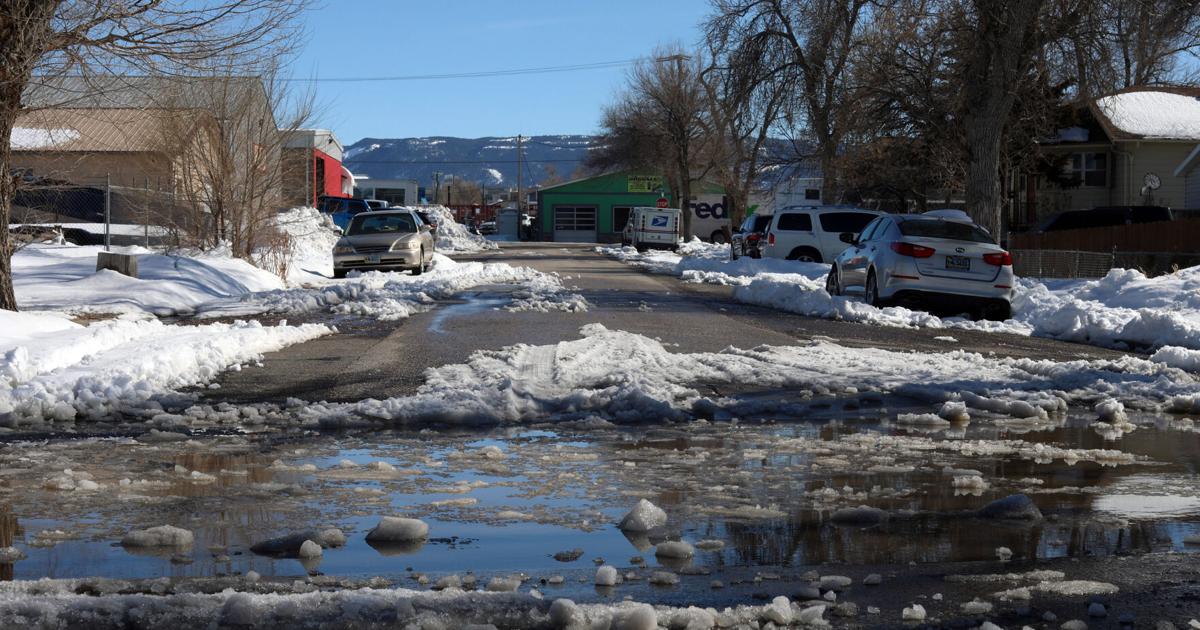
Western and central Wyoming might expertise flooding over the weekend and into early subsequent week, the Nationwide Climate Service warned Friday.
Temperatures in some elements of the state are anticipated to climb as excessive because the 70s, inflicting fast melting of the above-average snowpack that has collected this winter, mentioned Lance VandenBoogart, a meteorologist on the NWS workplace in Riverton. Casper might see highs within the mid-60s on Tuesday and Wednesday.
“The temperatures are usually not uncommon for this time of yr,” VandenBoogart mentioned. “What has been uncommon is the comparatively chilly winter that we’ve had, and the quantity of snow, particularly the low-elevation snow.”
In mountain basins and foothills, he mentioned, the persistent chilly has allowed snow ranges to succeed in double and even triple a typical winter’s — elevating flood threat for low-lying areas when it inevitably begins to soften. The record-breaking snowstorm that dumped practically three toes of snow over Casper this week made the state of affairs much more regarding.
Persons are additionally studying…
Statewide, snowpack ranged from 101% to 144% of the day by day 30-year median in all however one basin as of Friday, in accordance with the Wyoming State Local weather Workplace. The very best ranges are concentrated within the southwestern nook of the state.
This winter already ranks as Casper’s third-snowiest on file, with the 132.7 inches town has documented so far defeated solely by the winters of 1982–1983 and 1983–1984, when it acquired 151.6 and 143.1 inches, respectively. On Thursday, Casper Mountain’s snowpack measured 117% of the day by day median. And extra snow this yr continues to be potential, if unwelcome.
Individuals in areas that might flood within the coming days ought to take precautions to stop or decrease harm — particularly in the event that they’ve had issues up to now throughout massive spring soften years, VandenBoogart mentioned. Earlier flooding is likely one of the greatest indicators that the identical factor might occur once more.
“It’s laborious to maneuver one’s home for every week after which put it again the following week, so we’re sympathetic to the truth that there’s not at all times quite a bit you are able to do,” he mentioned. “However there are some easy steps.”
Clearing snow, ice and particles out of culverts and circulation paths will assist the water keep the place it’s imagined to. Shifting snow away from the foundations of homes and different buildings will assist to stop water from pooling there and seeping inside. (The NWS cautioned that snowmelt may cause basement flooding even outdoors of flood zones.)
Temperatures by the remainder of the spring will decide how lengthy — and to what extent — flooding will probably be a supply of concern for Wyoming. If it doesn’t actually begin to heat up for some time, the melt-off might be uneventful, VandenBoogart mentioned. Early warming or a giant rain occasion might complicate issues.
“Proper now, I believe the takeaway message could be that there’s extra snow than regular within the mountains,” he mentioned, “and that’s one issue that might lead in direction of extra main-stem river flooding later this spring.”
PHOTOS: Casper digs itself out after large blizzard
Snowstorm

