Science
Unearthing a Maya Civilization That ‘Punched Above its Weight’

CHIAPAS, Mexico — On a brilliant, buggy morning in early summer season, Charles Golden, an anthropologist at Brandeis College, slashed via the knee-high grass of a cattle ranch deep within the Valle de Santo Domingo, a sparsely populated area of thick brush and virtually impenetrable jungle. Solely the raucous half-roar, half-bark of howler monkeys pierced the ceaseless mating name of cicadas. “We’re coming to what’s left of the Sak Tz’i’ dynasty,” Dr. Golden stated.
Dr. Golden approached a barbed wire fence enclosing a pasture, then limboed below it and surveyed the vista past: the crumbling ruins of Sak Tz’i’, a Maya settlement a minimum of 2,500 years outdated. Unfold throughout 100 acres of tangled vines and lumpy earth had been reminders of misplaced grandeur: big heaps of rock and rubble that had as soon as been temples, plazas, reception halls and a towering, terraced palace.
Straight forward had been the stays of a fancy of platforms that had shaped the acropolis. In its prime, it was dominated by a 45-foot-high pyramid wherein members of the royal household may need been entombed. The place the pyramid and several other elite residences as soon as stood had been toppled partitions of minimize stone. Dr. Golden famous that the doorway to the pyramid had in all probability featured a line of free-standing aid sculptures, referred to as stelae, most of which had been now buried within the particles or had been hacked off and carried away by thieves.
To the southeast he famous an alley crammed with scree — it was a timeworn ball courtroom, 350 ft lengthy and 16 ft vast with sloping sides. The sport, a non secular occasion symbolizing regeneration, required gamers to maintain a stable rubber ball aloft utilizing solely their hips and shoulders. Close by, amid what had been a cluster of ceremonial facilities, was a jumble of stones the place commoners would have gathered for public observances and kings would have held courtroom. Dr. Golden pointed to the previous courtyard, now a jigsaw mound. “From this place,” he stated, “the Sak Tz’i’ rulers sought to command their topics — efficiently or not — and engaged with the politics of a panorama over which a number of kingdoms struggled for management.”
Small and scrappy, Sak Tz’i’ — White Canine, within the language of historical Mayan inscriptions — was the someday ally, someday vassal, someday foe of a number of of the most important and strongest regional gamers, together with Piedras Negras in what’s now Guatemala and Bonampak, Palenque, Tonina and Yaxchilan in present-day Chiapas. The dynasty flourished in the course of the Basic interval of Maya tradition, from 250 to 900 A.D., when the civilization counted its best achievements in structure, engineering, astronomy and arithmetic.
For causes which are nonetheless unclear, Sak Tz’i’ and a whole bunch of different settlements had been deserted and whole areas had been left abandoned in the course of the ninth century. Though descendants nonetheless dwell within the area, the vagaries of nature buckled temple partitions, the tomb robbers disassembled pyramids and a thickening jungle cover hid plazas and causeways. Sak Tz’i’ was successfully erased from reminiscence.
Students started looking for bodily proof of the realm solely in 1994, when epigraphers studying a stela — discovered a century earlier at a dig in Guatemala — realized {that a} glyph described the seize of a Sak Tz’i’ king in 628 A.D.
Three summers in the past, a workforce of researchers and native work crews led by Dr. Golden and Andrew Scherer, a bioarcheologist at Brown College, explored the pasture and found the stays of dozens of stone stelae, cooking instruments and the corpse of a middle-aged lady who had died a minimum of 2,500 years earlier. Radiocarbon courting indicated that the positioning, which the researchers named Lacanjá Tzeltal after the close by trendy neighborhood, was seemingly colonized by 750 B.C. and occupied till the top of the Basic interval. Maybe most remarkably, Dr. Golden and Dr. Scherer established that the cattle ranch had been a — if not the — capital of the Sak Tz’i’ dynasty.
Simon Martin, a curator on the Penn Museum of the College of Pennsylvania who was not concerned within the venture, stated that the proof offered by the 2 researchers and their colleagues made a powerful case that Lacanjá Tzeltal was the actual Sak Tz’i’ or a minimum of a seat of the dynasty for a part of its historical past.
“The discarded carcasses of looted monuments at this website match a few of these beforehand hooked up to Sak Tz’i’,” he stated, “whereas the invention of a brand new monument commissioned by a Sak Tz’i’ ruler is equally telling.”
From Carnitas to Hieroglyphics
Dr. Golden, 50, and Dr. Scherer, 46, have been collaborating within the backwaters of historic Mesoamerica because the late Nineties. They had been the primary archaeologists to doc newly found programs of fortifications on the Late Basic Maya websites of Tecolote, in 2003, and Oso Negro, in 2005, each in Guatemala.
“The division of labor actually comes right down to our areas of experience,” stated Dr. Golden, who’s in command of organizing geographic knowledge, mapping and distant sensing with drones. Dr. Scherer analyzes human bones and something to do with eating regimen, isotopes and burials.
Tall, trim and droll, Dr. Golden was born in Chicago, and as a youth he was captivated by the artifacts within the Oriental Institute Museum. “I used to be scared of the mummies, I couldn’t even be in the identical room with them,” he stated. “However I used to be additionally dazzled by items of the Ishtar Gate from Babylon and the opposite relics from Mesopotamia. It was gorgeous to see precise fragments from locations I had heard about within the Bible.”
Dr. Golden studied archaeology on the College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, however an important lesson he discovered, he stated, was as a summer season intern at an excavation in Belize in 1993. He had been digging a check pit when he pulled from the bottom a small, ridged tube. “I used to be positive that it was an ornamental pre-Columbian bead,” he stated. Grinning proudly, he confirmed the item to his supervisor, who turned it over in his fingers and responded: “Somebody will need to have dropped this at lunch. It’s Kraft macaroni and cheese.” The would-be Louis Leakey slunk again to his check pit, a lot the wiser.
Dr. Scherer is shorter and stockier, with hair pulled right into a ponytail and a beard that dusts his chin with grey. He grew up in central Minnesota and caught the archaeology bug in faculty — Hamline College in St. Paul — whereas doing a area research at a 2,000-year-old Native American encampment. The course was collectively led by Ojibwe elders, who taught him how one can knap flint, tan hides and construct wigwams.
Each researchers had been drawn to Maya tradition as a result of it’s the just one within the historical Americas with a written historical past extending again into the primary millennium. “We all know the names of the kings and queens who ruled the locations we research, who had been their enemies and their allies, once they went to warfare, once they had been born and died,” Dr. Scherer stated.
He and Dr. Golden had been tipped off to the existence of the Lacanjá Tzeltal ruins by one in all their former analysis assistants. In 2014, a College of Pennsylvania grad scholar named Whittaker Schroder was scouting out archaeological digs close to the Guatemalan border for a dissertation matter. Whereas driving via the tiny rainforest city of Nuevo Taniperla, Dr. Schroder, now a postdoctoral affiliate on the College of Florida, handed a roadside carnitas stand. The seller tried to flag him down, however Dr. Schroder, a vegetarian, stored going.
Not lengthy after, Dr. Schroder once more drove by the stand. Once more the seller tried to catch his consideration. This time Schroder stopped to speak. “The seller stated he had a buddy with a stone that he wished an archaeologist to have a look at,” Dr. Schroder recalled. “I requested him to elaborate, and he defined that the stone had a carving with the Maya calendar and different glyphs.”
Later that night a buddy of the seller confirmed Dr. Schroder a photograph on a cellphone that, though grainy, clearly displayed a small wall panel illustrated with hieroglyphics. In a decrease nook was a dancing determine in ceremonial headdress, wielding an ax in his proper hand and a bludgeon in his left. Jacinto Gomez Sanchez, a cattle rancher who lived 25 miles away, had unearthed the limestone slab in some rubble on his property a few years earlier than.
Dr. Schroder reached out to Dr. Golden and Dr. Scherer. “We incessantly get requests to have a look at stone collectible figurines and sculptures in personal collections,” Dr. Scherer stated. “Whereas the vases and different ceramic objects are virtually invariably historical, the stone sculptures are normally trendy objects crafted for vacationers. So when somebody says, ‘Come see my pre-Columbian sculpture,’ we are likely to assume we’re going to have a look at a memento knockoff.”
To the good shock of each Mayanists, the photograph that was texted to them confirmed a full-size monument bearing glyphs of the Sak Tz’i’ dynasty. It took them one other 4 years to barter permission to excavate on the property. In 2019, the analysis workforce flew drones and planes over the positioning that had been geared up with a sensing software referred to as LIDAR, which may see via the forest cover to visualise the land and archaeology beneath. The researchers estimated that at its peak, round 750 A.D., the settlement had as many 1,000 inhabitants.
This June, after a two-year delay due to the coronavirus, Dr. Golden, Dr. Scherer and their workforce returned to the positioning to proceed the dig. A lot of the work was preventive upkeep. With the stone partitions of the acropolis in peril of collapse, Mexican anthropologist Fernando Godos and an area crew had been enlisted to bolster and stabilize the crumbling masonry.
Remnants of low partitions encircle elements of the excavation website, particularly close to the palace, which is uncommon for the area’s bygone kingdoms; usually such bulwarks had been constructed on the outskirts. One purpose of the subsequent season of analysis is to find out whether or not the partitions had been unexpectedly constructed within the dynasty’s closing days, as Dr. Scherer believes, or in the event that they had been a part of the unique development, or a minimum of modification, of the Basic interval website heart. Protection appears to have been the overarching concern at Lacanjá Tzeltal, a densely packed stronghold hemmed in by arroyos and steep riverbanks. The stone barricades presumably strengthened wood palisades.
The Maya, with their staggeringly exact calendars, refined hieroglyphs, extremely productive agricultural system and skill to foretell celestial phenomena equivalent to eclipses, had been arguably probably the most enlightened tradition of the New World. They constructed luxurious settlements with out assistance from the wheel, steel instruments or beasts of burden.
“The Maya had been really the Greeks of the traditional Americas,” Dr. Martin stated. “They constructed a complicated civilization regardless of, or maybe even due to, profound political divisions — with effectively over 100 competing kingdoms.”
Maya society prolonged past trendy borders, north from Guatemala into the Yucatán Peninsula, east into Belize and south via the western extremities of El Salvador and Honduras. By no means politically unified, the Maya of the Basic interval had been a hodgepodge of city-states.
“You’ve received large kingdoms within the central lowlands, like Tikal and Calakmul — the USA and Soviet Union of their time,” stated Dr. Scherer. “Our workforce offers with a lot smaller realms concerned in their very own type of political alliances that break down and switch into conflicts at a extremely tiny, localized scale.” Inscriptions on the monuments of these settlements usually hint the historical past of civilization to a common flood. The Lengthy Rely calendar stored monitor of the times that had handed because the legendary beginning date of the Maya creation, Aug. 11, 3,114 B.C.
The panorama of the traditional Maya is stippled with ruins whose names are unknown to students and whose hieroglyphic inscriptions point out scores of locations the places of which at the moment are misplaced. “Sak Tz’i’ fell into the latter class, and the dogged pursuit of its identification has engaged students for some three many years,” Dr. Martin stated. “Why? As a result of Sak Tz’i’ was an important of the remaining ‘homeless’ political actors.”
Essentially the most well-known point out of the society, apart from stone inscriptions present in museums and personal collections, appeared in lintels over doorways at Bonampak, wherein Sak Tz’i’ captives are depicted defeated and humiliated.
The references to Sak Tz’i’ helped slim down its location in japanese Chiapas however nonetheless left a whole bunch of sq. miles, most below tree cowl, inside which it may lie hidden. A 2003 paper within the journal Latin American Antiquity triangulated the settlement’s geographical coordinates, however the pc mannequin was simply that — a mannequin that required affirmation.
There have been false begins. Plan de Ayutla in Chiapas, a powerful website rediscovered in the course of the mid-Nineties, was roughly in the best spot and contained a formidable assortment of temples and the most important ball courtroom within the area. Though the scraps of Mayan textual content at Plan de Ayutla offered no identify for the place, the positioning appeared a probable contender for Sak Tz’i’. “Sadly, there has by no means been any glyphic proof to hyperlink Plan de Ayutla to the Sak Tz’i’ kingdom,” Dr. Golden stated.
Items of a Puzzle
At 46, Mr. Gomez is sturdy and cheerful, with silver in his smile and, when mandatory, has a resolute stare. He lives on his cattle ranch along with his spouse, 4 kids and pet spider monkey, Pancho. His grandfather helped discovered the village of Lacanjá Tzeltal in 1962.
Mr. Gomez remembers frolicking via the Sak Tz’i’ rubble as a baby. His father and grandfather instilled in him the necessity to defend the monuments and sculptures on the property. “They remind me of my heritage,” Mr. Gomez stated. A decade in the past, when looters threatened to sneak in at evening to steal relics, he determined to seek the advice of archaeologists in regards to the wall panel, and enlisted the carnitas seller as a go-between.
In June, within the fading daylight of a Chiapas afternoon, Mr. Gomez confirmed Dr. Scherer across the off-site facility wherein probably the most treasured relics had been saved. He identified instruments, clay pots, sling stones, grinding stones, a stucco jaguar head. When he introduced forth a handsomely carved flint spear level, Dr. Scherer beamed with familiarity.
In 2019, whereas excavating the ball courtroom, Dr. Scherer had unearthed a stone altar. Beneath the altar he discovered the spear level in addition to obsidian blades, spiny oyster shells and fragments of greenstone. In Maya cosmology, Dr. Scherer defined, flint connoted warfare and the solar or sky; obsidian, darkness and sacrifice. Oyster shells and greenstone had been equated with life, vitality and photo voltaic rebirth within the sea.
Though the altar was badly eroded, Dr. Golden created a 3-D mannequin and demonstrated that its glyph depicted two certain, prostrated captives and the pincers of a monstrous centipede — a motif the Maya used to mark a subterranean or underworld scene.
The gem of the recovered antiquities was the 2-by-4-foot wall panel, lately dated to 775 A.D., that had set the excavation in movement. A translation of the inscription by Stephen Houston, an anthropologist at Brown College, revealed tales of battles, rituals, a legendary flood and a fantastical water serpent described in poetic couplets as “shiny sky, shiny earth.”
Dr. Scherer acknowledged that though different Maya settlements additionally had mythic accounts of creation, the story recorded on the Lacanja Tzeltal pill was distinctive to the positioning and could possibly be an allegory for its development. “The tales contact on the neighborhood’s relationship to the encircling pure setting,” he stated. “The world is thick with streams and waterfalls and incessantly floods.”
The glyphs additionally spotlight the lives of dynastic rulers such because the delightfully named Okay’ab Kante’, together with when every one died, how they had been memorialized and below what circumstances their successors got here to the throne. In a single glyph, the Sak Tz’i’ ruler seems because the dancing Yopaat, a divinity related to violent tropical storms. The ax in his proper hand is a lightning bolt, the snake-footed deity Okay’awiil; in his left he carries a “manopla,” a stone membership utilized in ritual fight. The lacking panel is presumed to have featured a prisoner of warfare, kneeling in supplication to Yopaat.
Dr. Martin referred to as the findings of Dr. Golden and Dr. Scherer a serious advance in our understanding of Basic interval Maya politics and tradition. “Such discoveries restore historical past to now lifeless ruins and, metaphorically a minimum of, repopulate them with long-dead rulers, nobles, warriors, artisans, retailers, farmers and the entire social matrix of historical Maya society,” he stated.
Scott Hutson, an archaeologist on the College of Kentucky who was not concerned within the analysis, famous that earlier than the placement of Sak Tz’i’ was pinned down, “archaeologists knew that its rulers engaged in high-stakes diplomacy, typically leading to warfare with highly effective neighbors.” The maps by Dr. Golden and Dr. Scherer, he added, “convey a concreteness and poignancy to this narrative, displaying that the positioning was smaller than most of its rivals and in a way punched above its weight.”
At Lacanjá Tzeltal, Dr. Golden stood astride a stone heap below an excavation tent and conjured up the heyday of the Sak Tz’i’ kingdom. Mud within the air caught the afternoon daylight, and the silence of the positioning appeared to echo. Trying to find the misplaced settlement, Dr. Golden stated, had been like assembling a map of medieval Europe from historic paperwork and never figuring out the place Burgundy ought to go. “Basically, we’ve positioned Burgundy,” he stated. “It’s that essential a chunk of the puzzle.”

Science
If you're living with a drug or mental health problem, here's where to look for help

Fatal overdoses in the U.S. fell for the first time in five years in 2023, according to preliminary estimates recently released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but UCLA researcher Joseph Friedman warns that the new findings should not be interpreted to mean that the nation’s drug and mental health crises are abating.
Friedman has analyzed “deaths of despair” that result from overdose, suicide and liver disease due to alcoholism and found that while death rates for white Americans have dipped, rates have risen in recent years among people of color in the U.S., especially among Native and Black Americans. Illegal opioids such as fentanyl have ravaged Black and low-income communities in Los Angeles.
While it’s difficult to pinpoint the exact reasons behind substance abuse or suicide, Friedman as well as other experts in addiction medicine and mental health say racial inequality, economic distress and historical trauma have aggravated those problems in marginalized communities.
If you or someone you know needs immediate help for a mental health, substance-use or suicidal crisis, call or text 988, or chat online by visiting the suicide and crisis line’s website. For mental health resources and referrals, call the Los Angeles County Department of Mental Health’s Help Line 24/7 at (800) 854-7771.
Here are other organizations that offer information, counseling and support services:
Nakeya Fields, a licensed clinical social worker in Pasadena, founded the Black Mental Health Task Force, a coalition that brings together mental health professionals, clients, nonprofits, community organizations, educators and others in California to raise awareness about mental wellness. Her Therapeutic Play Foundation offers activities designed to improve resilience and coping skills through creative arts, play and sports. It provides individual, couples, group and family therapy for Black, Latinx, LGBTQ+ and other members of marginalized populations.
The American Indian Counseling Center, a division of the Los Angeles County Mental Health Department, offers crisis intervention, 24/7 intensive mental health services and counseling for all ages, as well as physician consultations for medications and referrals to culturally relevant support groups. Call (562) 402-0677 and ask to speak with the on-duty worker.
United American Indian Involvement’s behavioral health program provides outpatient substance use disorder treatment and mental health services to American Indians and Alaska Natives living throughout Los Angeles County. Visit the website or call (213) 202-3970.
Melanin and Mental Health offers an online network of Black and brown mental healthcare providers that is searchable by geographic area, issue type and treatment sought. It’s also possible to filter results by therapists’ racial background and specialty, as well as by insurance carrier.
The Black Mental Health Alliance offers confidential referrals to culturally competent mental health professionals who are in its database of licensed therapists.
Painted Brain advocates for mental wellness in underserved L.A. communities by offering self-care, relaxation and therapeutic art and play sessions, support groups and trainings for mental health professionals. As part of its peer-led model, many of the staff have experienced mental health issues themselves. Its community center and art space is located at 5980 W. Pico Blvd. in Los Angeles.
The Los Angeles LGBT Center offers individual, couples, family, group therapy and psychiatric care, as well as support for people struggling with substance use. The center has locations in West Hollywood, at Mi Centro in East L.A., at its Trans Wellness Center near MacArthur Park and in South L.A.’s Leimert Park neighborhood.
The Community Health Project Los Angeles provides services to people who use drugs by way of a harm-reduction approach that emphasizes offering clean needles as well as education on how to respond to an overdose.
Science
Are 'deaths of despair' really more common for white Americans? A UCLA report says no
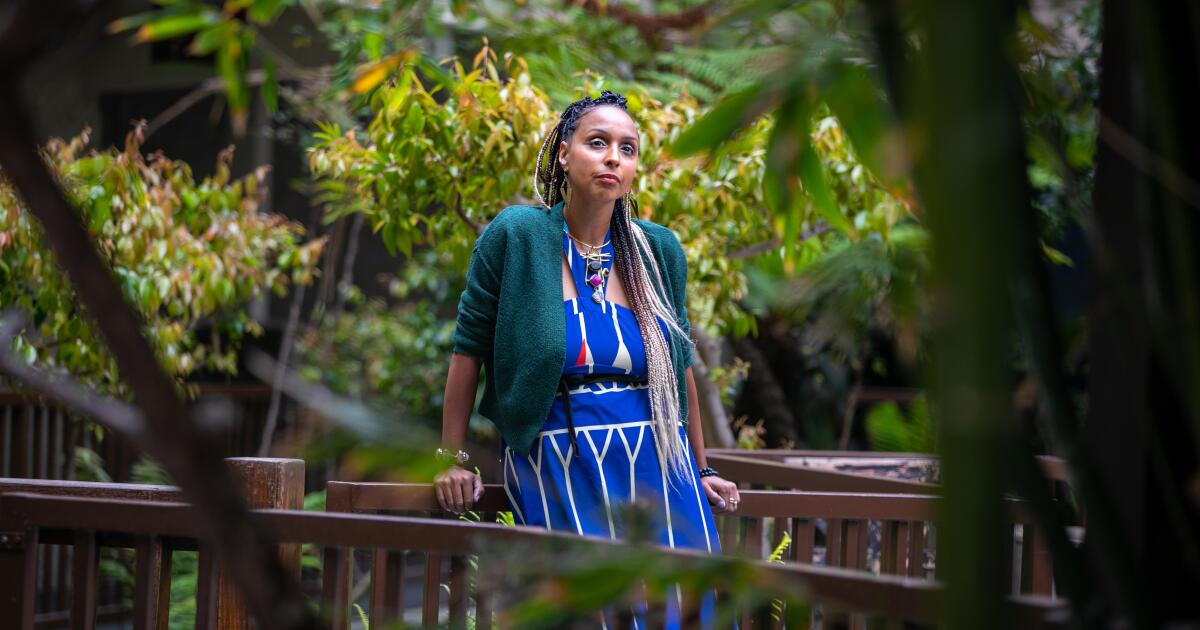

Nakeya Fields has seen how the stresses that come with being Black — racial injustice, financial strain, social isolation — can leave people feeling hopeless and push some into substance abuse.
It’s one of the reasons the Pasadena social worker started offering “therapeutic play” gatherings for Black mothers like herself and children.
“I’m trying to host more safe spaces for us to come and share that we’re suffering,” the 32-year-old said. “And honestly, the adults need play more than kids.”
Yet while Black and brown mental health practitioners such as Fields have labored to address these issues within their communities, a very different conversation has been occurring in the nation at large.
For years, discussions about America’s substance-abuse crisis have focused almost exclusively on the narrative that it is white, middle-age adults who face the greatest risk of dying from drug overdoses, alcoholic liver disease and suicide.
The theory, which was presented by two Princeton economists in 2015 and based on data from 1999 to 2013, argued that despair was behind rising premature mortality rates among white Americans, especially those who were less educated.
Virtually overnight, the “deaths of despair” concept began to drive the national discourse over populist far-right politics; the rise of Donald Trump; and deepening political polarization over such topics as addiction treatment, law enforcement and immigration.
But after roughly a decade, researchers at UCLA and elsewhere have begun to dismantle this idea.
In a study published recently in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, authors found that deaths of despair rates for middle-age Black and Native Americans have surged past those of white Americans as the overdose crisis moves from being driven by prescription opioids to illegal drugs such as fentanyl and heroin.
While the opioid crisis did raise drug overdose deaths among white Americans for a time, it was an anomaly, said Joseph Friedman, a social medicine expert at UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine who was the lead author of the journal analysis. In fact, by 2022 the rate for white Americans had started to dip.
“What’s really important is that now, with these three causes of death, the gap has closed, and it’s moving in the other direction,” Friedman said.
Sandra Mims, a community health worker with Community Health Project L.A., puts out boxes of Narcan — a naloxone nasal spray that reverses the effects of opioid overdose — at an event at MacArthur Park in Los Angeles on International Overdose Awareness Day.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
The analysis found that deaths of despair for Black Americans hit a rate of 103.81 per 100,000 people in 2022, compared with 102.63 for white Americans. The rate for Native American and Alaska Native populations was even higher at 241.7 per 100,000 people in 2022.
The UCLA analysis doesn’t specify the midlife personal issues that might have led to addiction or suicide.
But the authors say that flaws in the methodology of the 2015 deaths of despair report skewed its conclusions about who was most at risk. Specifically, Friedman said that it failed to give enough consideration to long-standing racial inequities that Black Americans experience in income, educational attainment, incarceration and access to quality medical care, all of which can contribute to drug use and poor mental health outcomes. And statistics for Native Americans weren’t factored in at all.
“It was burned into the American psyche that it was white people in the rural U.S.,” Friedman said. “It was just a very small piece of the truth that was very interesting but was widely sold as something it wasn’t.”
Another recent worrying sign, Friedman says: Deaths of despair among Latinos are starting to catch up to those among Black and Native Americans.
Princeton professors Anne Case and her husband Angus Deaton, winner of the 2015 Nobel Prize in economic sciences, were thrust into the media spotlight when their deaths of despair findings were first published. Deaton told NPR that during a visit to the White House, even President Obama asked him about the phenomenon.
Their 2020 book, “Deaths of Despair and the Future of Capitalism,” was described by publisher Princeton University Press as “a troubling portrait of the American dream in decline.”
“For the white working class, today’s America has become a land of broken families and few prospects. As the college educated become healthier and wealthier, adults without a degree are literally dying from pain and despair,” the publisher said.
Fields, who employs yoga and pottery in her therapy, said this framing was misleading and racially biased.
“I’m actually flabbergasted that somebody has a term called ‘deaths of despair,’” Fields said. “It’s ‘despair’ when white people experience this suffering. But when we experience it, it’s just what we have to deal with.”
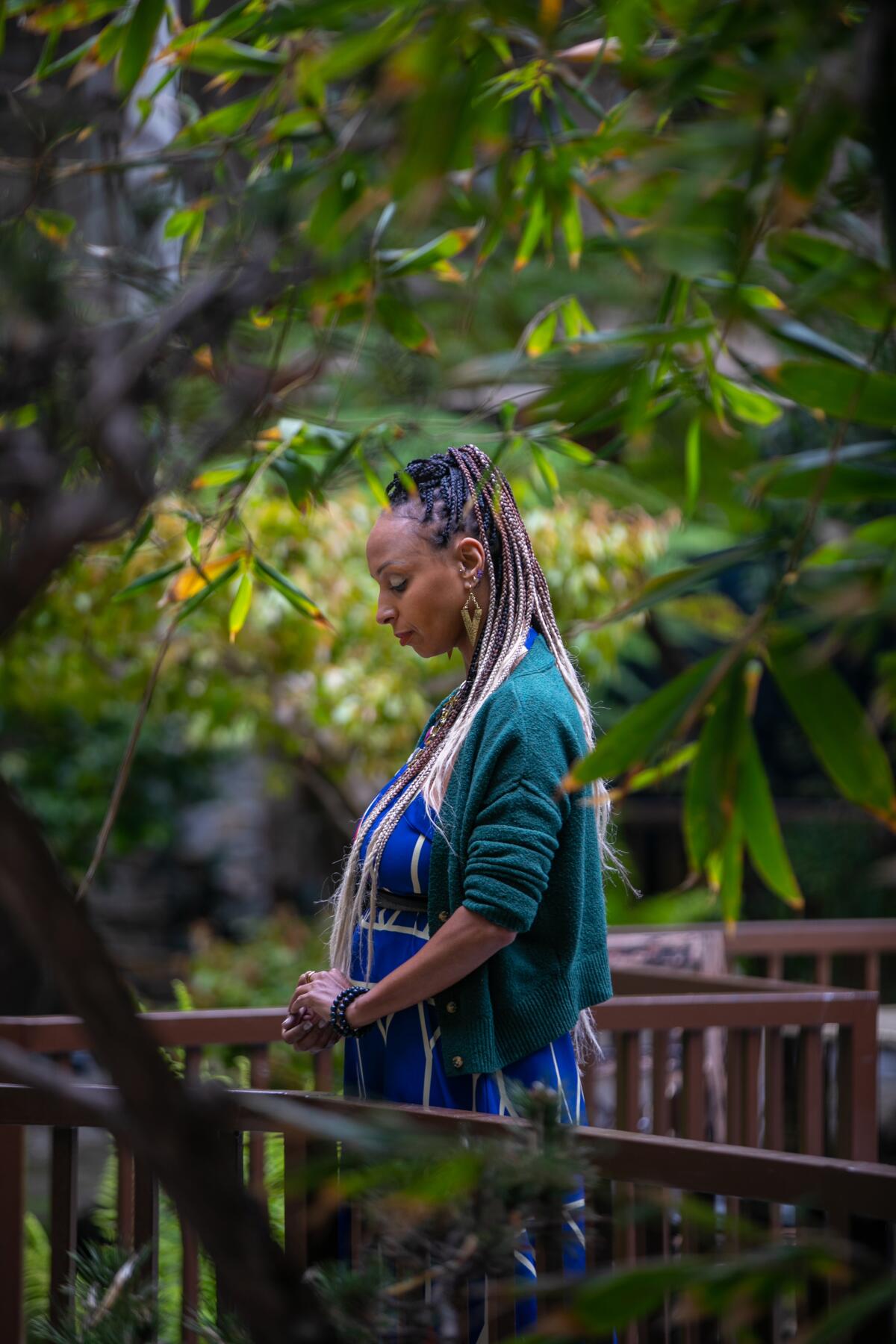

Nakeya Fields says it’s important to address mental wellness issues early, before people reach a crisis point and become another statistic.
(Jason Armond / Los Angeles Times)
Both Friedman and Fields say their critiques are not intended to minimize deaths among white Americans.
Still, Friedman wonders: “How do we empower Black and Native American communities in a way that enables them to treat these problems?”
Racism must be considered when trying to make sense of the crisis in premature deaths, says Dr. Helena Hansen, head of UCLA’s Department of Psychiatry and a senior author on Friedman’s analysis. Hansen, who is Black and specializes in addiction psychiatry, also co-authored the book “Whiteout: How Racial Capitalism Changed the Color of Opioids in America.”
For years, pharmaceutical companies steered expensive prescription pain medications, such as the opioid Oxycontin, as well as the most effective medications for opioid-use disorder, to white Americans with good access to healthcare, she said.
But at the same time, Black and brown Americans were unfairly subjected to law enforcement policies that prioritized incarceration for illegal drug use over increasing access to more humane medical strategies to help them, further harming already vulnerable communities, Hansen said.
“In our society, people with access to the new technologies and pharmaceuticals are more likely to be white,” Hansen says. “None of this is by accident. All of this is the direct result of careful racially and class-segmented marketing strategies by pharmaceutical companies.”
This two-tiered system arose because drug manufacturers, doctors and policymakers have for too long failed to see people from historically marginalized communities who live with addiction and mental health crises as worthy of the same sympathy and treatments that many white Americans receive, Hansen says.
Joseph Gone, a professor of anthropology at Harvard who has spent 25 years studying the intersection of colonialism, culture and mental health in Indigenous communities, agreed.
“Deaths of despair have been a reality for Indigenous communities since conquest and dispossession,” he said.
“It’s amazing how much grief our people contend with from early deaths — there are not that many communities in America that bear it quite the way we do,” said Gone, who is a member of the Aaniiih-Gros Ventre tribal nation of north-central Montana. “Until we acknowledge and take responsibility for the casualties of colonization, which endure to this day through deaths of despair, it’s going to be very hard to turn this around.”
Gone, who has collaborated with Friedman on previous research, says the mental health crisis in tribal nations is aggravated by widespread joblessness and generational poverty, and a lack of healthcare resources to treat people in need of immediate or long-term treatment.
Just one traveling psychiatrist serves reservations spread across both Montana and Wyoming — a region covering more than 243,300 square miles — mostly to manage patients’ prescriptions, he says.
And “for all of Indian country, we’re talking about a very small number of in-patient psychiatric facilities,” Gone says.
General practitioners can serve as a first line of defense, but they are not necessarily equipped to address the ongoing life crises that can lead to excessive drug and alcohol use, Gone says.
Fields says it’s important to address mental wellness issues early, before people reach a crisis point and become another statistic.
While her focus remains on Black women, she’s developed additional programming for adults, families and children, such as developmental screenings that measure for high stress levels. In June, Fields will co-present “Rap 4 Peace,” a conference and gala featuring hip-hop artists talking about mental health and reducing gun violence.
“This ‘tragedy of despair’ lives in us,” Fields says. “We breathe it. We go outside hoping that nobody will harm us or our children because they feel threatened by us. This is truly harmful to our bodies.”
Science
SpaceX plans to launch 90 rockets from Vandenberg Space Force Base by 2026. Could that harm the coast?
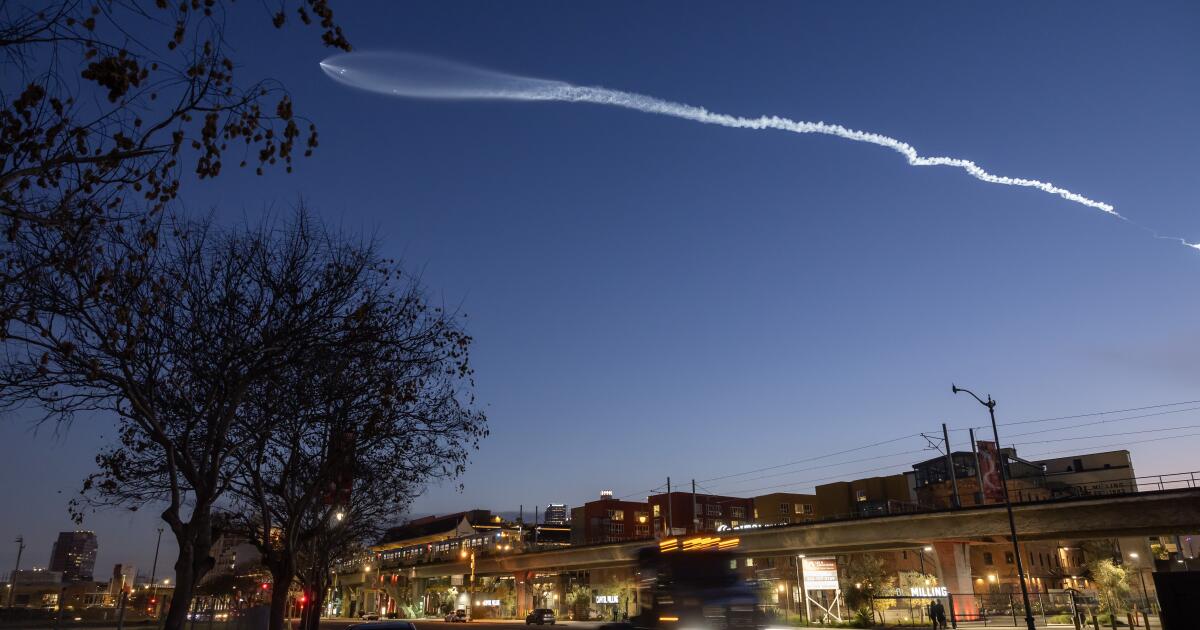

SpaceX plans to launch 90 rockets into space from a Santa Barbara County military base by 2026, tripling the number of blasts rocking the coastal community — and raising concerns from neighbors and environmental groups about the effects on marine life.
Founded by billionaire Elon Musk, SpaceX has ramped up the number of rocket launches from Vandenberg Space Force Base in recent years, and it has made clear its desire to increase the frequency of blastoffs. But during a California Coastal Commission hearing Friday, U.S. Space Force officials outlined for the first time its own plans to multiply the number of launches from the base, from 37 in 2023 to more than 120 a year by 2026.
The overwhelming majority of those rocket liftoffs would be conducted by SpaceX, which has already done more launches from the base than the commission has approved.
Last year SpaceX breached an agreement with the commission that limited the number of launches to six, sending 28 rockets into space.
It is seeking an agreement with the commission to do 36 launches a year, increasing to 90 in 2026.
The decision by the commission, which was created to protect the state’s coastal resources, will directly affect residents and marine life near the military base that hear and feel the rockets’ sonic booms.
It could also redirect the future of SpaceX, whose pursuit to redefine space exploration is already closely tied with U.S. military interests, given its work as a military contractor.
“The ultimate goal is for this to be more routine and not a huge deal,” said Space Force Col. Bryan Titus, operations vice commander at the base.
Formed in 2019, the U.S. Space Force has been looking to improve its ability to send rockets into space, Titus said, so SpaceX’s ability to launch with more frequency is a benefit to the U.S. military.
SpaceX launched 96 rockets in 2023 from Vandenberg and three other facilities: Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Fla., and SpaceX Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas.
Environmental groups argue that turning launches into a routine event could affect marine life.
“We’re concerned that more frequent launches will result in permanent changes,” said Ana Citrin, legal and policy director for the Gaviota Coast Conservancy.
Federal agencies, including the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and National Marine Fisheries Service, monitor the effects of the liftoffs on such animals as sea otters, bats, western snowy plovers, California least terns and California red-legged frogs.
Thus far, the monitoring has shown that some of the animals might react to the blastoff by flushing, or fleeing from their nests and homes, but they return soon after, according to U.S. Space Force officials. No long-term effects have been seen, they said.
SpaceX did not respond to a request for comment.
Flushing or hunkering down after a blast are already signs of wildlife exhibiting signs of stress, said Duncan Leitch, a professor of integrative biology at UCLA.
Most animals can adapt to infrequent incidents, but exposure to more frequent stressful incidents can change their biology as well as their behavior, he said.
In the worst-case scenarios, he said, the ability of birds to communicate could be impeded, and migratory birds could avoid the area. Fish and other animals that use sound to communicate and navigate underwater — including whales — could be affected too.
“Over a longer period of time, there may be reductions in the population of fish as they move away from the sound, or they may be affected to the point that it affects their health,” Leitch said. “It would change the ecosystem as far as other animals that rely on the fish.
“Having sounds that are well into the damaging, or painful, range of decibels now occurring [100] times a year, the animals might not have the ability to change their behavior or accommodate these types of sounds.”
Some environmental groups, including the Surfrider Foundation, are asking the commission to reject the increase.
SpaceX “intends to begin increasing very rapidly, so we’re very concerned about this,” said Mandy Sackett, senior California policy coordinator for the Surfrider Foundation.
More frequent launches could change the way wildlife in the area responds in the long term, environmental groups said.
Members of the California Coastal Commission are also asking whether SpaceX should be entitled to circumvent the permit process, as federal agencies are.
Federal entities negotiate agreements with the commission but ultimately can move ahead even without commission approval. In such cases, the commission’s recourse would be through mediation or the courts.
Because SpaceX is a U.S. Space Force contractor, military officials argue that all launch operations at the base by the company are “federal activities.”
But U.S. Space Force officials said only 25% of the rockets launched into space by SpaceX are carrying payloads for the Department of the Defense.
The vast majority of the liftoffs are for the company’s private benefit, raising questions about why SpaceX can dispense with permits when 75% of its blasts from the base don’t involve the U.S. government.
“That is still pretty skewed for me,” Commissioner Mike Wilson said during a meeting Friday.
Some commissioners — whose focus is usually on environmental protection, development and water issues during their monthly meetings — also brought up the war in Ukraine during Friday’s discussion.
“I question the national security public benefit of concentrating that much power, literally communication power, in one company that we’re enabling in this case,” Wilson said. “[SpaceX] has already showed that it will play in international conflicts at the will of one human being.”
Wilson was referring to reports that Musk’s company refused to allow Ukraine to use satellite internet service from Starlink, a subsidiary of SpaceX, to help it carry out an attack against Russia in September 2022.
“If the idea is that we’re supporting these permits on the side that we’re promoting national defense, and then a single company is able to dismantle our allies during armed conflict — that really doesn’t align,” Commissioner Justin Cummings said.
“I suspect that would violate our strategies around national defense.”
Titus declined to address the question, saying it was “out of my lane,” but he said he would try to get answers to address the commissioners’ concerns.
Some commissioners on Friday also argued that SpaceX, not U.S. military officials, should be making the company’s case in front of the agency.
“When this comes back, I think it would be really important that a representative from SpaceX comes to the meeting,” Cummings said.
Cummings said it was “ridiculous” for SpaceX not to appear at the meeting, despite multiple efforts from the agency to have SpaceX officials speak.
“They obviously refuse to because they’ve never shown up,” he said.
On Friday, Commission Chair Caryl Hart suggested an agreement might not be possible unless SpaceX changes its stance.
“From my perspective,” Hart said, “I think we’re going to continue to hit significant obstacles in achieving a federal consistency ruling without having SpaceX.”
-
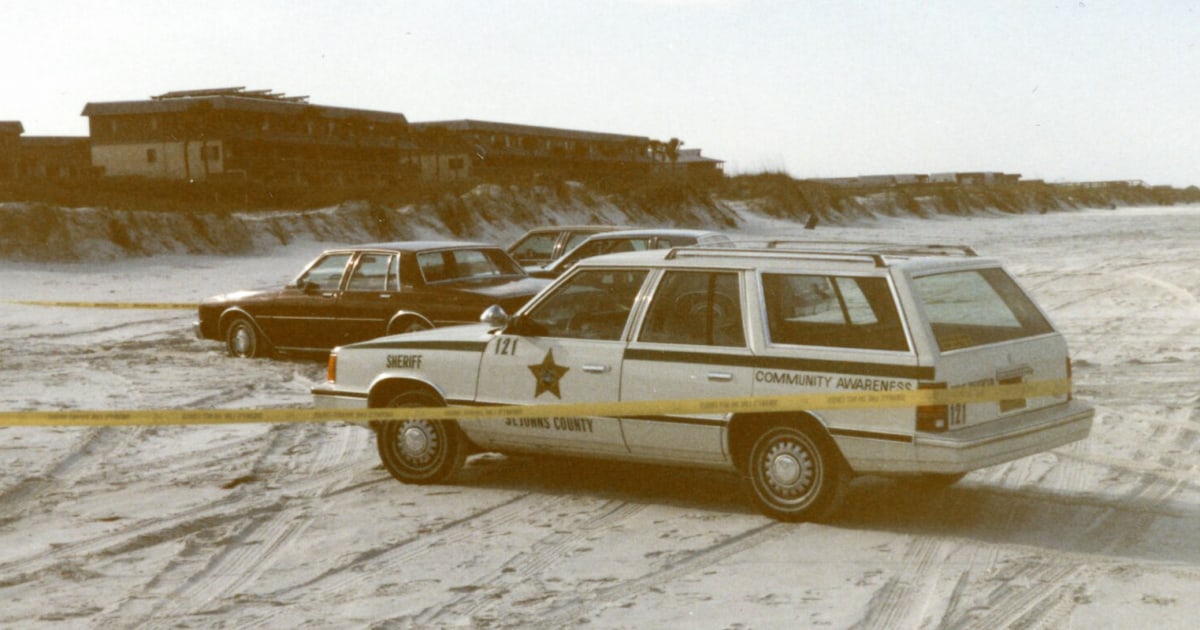

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSkeletal remains found almost 40 years ago identified as woman who disappeared in 1968
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIndia Lok Sabha election 2024 Phase 4: Who votes and what’s at stake?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUkraine’s military chief admits ‘difficult situation’ in Kharkiv region
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoAavesham Movie Review
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTrump, Reciting Songs And Praising Cannibals, Draws Yawns And Raises Eyebrows
-
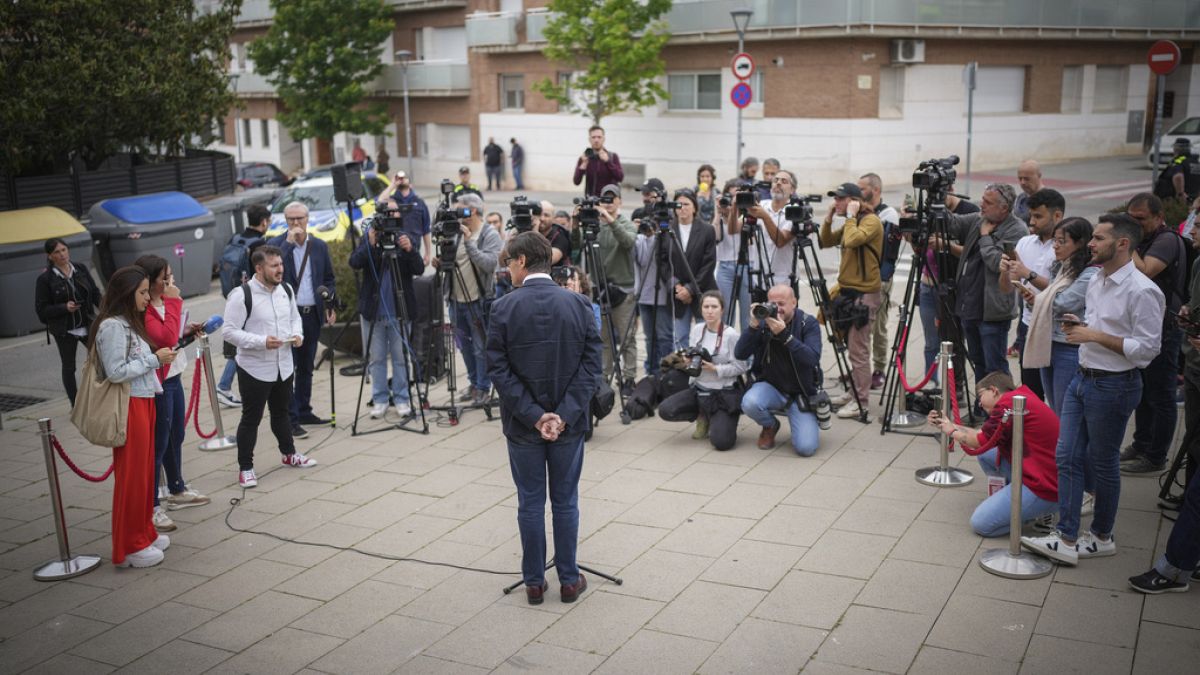

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCatalans vote in crucial regional election for the separatist movement
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoUnfrosted Movie Review: A sweet origins film which borders on the saccharine
-
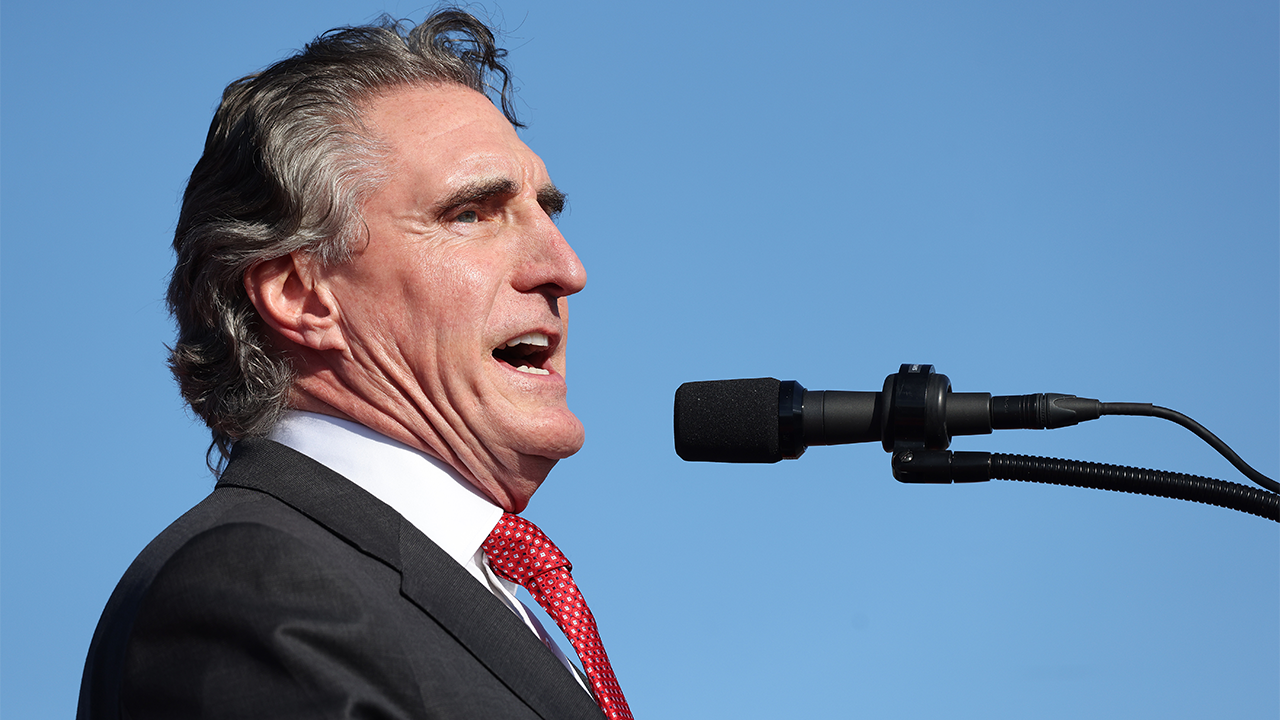

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNorth Dakota gov, former presidential candidate Doug Burgum front and center at Trump New Jersey rally