World
Biden’s shift on F-16s for Ukraine came after months of internal debate

WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden’s decision to allow allies to train Ukrainian forces on how to operate F-16 fighter jets — and eventually to provide the aircraft themselves — seemed like an abrupt change in position but was in fact one that came after months of internal debate and quiet talks with allies.
Biden announced during last week’s Group of Seven summit in Hiroshima, Japan, that the U.S. would join the F-16 coalition. His green light came after President Volodymyr Zelenskyy spent months pressing the West to provide his forces with American-made jets as he tries to repel Russia’s now 15-month-old grinding invasion.
Long shadowing the administration’s calculation were worries that such a move could escalate tensions with Russia. U.S. officials also argued that learning to fly and logistically support the advanced F-16 would be difficult and time consuming.
But over the past three months, administration officials shifted toward the view that it was time to provide Ukraine’s pilots with the training and aircraft needed for the country’s long-term security needs, according to two officials familiar with the deliberations who requested anonymity to discuss internal deliberations.
Still, the change in Biden’s position seemed rather sudden.
In February, Biden was insistent in an interview with ABC’s David Muir that Ukraine “doesn’t need F-16s now” and that “I am ruling it out for now.” And in March, a top Pentagon policy official, Colin Kahl, told U.S. lawmakers that even if the president approved F-16s for Ukraine, it could take as long as two years to get Ukrainian pilots trained and equipped.
But as the administration was publicly playing down the prospect of F-16s for Ukraine in the near term, an internal debate was heating up.
Quiet White House discussions stepped up in February, around the time that Biden visited Ukraine and Poland, according to the U.S. officials.
Following the trip, discussions that included senior White House National Security Council, Pentagon and State Department officials began on the pros and cons and the details of how such a transfer might work, officials said. Administration officials also got deeper into consultations with allies.
In April, Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin heard from defense leaders from allied countries during a meeting of the Ukraine Defense Contact Group who were looking for U.S. permission to train the Ukrainians on F-16s, according to a Defense Department official who was not authorized to comment publicly. Austin raised the matter during the NSC policy discussions and there was agreement that it was time to start training.
Austin also raised the issue with Biden before the G7 summit with a recommendation “to proceed with approving allies” to train the Ukrainians and transfer the aircraft, the department official said.
U.S. national security adviser Jake Sullivan traveled to London on May 8 for talks with British, French and German allies on Ukraine, and F-16s were high on the agenda. They got into the nitty gritty on how to go about provide training and which countries might be willing to transfer jets to Ukraine. It was agreed that the focus would be on training first, the other official said.
Sullivan, before leaving London, spoke by phone with his counterparts from the Netherlands and Poland, both countries that have F-16s and “would be essential to any efforts to provide Ukraine jets for any future use.” Denmark also could potentially provide the jets, the official added.
Biden and Sullivan discussed how the upcoming G7 summit in Hiroshima could provide a good opportunity for him to make the case to key allies on the administration’s shifting stance on fighter jets.
They also discussed Biden backing allies providing jets to Ukraine — a line he had previously appeared not to want to cross out of concern that it could draw the West into what could be seen as direct confrontation with Moscow.
Biden, in private talks with fellow G7 leaders on Friday, confirmed that the U.S. would get behind a joint effort to train Ukrainian pilots on the F-16 and that as things went on, they would work together on who would provide them and how many would be sent.
State, Pentagon and NSC officials are now developing the training plan and “when, where and how to deliver F-16s” to Ukraine as part of the long-term security effort, the official said.
U.S. officials say it will take several months to iron out details, but the U.S. Air Force has quietly determined that the actual training could realistically be done in about four months. The Air Force based the far shorter estimate on a visit by two Ukrainian pilots to a U.S. air base in March, where they got to learn about the F-16 and fly simulators. The training, officials say, would take place in Europe.
White House officials have bristled at the notion that Biden’s decision amounted to a sea change.
The administration had been focused on providing Ukraine with weapons — including air defense systems, armored vehicles, bridging equipment and artillery — that were needed for a coming counteroffensive. There also were concerns that sending F-16s would eat up a significant portion of the money allocated for Ukraine.
What changed, the official added, is that other allies got to a point where they were willing to provide their own jets as part of a U.S.-based coalition.
The Biden administration is still examining whether it will directly provide its own F-16s to Ukraine. Regardless, it needed buy-in from other allies because the U.S. wouldn’t be able to provide the full fleet of jets Zelenskyy says is needed.
Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall said the F-16 will give Ukraine a key capability for the long term but it won’t be a “game changer.”
Kendall told a gathering of reporters on Monday there has been an awareness that “we needed to go there at some point, but we didn’t have a sense of urgency about this. I think we’re at a reasonable place to make that decision now.”
Another potential wrinkle in the F-16 conversation involves Turkey.
Turkey wants to buy 40 new F-16s from the U.S., but some in Congress oppose the sale until Turkey approves NATO membership for Sweden, which applied to join the alliance in the aftermath of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has objected to Sweden’s perceived support of the banned Kurdistan Workers Party, or PKK, the leftist extremist group DHKP-C and followers of the U.S.-based Muslim cleric Fethullah Gulen, who Ankara claims was behind a failed military coup attempt in 2016.
Erdogan is facing opposition leader Kemal Kilicdaroglu in a runoff election on Sunday. If Erdogan wins, as expected, White House officials are increasingly hopeful that the Turkish leader will withdraw his opposition to Sweden’s membership, according to the U.S. official.
If Erdogan drops opposition to Sweden joining NATO, it could lead to Turkey getting its long desired F-16s and may eventually add to the number of older F-16s in circulation, which could benefit Ukraine.

World
US Threatens Mexican Airline Flights Over Airline Competition Issues
World
Farage slams secret Afghan refugee resettlement to UK, claims sex offenders among arrivals

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Nigel Farage, the leader of the right-wing Reform UK party, slammed the Conservative and Labour parties after it was revealed this week thousands of Afghan refugees were secretly resettled into the country without the public’s knowledge.
Farage claimed some of those Afghans are sex offenders, sparking a row with the ruling Labour Party, which denied the claims.
Around 4,500 Afghans have been relocated to the U.K. so far with around 6,900 expected to be relocated overall.
Reform UK leader Nigel Farage speaks during a press conference in Westminster, United Kingdom, June 10, 2025. (Thomas Krych/Anadolu via Getty Images)
EUROPEAN NATIONS DEMAND POWER TO DEPORT IMMIGRANTS WHO COMMIT CRIMES
Meanwhile, waves of migrants continue arriving by boat, further inflaming public frustration over unchecked immigration.
“Amongst the number that have come are convicted sex offenders – I am not, I promise you, making any of this up, and the total cost of this operation has been a staggering £7 billion [$9 billion],” Farage said in a post on X.
“The numbers are off the charts, the cost is beyond comprehension and the threat to women walking the streets of this country, frankly, is incalculable.”
Relocating the 6,900 Afghans is expected to cost £850 million [$1.1 billion]. The £7 billion Farage referenced is likely the total cost of all Afghan resettlement programs since 2021 of about 36,000 Afghans through multiple schemes.
The British government earlier this week revealed it secretly resettled thousands of Afghan nationals in the U.K. after a catastrophic data breach exposed nearly 19,000 applicants who had worked with U.K. forces, an operation kept under wraps by a rare “super injunction” that barred even the mention of its existence.
The injunction was lifted Tuesday in conjunction with a decision by Britain’s current Labour Party government to make the program public.
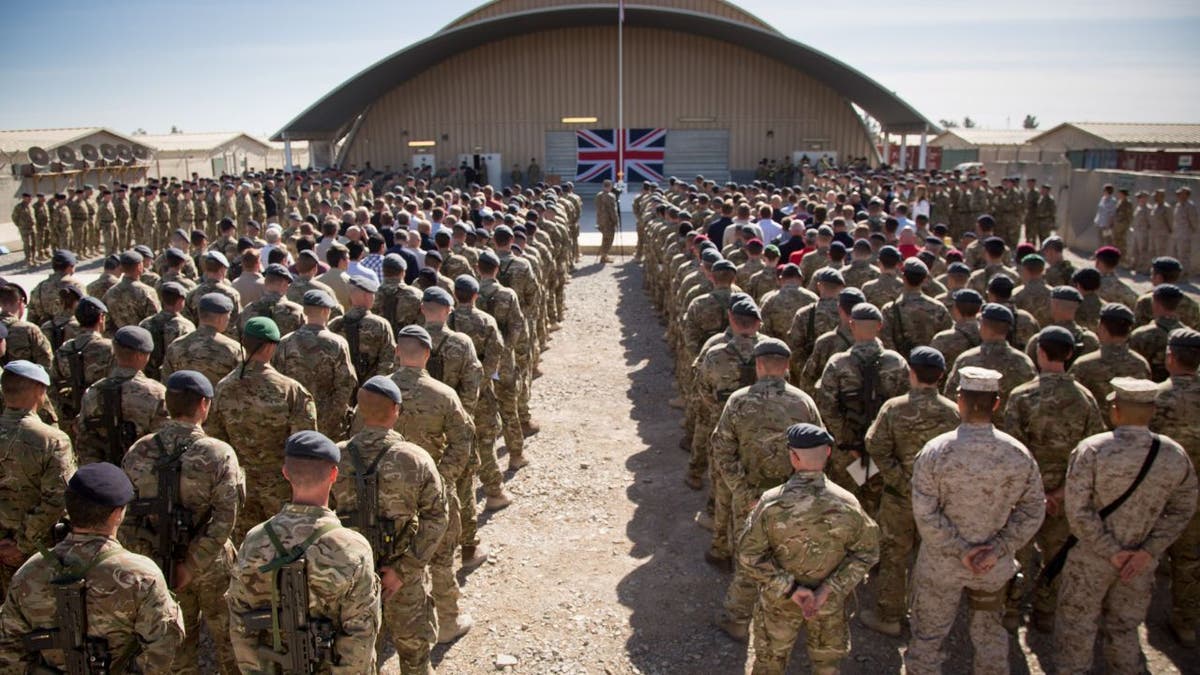

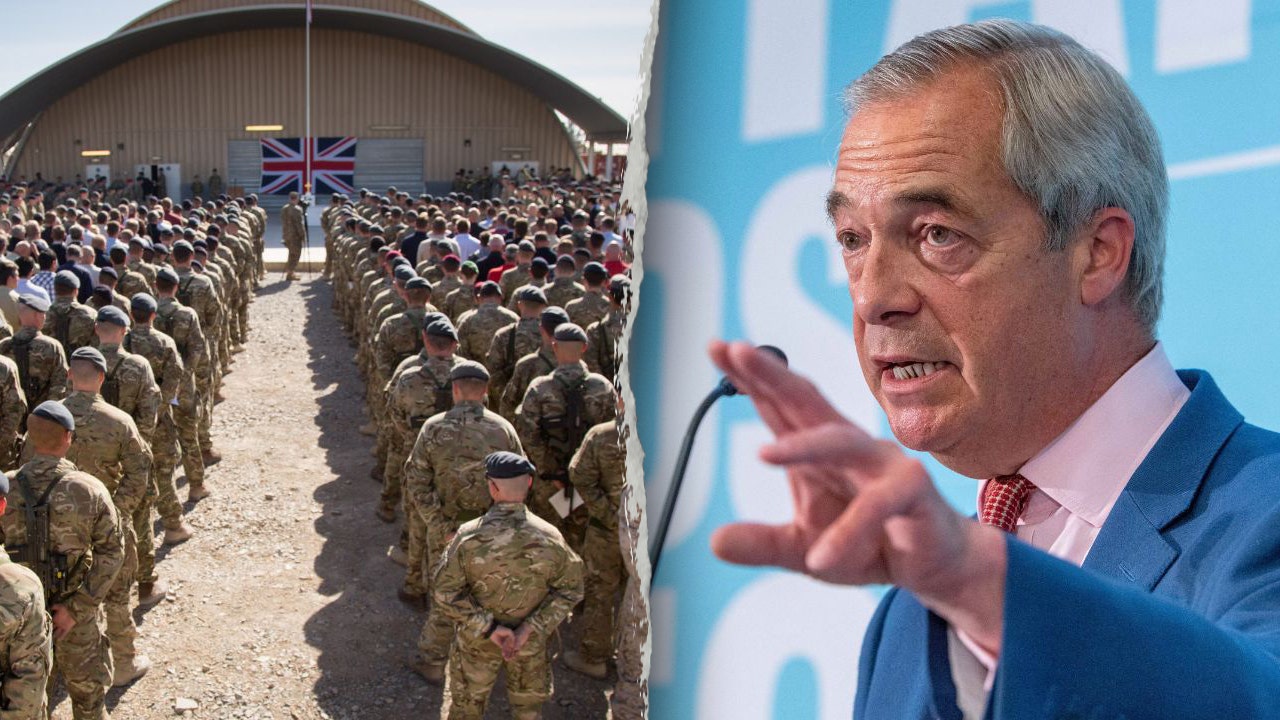
The national flag of the United Kingdom is displayed as British troops and service personnel remaining in Afghanistan are joined by International Security Assistance Force personnel and civilians for a Remembrance Sunday service at Kandahar Airfield Nov. 9, 2014, in Kandahar, Afghanistan. (Matt Cardy/Getty Images)
‘AFGHANS FOR TRUMP’ GROUP FEELS ABANDONED AFTER ADMINISTRATION REVOKES REFUGEE PROTECTIONS
A spreadsheet containing the personal information of the nearly 19,000 people who had applied to relocate to the U.K. after the Taliban takeover of Afghanistan was accidentally released in 2022 because of a defense official’s email error. The government only became aware of the leak when some of the data was published on Facebook 18 months later.
“I can’t think of a better example of the total incompetence, dishonesty and genuine lack of understanding of what the priorities of a British government are than this Afghan scandal,” Farage added.
But U.K. Defense Secretary John Healey denied any known sex offenders had been allowed into the U.K. under the program and insisted everyone had been checked “carefully” for any criminal records
He said if Farage had any “hard evidence,” he should report it to the police.

Demonstrators hold placards as Afghans living in London and their supporters attend a protest called by Stand Up To Racism at the Home Office to demand that more refugees from Afghanistan be allowed into the U.K. Aug. 23, 2021, in London. (Guy Smallman; Getty)
“Anyone who has come into this country under any of the government schemes that was under the previous government and now from Afghanistan is checked carefully for security, checked carefully for any of those sort of criminal records that would preclude and prevent them coming to this country,” Healey told Times Radio, according to The Sun.
British soldiers were sent to Afghanistan as part of an international deployment against al Qaeda and Taliban forces in the war on terror after the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks. At the peak of the operation, there were almost 10,000 U.K. troops in the country, mostly in Helmand province in the south.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
World
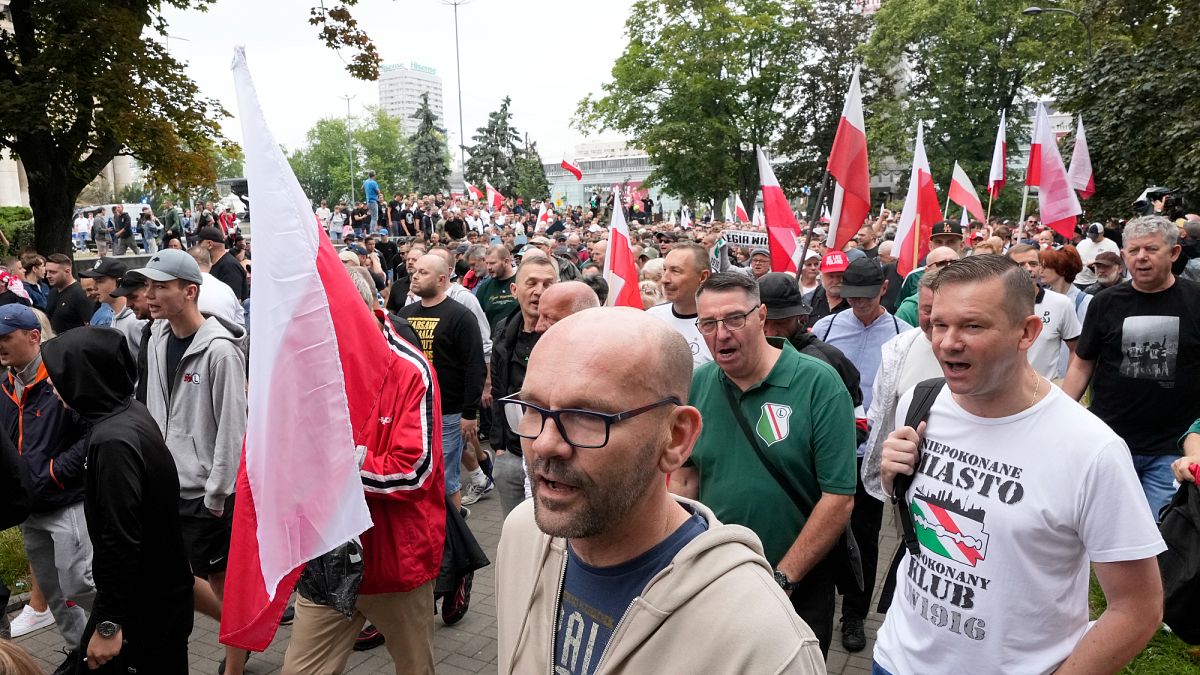
Anti-immigration demonstrations in more than 80 cities across Poland

ADVERTISEMENT
Anti-immigration protests organised by the far-right Confederation Libery and Independence party took place in more than 80 cities across Poland, including in Warsaw, Krakow, Poznan, Wroclaw, and Bialystok.
Demonstrators demanded the closure of the borders with Lithuania, Ukraine, Belarus and Slovakia.
“Enough of the years-long policy of ‘let everyone in, and who they are will be determined later’,” Krzysztof Bosak, one of Confederation party’s leaders, wrote on X.
“Polish women and men have the right to be concerned about the level of security in their own homeland,” he added.
In a speech at the start of the march, Bosak demanded the resignation of Donald Tusk’s government, the closure of the borders with Lithuania, Ukraine, Belarus and Slovakia to curb illegal immigration, and the permission for soldiers to shoot at people who cross the border illegally.
“Without closing Poland to illegal immigration, without launching a deportation operation, without renouncing political correctness, without equipping the Border Guard and the forces responsible for controlling the legality of residence, and without controlling the labour market, security will gradually deteriorate,” he said, calling for a change in policy.
The protests come shortly after Poland introduced border controls with Germany and Lithuania, which came into effect on 7 July.
On the Polish-German border, controls are in place at 52 places and on the Polish-Lithuanian border at 13.
The issue of migration has been widely up for debate, and a contentious topic in Polish politics, particularly as the country has experienced a rise in immigration in recent years.
In the first round of the presidential elections held in May, candidates of the far-right performed well, with Slawomir Mentzen of the Confederation Libery and Independence party and Grzegorz Braun of Confederation of the Polish Crown party coming in third and fourth, respectively.
Many believe that both candidates’ successes were due to their hardline stance on migration.
Interior ministers agree on asylum rules
On Friday, Poland and five other EU countries, agreed a set of targets for tightening asylum rules. During the meeting hosted by Germany’s interior minister, German Chancellor Friedrich Merz admitted that he was “pleased that Poland is carrying out border controls.”
Last year, Poland saw an increase in asylum applications due to the recurring crisis on its eastern border with Belarus, which has been ongoing since 2021.
As a result, the Polish parliament passed a law temporarily suspending the right to apply for asylum for those who crossed the Belarusian border.
Both Polish and European leaders have long accused Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko of orchestrating the influx of migrants to destabilise the EU.
On Saturday morning, the Ministry of Interior and Administration published statistics on the number of approvals issued for special protection for foreigners on X.
“In 2024, we issued 40 per cent fewer approvals for special protection for foreigners than in 2021. This is the result of a better managed system, our operations at the border and more efficient procedures,” the post read.
“The government is pursuing a responsible and well-considered migration policy, taking care of the stability and security of citizens,” it added.
Counter demonstrations in many cities
Counter-manifestations against the Confederation marches were also held in Warsaw, Katowice, Olsztyn and other cities on Saturday.
Demonstrators carried banners with the slogans: “Accept the refugees, delete the fascists,” “Action Democracy” and “We defend the right to asylum.”
“Everyone, regardless of their skin colour and origin, should feel comfortable not only in Poland, but also in Europe,” Maria Książak of the International Humanitarian Initiative Foundation said during the demonstration.
-

 Iowa1 week ago
Iowa1 week ago8 ways Trump’s ‘Big, Beautiful Bill’ will affect Iowans, from rural hospitals to biofuels
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoConstitutional scholar uses Biden autopen to flip Dems’ ‘democracy’ script against them: ‘Scandal’
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDOJ rejects Ghislaine Maxwell’s appeal in SCOTUS response
-
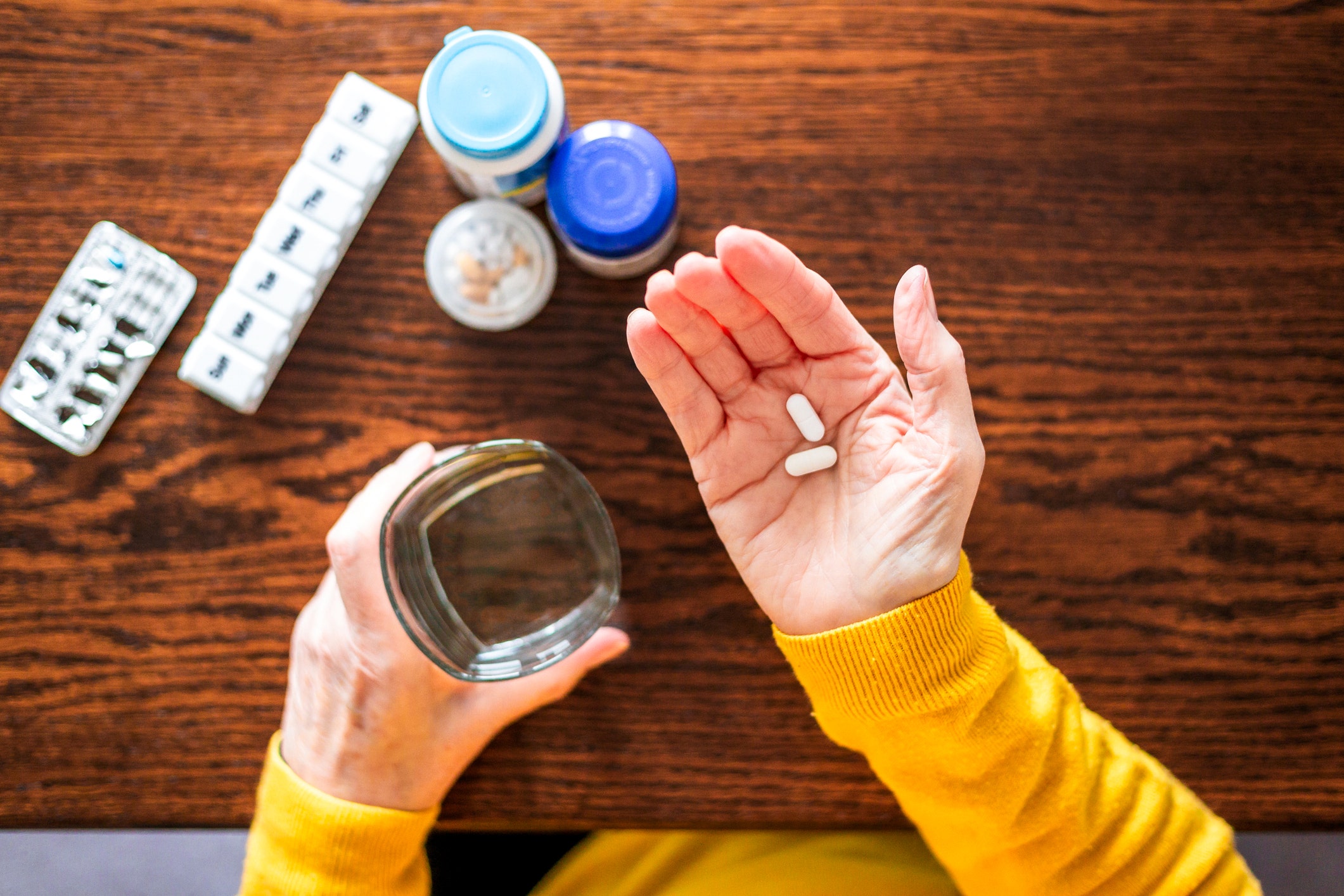
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoNew weekly injection for Parkinson's could replace daily pill for millions, study suggests
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoTest Your Knowledge of French Novels Made Into Musicals and Movies
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSCOTUS allows dismantling of Education Dept. And, Trump threatens Russia with tariffs
-
Business1 week ago
Musk says he will seek shareholder approval for Tesla investment in xAI
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoEx-MLB pitcher Dan Serafini found guilty of murdering father-in-law




















