Science
This Nonprofit Health System Cuts Off Patients With Medical Debt

Many hospitals in the United States use aggressive tactics to collect medical debt. They flood local courts with collections lawsuits. They garnish patients’ wages. They seize their tax refunds.
But a wealthy nonprofit health system in the Midwest is among those taking things a step further: withholding care from patients who have unpaid medical bills.
Allina Health System, which runs more than 100 hospitals and clinics in Minnesota and Wisconsin and brings in $4 billion a year in revenue, sometimes rejects patients who are deep in debt, according to internal documents and interviews with doctors, nurses and patients.
Although Allina’s hospitals will treat anyone in emergency rooms, other services can be cut off for indebted patients, including children and those with chronic illnesses like diabetes and depression. Patients aren’t allowed back until they pay off their debt entirely.
Nonprofit hospitals like Allina get enormous tax breaks in exchange for providing care for the poorest people in their communities. But a New York Times investigation last year found that over the past several decades, nonprofits have fallen short of their charitable missions, with few consequences.
Allina has an explicit policy for cutting off patients who owe money for services they received at the health system’s 90 clinics. A 12-page document reviewed by The Times instructs Allina’s staff on how to cancel appointments for patients with at least $4,500 of unpaid debt. The policy walks through how to lock their electronic health records so that staffers cannot schedule future appointments.
“These are the poorest patients who have the most severe medical problems,” said Matt Hoffman, an Allina primary care doctor in Vadnais Heights, Minn. “These are the patients that need our care the most.”
Allina Health said it has a robust financial assistance program that in an average year helps over 12,000 of its 1.9 million patients with medical bills. The hospital system cuts off patients only if they have racked up at least $1,500 of unpaid debt three separate times. It contacts them by phone and with repeated letters that include information about applying for financial help, said Conny Bergerson, a hospital spokeswoman.
“Allina Health’s goal is, and will always be, to have zero patients go without services for financial reasons,” Ms. Bergerson said. She said that cutting off services was “rare” but declined to provide information on how often it happens.
Allina suspended its policy of cutting off patients in March 2020, at the onset of the coronavirus pandemic, before reinstating it in April 2021.
An estimated 100 million Americans have medical debts. Their bills make up about half of all outstanding debt in the country.
About 20 percent of hospitals nationwide have debt-collection policies that allow them to cancel care, according to an investigation last year by KFF Health News. Many of those are nonprofits. The government does not track how often hospitals withhold care.
Under federal law, hospitals are required to treat everyone who comes to the emergency room, regardless of their ability to pay. But the law — called the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act — is silent on how health systems should treat patients who need other kinds of lifesaving care, like those with aggressive cancers or diabetes.
In 2020, thanks to its nonprofit status, Allina avoided roughly $266 million in state, local and federal taxes, according to the Lown Institute, a think tank that studies health care.
In exchange, the Internal Revenue Service requires Allina and thousands of other nonprofit hospital systems to benefit their local communities, including by providing free or reduced-cost care to patients with low incomes.
But the federal rules do not dictate how poor a patient needs to be to qualify for free care. In 2020, Allina spent less than half of 1 percent of its expenses on charity care, well below the nationwide average of about 2 percent for nonprofit hospitals, according to an analysis of hospital financial filings by Ge Bai, a professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Allina is one of Minnesota’s largest health systems, having largely grown through acquisitions. Since 2013, its annual profits have ranged from $30 million to $380 million. Last year was the first in the past decade when it lost money, largely owing to investment losses.
The financial success has paid dividends. Allina’s president earned $3.5 million in 2021, the most recent year for which data is available. The health system recently built a $12 million conference center.
Yet Allina sometimes plays hardball with patients. Doctors have become accustomed to seeing messages in the electronic medical record notifying them that a patient “will no longer be eligible to receive care” because of “unpaid medical balances.”
Dr. Rita Raverty, a primary care doctor who works at an Allina clinic, said the notifications were alarming because they meant she could not provide continuous care for some of her patients facing a number of health risks.
“Nobody wins when patients can’t get preventive care,” Dr. Raverty said. “It creates worse disease outcomes when you’re not catching things early.”
Doctors and patients described being unable to complete medical forms that children needed to enroll in day care or show proof of vaccination for school.
Serena Gragert, who worked as a scheduler at an Allina clinic in Minneapolis until 2021, said the computer system simply wouldn’t let her book future appointments for some patients with outstanding balances.
Ms. Gragert and other Allina employees said some of the patients who were kicked out had incomes low enough to qualify for Medicaid, the federal-state insurance program for poor people. That also means those patients would be eligible for free care under Allina’s own financial assistance policy — something many patients are unaware exists when they seek treatment.
Ms. Bergerson, the Allina spokeswoman, did not dispute that but said the health system goes “to tremendous lengths to assist patients with their financial obligations for medical care.”
Allina employees said the policy has forced them to ration care.
Beth Gunhus, a pediatric nurse practitioner, recalled a case in which a mother brought in her three children. One had scabies, an intensely itchy skin condition caused by mites burrowing into the body. She wanted to follow best practices and treat the entire family, who were sharing one bed in a single room they rented, to ensure it didn’t spread further. But she could write a prescription for only two of the children. The third’s account was locked because of unpaid bills.
“There are so many better ways of saving money than what we’re doing,” Ms. Gunhus said.
Allina says the policy applies only to debts related to care provided by its clinics, not its hospitals. But patients said in interviews that they got cut off after falling into debt for services they received at Allina’s hospitals.
Because Allina is the dominant health system in some rural parts of Minnesota, getting kicked out can leave patients with few options.
Jennifer Blaido lives in Isanti, a small town outside Minneapolis, and Allina owns the only hospital there. Ms. Blaido, a mechanic, said she racked up nearly $200,000 in bills from a two-week stay at Allina’s Mercy Hospital in 2009 for complications from pneumonia, along with several visits to the emergency department for asthma flare-ups. Ms. Blaido, a mother of four, said most of the hospital stay was not covered by her health insurance and she was unable to scrounge together enough money to make a dent in the debt.
Last year, Ms. Blaido had a cancer scare and said she couldn’t get an appointment with a doctor at Mercy Hospital. She had to drive more than an hour to get examined at a health system unconnected to Allina.
Allina does not make this policy explicit to patients. It is not mentioned in the health system’s list of “frequently asked questions” about billing practices. In at least one case, Allina has denied that it even existed.
In a lawsuit filed last year in state court in Minnesota, Allina sued a couple, Jordan and JoLynda Anderson, for nearly $10,000 in unpaid medical bills.
In court filings, the couple described how Allina canceled Ms. Anderson’s appointments and told her that she could not book new ones until she had set up three separate payment plans — one with the health system and two with its debt collectors.
Even after setting up those payment plans, which totaled $580 a month, the canceled appointments were never restored. Allina allows patients to come back only after they have paid the entire debt.
Ms. Anderson recalls being devastated about losing her visit to an endocrinologist that specialized in a chronic condition she has. She had already been waiting four months for the appointment, and was unable to get a new one.
“It felt like I was being punished, and the punishment was you get to stay ill,” she said.
Ms. Bergerson declined to comment on these cases, citing patient privacy.
When the Andersons asked in court for a copy of Allina’s policy of barring patients with unpaid bills, the hospital’s lawyers responded: “Allina does not have a written policy regarding the canceling of services or termination of scheduled and/or physician referral services or appointments for unpaid debts.”
In fact, Allina’s policy, which was created in 2006, instructs employees on how to do exactly that. Among other things, it tells staff to “cancel any future appointments the patient has scheduled at any clinic.”
It does provide a few ways for patients to continue being seen despite their unpaid bills. One is by getting approved for a loan through the hospital. Another is by filing for bankruptcy.
Susan C. Beachy contributed research.

Science
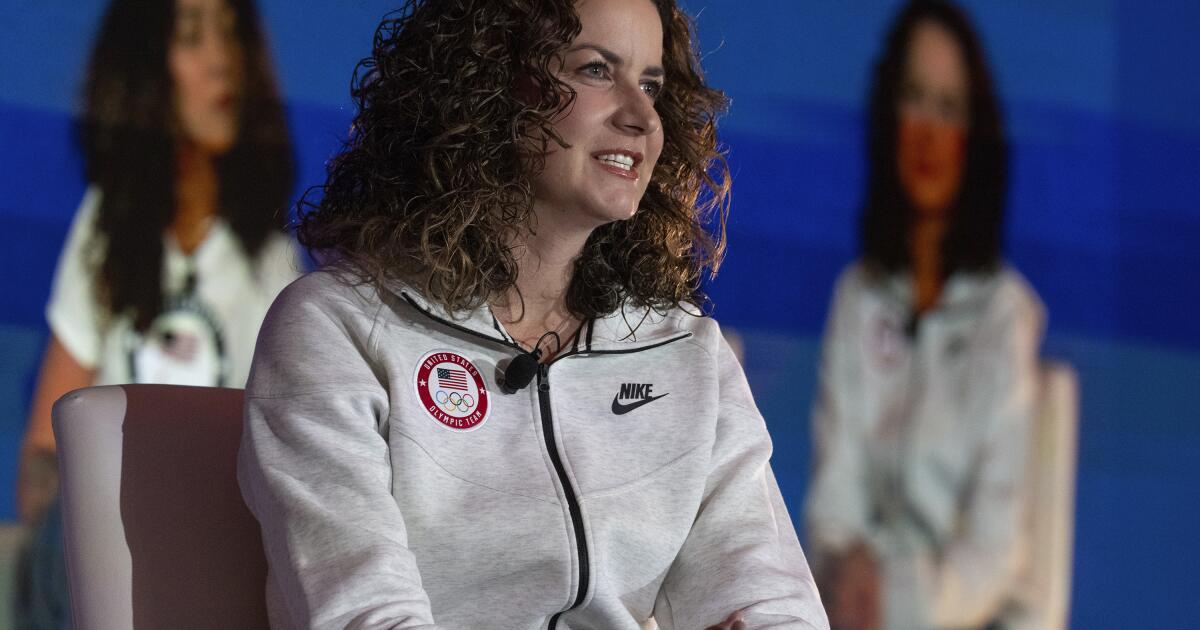
Q&A: Learn how Olympians keep their cool from Team USA's chief sports psychologist

Your morning jog or weekly basketball game may not take place on an Olympic stage, but you can use Team USA’s techniques to get the most out of your exercise routine.
It’s not all about strength and speed. Mental fitness can be just as important as physical fitness.
That’s why the U.S. Olympic & Paralympic Committee created a psychological services squad to support the mental health and mental performance of athletes representing the Stars and Stripes.
“I think happy, healthy athletes are going to perform at their best, so that’s what we’re striving for,” said Jessica Bartley, senior director of the 15-member unit.
Bartley studied sports psychology and mental health after an injury ended her soccer career. She joined the USOPC in 2020 and is now in Paris with Team USA’s 592 competitors, who range in age from 16 to 59.
Bartley spoke with The Times about how her crew keeps Olympic athletes in top psychological shape, and what the rest of us can learn from them. Her comments have been edited for length and clarity.
Why is exercise good for mental health?
It gets you moving. It gets the endorphins going. And there’s often a lot of social aspects that are really helpful.
There are a number of sports that stretch your brain in ways that can be really, really valuable. You’re thinking about hand-eye coordination, or you’re thinking about strategy. It can improve memory, concentration, even critical thinking.
What’s the best way to get in the zone when it’s time to compete?
When I work with athletes, I like to understand what their zone is. If a 0 or a 1 is you’re totally chilled out and a 10 is you’re jumping around, where do you need to be? What’s your number?
People will say, “I’m at a 10 and I need to be at an 8 or a 7.” So we’ll talk about ways of bringing it down, whether it’s taking a deep breath, listening to relaxing music, or talking to your coach. Or there’s times when people say they need to be more amped up. That’s when you see somebody hitting their chest, or jumping up and down.
If you make a mistake in the middle of a competition, how do you move on instead of dwelling on it?
I often teach athletes a reset routine. I played goalie, so I had a lot of time to think after getting scored on. I would undo my goalie gloves and put them back on, which to me was a reset. I would also wear an extra hairband on my wrist, and when I would snap it, that meant I needed to get out of my head.
It’s not just a physical reset — it helps with a mental reset. If you do the same thing every single time, it goes through the same neural pathway to where it’s going to reset the brain. That can be really impactful.
Do Olympic athletes have to deal with burnout?
Oh, yeah. Everybody has a day where they don’t want to do whatever it is. That’s when you have to ask, “What’s in my best interests? Do I need a recovery day, or do I really need to get in the pool, or get in the gym?”
Sometimes you really do need what we like to refer to as a mental health day.
How can you psych yourself up for a workout when you just aren’t feeling it?
It’s really helpful to think about why you’re doing this and why you’re pushing yourself. Do you have goals related to an activity or sport? Is there something tied to values around hard work or discipline, loyalty or dependability?
When you don’t want to get in the gym, when you don’t want to go for a run, think about something bigger. Tie it back to values.
Is sleep important for maintaining mental health?
Yes! We started doing mental health screens with athletes before the Tokyo Games. We asked about depression, anxiety, disordered eating and body image, drugs and alcohol, and sleep. Sleep was actually our No. 1 issue. It’s been a huge initiative for us.
How much sleep should we be getting?
It’s different for everyone, but generally we know seven to nine hours of sleep is good. Sometimes some of these athletes need 10 hours.
I highly recommend as much sleep as you need. If you didn’t get enough sleep, napping can be really valuable.
Is napping just for Olympic athletes or is it good for everybody?
Everybody! Naps are amazing.
What if there’s no time for a nap?
There are different ways of recharging. Naps could be one of them, but maybe you just need to get off your feet for 20 minutes. Maybe you need to do a meditation or mindfulness exercise and just close your eyes for five minutes.
How do you minimize the effects of jet lag?
We try to shift one hour per day. That’s the standard way of doing it. If you can, it’s super helpful. But it’s not always possible.
The thing we tell athletes is that our bodies are incredible, and you will even things out if you can get back on schedule. One or two nights of crummy sleep is not going to impact your overall performance.
What advice do you give athletes who have trouble falling asleep the night before a competition?
You don’t want to change much right before a competition, so I usually direct athletes to do what they would normally do.
Do you need to unwind by reading a book? Do you need to talk on the phone with somebody and get your mind off things? Can you put your mind in a really restful place and think about things that are really relaxing?
Are there any mindfulness or meditation exercises that you find helpful?
There are some athletes who benefit greatly from an hourlong meditation. I love something quick, something to reset my brain, maybe close my eyes for a minute.
If I’m feeling like I need to take a moment, I love mindful eating. You savor a bite and go, “Oh, my gosh, I have not been fully engaged with my senses today.” Or you could take a mindful walk and take in the sights, the smells, all of the things that are around you.
What do you eat when you need a quick nutrition boost?
Cashews. I tend to carry those with me. They’ve got enough energy to make sure I keep going, physically.
I’ve always got gummy bears on me too. There’s no nutritional value but they keep me going mentally. I’m a big proponent of both.
Is it OK to be superstitious in sports?
It depends how flexible you are. Maybe you put on your socks or shoes a certain way, or listen to certain music. Routines are really soothing. They set your brain up for success in a particular performance. It can be really, really helpful.
But I’ve also seen an athlete forget their lucky underwear or their lucky socks, and they’re all out of sorts. So your routine has to be flexible enough that you’re not going to completely fall apart if you don’t do it exactly.
Are Olympians made of stronger psychological stuff than the rest of us?
Not necessarily. There are some who don’t get feathers ruffled and have a high tolerance for the fanfare. There’s also a lot of regular human beings who just happen to be fantastic at a particular activity.
Science
‘Ready, Steady, Slow’: Championship Snail Racing at 0.006 M.P.H.

Earlier this month, the rural village of Congham, England, played host to a less likely group of athletes: dozens of garden snails. They had gathered to compete in the World Snail Racing Championships, where the world record time for completing the 13.5 inch course stands at 2 minutes flat. At that speed — roughly 0.006 miles per hour — it would take the snails more than six days to travel a mile.
Science
Caring for condor triplets! Record 17 chicks thrive at L.A. Zoo under surrogacy method
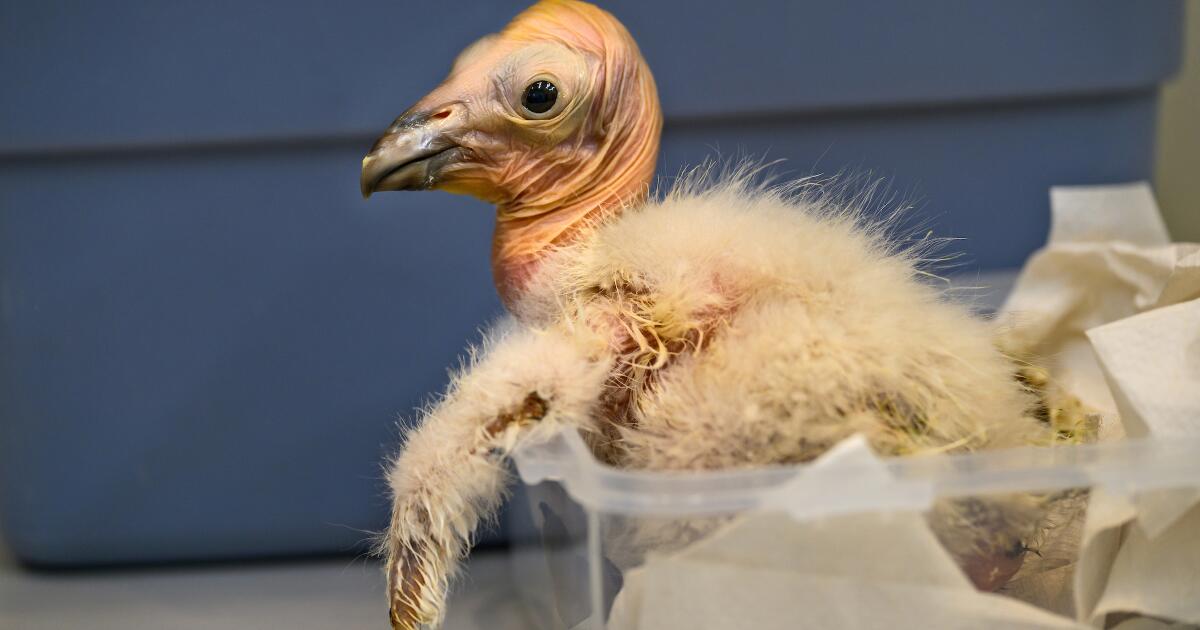

A new method of rearing California condors at the Los Angeles Zoo has resulted in a record-breaking 17 chicks hatched this year, the zoo announced Wednesday.
All of the newborn birds will eventually be considered for release into the wild under the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s California Condor Recovery Program, a zoo spokesperson said.
“What we are seeing now are the benefits of new breeding and rearing techniques developed and implemented by our team,” zoo bird curator Rose Legato said in a statement. “The result is more condor chicks in the program and ultimately more condors in the wild.”
