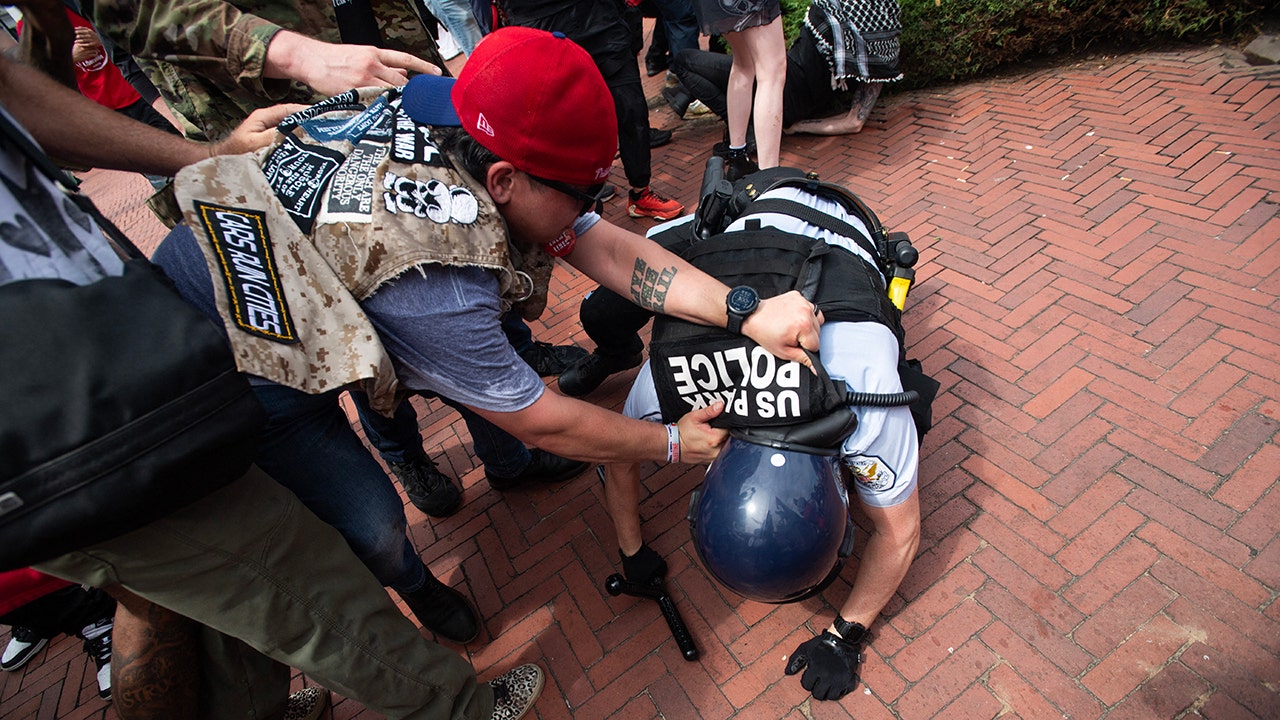Science
Column: Two Rutgers professors are accused of poisoning the debate over COVID's origins. Here's why

In a Dec. 2 tweet, Richard H. Ebright, a professor of chemistry and chemical biology at Rutgers University, stated that Anthony Fauci, the respected virologist and retired official of the National Institutes of Health, “is likely a murderer and provably a felon.”
In another tweet a few weeks earlier, he had compared Fauci to the Cambodian dictator Pol Pot, who was responsible for the genocidal massacre of as many as 2 million people in the 1970s.
Referring to an event at Case Western Reserve University honoring Fauci, Ebright wrote: “You may have missed the chance to hobnob with Pol Pot, but, Case Western will give you the chance to hobnob with Fauci, whose policy violations … likely killed 20 million.”
Every time I speak publicly, I now have a thought that there might be someone who has ingested this steady stream of distortions who might shoot me while I’m speaking.
— Michael Worobey, University of Arizona
In a tweet Aug. 25, 2022, Ebright’s colleague Bryce Nickels, a professor in the Rutgers department of genetics, called the “coordination” among virology researchers including Angela Rasmussen of the University of Saskatchewan and Michael Worobey of the University of Arizona an example of “pure, unfiltered evil.”
He illustrated the tweet with a GIF from the 1976 movie “Marathon Man” showing Dustin Hoffman being tortured by a character played by Lawrence Olivier and plainly inspired by Nazi doctor Josef Mengele.
This is the landscape on which a conflict over two theories about the origin of COVID-19 has been waged. One theory attributes the origin to unregulated trading in China of disease-susceptible wildlife, from which the virus that causes the disease is thought to have leaped to humans in a process known as a zoonotic spillover.
The other, the lab leak hypothesis, posits that the virus escaped from a virology lab in Wuhan, China, where it may have been deliberately concocted.
Let’s be clear: There is no evidence for a lab leak. No one has ever produced anything in its favor other than innuendo and conjecture. By contrast, evidence for a zoonotic transfer is almost overwhelming, has grown ever stronger over the years and is widely accepted by virologists and epidemiologists.
Ebright and Nickels are advocates of the lab-leak theory. For years they have been posting online insinuations or outright accusations of fraud, perjury, felonies and murder aimed at scientists who advocate for the zoonotic transfer theory.
Now a dozen scientists, some of whom have been direct targets of Ebright and Nickels, have called on Rutgers to open a formal investigation into whether its two faculty members have crossed the line distinguishing between responsible scientific debate and defamation, harassment, intimidation and threats.
Among the concerns the signatories aired in their March 14 complaint letter is that the professors’ actions and “inflammatory language,” such as “comparisons of working scientists to historical war criminals and mass murderers,” could “put some of us and … our colleagues in physical danger.”
Ebright’s and Nickels’ behavior, the complaint says, has unfolded in an atmosphere that had already produced “harassment including threats of death and/or violence because of our … scientific research.”
Ebright and Nickels say the complaint misrepresents their words and activities. “I never have compared any of the signatories to Josef Mengele or Pol Pot, and I never have characterized any of the signatories as murderers,” Ebright told me by email. He adds, “I also never have threatened or incited violence against any of the signatories.”
He did acknowledge calling four signatories “fraudsters,” based on their authorship of a 2020 scientific paper that favored zoonosis as the origin of COVID-19 and dismissed the lab-leak theory as implausible. “I stand by this characterization,” he wrote. He called the complaint “an effort to silence opponents and to prop up a collapsing narrative.”
Nickels told me by email, “the assertion that I have labeled any of the 12 signatories as murderers or endangered them or their colleagues is false and is defamatory with malice.” In his email, he accused the same four signatories mentioned by Ebright of fraud.
More on that shortly.
The complaint letter says that Ebright and Nickels have engaged in online harassment, intimidation and threats for years. According to Kristian Andersen, an evolutionary biologist at Scripps Research in La Jolla and the organizer of the complaint, a new element in their approach recently appeared: encouraging their followers to engage in physical contact with zoonosis advocates.
On March 12, Nickels tweeted a notice of a scientific conference in Washington at which Peter Daszak, the head of a research funding organization who has long been the target of vituperation by lab-leak advocates, would appear on a panel.
“Don’t miss your chance to meet Peter Daszak, author of the grant many consider the ‘Blueprint’ for SARS-CoV2!” he wrote. The reference was to a groundless accusation beloved by lab-leak advocates that a grant proposal sponsored by Daszak’s organization involved creating a virus in a Chinese lab that became SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID. Virologists say the grant proposal would not have produced such a virus. In any event, it was not funded.
“That was so far outside of what I would consider to be normal and ethical conduct in science that I said, we need to file a formal complaint,” Andersen told me. The scientists’ letter to Rutgers administrators doesn’t ask for any disciplinary action, but calls for “immediate and serious review by the administration” of public behavior by Ebright and Nickels.
The call by Ebright and Nickels for followers to show up at a talk by Daszak stepped up the anxiety many scientists feel about their own public appearances.
“Every time I speak publicly, I now have a thought that there might be someone who has ingested this steady stream of distortions who might shoot me while I’m speaking,” says Worobey, a signatory of the complaint whose research helped to establish a seafood and wildlife market in Wuhan, not a lab, as the likely site of the first zoonosis transfers. “With those escalations recently, I thought it was time to deal with it head-on.”
Vaccine science, immigration and elections are all battlegrounds for the war between information and disinformation today. The temperature of debates on these topics is only heightened by the tendency of social media platforms such as Twitter (now X) to encourage intemperate speech. But science and health seem to be areas especially vulnerable to efforts at falsification.
A brief primer on the lab-leak hypothesis may be useful here. During the earliest weeks of the COVID pandemic, many virologists examining the SARS-CoV-2 virus, including Andersen, spotted unfamiliar features, some so unusual that they conjectured the features might have been man-made.
Further research in the ensuing weeks revealed, however, that these features were not unusual, but common, and that they could develop in viruses such as SARS2 through natural processes. Andersen and others eventually concluded that a laboratory role in COVID’s emergence was implausible.
That conclusion was written into a seminal paper on the virus published in Nature Medicine on March 17, 2020, and titled “The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2.” Its authors included Andersen, Robert F. Garry of Tulane University, Andrew Rambaut of the University of Edinburgh and Edward C. Holmes of the University of Sydney.
All four signed the complaint letter to Rutgers. They’re the four scientists Ebright and Nickels accused of fraud in their emails to me, based on the Rutgers scientists’ claim that the proximal origin paper was fashioned to serve what Ebright and Nickels assert was the authors’ and Fauci’s desire to downplay
Fauci’s role in funding virology research in China.
Ebright further accused Andersen and Garry of perjury, based on their denials at a congressional hearing in July that Fauci pressured them to advocate for the zoonosis theory in their paper.
After the paper’s publication, the lab-leak hypothesis moved into the partisan political realm. Republicans in Congress cherish the notion that Andersen and his colleagues deliberately minimized a laboratory role at Fauci’s behest.
There is not a scintilla of evidence for that assertion, as Andersen and Garry made clear by cogently explaining at the July hearing called by conspiracy-addled House Republicans how the normal process of scientific research led them to the paper’s conclusions.
Last March, FBI Director Christopher Wray stated in an interview with Fox News that the bureau had concluded with “moderate confidence” that the virus had escaped from the Chinese lab, but he cited no evidence and didn’t explain its grounds.
The FBI’s assessment had been part of a survey of all U.S. intelligence agencies that largely contradicted the FBI’s position. In June, it was further contradicted by a report from the Office of the Director of National Intelligence, which refuted claims that the Chinese lab had played a role in the pandemic.
That brings us back to Ebright and Nickels. Although insults and invective are hardly uncommon in exchanges over COVID’s origins, their contributions have often carried a remarkably noxious tone.
The defense by both that they never compared the complainants to Pol Pot or Mengele or characterized them as murderers may be true as far as it goes. But it’s too clever by half. The complainants didn’t say in their letter to Rutgers that they themselves were necessarily the targets of Ebright’s and Nickels’ odious comparisons. Their complaint says the pair had “made comparisons of working scientists” — i.e., other scientists — “to historical war criminals and mass murderers.”
So let’s look at the record.
Ebright has repeatedly intimated that Fauci is a murderer, based on his view that his agency funded dangerous virology research in the Chinese lab that produced the pandemic. There is no evidence that any research the U.S. government funded in China produced the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or even that any such research at that lab was scientifically possible.
On Nov. 13, Ebright wrote of Fauci, “any person whose violations of U.S. government policies … resulted in 20 million deaths is, by any rational standard, a murderer.” It’s unclear what “violations” he was referring to.
In a June 27 tweet, Ebright described Fauci as “an octogenarian serially misfeasant, serially malfeasant, serially perjurious, former bureaucrat likely to face criminal charges after Jan 2025” (i.e., presumably assuming that Donald Trump would then take office again).
On Dec. 23 he tweeted that the “only option” to “mitigate the negative effects” of the proximal origin paper was the referral of Andersen and his colleagues “for criminal prosecution.”
On July 10, 2021, Ebright responded with the following comment to a tweet that apparently had alluded to critics of the lab-leak theory: “Sociopaths will be sociopaths … See Mengele. See Ishii.” The latter reference is to Shirō Ishii, who headed Japan’s World War II bioweapons program, which has been blamed for the deaths of as many as 300,000 people.
On Sept. 5 and 6, 2022, Ebright summarized the case for the lab-leak hypothesis, which he tied to “labs conducting world’s largest research program on bat SARS-like coronaviruses.” He ended the thread with the phrase “The banality of evil” — philosopher Hannah Arendt’s description of the impression left on her by Adolph Eichmann, the architect of the Nazi program of Jewish genocide, whose trial in Israel she reported on.
Nickels, in addition to posting the Mengele-linked film clip, earlier this month tweeted “massive respect to … military veterans that have taken a stand” against scientists he asserted had lied about research “impacting national security.” He called the behavior of such scientists “treasonous” and he specifically named among those deserving respect, one Andrew G. Huff.
One day earlier, Huff, who labels the zoonosis theory a “lie,” tweeted a call for Fauci, Daszak and virologist Ralph Baric of the University of North Carolina to be hauled before a military tribunal. Subsequently, he tweeted that his followers had voted in an online poll that if convicted, they should be hanged. He illustrated that tweet with a film clip of three people plunging to their deaths on a gallows.
The ball is now in Rutgers’ court. The university says the complaint “will be forwarded to the appropriate offices for review.” It didn’t say what issues would be considered. But certainly a determination would be warranted of whether its faculty members’ actions conform to the school’s policy on free expression, which frowns on actions or behaviors that “threaten individuals or cause an injury to someone” or “harass, threaten violence, or intimidate others.”
Whatever the outcome is of any such inquiry, the scientific community is right to be appalled by Ebright’s and Nickels’ activities. There’s vast latitude in science for disagreement and debate, but calling one’s adversaries or critics criminals or traitors, or placing them in the same category as Mengele, Eichmann and Pol Pot? That isn’t scientific debate.
In the world of science, the reputations of Andersen, Worobey, Garry, Holmes and Rambaut are secure; their finding that COVID most likely originated in the wildlife trade has not only held up over time but also been validated by subsequent studies. The same is true of the other eight signatories of the complaint letter, and Fauci and Daszak (who are not signatories).
Ebright and Nickels? They may be a different story.

Science
Q&A: Learn how Olympians keep their cool from Team USA's chief sports psychologist

Your morning jog or weekly basketball game may not take place on an Olympic stage, but you can use Team USA’s techniques to get the most out of your exercise routine.
It’s not all about strength and speed. Mental fitness can be just as important as physical fitness.
That’s why the U.S. Olympic & Paralympic Committee created a psychological services squad to support the mental health and mental performance of athletes representing the Stars and Stripes.
“I think happy, healthy athletes are going to perform at their best, so that’s what we’re striving for,” said Jessica Bartley, senior director of the 15-member unit.
Bartley studied sports psychology and mental health after an injury ended her soccer career. She joined the USOPC in 2020 and is now in Paris with Team USA’s 592 competitors, who range in age from 16 to 59.
Bartley spoke with The Times about how her crew keeps Olympic athletes in top psychological shape, and what the rest of us can learn from them. Her comments have been edited for length and clarity.
Why is exercise good for mental health?
It gets you moving. It gets the endorphins going. And there’s often a lot of social aspects that are really helpful.
There are a number of sports that stretch your brain in ways that can be really, really valuable. You’re thinking about hand-eye coordination, or you’re thinking about strategy. It can improve memory, concentration, even critical thinking.
What’s the best way to get in the zone when it’s time to compete?
When I work with athletes, I like to understand what their zone is. If a 0 or a 1 is you’re totally chilled out and a 10 is you’re jumping around, where do you need to be? What’s your number?
People will say, “I’m at a 10 and I need to be at an 8 or a 7.” So we’ll talk about ways of bringing it down, whether it’s taking a deep breath, listening to relaxing music, or talking to your coach. Or there’s times when people say they need to be more amped up. That’s when you see somebody hitting their chest, or jumping up and down.
If you make a mistake in the middle of a competition, how do you move on instead of dwelling on it?
I often teach athletes a reset routine. I played goalie, so I had a lot of time to think after getting scored on. I would undo my goalie gloves and put them back on, which to me was a reset. I would also wear an extra hairband on my wrist, and when I would snap it, that meant I needed to get out of my head.
It’s not just a physical reset — it helps with a mental reset. If you do the same thing every single time, it goes through the same neural pathway to where it’s going to reset the brain. That can be really impactful.
Do Olympic athletes have to deal with burnout?
Oh, yeah. Everybody has a day where they don’t want to do whatever it is. That’s when you have to ask, “What’s in my best interests? Do I need a recovery day, or do I really need to get in the pool, or get in the gym?”
Sometimes you really do need what we like to refer to as a mental health day.
How can you psych yourself up for a workout when you just aren’t feeling it?
It’s really helpful to think about why you’re doing this and why you’re pushing yourself. Do you have goals related to an activity or sport? Is there something tied to values around hard work or discipline, loyalty or dependability?
When you don’t want to get in the gym, when you don’t want to go for a run, think about something bigger. Tie it back to values.
Is sleep important for maintaining mental health?
Yes! We started doing mental health screens with athletes before the Tokyo Games. We asked about depression, anxiety, disordered eating and body image, drugs and alcohol, and sleep. Sleep was actually our No. 1 issue. It’s been a huge initiative for us.
How much sleep should we be getting?
It’s different for everyone, but generally we know seven to nine hours of sleep is good. Sometimes some of these athletes need 10 hours.
I highly recommend as much sleep as you need. If you didn’t get enough sleep, napping can be really valuable.
Is napping just for Olympic athletes or is it good for everybody?
Everybody! Naps are amazing.
What if there’s no time for a nap?
There are different ways of recharging. Naps could be one of them, but maybe you just need to get off your feet for 20 minutes. Maybe you need to do a meditation or mindfulness exercise and just close your eyes for five minutes.
How do you minimize the effects of jet lag?
We try to shift one hour per day. That’s the standard way of doing it. If you can, it’s super helpful. But it’s not always possible.
The thing we tell athletes is that our bodies are incredible, and you will even things out if you can get back on schedule. One or two nights of crummy sleep is not going to impact your overall performance.
What advice do you give athletes who have trouble falling asleep the night before a competition?
You don’t want to change much right before a competition, so I usually direct athletes to do what they would normally do.
Do you need to unwind by reading a book? Do you need to talk on the phone with somebody and get your mind off things? Can you put your mind in a really restful place and think about things that are really relaxing?
Are there any mindfulness or meditation exercises that you find helpful?
There are some athletes who benefit greatly from an hourlong meditation. I love something quick, something to reset my brain, maybe close my eyes for a minute.
If I’m feeling like I need to take a moment, I love mindful eating. You savor a bite and go, “Oh, my gosh, I have not been fully engaged with my senses today.” Or you could take a mindful walk and take in the sights, the smells, all of the things that are around you.
What do you eat when you need a quick nutrition boost?
Cashews. I tend to carry those with me. They’ve got enough energy to make sure I keep going, physically.
I’ve always got gummy bears on me too. There’s no nutritional value but they keep me going mentally. I’m a big proponent of both.
Is it OK to be superstitious in sports?
It depends how flexible you are. Maybe you put on your socks or shoes a certain way, or listen to certain music. Routines are really soothing. They set your brain up for success in a particular performance. It can be really, really helpful.
But I’ve also seen an athlete forget their lucky underwear or their lucky socks, and they’re all out of sorts. So your routine has to be flexible enough that you’re not going to completely fall apart if you don’t do it exactly.
Are Olympians made of stronger psychological stuff than the rest of us?
Not necessarily. There are some who don’t get feathers ruffled and have a high tolerance for the fanfare. There’s also a lot of regular human beings who just happen to be fantastic at a particular activity.
Science
‘Ready, Steady, Slow’: Championship Snail Racing at 0.006 M.P.H.

Earlier this month, the rural village of Congham, England, played host to a less likely group of athletes: dozens of garden snails. They had gathered to compete in the World Snail Racing Championships, where the world record time for completing the 13.5 inch course stands at 2 minutes flat. At that speed — roughly 0.006 miles per hour — it would take the snails more than six days to travel a mile.
Science
Caring for condor triplets! Record 17 chicks thrive at L.A. Zoo under surrogacy method
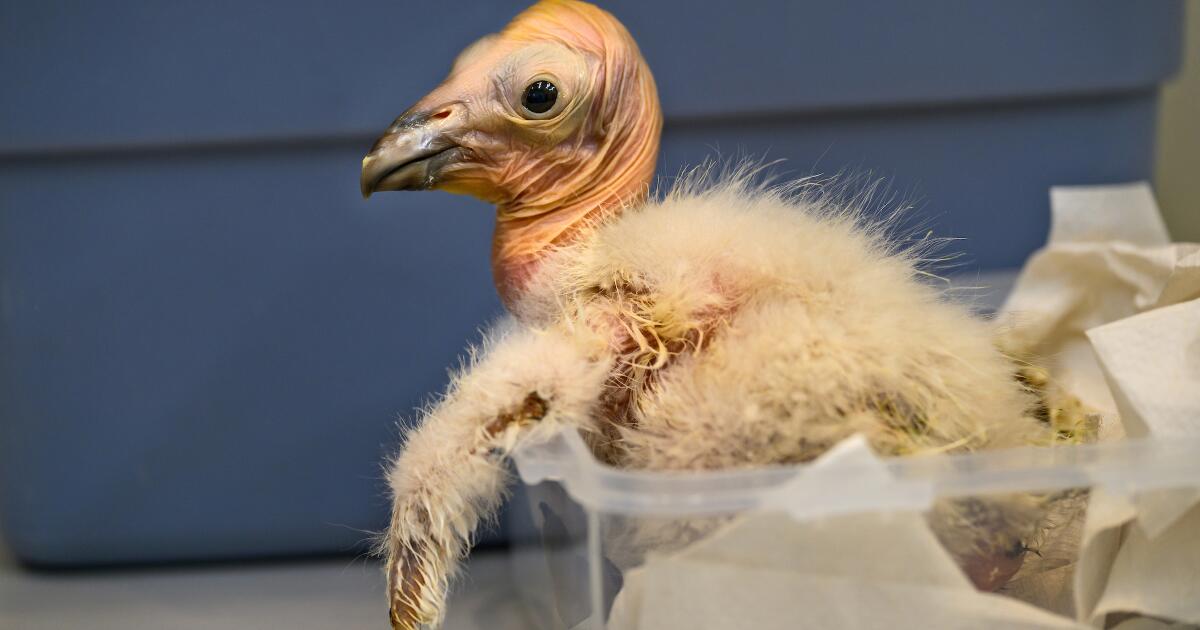

A new method of rearing California condors at the Los Angeles Zoo has resulted in a record-breaking 17 chicks hatched this year, the zoo announced Wednesday.
All of the newborn birds will eventually be considered for release into the wild under the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s California Condor Recovery Program, a zoo spokesperson said.
“What we are seeing now are the benefits of new breeding and rearing techniques developed and implemented by our team,” zoo bird curator Rose Legato said in a statement. “The result is more condor chicks in the program and ultimately more condors in the wild.”
Breeding pairs of California condors live at the zoo in structures the staff “affectionately calls condor-miniums,” spokesperson Carl Myers said. When a female produces a fertilized egg, the egg is moved to an incubator. As its hatching approaches, the egg is placed with a surrogate parent capable of rearing the chick.
California condor eggs are cared for at L.A. Zoo. The animal is critically endangered.
(Jamie Pham / L.A. Zoo)
This bumper year of condor babies is the result of a modification to a rearing technique pioneered at the L.A. Zoo.
Previously, when the zoo found itself with more fertilized eggs than surrogate adults available, staff raised the young birds by hand. But condors raised by human caretakers have a lower chance of survival in the wild (hence the condor puppets that zookeepers used in the 1980s to prevent young birds from imprinting on human caregivers).
In 2017, the L.A. Zoo experimented with giving an adult bird named Anyapa two eggs instead of one. The gamble was a success. Both birds were successfully released into the wild.
Faced with a large number of eggs this year, “the keepers thought, ‘Let’s try three,’” Myers said. “And it worked.”
The zoo’s condor mentors this season ultimately were able to rear three single chicks, eight chicks in double broods and six chicks in triple broods. The previous record number of 15 chicks was set in 1997.
Condor experts applauded the new strategy.
“Condors are social animals and we are learning more every year about their social dynamics. So I’m not surprised that these chick-rearing techniques are paying off,” said Jonathan C. Hall, a wildlife ecologist at Eastern Michigan University. “I would expect chicks raised this way to do well in the wild.”
The largest land bird in North America with an impressive wingspan up to 9½ feet, the California condor could once be found across the continent. Its numbers began to decline in the 19th century as human settlers with modern weapons moved into the birds’ territory. The scavenger species was both hunted by humans and inadvertently poisoned by lead bullet fragments embedded in carcasses it ate. The federal government listed the birds as an endangered species in 1967.
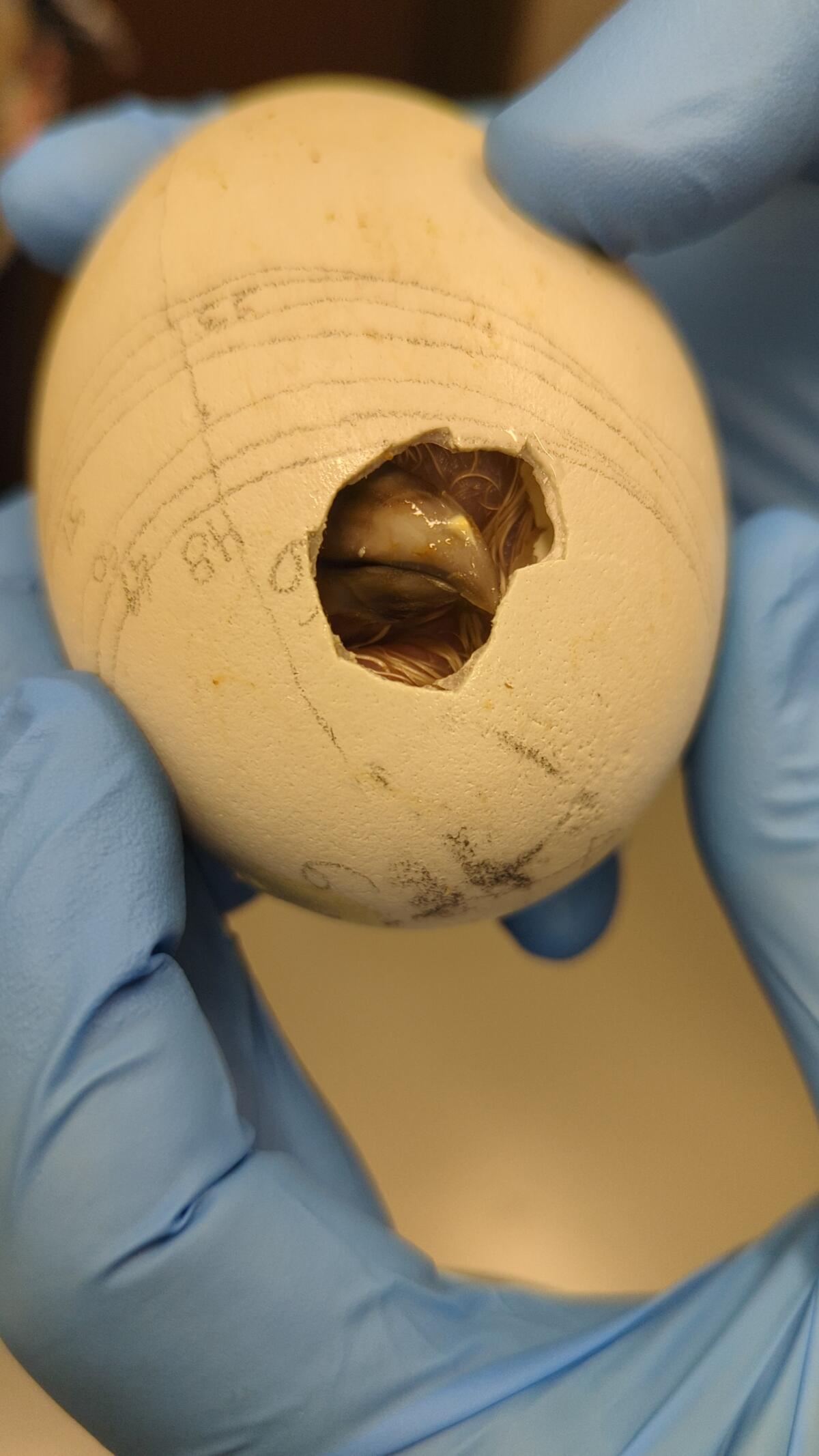

A condor, one of a record-breaking 17 at the zoo, makes its way out of its shell.
(Jamie Pham / L.A. Zoo)
When the California Condor Recovery Program began four decades ago, there were only 22 California condors left on Earth. As of December, there were 561 living individuals, with 344 of those in the wild. Despite the program’s success in raising the population’s numbers, the species remains critically endangered.
In addition to the ongoing threat of lead poisoning, the large birds are also at risk from other toxins. One 2022 study found more than 40 DDT-related compounds in the blood of wild California condors — chemicals that had made their way from contaminated marine life to the top of the food chain.
“Despite our success in returning condors to the wild, free-flying condors continue to face many obstacles with lead poisoning being the No. 1 cause of mortality,” said Joanna Gilkeson, spokesperson for Fish and Wildlife’s Pacific Southwest Region. “Innovative strategies, like those the L.A. Zoo is implementing, help us to produce more healthy chicks and continue releasing condors into the wild.”
The chicks will remain in the zoo’s care for the next year and a half before they are evaluated for potential release to the wild. Thus far, the zoo has contributed 250 condor chicks to Fish and Wildlife’s program, some of which the agency has redeployed to other zoos as part of its conservation efforts.
In a paper published earlier this year, a team of researchers found that birds born in captivity have slightly lower survival rates for their first year or two but then have equally successful outcomes to wild-hatched birds.
“Because condors reproduce slowly, releases of captive-bred birds are essential to the recovery of the species, especially in light of ongoing losses due to lead-related mortality,” said Victoria Bakker, a quantitative ecologist at Montana State University and lead author of the paper. “The team at the L.A. Zoo should be recognized for their innovative and important contributions to condor recovery.”
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt