Colorado
Colorado crews planning mitigation of second underground coal mine fire near Marshall Fire’s origin

State mining safety crews are moving forward with plans to unearth a second active underground fire later this year in the area where the most destructive wildfire in Colorado history was ignited.
The Marshall Fire destroyed more than 1,000 homes on Dec. 30, 2021. It was pushed by 100 mph winds across open space and into the communities of Superior and Louisville. Two residents there were killed.
RELATED Marshall Fire investigation reveals most destructive fire in Colorado history was composed of 2 fires (2023)
Authorities, after an 18-month investigation, determined there were two ignition points – the first a smoldering wood pile on private property, the second below power lines. The latter is a point of contention, with Xcel Energy disagreeing with investigators’ conclusions. The company is fighting litigation blaming its lines for at least partially causing the blaze.
RELATED Investigators: Burning remnants of underground coal mines are possible cause of Marshall Fire (2022)
The investigation did not rule out the possibility that coal burning below ground for decades contributed to the fire. Winds as strong as those experienced during the Marshall Fire could conceivably draw heat from the underground coal fires to the surface.
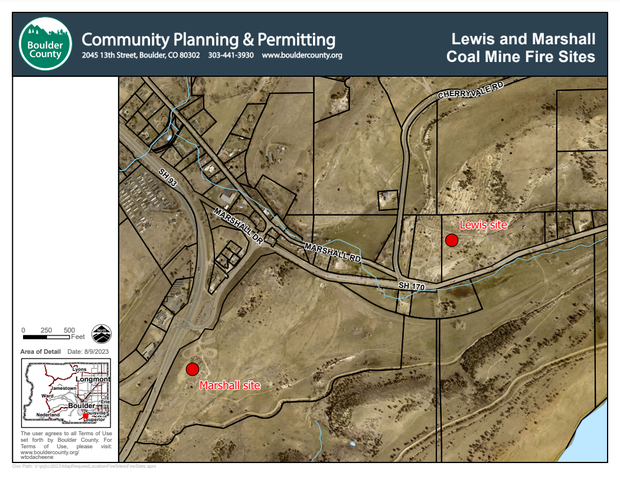
One such site contains the Lewis Mines that were abandoned and buried in 1946. A surface vent emitting heat measured at 120 degrees was discovered in 2018.
RELATED Disaster declaration issued for area in Boulder County to mitigate underground coal mine fire (2023)
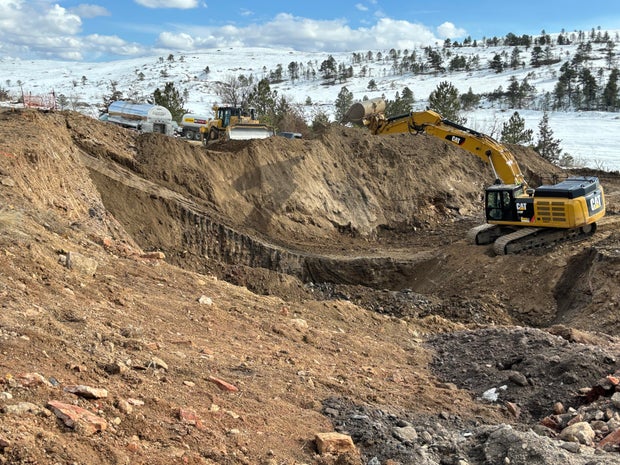
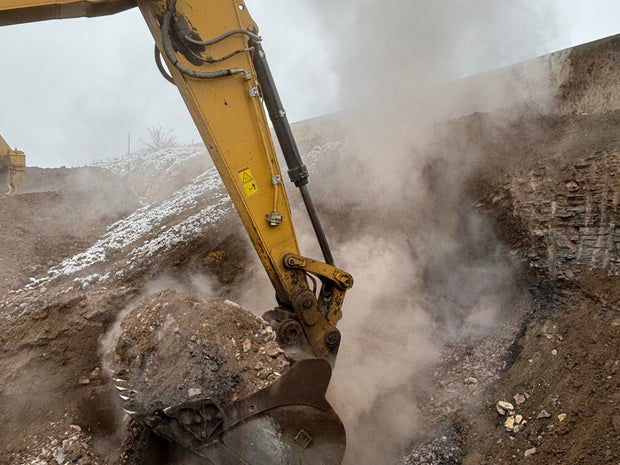
Crews from Colorado’s Division of Reclamation, Mining and Safety started an overhaul of the Lewis Mine site in January. Excavators carefully extracted land adjacent to the Davidson Ditch, alternately digging and filling 10-foot “fingers” of steaming ground to keep the concrete irrigation channel from collapsing.
Crews dug 30 feet deep and encountered temperatures as high as 600 degrees. Where readings were greater than 90 degrees, crews mixed the heated soil with cool soil and rock until temperatures fell below that mark.
The project wrapped up in early April ahead of schedule.
Crews are now planning to turn ground 2,000 feet away above the Marshall Mines, a DRMS spokesman confirmed. The department is currently in the permitting process with Boulder County since the project, slated to start later this summer or fall, will affect access to county open space at the Marshall Mesa trailhead.
It will be the second time mitigation efforts have occurred at the Marshall Mines. A vent from the mines there was blamed for starting a small brush fire in 2005. Three years later, 275 tons of rock was dumped on the site, raising its surface 18 inches.
The recent Lewis Mines mitigation cost $316,002, according to the department’s spokesman, Chris Arend. The Marshall mitigation will be done now that additional federal money has been received by the department to address coal mine fires throughout the state.
In a 2018 DRMS study, there are 1,736 know abandoned coal mines in Colorado. A contractor hired by the state to examine them found 38 were actively burning or were dormant and extinguished after previously burning.

