California
Most intense atmospheric river storm yet slams California with flooding, high winds
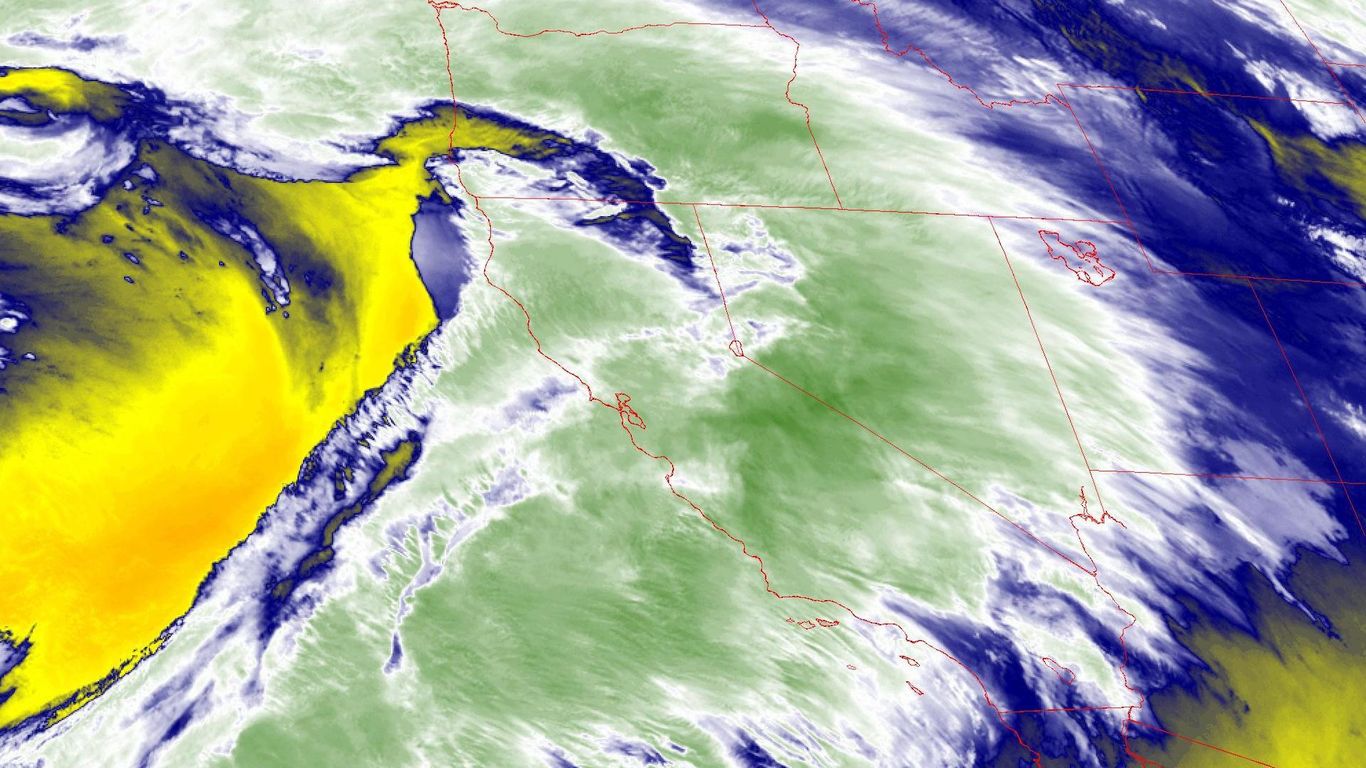
Satellite tv for pc picture exhibiting a robust atmospheric river hitting California on Jan.9. Picture: NOAA.
Probably the most highly effective in a “relentless parade” of atmospheric rivers is bearing down on California right this moment by Wednesday. It brings with it the chance of widespread flash flooding, river flooding, mudslides and staggeringly excessive mountain snowfall totals.
Why it issues: The whiplash from a bone dry to flood-prone state is an indication of how human-caused local weather change is accentuating California’s naturally fickle precipitation patterns.
- Whereas flooding, energy outages and landslides threaten Californians within the near-term, these storms are boosting reservoir ranges, severely depleted by the Southwest’s megadrought.
State of play: California Gov. Gavin Newsom requested President Biden on Sunday to make an emergency declaration in response to a sequence of lethal storms.
- An estimated 125,000 clients have been nonetheless with out energy on Monday morning, because the Workplace of Emergency Administration issued evacuation warnings for a number of areas in Santa Barbara County “as a result of potential flooding and particles flows.”
Risk stage: With a number of extra atmospheric river storms lined up throughout the Pacific, these storms have the potential to trigger lethal mudslides and particles flows in areas the place the bottom has been weakened by latest wildfires.
- The are additionally priming the slopes of the Sierra Nevada Mountains for avalanches, as snow ranges shift with every climate system, and as much as 5 to 7 inches of snow pile up per hour.
- Whole snowfall by Tuesday is predicted to be upwards of 6 toes for elevations above 7,000 toes, per the NWS. Some locations have already seen 100 inches pile up in simply the previous two weeks.
- The NWS’ Climate Prediction Heart notes there’s a better than 50% likelihood that flash flood thresholds shall be exceeded throughout an enormous expanse of the state, from Sacramento to the hills of Southern California.
Between the strains: The flood menace on Tuesday appears to be centered extra in Southern California, because the firehose of moisture concentrates there, with as much as a foot of rain falling within the hills of LA, Santa Barbara and Ventura Counties.
- Downtown LA might see as much as 5 inches of rain by Wednesday morning.
What they’re saying: “The timing, period and time between every of doubtless 4 extra storms shall be key to how flood impacts amplify, and drought situations evolve,” Michael Anderson, California state climatologist with the California Division of Water Sources, informed Axios through electronic mail.
- “Whereas every particular person storm is probably not unusually giant, the impacts shall be bigger because of the variety of storms and the way rapidly they arrive,” he mentioned.
- Anderson mentioned there’s sufficient reservoir capability within the Sacramento River system to soak up the precipitation, however streams and creeks will rise, and there shall be larger water alongside the Sacramento.
- “Forecasts for incoming storms present elevated impacts to the San Joaquin Valley and Monterey County,” Anderson mentioned, noting that the state flood operations middle is carefully monitoring the state of affairs.
Context: The hydrological whiplash from the depths of its worst long-term drought in additional than a millennium to flooding demonstrates California’s capricious historical past of precipitation extremes.
- It is also in keeping with what research have been warning about for years — human-caused local weather change is amplifying the results of those extremes, making the dry years drier, and the moist durations wetter.
- It’s also making the swings wider.
- On the similar time, the portion of California’s annual precipitation that comes from atmospheric rivers is predicted to extend because the local weather warms, based on Julie Kalansky of Scripps’ Heart for Western Climate and Water Extremes.
- “Atmospheric rivers are going to turn out to be extra extra necessary when it comes to our water provide, or the precipitation all through California, and the opposite sorts of storms are going to lower when it comes to the quantity of precipitation that they contribute,” Kalansky informed Axios in an interview.
What’s subsequent: The NWS is terming this a “barrage” and “relentless parade” of storms streaming in from the Pacific for a cause: no finish is in sight, at the least not by the top of the month.
Rebecca Falconer contributed reporting.

California
California wildfires live updates: Firefighters battle to contain blazes while thousands wait to return home
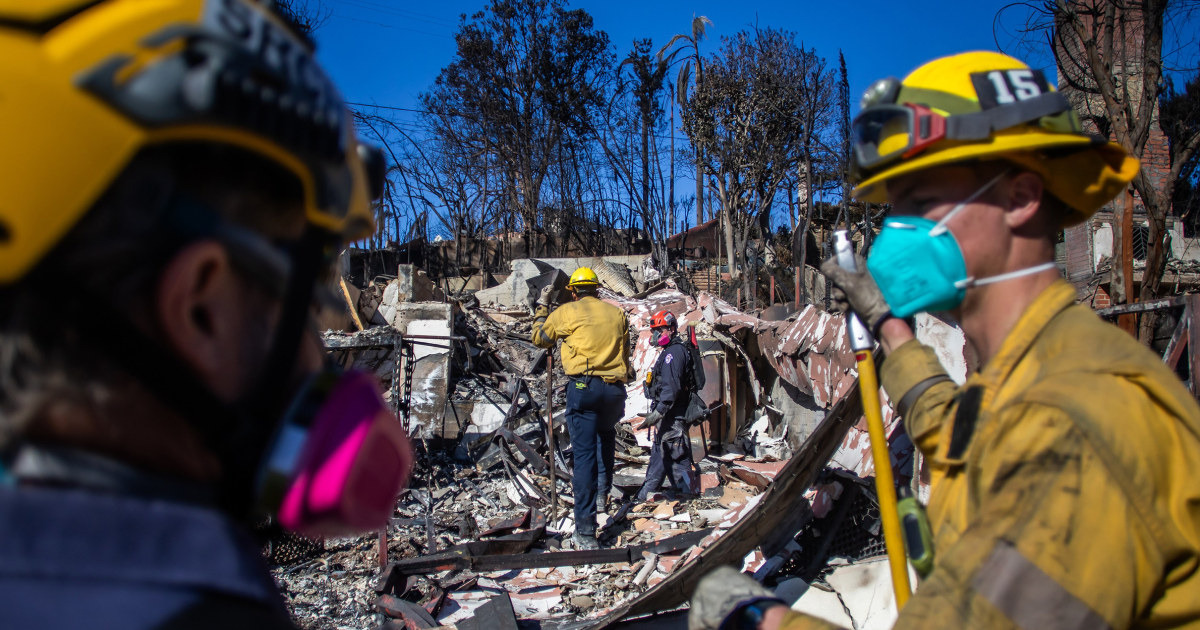

As winds die down in Southern California, firefighters have been able to get some of the most devastating wildfires under control. But as residents are allowed to return to the areas, the challenges of recovery are becoming painfully clear. Former FEMA Administrator Craig Fugate joins Stephanie Ruhle to discuss.
California
Handful of dirt bikes and ATV join pair of riders during LA County pursuit

A handful of dirt bikes and an ATV joined a pair of riders being chased by the California Highway Patrol Thursday afternoon.
The pursuit started in East Los Angeles when officers spotted two dirt bikers riding along the roads. It continued through a handful of freeways as officers on the ground dropped back to allow a police helicopter to track them.
The original riders continued to weave through traffic until more dirt bikers and a few ATVs joined them on their drive around LA County.
California
Endangered plant may have made California wildfires worse

A move to protect a federally endangered plant by halting the state construction of new utility lines is being highlighted in a newspaper report as a potential factor in California’s Palisades fire.
Downed utility lines in the area are being investigated for fuelling, and potentially even causing, the immense Palisades fire, says The New York Times.
However, the California Coastal Commission, who intervened in the utility line construction, have said that they did give out new permits for the utility pole project and “are very supportive of wildfire resiliency work.”
Why It Matters
The cause of the Pacific Palisades fire is under investigation by the Bureau for Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF), and if government negligence was found to play a part, it would further fuel existing frustration with Mayor Bass, and Governor Newsom expressed by some California residents.
LA is also facing a climate-change-shaped future of increased droughts which will further impact the scope of wildfires, and needs to figure out how to balance everyday conservation with fire protection for the entire region.
Left: Michael Charters, Right: Carolyn Kaster/Left: US Forest Service, Right: Associated Press
What To Know
In 2020, the California Coastal Commission fined the Los Angeles Department of Public Works (LADWP) $1.9 million over their utility pole project in the Pacific Palisades, as the project had bulldozed almost 200 federally protected Braunton’s milkvetch (Astragalus brauntonii) plants.
According to the Sierra Club, there are only 3,000 of these “purple-petalled perennial wildflower” plants left in the mountains, and they are listed under the Endangered Species Act.
The utility pole project policed by the Coastal Commission in 2020 was a public works project designed to install stronger, metal, utility poles in the Palisades, as some of the utility poles in the area were built almost 100 years ago. Downed utility lines have caused blazes in the past, and reporters from The New York Times have now found bits of power line debris in the Palisade hills.
The Coastal Commission told the LADWP in 2020 that they needed to seek a permit from the Coastal Commission to restart the development, as well as undo their roadwork and revegetate the area. While the LADWP paid the fine, it does not appear they ever restarted the utility poles project.
The LADWP has been contacted via phone call and voicemail for comment.
Sarah Christie, a spokesperson for the Coastal Commission, spoke to Newsweek about this incident saying: “In 2019, a hiker reported unpermitted bulldozing through an area of endangered plants and hiking trails in Topanga State Park.
“In addition to damaging native plants and public trails, this type of grading also can also encourage highly flammable, non-native grasses to flourish. But the damage was repaired the following year, and the Commission approved a permit for the Utility to move forward with their work to replace the poles.
“We are very supportive of wildfire resiliency work and will continue to promote efforts to harden homes and public infrastructure and create defensible space.”
What People Are Saying
Eric Edmunds, Chair of the Santa Monica Mountains Task Force in a 2020 letter: “Our task force has been involved with far too many cases of utility companies not using good judgment and failing to comply with the laws, policies, and ordinances that are in place to protect and preserve our finite natural resources.”
The LADWP in 2020: “[This project is] essential in regards to our wildfire mitigation plan.”
What Happens Next
The cause of the Palisades fire is still under investigation by the ATF, who have said it will take time to figure out the root cause of the blaze.
In the meantime, Angelenos are still combating active blazes, with the Eaton fire now at 55 percent containment, and the Palisades fire at 22 percent containment.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science6 days ago
Science6 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLas Vegas police release ChatGPT logs from the suspect in the Cybertruck explosion
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPhotos: Pacific Palisades Wildfire Engulfs Homes in an L.A. Neighborhood
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoFour Fraternity Members Charged After a Pledge Is Set on Fire
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoMeta Drops Rules Protecting LGBTQ Community as Part of Content Moderation Overhaul
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump trolls Canada again, shares map with country as part of US: 'Oh Canada!'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg) Technology5 days ago
Technology5 days agoAmazon Prime will shut down its clothing try-on program

















