Alaska
Hepatitis vaccines credited as life-saving for Alaska children may be upended

Western Alaska, where almost all the residents are Indigenous, used to have the world’s highest rate of childhood liver cancer caused by hepatitis B. After decades of screenings and vaccinations, that problem has been eliminated; since 1995, only one person under the age of 30 has been diagnosed with hepatitis-caused cancer.
Now the Trump administration is seeking to end one of the key tools credited with accomplishing that goal: hepatitis B vaccinations of newborns.
The federal Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on Friday voted to drop a longstanding recommendation for universal hepatitis vaccines for newborns. That is in accordance with the controversial views of U.S. Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a vaccine skeptic who fired all members of the previous committee and appointed like-minded members to replace them.
Current federal childhood hepatitis B vaccination guidelines recommend one dose of the vaccine at birth, followed by additional doses at intervals through 18 months. The recommendation for newborn vaccinations has been in place since 1991.
The advisory committee, part of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, determined that children under 2 months should not be vaccinated unless their mothers are infected or could be infected by hepatitis B.
Some vaccine critics in the administration, including Kennedy and President Donald Trump themselves, argue — contradicting medical experts and years of medical research — that hepatitis B vaccines for young children are unnecessary, claiming that it is spread primarily or exclusively through adult behavior like sex and sharing of needles for illegal drug use.
“Hepatitis B is sexually transmitted. There’s no reason to give a baby that’s almost just born hepatitis B. So I would say wait till the baby is 12 years old and formed and take hepatitis B,” Trump said at a Sept. 22 news conference.
Those claims are false, said Dr. Brian McMahon, medical and research director of the liver and hepatitis program at the Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium.
There is no credible evidence of a link between the vaccine and autism of any other health problem, McMahon said.
And sexual transmissions accounted for only a tiny percentage of Alaska’s hepatitis B cases, he said.
Aside from mother-to-infant transmissions, which occur during childbirth, hepatitis B was predominantly spread in Western Alaska through normal daily activities. That is because, unlike the HIV virus or other hepatitis viruses, the hepatitis B virus can live for seven days on surfaces in schools and homes, like tables and personal-grooming items.
“The virus can be found all over, on school luncheon tabletops, counters and homes,” McMahon said. “Kids have open cuts and scratches from bug bites or anything else, and then they shed millions of particles of the virus on environmental surfaces. And then another kid comes along with an open cut or scratch.”
Such risks are exacerbated in rural Alaska, he said, where homes can be crowded and people pursue traditional subsistence lifestyles with a lot of outdoor activities.
“They’re hunting, fishing, cutting up meat, et cetera, and mosquito bites are real prominent,” he said.

Nationally, only 12.6% of chronic hepatitis B cases recorded from 2013 to 2018 were attributable to sexual transmission, according to a 2023 CDC study. Transmissions of all forms of hepatitis, including hepatitis B, are possible through contact sports like football, rugby and hockey, researchers have found.
Alaska’s disease and vaccination success
Before the past decades of vaccination and screening, hepatitis B was so prevalent in Western Alaska that it was classified as endemic there. It was the only part of the United States with such a classification. In some villages, 20% to 30% of the residents were infected, McMahon said.
Geography and ancient migration patterns accounted for historically high rates of the disease in Western Alaska, as well as other Indigenous regions of the Arctic.
Various strains have been carried from Asia to Alaska over millennia, according to scientists. And the remoteness of Indigenous communities meant isolation from medical services, making early diagnosis difficult in the past, allowing infections to linger and be passed down through generations, according to scientists.
In Alaska, children infected with the virus early in life had a high likelihood of winding up with chronic infections that caused serious complications later, such as liver failure. The worst cases resulted in cancer, and even death.
For McMahon, now in his 80s, treating cancer-stricken children in the Yukon-Kuskokwim region, where he worked in the 1970s, was harrowing.
One of his patients was a 17-year-old high school valedictorian. A few months earlier, she started having abdominal pains, but she ignored them.
“She was really busy with school, and she’d gotten a full ride scholarship and was excited about going to the University of Alaska, representing her community,” McMahon said.
The pains turned out to be cancer, caused by a hepatitis B infection that she had not known she had. Too sick to be flown home, she died in the Bethel hospital.
“It was horrible,” McMahon said.
Another patient was an 11-year-old boy, also diagnosed after he complained of similar abdominal pain. McMahon visited him at home, where the boy was “in horrible pain” and yellow from jaundice.
“He was just crying. He said, ‘I know I’m going to die. Just help me with my pain,’” McMahon said.
“My wife was with me. She was a public health nurse. She was in tears. The community health aide practitioner was in tears. I was fighting my tears and pulling everything I could out of my bag to try to help this patient sedate. It was just something I’ll never forget. Never,” McMahon said.
He has relayed these and other experiences to the vaccine advisory committee in hopes of persuading members to keep the infant recommendations in place.
“I said, ‘Do you want to be responsible for children getting liver cancer because of this decision?’” McMahon said. “So I’m probably not very popular right now.”
Alaska was one of the first places in the world where the hepatitis B vaccine was used as soon as it became available in 1981.

The pilot vaccination project was at the insistence of Alaska Native organizations, along with the state government and the Alaska congressional delegation. Under that pilot program, according to newly published study by McMahon and other researchers from ANTHC and the CDC’s Arctic program, tribal health organizations and their partners screened 53,860 Alaska Native people for infection and gave vaccines to 43,618 Alaska Native people who tested negative, along with starting the universal newborn vaccinations.
Health officials have followed the outcomes since then, and the new study lists several achievements 40 years after universal newborn vaccination started.
Since 1995, according to the study, there have been no new symptomatic cases of hepatitis B among Alaska Natives under 20 anywhere in the state. Since 2000, no new cases of hepatitis-related liver cancer have been identified among Alaska Natives of any age in the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta, a region where prevalence was concentrated in the past, the study said. And follow-up surveillance has revealed that childhood hepatitis B vaccinations remain effective for at least 35 years, the study said.
Successes are also reflected in the trend of acute hepatitis, the form of infection that is short-lived and can be cleared from the body.
There have been no identified cases of acute hepatitis among Alaska Native children since 1992, according to Johns Hopkins University. The rate of acute hepatitis among Alaskans of all ages and ethnicities dropped from 12.1 cases per 100,000 people to 0.9 per 100,000 in the 2002-2015 period, according to the state Department of Health’s epidemiology section.
Alaska’s rate of chronic hepatitis B — the long-term and persistent infection that can lead to serious liver problems — remains higher than the national average. As of 2020, Alaska’s rate of chronic hepatitis B was 14.2 cases per 100,000 people, nearly triple the national rate of 5 cases per 100,000 people, according to a report by the state Department of Health’s epidemiology section.
McMahon said that is partly because of the legacy of infections in the older Native population, people whose childhood predated widespread vaccination, and prevalence among foreign-born residents who come from countries without widespread vaccination.
Debate over hepatitis B risks
This year, vaccine skeptics who are members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, however, along with people who are advising the committee, have argued that the risks of hepatitis B among children are too low to justify universal infant vaccination.
One of the officials making that argument at Thursday’s committee meeting was Dr. Cynthia Nevison, a vaccine skeptic hired as a CDC consultant. She contradicted McMahon’s description of children spreading the virus through casual contact with contaminated surfaces — a process known as “horizontal transmission.”
“There’s very little evidence that horizontal transmission has ever been a significant threat to the average American child, and the risk probably has been overstated,” she said at the meeting. Also overstated, she said, are the risks of “vertical transmission,” the viral transmission between mothers and their newborns.
The committee’s new recommendation must be approved by the CDC administrator before it becomes federal policy.
McMahon said that no matter how national policy might change, Alaska Native tribal health organizations will continue administering hepatitis B vaccines to newborns.
“I know they’re not going to stop. Even if they have to pay for it. They’re so aware of this,” he said.
His fears, he said, are for low-income families who depend on free vaccinations through state programs that might lose funding and for parents who are getting conflicting messages that may lead to conclusions that the vaccine is not necessary.
“It could be a real mess,” he said.
Originally published by the Alaska Beacon, an independent, nonpartisan news organization that covers Alaska state government.

Alaska
Dozens of vehicle accidents reported, Anchorage after-school activities canceled, as snowfall buries Southcentral Alaska

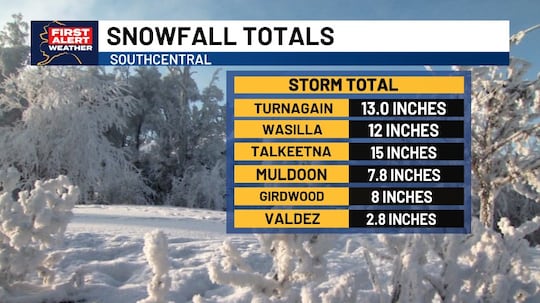
ANCHORAGE, Alaska (KTUU) – Up to a foot of snow has fallen in areas across Southcentral as of Tuesday, with more expected into Wednesday morning.
All sports and after-school activities — except high school basketball and hockey activities — were canceled Tuesday for the Anchorage School District. The decision was made to allow crews to clear school parking lots and manage traffic for snow removal, district officials said.
“These efforts are critical to ensuring schools can safely remain open [Wednesday],” ASD said in a statement.
The Anchorage Police Department’s accident count for the past two days shows there have been 55 car accidents since Monday, as of 9:45 a.m. Tuesday. In addition, there have been 86 vehicles in distress reported by the department.
The snowfall — which has brought up to 13 inches along areas of Turnagain Arm and 12 inches in Wasilla — is expected to continue Tuesday, according to latest forecast models. Numerous winter weather alerts are in effect, and inland areas of Southcentral could see winds up to 25 mph, with coastal areas potentially seeing winds over 45 mph.
Some areas of Southcentral could see more than 20 inches of snowfall by Wednesday, with the Anchorage and Eagle River Hillsides, as well as the foothills of the Talkeetna Mountain, among the areas seeing the most snowfall.
See a spelling or grammar error? Report it to web@ktuu.com
Copyright 2026 KTUU. All rights reserved.
Alaska
Yundt Served: Formal Charges Submitted to Alaska Republican Party, Asks for Party Sanction and Censure of Senator Rob Yundt

On January 3, 2026, Districts 27 and 28 of the Alaska Republican Party received formal charges against Senator Rob Yundt pursuant to Article VII of the Alaska Republican Party Rules.
According to the Alaska Republican Party Rules: “Any candidate or elected official may be sanctioned or censured for any of the following
reasons:
(a) Failure to follow the Party Platform.
(b) Engagement in any activities prohibited by or contrary to these rules or RNC Rules.
(c) Failure to carry out or perform the duties of their office.
(d) Engaging in prohibited discrimination.
(e) Forming a majority caucus in which non-Republicans are at least 1/3 or more of the
coalition.
(f) Engaging in other activities that may be reasonably assessed as bringing dishonor to
the ARP, such as commission of a serious crime.”
Party Rules require the signatures of at least 3 registered Republican constituents for official charges to be filed. The formal charges were signed by registered Republican voters and District N constitutions Jerad McClure, Thomas W. Oels, Janice M. Norman, and Manda Gershon.
Yundt is charged with “failure to adhere and uphold the Alaska Republican Party Platform” and “engaging in conduct contrary to the principles and priorities of the Alaska Republican Party Rules.” The constituents request: “Senator Rob Yundt be provided proper notice of the charges and a full and fair opportunity to respond; and that, upon a finding by the required two-thirds (2/3) vote of the District Committees that the charges are valid, the Committees impose the maximum sanctions authorized under Article VII.”
If the Party finds Yundt guilty of the charges, Yundt may be disciplined with formal censure by the Alaska Republican Party, declaration of ineligibility for Party endorsement, withdrawal of political support, prohibition from participating in certain Party activities, and official and public declaration that Yundt’s conduct and voting record contradict the Party’s values and priorities.
Reasons for the charges are based on Yundt’s active support of House Bill 57, Senate Bill 113, and Senate Bill 92. Constituents who filed the charges argue that HB 57 opposes the Alaska Republican Party Platform by “expanding government surveillance and dramatically increasing education spending;” that SB 113 opposes the Party’s Platform by “impos[ing] new tax burdens on Alaskan consumers and small businesses;” and that SB 92 opposes the Party by “proposing a targeted 9.2% tax on major private-sector energy producer supplying natural gas to Southcentral Alaska.” Although the filed charges state that SB 92 proposes a 9.2% tax, the bill actually proposes a 9.4% tax on income from oil and gas production and transportation.
Many Alaskan conservatives have expressed frustration with Senator Yundt’s legislative decisions. Some, like Marcy Sowers, consider Yundt more like “a tax-loving social justice warrior” than a conservative.
Related
Alaska
Pilot of Alaska flight that lost door plug over Portland sues Boeing, claims company blamed him

The Alaska Airlines captain who piloted the Boeing 737 Max that lost a door plug over Portland two years ago is suing the plane’s manufacturer, alleging that the company has tried to shift blame to him to shield its own negligence.
The $10 million suit — filed in Multnomah County Circuit Court on Tuesday on behalf of captain Brandon Fisher — stems from the dramatic Jan. 5, 2024 mid-air depressurization of Flight 1282, when a door plug in the 26th row flew off six minutes after take off, creating a 2-by-4-foot hole in the plane that forced Fisher and co-pilot Emily Wiprud to perform an emergency landing back at PDX.
None of the 171 passengers or six crew members on board was seriously injured, but some aviation medical experts said that the consequences could have been “catastrophic” had the incident happened at a higher altitude.
Fisher’s lawsuit is the latest in a series filed against Boeing, including dozens from Flight 1282 passengers. It also names Spirit AeroSystems, a subcontractor that worked on the plane.
The lawsuit blames the incident on quality control issues with the door plug. It argues that Boeing caught five misinstalled rivets in the panel, and that Spirit employees painted over the rivets instead of reinstalling them correctly. Boeing inspectors caught the discrepancy again, the complaint alleges, but when employees finally reopened the panel to fix the rivets, they didn’t reattach four bolts that secured the door panel.
The complaint’s allegations that Boeing employees failed to secure the bolts is in line with a National Transportation Safety Board investigation that came to the conclusion that the bolts hadn’t been replaced.
Despite these internal issues, Fisher claims Boeing deliberately shifted blame towards him and his first officer.
Lawyers for Boeing in an earlier lawsuit wrote that the company wasn’t responsible for the incident because the plane had been “improperly maintained or misused by persons and/or entities other than Boeing.”
Fisher’s complaint alleges that the company’s statement was intended to “paint him as the scapegoat for Boeing’s numerous failures.”
“Instead of praising Captain Fisher’s bravery, Boeing inexplicably impugned the reputations of the pilots,” the lawsuit says.
As a result, Fisher has been scrutinized for his role in the incident, the lawsuit alleges, and named in two lawsuits by passengers.
Spokespeople for Boeing and Spirit AeroSystems declined to comment on the lawsuit.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHamas builds new terror regime in Gaza, recruiting teens amid problematic election
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoFor those who help the poor, 2025 goes down as a year of chaos
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoWe Asked for Environmental Fixes in Your State. You Sent In Thousands.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoA tale of two Ralphs — Lauren and the supermarket — shows the reality of a K-shaped economy
-

 Detroit, MI4 days ago
Detroit, MI4 days ago2 hospitalized after shooting on Lodge Freeway in Detroit
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCommentary: America tried something new in 2025. It’s not going well
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoMarjorie Taylor Greene criticizes Trump’s meetings with Zelenskyy, Netanyahu: ‘Can we just do America?’
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoRecord-breaking flu numbers reported in New York state, sparking warnings from officials