Colorado
Avalanche discipline, power play falters, Central Division lead shrinks in 5-2 loss to Wild

The Colorado Avalanche had a chance Thursday night to regain some real separation between them and the Minnesota Wild.
It didn’t happen, and special teams were again an issue.
Minnesota’s Joel Eriksson Ek scored a pair of power-play goals, while the Avalanche took too many penalties and did not convert its chances with the extra man in a 5-2 loss at Ball Arena. The Wild scored on two of six power plays, both in the second period, then added a shorthanded goal into an empty net for good measure.
“We took six (penalties). Six is too many, especially against a power play like theirs,” Avs coach Jared Bednar said. “We had a slow start to the second and then just kind of started getting going, then took a bunch of penalties and kind of took the momentum away and swung it back in their favor again.”
Mackenzie Blackwood was excellent early in this contest and stopped 31 of 34 shots for the Avs in his first start since the Olympic break. Colorado, which went 0-for-3 on the power play, has not scored an extra-man goal in back-to-back games since Dec. 31 and Jan. 3. The Avs are 2-for-31 with the man advantage since Jan. 16, and at 15.1% are last in the NHL.
The Wild are now just five points behind the Avs in the Central Division, though Colorado has two games in hand. Filip Gustavsson made 44 saves for the visitors.
“I think we crated enough chances to win the hockey game,” Bednar said. “We give up the (second power-play goal) and that’s the difference in the hockey game for me. We had a chance (on the power play) … we score and it’s a tie game. We haven’t had an easy time capitalizing on some of our chances that we created in the last month.
“I’d like to see that turn around a little bit.”
Minnesota took advantage of three penalties on Colorado in a span of 53 seconds to take the lead with 2:23 left in the second period. Captain Gabe Landeskog was sent to the box for elbowing Eriksson Ek away from the play at 14:15 and Valeri Nichushkin was called for cross-checking at 15:04.
That gave the Wild a 5-on-3, but it went from bad to worse in a hurry for the home side. Brock Nelson won the 3-on-5 in his own end, but Brent Burns’ backhanded attempt to clear the puck out of the zone went into the stands for a delay of game.
Minnesota had a 5-on-3 for 1:56, which Colorado successfully killed off, but because Burns’ two minutes didn’t start until Landeskog’s penalty ended, there was more 5-on-4 time and Eriksson Ek scored his second of the night. The Swedish Olympian was trying to send a cross-crease pass to Kirill Kaprizov, but it hit the inside of Blackwood’s right leg and pinballed across the goal line.
Because of the extended penalty time, both Eriksson Ek and Boldy officially logged a shift of more than four minutes, leading to that goal.
“I’m not a big fan of the penalties we took, necessarily,” Landeskog said. “Obviously, mine is a penalty. Val, I felt like he was protecting himself and Burns, that’s a penalty. There’s nothing to argue about there. But yeah, that tilts the ice for sure and just gives them unnecessary momentum.
“So yeah, undisciplined and we’ve got to be better there for sure.”
Eriksson Ek put Minnesota in front at 7:48 of the second period. Cale Makar was called for slashing when his one-handed swipe while Yakov Trenin was attempting to shoot from the left wing. Trenin’s stick broke, so Makar went to the box.
Blackwood made the initial save on Matt Boldy’s shot from the high slot, but Eriksson Ek was there near the left post to clean up the rebound.
Martin Necas continued his hot run with a goal to even the score at 13:30 of the middle frame. Nathan MacKinnon picked up the puck in his own zone and carried it into the offensive end. He left a drop pass for Necas near the right point and then played fullback, driving Wild defenseman Daemon Hunt back to give Necas space and then providing a screen on a lethal wrist shot from his Czech linemate.
That was Necas’ 24th goal of the season. He added a second goal in the final minute after the Wild had built a three-goal advantage to give him 25 on the season.
It’s also three in two games since the Olympic break. Necas had three goals and eight points in five games for Czechia at the Olympics in Milan, equaling his country’s record for points at the event.
MacKinnon missed Colorado’s first game back on Wednesday because of maintenance. He actually slipped to third in the NHL scoring race as of Thursday morning, in part because Tampa Bay’s Nikita Kucherov has now has 53 points in his past 23 games to track down MacKinnon and Edmonton’s Connor McDavid to make it a three-man race for the Art Ross Trophy.
McDavid (five times) and Kucherov (three) have combined to win the Art Ross in eight of the past nine years. MacKinnon has never won it, but has finished second each of the past two seasons.
Minnesota scored a second goal off a Colorado player to make it a 3-1 game and then added two empty-net tallies around Necas’ second goal to seal the Wild’s sixth win in a row.
Want more Avalanche news? Sign up for the Avalanche Insider to get all our NHL analysis.
Colorado
Firefighters stop spread of wildfire in Colorado’s Golden Gate Canyon