Aaron Cawiezell and his canine Dixie clear a path Wednesday for his spouse to have the ability to go away their home so she will get to work as a nurse after a record-breaking snowstorm.
Snowstorm

Stan Campbell digs out his and a few of his fellow residents’ automobiles on Wednesday in downtown Casper. The blizzard that struck Monday and Tuesday left behind big piles of snow.
Snowstorm

Document-breaking snow blankets Heart Avenue on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in downtown Casper.
Snowstorm

Donna Mikuta clears the snow off her of from the recording-breaking snow storm on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Document-breaking snow blankets Heart Avenue on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in downtown Casper.
Snowstorm

Document-breaking snow blankets East Second Avenue on Wednesday in downtown Casper. Many companies remained closed as a result of troublesome of journey.
Snowstorm

Document-breaking snow blankets East Second Avenue on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in downtown Casper.
Snowstorm

Stan Campbell digs out his automobile and a few of his fellow residents automobiles to assist them out from underneath the recording-breaking snow pack on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Stan Campbell digs out his automobile and a few of his fellow residents automobiles to assist them out from underneath the recording-breaking snow pack on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Donna Mikuta clears the snow off her of from the recording-breaking snow storm on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Aaron Cawiezell and his canine Dixie clear a path for his spouse to have the ability to go away their home so she will get to work that night time as a nurse on the hospital after a record-breaking snow storm on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Aaron Cawiezell and his canine Dixie clear a path for his spouse to have the ability to go away their home so she will get to work that night time as a nurse on the hospital after a record-breaking snow storm on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Aaron Cawiezell and his canine Dixie clear a path for his spouse to have the ability to go away their home so she will get to work that night time as a nurse on the hospital after a record-breaking snow storm on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Snow blanket the streets of Casper, trapping many residents on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Aaron Cawiezell and his canine Dixie clear a path for his spouse to have the ability to go away their home so she will get to work that night time as a nurse on the hospital after a record-breaking snow storm on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Aaron Cawiezell and his canine Dixie clear a path for his spouse to have the ability to go away their home so she will get to work that night time as a nurse on the hospital after a record-breaking snow storm on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Snow blanket the streets of Casper, trapping many residents on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Snow blanket the streets of Casper, trapping many residents on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Snow blanket the streets of Casper, trapping many residents on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Snow blanket the streets of Casper, trapping many residents on Wednesday, April 5, 2023, in Casper.
Snowstorm

Snow blanket the streets of Casper, trapping many residents on Wednesday following a file snowstorm.
























/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)

/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)




/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg)