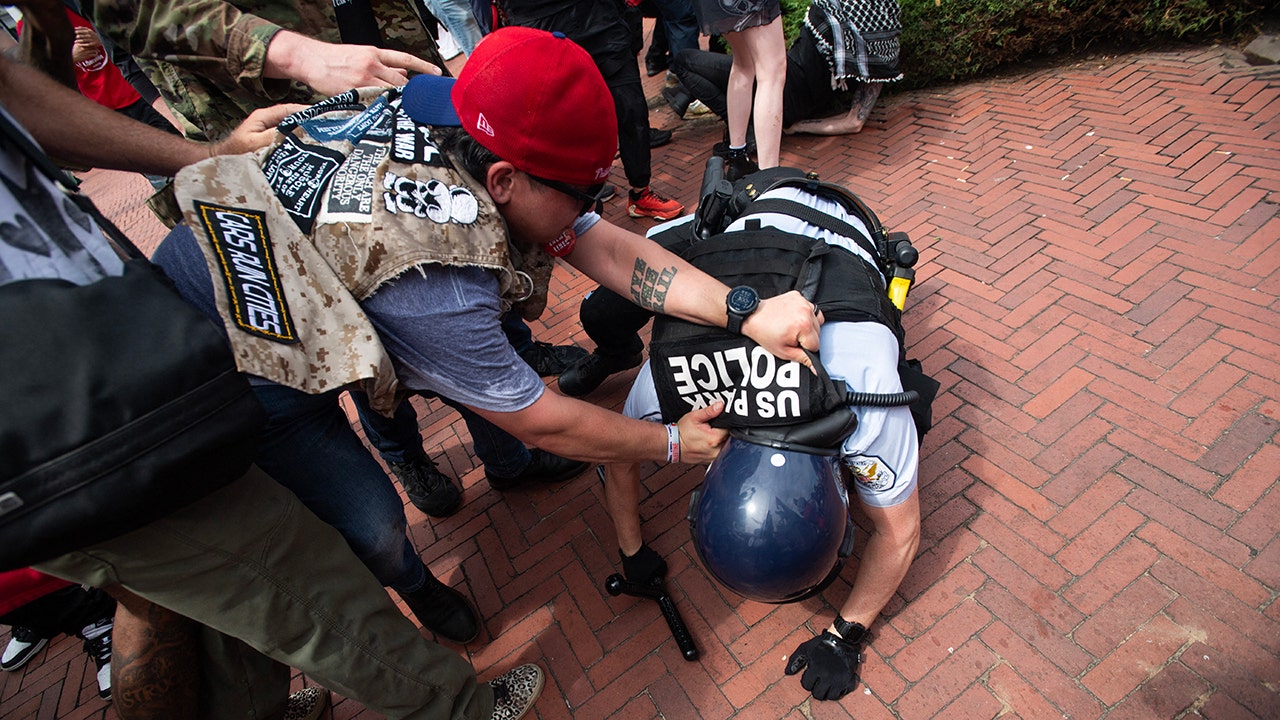World
Biotech strategy launch, Newsletter

Key diary dates
• Tuesday 19 March: European Parliament’s committee vote on the reform of EU pharmaceutical rules.
• Wednesday 20 March: Presentation of the European Commission‘s first ‘EU Biotech and Biomanufacturing Initiative’.
• Tuesday 19-Friday 22 March: European Commission organises Digital Markets Act workshops with gatekeepers.
In spotlight
This Wednesday (20 March) the European Commission is expected to unveil a new ‘EU Biotech and Biomanufacturing Initiative’ .
Despite half-hearted attempts at regulatory simplification in the sector in the past, life science technologies are increasingly drawing attention from policymakers.
Last month Euronews first reported on the health component of this initiative based on a leaked draft document that highlighted a focus on the vibrant biopharmaceutical sector – responsible for providing breakthrough messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules playing an essential role in COVID-19 vaccines.
But biotech applications are not limited to the health sector, ranging from sustainable sourcing of advanced materials to climate-smart production and other components essential to a fossil-free and circular economy.
A ‘blue’ biotech is also emerging, with new research on aquatic organisms and microalgae fermentation ready for commercial exploitation – not to mention the potential of new genomic techniques (NGTs) for food production, already under discussion by EU lawmakers.
The main goals of this initiative will be to survey the status quo and track future challenges facing the biotech sector to orientate policy efforts in readiness for the next legislative mandate.
Some policy ideas are likely to be proffered, such as a one-stop shop to permit and authorise biotech manufacturing – while a controversial proposal for an R&I tax credit for biotech companies is rumoured to have been shelved for the moment.
This first dedicated attempt to address the sector won’t be the last, with economic security and strategic autonomy likely to be key buzzwords for the next commission.
Biotech is expected to be a new beat to keep a close eye on and it has already been listed as a critical technology for the continent, together with semiconductors and artificial intelligence.
The defence imperative dominating current commission thinking involves European independence from military aircraft to sourcing these critical new technologies.
Policy newsmakers
@Hahn @Wiewiórowski
Commission under data notice
The European Commission was ordered last week to bring its use of Microsoft 365 office programs in line with its own rulebook, after European Data Protection Supervisor (EDPS) Wojciech Wiewiórowski found following an investigation that the commission breached EU rules on transfers of personal data outside the EU. The commission now needs to suspend all data flows resulting from its use of Microsoft 365 to Microsoft and to its affiliates and sub-processors located in countries outside the EU/EEA that are not covered by a data transfer agreement. The commissioner responsible for admin, Johannes Hahn, will have to demonstrate compliance with the orders by 9 December 2024.
Policy Poll
Should profits generated by Russian state assets frozen in Europe be:
Kept in trust for Russia
Used to rebuild Ukraine
Used to arm Ukraine
Vote
Subscribe here to see the results of last week’s poll and stay informed on the latest EU policy developments with our weekly newsletter, “The Policy Briefing”. Your weekly insight on European rulemaking, policy issues, key events, and data trends.
Data brief
EU carbon dioxide emissions

World
Celine Dion Makes Triumphant Comeback at Paris Olympics Opening Ceremony — Watch Full Performance

ad
World
95 Libyan nationals arrested in South Africa at suspected secret military training camp
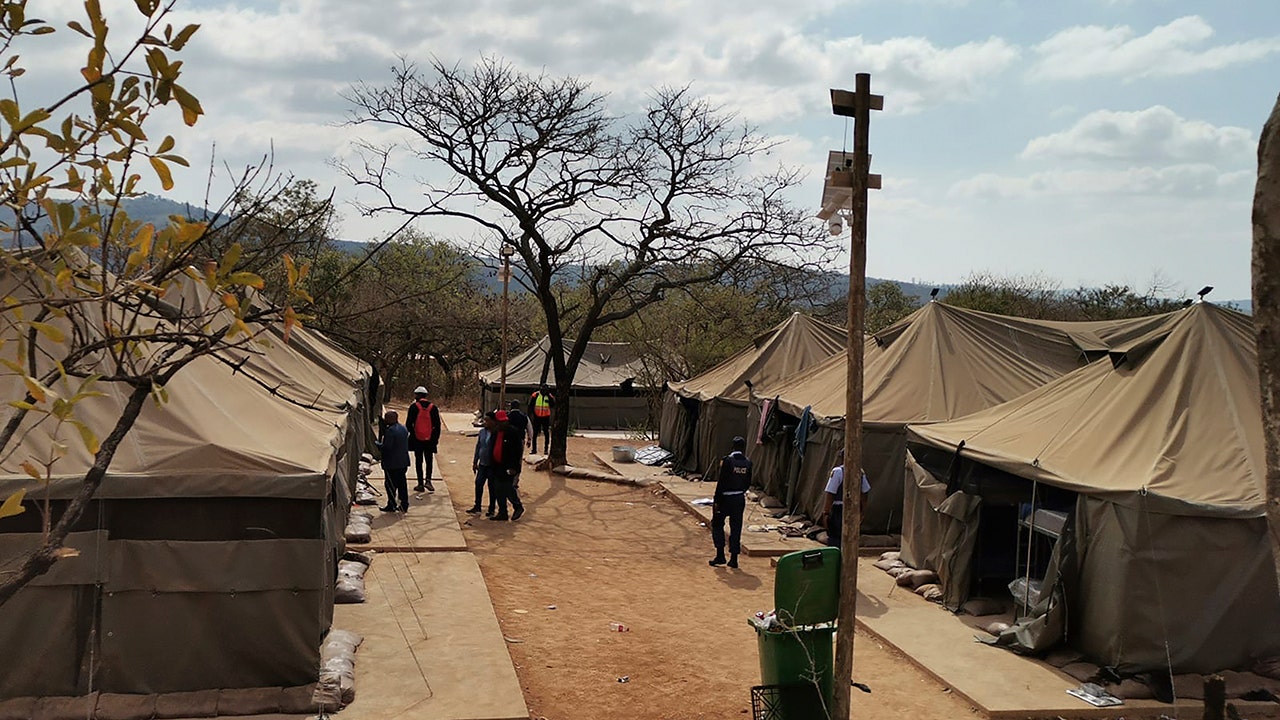