Late Thursday morning, a house fire spreading into the nearby woods in Colorado’s Golden Gate Canyon prompted officials to issue a pre-evacuation order to nearby residents. Firefighters have since brought the blaze under control.
According to the Jefferson County Sheriff’s Office, a house fire broke out around 11:30 a.m. in the 10600 block of Ralston Creek Road in Golden Gate Canyon, located around 25 miles west of Denver. The fire then began to spread into the nearby trees and grass.
Multiple fire units quickly responded to the scene, and the JCSO issued a pre-evacuation notice to all residents within a three-mile radius, warning them to be prepared to leave at a moment’s notice.
At 12:34 p.m., the sheriff’s office announced that the fire is no longer spreading and the burn area has been contained to less than an acre. A photo shared by JCSO shows a structure nearly completely destroyed by the fire.
Pre-evacuation orders were lifted around 1 p.m.
Colorado
Toyota Game Recap: 2/25/2026 | Colorado Avalanche

ColoradoAvalanche.com is the official Web site of the Colorado Avalanche. Colorado Avalanche and ColoradoAvalanche.com are trademarks of Colorado Avalanche, LLC. NHL, the NHL Shield, the word mark and image of the Stanley Cup and NHL Conference logos are registered trademarks of the National Hockey League. All NHL logos and marks and NHL team logos and marks as well as all other proprietary materials depicted herein are the property of the NHL and the respective NHL teams and may not be reproduced without the prior written consent of NHL Enterprises, L.P. Copyright © 1999-2025 Colorado Avalanche Hockey Team, Inc. and the National Hockey League. All Rights Reserved. NHL Stadium Series name and logo are trademarks of the National Hockey League.
-

 World2 days ago
World2 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts2 days ago
Massachusetts2 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Montana1 week ago
Montana1 week ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Oklahoma1 week ago
Oklahoma1 week agoWildfires rage in Oklahoma as thousands urged to evacuate a small city
-

 Louisiana5 days ago
Louisiana5 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Denver, CO2 days ago
Denver, CO2 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making