Breeding pairs of California condors live at the zoo in structures the staff “affectionately calls condor-miniums,” spokesperson Carl Myers said. When a female produces a fertilized egg, the egg is moved to an incubator. As its hatching approaches, the egg is placed with a surrogate parent capable of rearing the chick.
California condor eggs are cared for at L.A. Zoo. The animal is critically endangered.
(Jamie Pham / L.A. Zoo)
This bumper year of condor babies is the result of a modification to a rearing technique pioneered at the L.A. Zoo.
Previously, when the zoo found itself with more fertilized eggs than surrogate adults available, staff raised the young birds by hand. But condors raised by human caretakers have a lower chance of survival in the wild (hence the condor puppets that zookeepers used in the 1980s to prevent young birds from imprinting on human caregivers).
In 2017, the L.A. Zoo experimented with giving an adult bird named Anyapa two eggs instead of one. The gamble was a success. Both birds were successfully released into the wild.
Faced with a large number of eggs this year, “the keepers thought, ‘Let’s try three,’” Myers said. “And it worked.”
The zoo’s condor mentors this season ultimately were able to rear three single chicks, eight chicks in double broods and six chicks in triple broods. The previous record number of 15 chicks was set in 1997.
Condor experts applauded the new strategy.
“Condors are social animals and we are learning more every year about their social dynamics. So I’m not surprised that these chick-rearing techniques are paying off,” said Jonathan C. Hall, a wildlife ecologist at Eastern Michigan University. “I would expect chicks raised this way to do well in the wild.”
The largest land bird in North America with an impressive wingspan up to 9½ feet, the California condor could once be found across the continent. Its numbers began to decline in the 19th century as human settlers with modern weapons moved into the birds’ territory. The scavenger species was both hunted by humans and inadvertently poisoned by lead bullet fragments embedded in carcasses it ate. The federal government listed the birds as an endangered species in 1967.
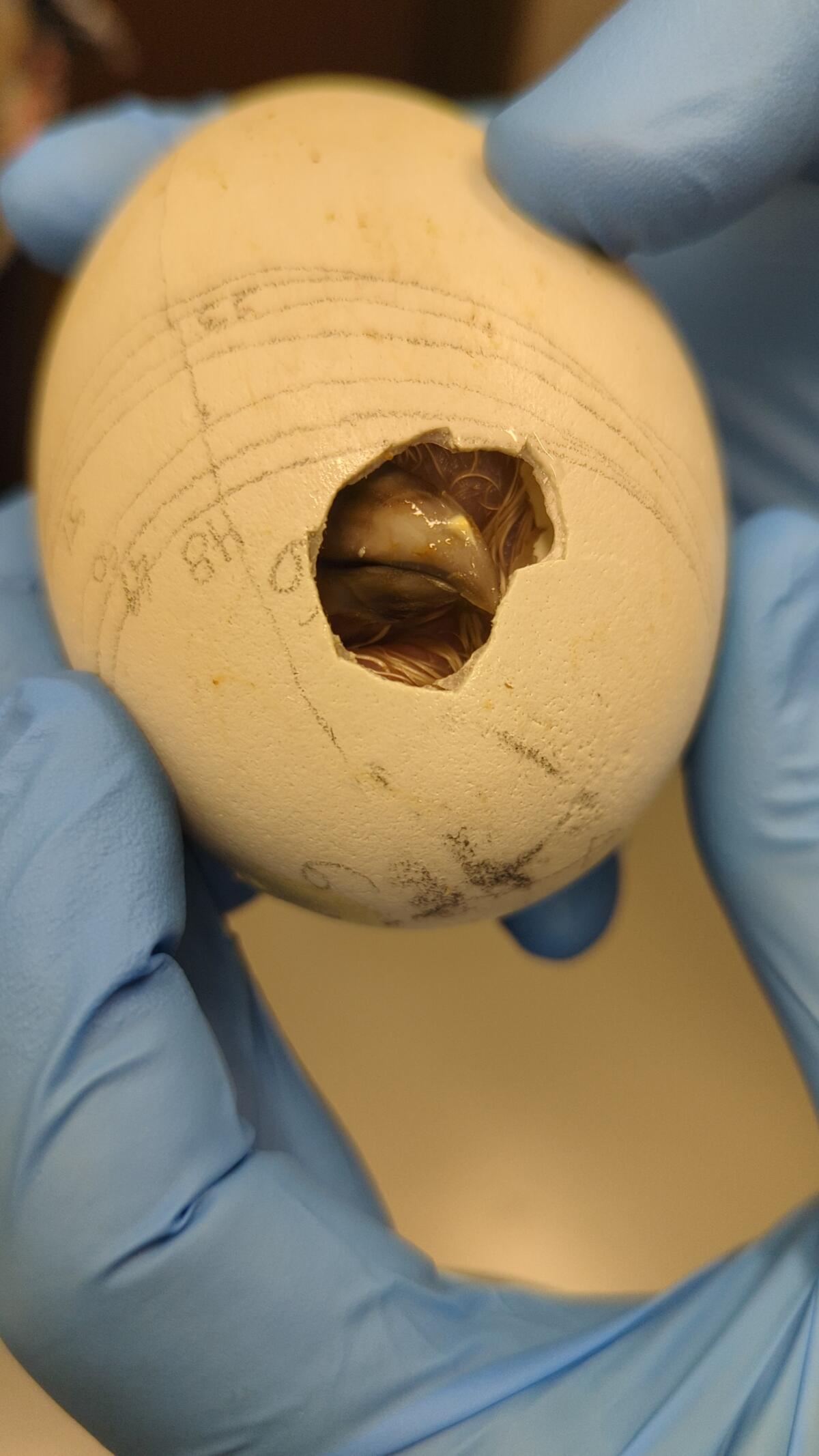

A condor, one of a record-breaking 17 at the zoo, makes its way out of its shell.
(Jamie Pham / L.A. Zoo)
When the California Condor Recovery Program began four decades ago, there were only 22 California condors left on Earth. As of December, there were 561 living individuals, with 344 of those in the wild. Despite the program’s success in raising the population’s numbers, the species remains critically endangered.
In addition to the ongoing threat of lead poisoning, the large birds are also at risk from other toxins. One 2022 study found more than 40 DDT-related compounds in the blood of wild California condors — chemicals that had made their way from contaminated marine life to the top of the food chain.
“Despite our success in returning condors to the wild, free-flying condors continue to face many obstacles with lead poisoning being the No. 1 cause of mortality,” said Joanna Gilkeson, spokesperson for Fish and Wildlife’s Pacific Southwest Region. “Innovative strategies, like those the L.A. Zoo is implementing, help us to produce more healthy chicks and continue releasing condors into the wild.”
The chicks will remain in the zoo’s care for the next year and a half before they are evaluated for potential release to the wild. Thus far, the zoo has contributed 250 condor chicks to Fish and Wildlife’s program, some of which the agency has redeployed to other zoos as part of its conservation efforts.
In a paper published earlier this year, a team of researchers found that birds born in captivity have slightly lower survival rates for their first year or two but then have equally successful outcomes to wild-hatched birds.
“Because condors reproduce slowly, releases of captive-bred birds are essential to the recovery of the species, especially in light of ongoing losses due to lead-related mortality,” said Victoria Bakker, a quantitative ecologist at Montana State University and lead author of the paper. “The team at the L.A. Zoo should be recognized for their innovative and important contributions to condor recovery.”
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt














Pingback: Report Calls Out Healthcare Provider for Canceling Appointments for Patients With Unpaid Debts – AccountsRecovery.net