South African police arrested 95 Libyan nationals in a raid on a suspected secret military training camp on Friday and authorities said they were investigating whether there were more illegal bases in other parts of the country.
The camp was discovered at a farm in White River in the Mpumalanga province, about 360 kilometers (220 miles) northeast of Johannesburg, police said.
ELEPHANTS KILL TOURIST IN SOUTH AFRICA AFTER HE TRIED TO GET CLOSE TO TAKE PICTURES
National police spokesperson Athlenda Mathe said in a post on the social media site X that the Libyans stated they had entered the country on study visas to train as security guards, but police investigations suggest they have received military training.
The Newzroom Afrika TV news channel broadcast pictures of the site of the arrests, showing a military-style camp with large green and khaki tents set up in a row. Dozens of men were seen lining up as they were arrested. They were wearing civilian clothing.
Local government official Jackie Macie said investigations were ongoing and the owner of the farm would be questioned. He said authorities received information that there were similar secret camps near two other towns in Mpumalanga province.
A camp where 95 Libyan nationals were arrested on suspicion of running an illegal military camp are seen lining up after their arrest on Friday, July 26, 2024 in White River, South Africa. Police say that 95 Libyan nationals were arrested on suspicion of receiving training at a secret military camp in the north of the country. (AP Photo/Bulelwa Maphanga)
The province borders neighboring countries Mozambique and Swaziland and is an area of concern for South African authorities with regards to illegal immigration.
Police and authorities have not said whether the camps are suspected of being connected to a particular group or conflict.
Macie said investigations would establish if there was a network of camps in South Africa and show “why they are here doing military training in our country.”
Police said the men may be linked to crimes reported in communities close to the farm in recent months.
“We have serious cases which have been opened with the police, including cases of rape and armed robberies, which complainants claim were committed by unknown foreigners who seem to be of Asian descent,” said police spokesman Donald Mdhluli.
“We take what we have found here today very seriously because we don’t know who was training them, what were they being trained for and why that training is happening here in South Africa. It may be a threat not only to South Africa but also to the entire southern Africa region.”
Police said the operation to arrest the Libyans and close down the camp began two days ago. Macie said the Libyan nationals had been in the country since at least April.
“The 95 individuals taken into custody are all Libyan nationals and are currently being questioned by the relevant authorities,” Mpumalanga acting provincial police commissioner Maj. Gen. Zeph Mkhwanazi said in a statement.
Mdhluli, the police spokesman, said the country’s security regulator had confirmed that the kind of training that appears to have been taking place at the camp was well beyond the scope of training for security guards.
“The kind of equipment we found here shows that there was intense military training taking place here. This was basically a military base.”
World
Passengers face long, uncertain wait at stations amid rail disruption

A deliberate fire in a signal box about 60 km south of Lille caused the disruption on the northern high-speed line, with traffic halted around 5 a.m. local time on Friday.
Travel was severely disrupted in Lille on Friday, one of the stations affected by the sabotage that hit major French rail lines ahead of the Paris Olympics opening ceremony.
Many passengers waited with hope that soon turned to resignation.
“We’ve been waiting since 10:38 a.m. for the 11:38 a.m. train, and now we’re just waiting for it to arrive at 2:08 p.m.,” said Delphine, one of the stranded passengers.
“It’s still quite a delay, and we’ll be even later since we’re on a secondary route. I work in Avignon at 9 p.m., so it’s going to be very, very tight. We have a concert tonight — will it even happen? This is all very confusing, and we don’t understand what’s going on.”
For one traveller, this was a rough start to the holidays. “The worst case would be if the train is cancelled entirely and we have to buy new tickets for next week. It would shorten our already brief vacation. That would be a huge problem,” said Hippolyte.
When asked if he had been informed of the delays, Hippolyte said he received the notification just before departure.
“At around 10 a.m. this morning, we were told we were an hour late and would be leaving at 1 p.m.”
“It just keeps getting later as the day goes on. Every time we approach the new departure time, it gets pushed back another hour and a half, or half an hour each time.”
A deliberate fire in a signal box about 60 km south of Lille caused the disruption on the northern high-speed line. Traffic was halted around 5 a.m. on Friday.
The recent acts of sabotage on the rail network highlight that the Olympic Games are turning France into a prime target.
The attack disrupted the transport system on the opening day of the Games, causing delays of up to two hours or even cancellations that affected hundreds of thousands of passengers nationwide.
Authorities in Paris have said they are deploying substantial human resources to counter any threats and to ensure the safety of the events.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt