Yemen’s Houthi rebels, on Saturday Sept. 14, 2024. (European Union’s Operation Aspides via AP)
Overall, the Houthis have launched over 200 missiles and 170 drones at Israel since Hamas’s Oct. 7, 2023, massacre of 1,200 people. Since then, the Houthis have also attacked more than six dozen commercial vessels – particularly in the Bab-el-Mandeb, the southern maritime gateway to Egypt’s Suez Canal.
On Saturday, a projectile launched into Israel from Yemen struck Tel Aviv and caused mild injuries to 16 people, Israeli officials said. The incident was a rare occasion where Israeli defense systems failed to intercept an attack.
NETANYAHU WARNS HOUTHIS AMID CALLS FOR ISREAL TO WIPE OUT TERROR LEADERSHIP AS IT DID WITH NASRALLAH, SINWAR
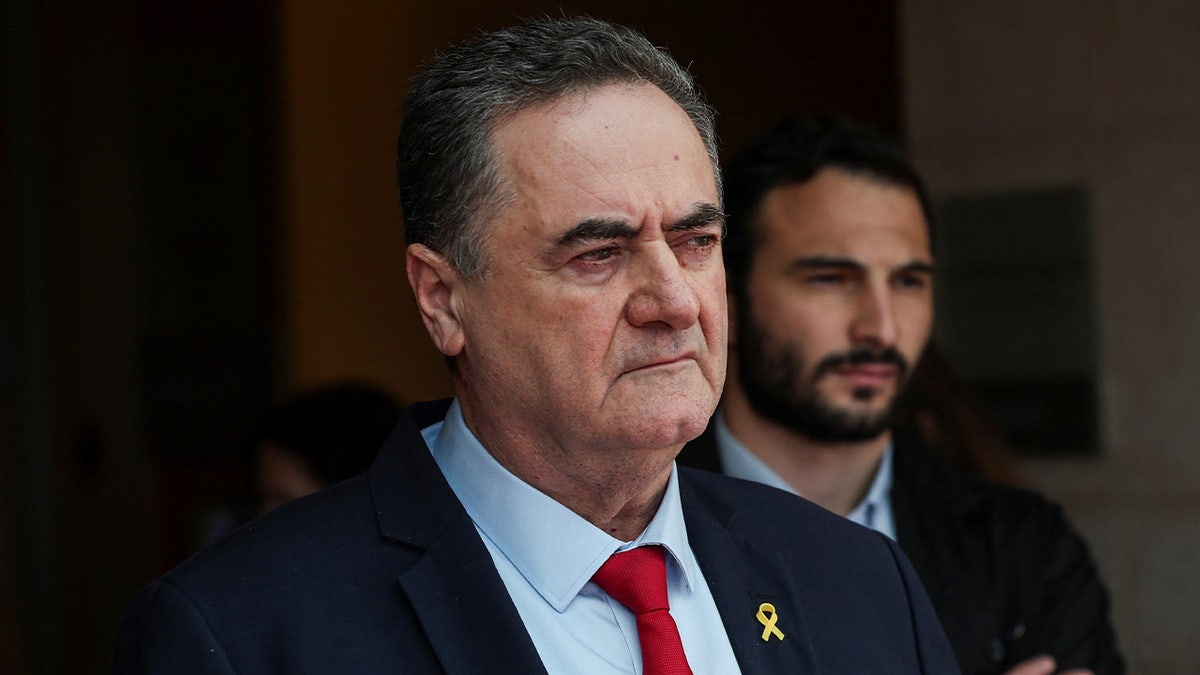

Israeli Defense Minister Israel Katz looks on, amid the ongoing conflict in Gaza between Israel and Hamas, in Jerusalem, November 7, 2024. (REUTERS/Ronen Zvulun)
Israel retaliated by striking multiple targets in areas of Yemen under Houthi control, including power plants in Sana’a.
Israeli leaders have vowed to eliminate Houthi leadership if the missile and drone attacks do not cease.
On Monday, Israeli Defense Minister Israel Katz said, “We will strike their strategic infrastructure and decapitate their leaders. Just as we did to [former Hamas chief Ismail] Haniyeh, Sinwar and Nasrallah, in Tehran, Gaza and Lebanon – we will do in Hodeidah and Sanaa.”
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has also urged Israelis to be “patient” and suggested that soon the military will ramp up its campaign against the Houthis.
“We will take forceful, determined and sophisticated action. Even if it takes time, the result will be the same,” he said. “Just as we have acted forcefully against the terror arms of Iran’s axis of evil, so too will we act against the Houthis.”
Fox News Digital’s Amelie Botbol contributed to this report.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24924653/236780_Google_AntiTrust_Trial_Custom_Art_CVirginia__0003_1.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24924653/236780_Google_AntiTrust_Trial_Custom_Art_CVirginia__0003_1.png) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoGoogle’s counteroffer to the government trying to break it up is unbundling Android apps
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoNovo Nordisk shares tumble as weight-loss drug trial data disappoints
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoIllegal immigrant sexually abused child in the U.S. after being removed from the country five times
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week ago'It's a little holiday gift': Inside the Weeknd's free Santa Monica show for his biggest fans
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoThink you can't dance? Get up and try these tips in our comic. We dare you!
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25672934/Metaphor_Key_Art_Horizontal.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25672934/Metaphor_Key_Art_Horizontal.png) Technology2 days ago
Technology2 days agoThere’s a reason Metaphor: ReFantanzio’s battle music sounds as cool as it does
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoFox News AI Newsletter: OpenAI responds to Elon Musk's lawsuit
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoFrance’s new premier selects Eric Lombard as finance minister