Nearly a year after catastrophic flooding struck Vermont, the city of Barre confronts the overwhelming task of steeling itself for the next climate disaster.
Vermont
Vermont Captive YouTube created

The Vermont Division of Financial Growth has opened a brand new YouTube channel on Vermont captives.
Within the newest Vermont Captive publication it stated that the channel is: “That includes every part Vermont Captive, from informational movies highlighting our wealthy, 42-year historical past and unparalleled legislative help to in-depth interviews with Vermont captive house owners, detailing how Vermont Captive has helped them thrive.
“Have a look and study why Vermont is called the Gold Normal of captive insurance coverage.”
You may entry the Vermont Captive YouTube channel right here.

Vermont
How ruinous floods put Vermont at the forefront of the climate battle

Across the country, state and local leaders are scrambling to find the money they need to protect their communities from worsening disasters fueled by climate change. For Barre, needed flood mitigation projects will cost the city an estimated $30 million over the next five years, Lauzon said.
Yet Vermont has a new answer to this problem.
Earlier this month, it became the nation’s first state to require fossil fuel companies and other big emitters to pay for the climate-related damage their pollution has already caused statewide. While conservative legal experts are skeptical the law will survive challenges, some Vermonters said they are both grateful and a little nervous that one of the nation’s least populous states has picked a fight with one of America’s most powerful industries.
“I’m proud to have this state stand up and say, ‘Look, you need to be held accountable, and you need to help us with the damage we incurred,’” Lauzon said. “But I’m also scared to death. I feel like we’re a pee wee football team going up against the 2020 New England Patriots.”
The Vermont law comes as oil and gas companies face dozens of climate lawsuits, both in the United States and abroad. While none of the state and local lawsuits have gone to trial yet — including Vermont’s own challenge, filed in 2021 — they pose a growing threat and add to the companies’ potential liabilities. If Vermont’s novel approach endures, it could reverberate across the industry.
Republicans are pushing back, arguing that individual states cannot apply their own laws to a global pollutant. Last month, Republican attorneys general in 19 states asked the Supreme Court to block the climate change lawsuits brought by California, Connecticut, Minnesota, New Jersey and Rhode Island against fossil fuel companies.
Vermont’s law authorizes the state to charge major polluters a fee for the share of greenhouse gas emissions they produced between 1995 and 2024. It is modeled on the 1980 federal Superfund law, which forces polluting companies to clean up toxic waste sites.
The law doesn’t spell out how much money should be paid; instead, it tasks the state treasurer with assessing the damage Vermont has suffered from climate change and what it will cost to prepare for future impacts. The final tally is expected to be comprehensive, factoring in an array of possible costs from rebuilding and raising bridges and roads to lower worker productivity from rising heat.
Bills similar to Vermont’s have been introduced in several states, including California, Maryland and Massachusetts. Last week, New York lawmakers passed a climate superfund law that would require polluters to pay $3 billion a year for 25 years. It is now awaiting Democratic Gov. Kathy Hochul’s signature.
The timing of the Vermont law was no accident, said Ben Edgerly Walsh, the climate and energy program director of the Vermont Public Interest Research Group. Memories of last July’s flooding — which inundated the state capitol of Montpelier, damaged thousands of homes and trapped people in small mountain towns — are still fresh.
Over the last year, Vermonters have also endured a freak late-spring frost that damaged crops, hazy skies from smoke blown south from hundreds of wildfires in Canada, and more flooding in mid-December. All these events primed state lawmakers to tackle climate change at the beginning of 2024.
“When we brought this idea to legislators, they came to it with a very open mind in a way that may have taken more time, more convincing, in another year,” Edgerly Walsh said. “But this was a moment we just knew we needed to act.”
As disaster recovery costs mount, it has not been lost on state leaders that oil companies are enjoying massive profits. In 2023, the warmest year on record, the two largest U.S. energy companies, ExxonMobil and Chevron, together made more than $57 billion.
It might seem unlikely for a state like Vermont, with a population just under 650,000, to stand up to the fossil fuel industry. The state’s Republican governor, Phil Scott, expressed skepticism in a letter to the secretary of the Vermont Senate, writing, “Taking on ‘Big Oil’ should not be taken lightly. And with just $600,000 appropriated by the Legislature to complete an analysis that will need to withstand intense legal scrutiny from a well-funded defense, we are not positioning ourselves for success.”
Yet Vermont’s small budget — it has the lowest GDP in the country — means that it feels the rising risks from heavy rains more acutely than wealthier states. A report by Rebuild by Design, a nonprofit that helps communities recover from disasters, found that Vermont ranked fifth nationally in per capita disaster relief costs from 2011-2021, with $593 spent per resident.
The costs are only expected to climb. A 2022 study from University of Vermont researchers predicted that the cost of property damage from flooding alone may top $5.2 billion over the next 100 years.
Ultimately, the governor allowed the law to go into effect without his signature, saying he understood “the desire to seek funding to mitigate the effects of climate change that has hurt our state in so many ways.”
Legal challenges will inevitably follow — the only question is when.
The oil and gas industry’s top lobbying group, the American Petroleum Institute, has said that states don’t have the power to regulate carbon pollution and can’t retroactively charge companies for emissions allowed under the law. It has also emphasized individuals’ responsibility for climate change, noting that Vermont residents use fossil fuels to heat their homes and power their cars. Scott Lauermann, a spokesman for the group, said API is “considering all our options to reverse this punitive new fee.”
“I think the courts are going to have problems with the idea that Vermont can penalize the companies for past actions that were completely legal and the state itself relies on,” said Jeff Holmstead, an energy lawyer who served in the Environmental Protection Agency under George W. Bush. “I’m skeptical this will actually pass muster.”
Supporters and environmentalists involved in drafting the law said they believed they had created a legally defensible way to recover damages from polluters by modeling it after the Superfund law, which has been repeatedly upheld in court. Several legal experts said the state had also taken a more conservative approach than others by requiring a study before assessing companies’ liability, ensuring the fines levied against them are proportional to the amount of damage caused by their products.
Cara Horowitz, executive director of the UCLA School of Law’s Emmett Institute on Climate Change and the Environment, said that, inevitably, fossil fuel companies will challenge any bills Vermont submits for damages. But that is years off, she said, and the industry is likely to move sooner than that.
The lawsuits “will start soon and last a long time,” Horowitz said. “It would surprise me if they don’t preemptively try to undermine the entire exercise by declaring the whole thing unlawful.”
In Barre, Lauzon said he isn’t confident litigation over the law will be resolved in his lifetime. But even if the fossil fuel companies are never made to pay, he said, the law’s passage was the right thing to do.
“I can’t look at the north end, I can’t look at the city of Barre and say no one needs to be held accountable,” he said.
Vermont
Vt. author releases book on dealing with betrayal

BURLINGTON, Vt. (WCAX) – A Vermont author has released a new book to help people trying to recover from betrayal.
Bruce Chalmer is a psychologist and couples counselor. He says he wrote “Betrayal and Forgiveness: How to Navigate the Turmoil and Learn to Trust Again” because he found many of his clients were dealing with some kind of betrayal by someone they trusted.
Chalmer says the couples he has worked with who are able to find the meaning in it are the ones who can heal.
“When I say heal, they don’t always stay together. You can heal and not stay together, heal and stay together. But especially the ones that heal and are able to stay together. I find it very inspiring, and I wanted to write a book that talked about what it was about those couples that made it possible for them to heal in that way.”
Watch the video to see our Cat Viglienzoni’s full conversation with Chalmer.
Click here for more on “Betrayal and Forgiveness: How to Navigate the Turmoil and Learn to Trust Again” and where to buy it.
Copyright 2024 WCAX. All rights reserved.
Vermont
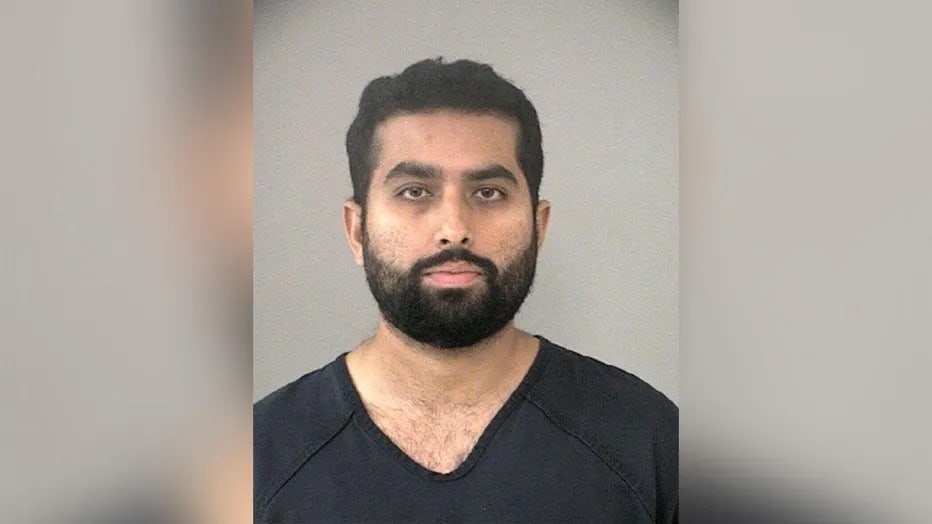
Two sought in Starksboro kidnapping, assault – Newport Dispatch

NEWPORT — On June 12, Vermont State Police responded to a reported kidnapping and assault stemming from an incident that took place on June 8 on Vermont Route 116 in Starksboro.
Authorities have identified the suspects as Anthony Seagroves, 32, from Hinesburg, and Katelynn Cannon, 28, from Essex.
The investigation alleges that Seagroves, armed with a baseball bat, coerced an adult household member into a vehicle and inflicted bodily harm while restraining the individual.
Cannon is accused of aiding Seagroves and assaulting the victim, attempting to cause serious injury.
Efforts to apprehend Seagroves on June 13 led to a pursuit when he fled in a gray Honda CR-V, with Vermont plates CRW914, believed to be driven by Cannon.
The current location of Seagroves and Cannon is unknown, and the public is urged not to approach them but to contact New Haven Barracks at 802-388-4919 or provide information anonymously at https://vsp.vermont.gov/tipsubmit.
The Burlington, Essex, Hinesburg, Shelburne, and University of Vermont police departments assisted the state troopers.
No further details have been released, but updates will be provided as the investigation continues.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIsrael used a U.S.-made bomb in a deadly U.N. school strike in Gaza
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 833
-
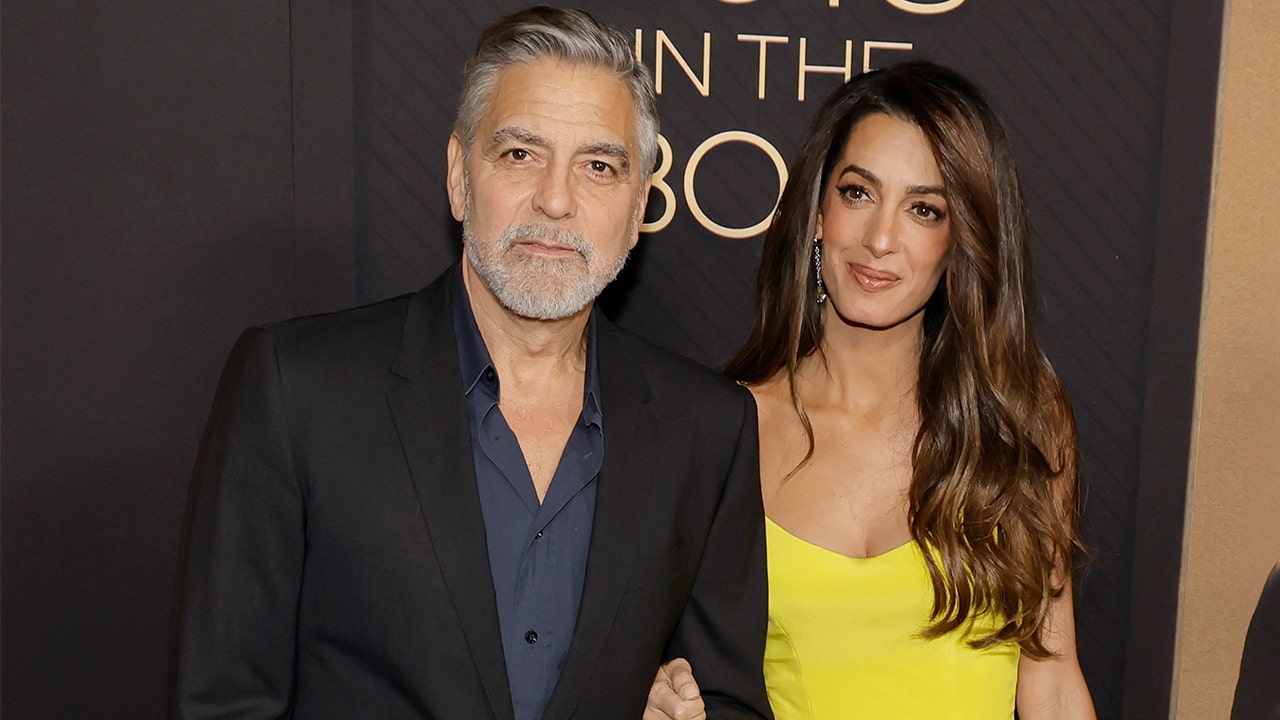

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoGeorge Clooney called White House to complain about Biden’s criticism of ICC and defend wife’s work: report
-
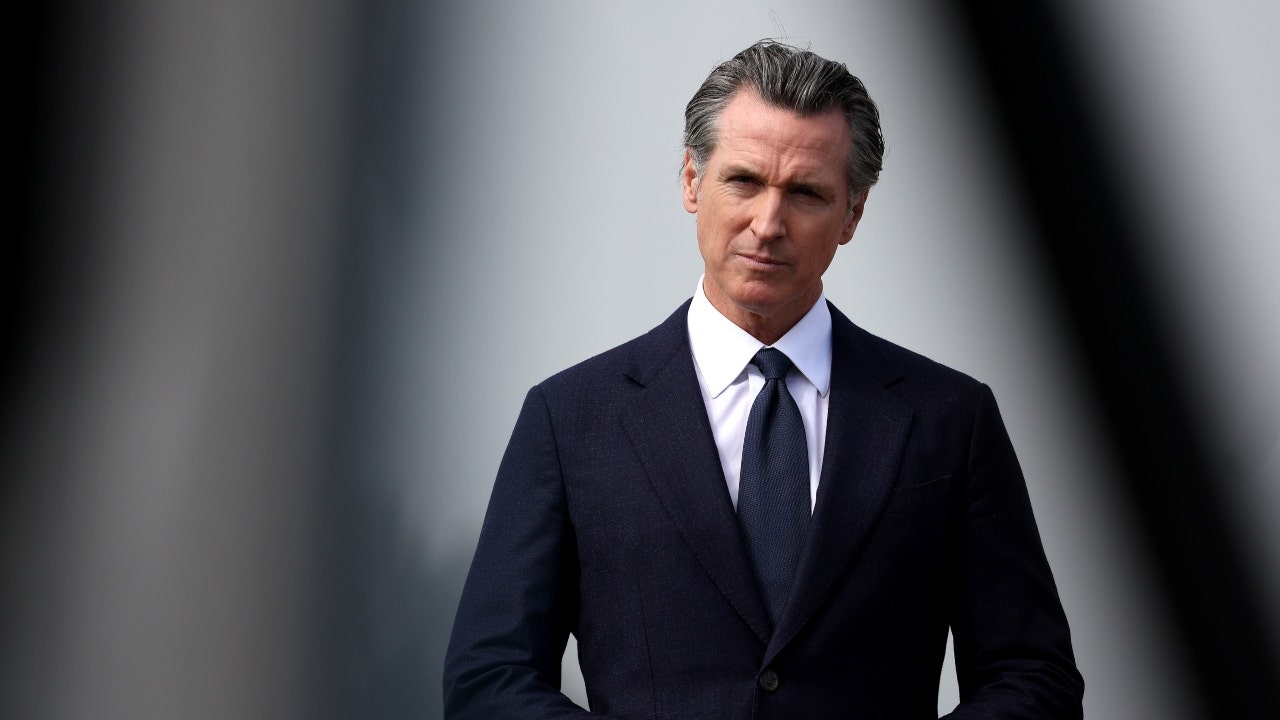

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNewson, Dem leaders try to negotiate Prop 47 reform off California ballots, as GOP wants to let voters decide
-
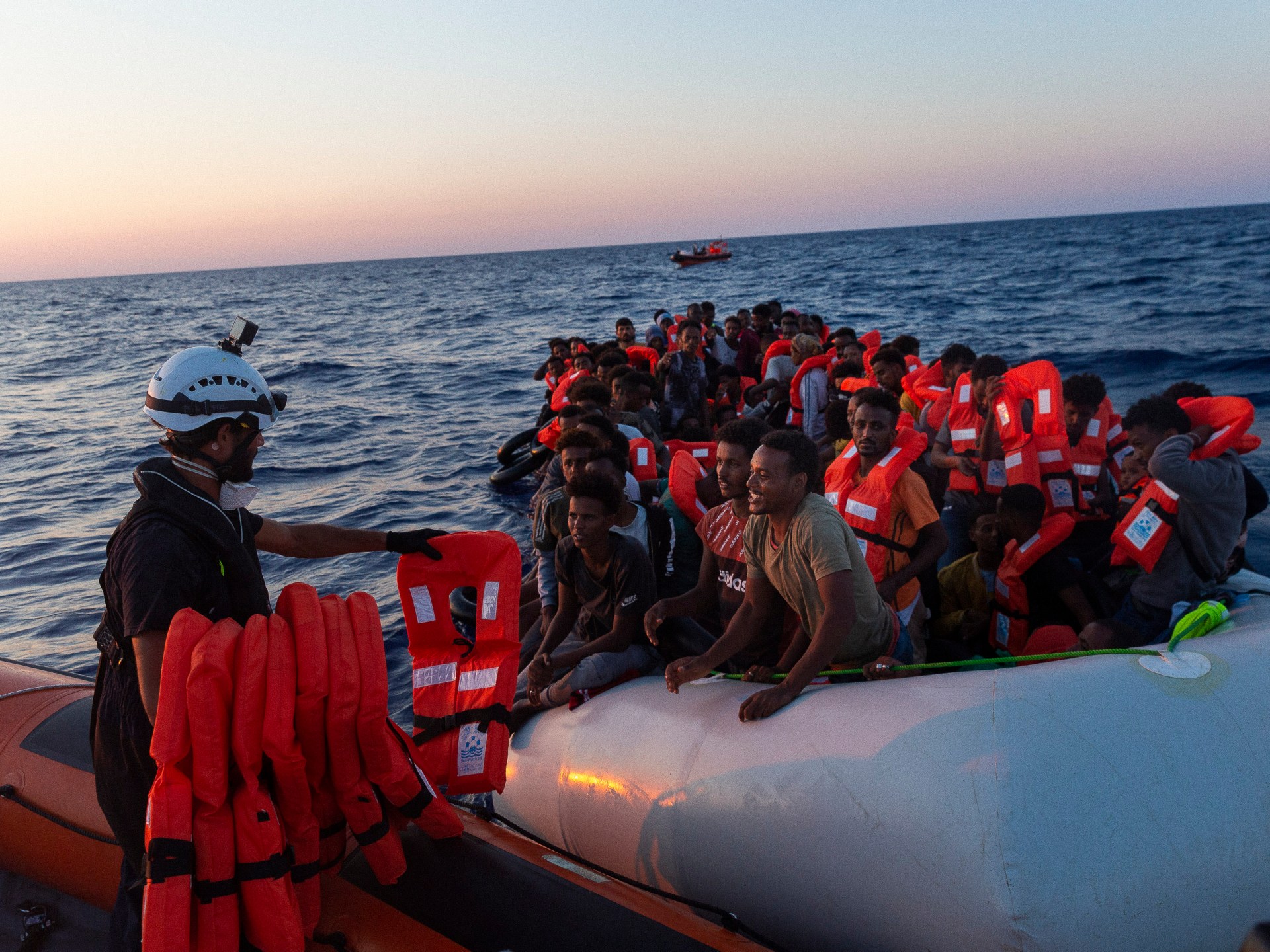

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago‘Bloody policies’: Bodies of 11 refugees and migrants recovered off Libya
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoEmbattled Biden border order loaded with loopholes 'to drive a truck through': critics
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoDozens killed near Sudan’s capital as UN warns of soaring displacement
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoVideo: U.S. Official Responds to Israeli Strike on a U.N. School in Gaza