Alaska
Study shows ancient Alaskans were freshwater fishers

Scientists work at the Upward Sun River site in Interior Alaska. (Photo by Ben Potter)
Fairbanks, Alaska (UAF) – A scientific team led by University of Alaska Fairbanks researchers has discovered the earliest-known evidence of freshwater fishing by ancient people in the Americas.
The research offers a glimpse at how early humans used a changing landscape and could offer insight for modern people facing similar changes.
“We are looking at humans as ecologists do, as biologists do,” said Ben Potter, a UAF anthropology professor and co-lead author of the paper. “Even very early on, they are able to adapt to changing conditions.”
The study, published recently in the journal Science Advances, shows that people living between 13,000 and 11,500 years ago in what is now Interior Alaska relied on freshwater fish like burbot, whitefish, and pike for food.
The study builds on earlier UAF findings that documented salmon fishing by the same population of ancient humans.
“That discovery was really surprising because it was far from the ocean, in an area near the edge of salmon habitat,” said Potter. “That started us thinking: This could be a whole other angle on human ecology beyond large mammal hunting.”
This new study began with a comprehensive review of all Interior Alaska archaeological sites 7,000 years old and older.
The scientists found fish bones at seven sites.
The team of archaeologists, anthropologists, and fisheries biologists analyzed the bones to determine their age and species.
The bones were found inside homes and hearths and tended to be associated with base camps, rather than short-term hunting camps.
They also were far from lakes and streams, so it’s unlikely that predators moved them.
The absence of fishhooks or spears at the sites suggests that the early Alaskans likely used nets and perhaps weirs to harvest the fish.
“This is a compelling, evidence-based case for freshwater fishing at the end of the last Ice Age,” Potter said.
Recent large-scale excavations of residential base camps in the Tanana River basin have offered scientists a new opportunity to study early human populations in the region, he said. “This is a first in the Americas because, up until the last few decades, we haven’t had fish remains clearly associated with human activities in these very early sites.”
Scientists have documented humans in Alaska as far back as about 14,000 years ago.
The heaviest use of freshwater fish by those early Alaskans appears to be between 13,000 and 11,500 years ago during the Younger Dryas, a period with cold and dry conditions in the midst of an overall warming trend at the end of the last ice age.
Until the beginning of the Younger Dryas, people relied more on waterfowl to augment large game like bison and elk.
When temperatures started dropping around 13,000 years ago, that changed.
Bones found at archaeological sites indicate they began to exploit multiple species of freshwater fish.
“While we don’t know why the use of waterfowl diminished, we know that the climate was changing,” Potter said. “One of the ways the people were able to adapt is to incorporate these new species and new technologies. Burbot, in particular, can be caught in late winter and early spring, when food resources were most scarce.”
The solid tie to modern subsistence activities is also compelling, he said.
“There are millennia and millennia of fish use that continues into the modern day. Indigenous people’s ancestors thousands of years ago were using the same resources. That has meaning to people today’,’ he said.
Other authors of the paper include co-lead author Carrin Halffman, and co-authors Holly McKinney, Josh Reuther, and Charles Holmes, all of the UAF Department of Anthropology; Bruce Finney of Idaho State University; François Lanoë of the University of Arizona; J. Andrés López of the UAF College of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences; Erica Palmer, Marie Capps, and Brian Kemp, all of the Laboratories of Molecular Anthropology and Microbiome Research at the University of Oklahoma. Reuther, Lanoë, and Lopez are also affiliated with the University of Alaska Museum of the North.

Burbot vertebrae from the Mead site are lined up. (Photo by Ben Potter)

Alaska
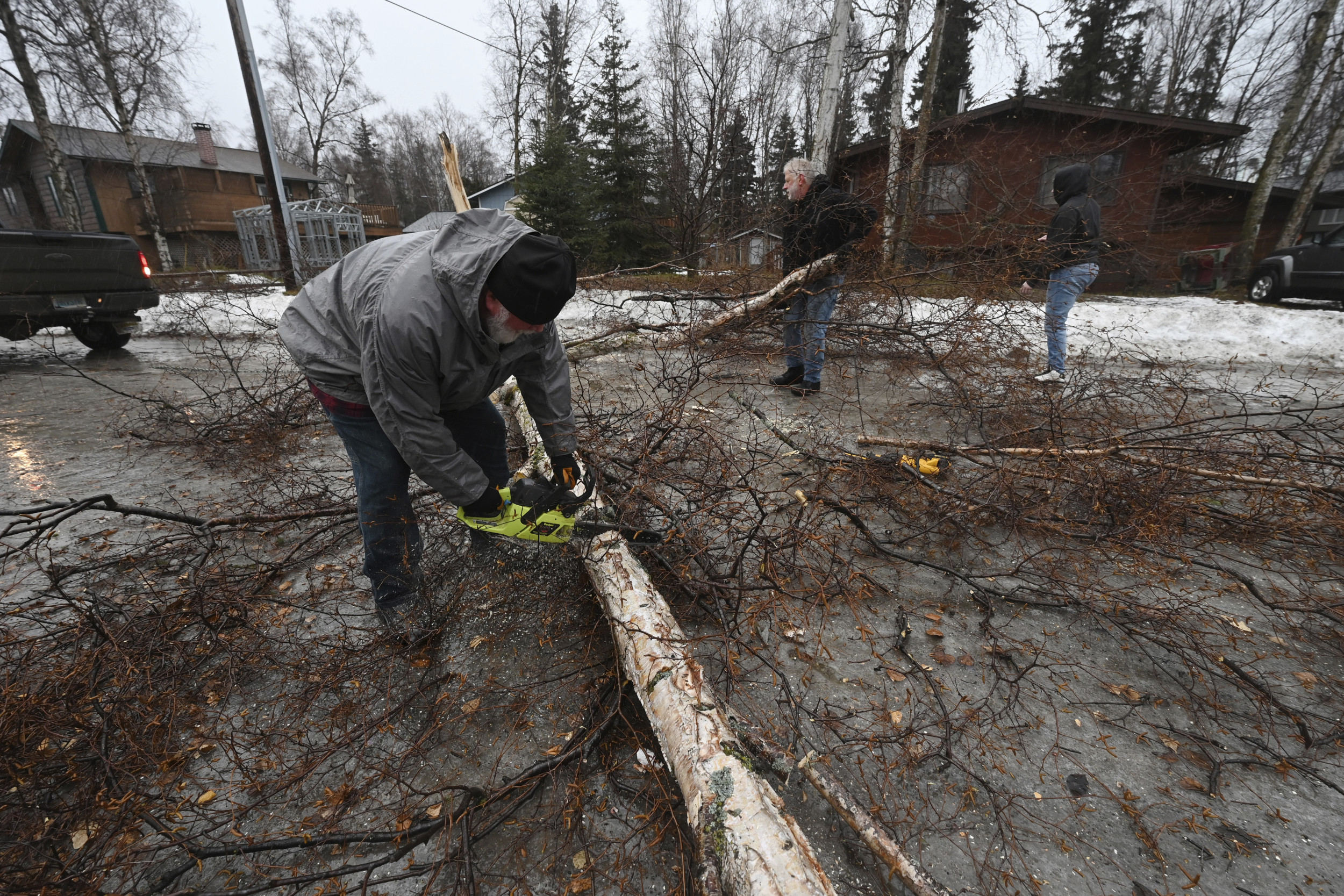
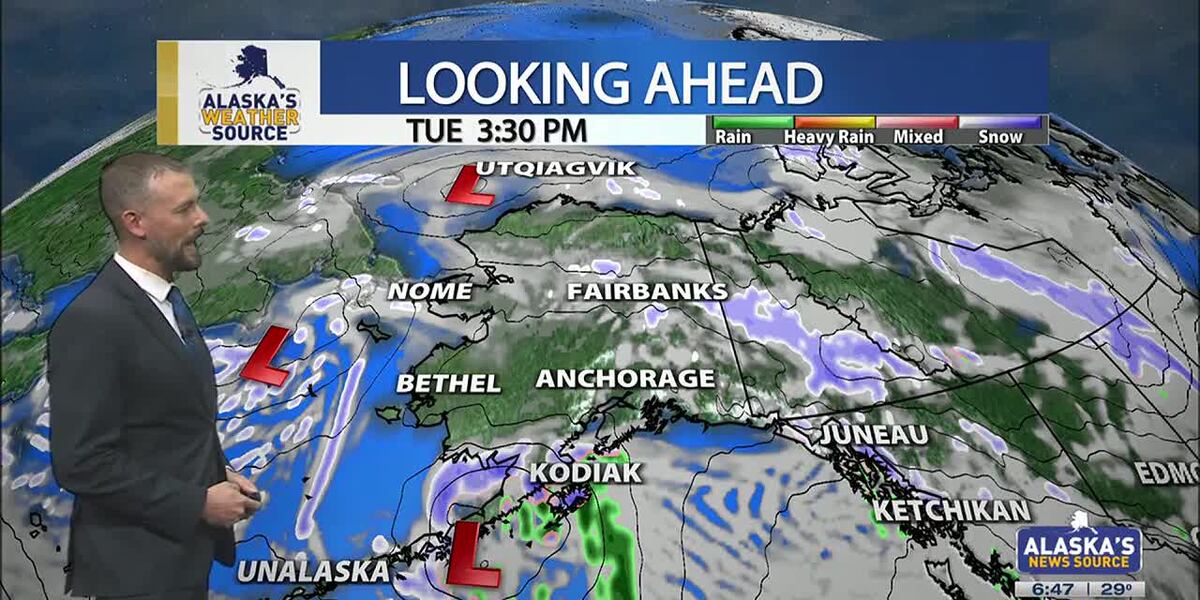
Western Alaska storm and southerly flow drives warmth back into the state

ANCHORAGE, Alaska (KTUU) – Gusty winds and heavy snow has begun to spread into Western and Southwest Alaska, with a surge of warmer air. Temperatures in Southwest Alaska is already 10 to 35 degrees warmer than yesterday morning. This warmth will spread across the rest of the state through the weekend, with some of the most pronounced warmth along the Slope. We’ll see many areas this weekend into next week remaining well-above average.
SOUTHCENTRAL:
Temperatures are slowly warming across Southcentral, with many areas seeing cloud coverage increasing. While we could see some peeks of sunshine today, most locations will see mostly cloudy conditions. While we can’t rule out light flurries for inland locations, most of the precipitation today will occur near the coast. Snow looks to be the primary precipitation type, although later this evening a transition to rain or wintry mix will occur. This comes as temperatures quickly warm across Southcentral.
We’ll see highs today in the upper 20s and lower 30s for inland areas, while coastal regions warm into the 30s and 40s. The southerly flow aloft will remain with us for several days, pumping in the warmth and moisture. As a result, Kodiak could see over an inch of rain today, with gusty winds.
While most of the precipitation this weekend remains near the coast, inland areas will see the best chance for wintry mix Sunday into Monday. Little to no accumulation is expected.
The key takeaways for this weekend, is snow transitioning to rain, with some gusty winds likely for parts of Southcentral this weekend.
SOUTHEAST:
Another fairly quiet day is expected across Southeast today, outside of some light snow near Yakutat. We’ll see a mix of sun and clouds with temperatures remaining on the cooler side. Parts of the Northern Panhandle may stay in the upper 20s today. The stretch of quiet weather will stay with us through the first half of Saturday, followed by an increase in precipitation and winds. This upcoming system may bring some heavy snowfall to Southeast, so be prepared for that potential this weekend. Temperatures warm into next week, back into the upper 30s and lower 40s for many areas.
INTERIOR:
While temperatures this morning have bottomed out as low as -30 near Fort Yukon, temperatures will warm into the weekend. A wind advisory for the Alaska Range goes into effect at 9 Friday morning, where winds up to 60 mph will warm the Interior. Temperatures today for many locations will warm into the single digits, with some of the greatest warming arriving Saturday through next week. It’s likely we’ll spend most of next week with temperatures in the 20s and 30s, with the warmest locations near the Alaska Range. While we will largely stay dry, there is a chance for some light snow arriving Sunday night into Monday.
SLOPE/WESTERN ALASKA:
Temperatures will remain slightly above average for parts of the Slope today, with warming winds to build into the Slope this weekend. This comes as our area of low pressure in the Bering Sea continues to move farther north. Be prepared for gusty easterly winds along the Slope, leading to blowing snow and reduced visibility. We’ll see temperatures quickly warm well above average, with highs climbing into the 20s and 30s along the Slope into next week. While some snow is possible through the weekend, the heaviest activity will occur for the Brooks Range. We’ll see the potential for 4 to 12 inches of snowfall, with the highest amounts occurring along the southern slopes of the Brooks Range near Kobuk Valley. Winds could gusts as high as 45 mph, leading to greatly reduced visibility.
Heavy snow is impacting Western and Southwest Alaska this morning, with winds gusting up to 50 mph. Numerous winter weather alerts, as well as a coastal flood advisory is in effect. The heaviest snow will fall for the Seward Peninsula and east of Norton Sound, where up to a foot or more of snow is to be expected. The heaviest amounts will fall today, with the activity set to lighten up through Sunday. In addition to the snow, gusty winds will lead to areas of blowing snow. Visibility could be reduced down to less than half a mile at times. As southerly flow continues to pump in warmth, we’ll see a transition from snow to rain later today into Saturday for parts of Southwest Alaska.
ALEUTIANS:
Gusty winds and heavy rain will fall through the Aleutians today, where up to .75″ of rain is possible. As the area of low pressure moves north, we’ll see a new low form just south of the Eastern Aleutians. This will lead to additional rain and winds into the weekend. Winds could gusts upwards of 50 mph through the Eastern Aleutians and through the Alaska Peninsula. With ridging to our east, more rain and winds remain with us into early next week. There is the potential that the Pribilof Islands see a return to snow Sunday, as colder air moves into the Bering Sea.
OUTLOOK AHEAD:
Well above average warmth will stay with us as we close out January. While one more short-lived cold snap is possible, we may have to wait until February before we tap into warmer conditions. Temperatures through the close of January will keep average monthly temperatures 5 to 12 degrees above average for much of the state. The overall trend still favors a wetter pattern, although with warmer weather the southern parts of the state will favor more rain or a mixed bag of precipitation.
Have a wonderful and safe holiday weekend.
See a spelling or grammar error? Report it to web@ktuu.com
Copyright 2025 KTUU. All rights reserved.
Alaska
Alaska governor, ally of Trump, will keep flags at full-staff for Inauguration Day • Alaska Beacon
Alaska will join several other Republican-led states by keeping flags at full-staff on Inauguration Day despite the national period of mourning following President Jimmy Carter’s death last month.
Gov. Mike Dunleavy announced his decision, which breaks prior precedent, in a statement on Thursday. It applies only to flags on state property. Flags on federal property are expected to remain at half-staff.
Flags on state property will be returned to half-staff after Inauguration Day for the remainder of the mourning period.
The governors of Indiana, Idaho, Iowa, Texas, Florida, Tennessee, Oklahoma, North Dakota, Nebraska, Montana and Alabama, among others, have announced similar moves.
U.S. Speaker of the House Mike Johnson, a Republican from Louisiana, said on Tuesday that flags at the U.S. Capitol would remain at full-staff on Inauguration Day.
Their actions follow a statement from President-elect Donald Trump, who said in a Jan. 3 social media post that Democrats would be “giddy” to have flags lowered during his inauguration, adding, “Nobody wants to see this, and no American can be happy about it. Let’s see how it plays out.”
Dunleavy is seen as a friend of the incoming president and has met with him multiple times over the past year. Dunleavy and 21 other Republican governors visited Trump last week in Florida at an event that Trump described as “a love fest.”
Since 1954, flags have been lowered to half-staff during a federally prescribed 30-day mourning period following presidential deaths. In 1973, the second inauguration of President Richard Nixon took place during the mourning period that followed the death of President Harry Truman.
Then-Gov. Bill Egan made no exceptions for Alaska, contemporary news accounts show, and no exception was made for Nixon’s inauguration in Washington, D.C., either.
A spokesperson for Dunleavy’s office said the new precedent is designed to be a balance between honoring the ongoing mourning period for former President Jimmy Carter and recognizing the importance of the peaceful transition of power during the presidential inauguration.
“Temporarily raising the flags to full-staff for the inauguration underscores the significance of this democratic tradition, while returning them to half-staff afterward ensures continued respect for President Carter’s legacy,” the spokesperson said.
GET THE MORNING HEADLINES.
Alaska
Federal disaster declaration approved for Northwest Alaska flooding
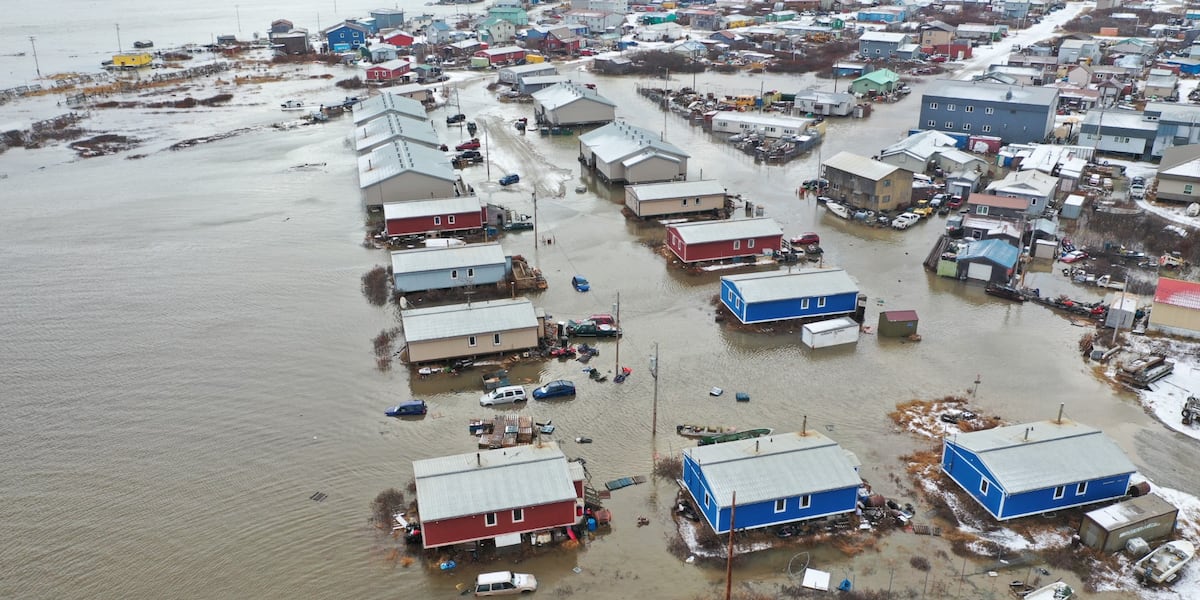

ANCHORAGE, Alaska (KTUU) – President Joe Biden announced the approval of federal disaster assistance on Thursday for recovery efforts in areas that sustained damage from flooding and storms in October 2024.
Those areas include the Bering Strait Regional Educational Attendance Area (REAA) and the Northwest Arctic Borough area where many structures were damaged by a severe storm from Oct. 20-23, 2024.

In a press release, FEMA announced that federal funding is available on a cost-sharing basis for emergency work to the state of Alaska, tribal and eligible local governments, and certain private nonprofit organizations.
The announcement comes just a few days after Biden released the major disaster declaration approval for the August Kwigillingok flooding.
See a spelling or grammar error? Report it to web@ktuu.com
Copyright 2025 KTUU. All rights reserved.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science6 days ago
Science6 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLas Vegas police release ChatGPT logs from the suspect in the Cybertruck explosion
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPhotos: Pacific Palisades Wildfire Engulfs Homes in an L.A. Neighborhood
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoFour Fraternity Members Charged After a Pledge Is Set on Fire
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoMeta Drops Rules Protecting LGBTQ Community as Part of Content Moderation Overhaul
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump trolls Canada again, shares map with country as part of US: 'Oh Canada!'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935558/acastro_STK103__01.jpg) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoAmazon Prime will shut down its clothing try-on program