Health
Once the Children Got Hungry, ‘the Fire Was Gone From Their Eyes’
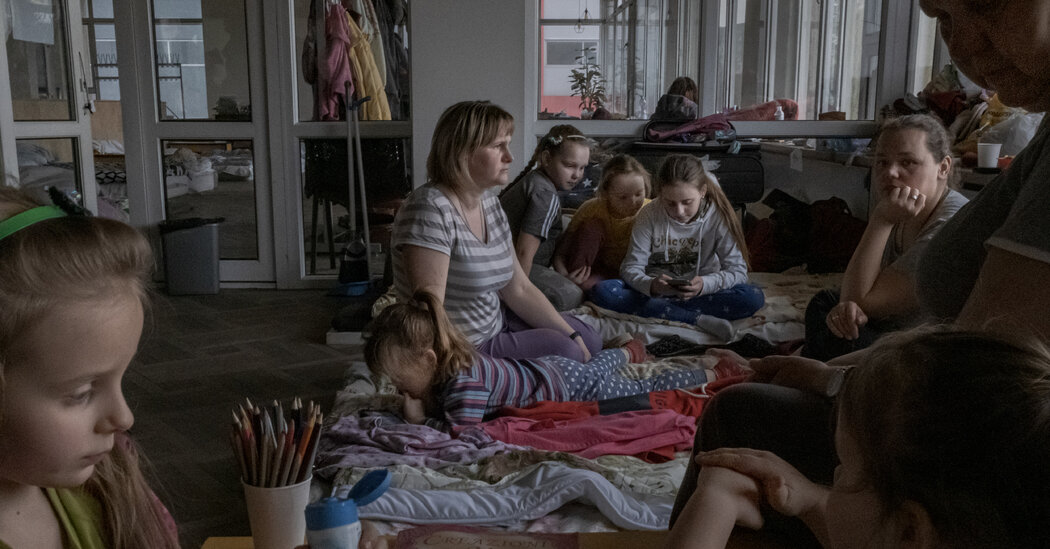

LVIV, Ukraine — After Russian forces surrounded the town of Mariupol in southern Ukraine, slicing off its water and gas and stopping assist convoys from coming into, Yulia Beley sheltered in a neighbor’s basement along with her three daughters and struggled to outlive.
Her husband was off defending the town, so she ventured out as bombs rained all the way down to fetch water from a distant nicely and tried to consolation her kids whereas the shelling shook the partitions and ceiling. In time, the household’s meals dwindled and Ms. Beley, a baker, stated she fed her hungry kids one bowl of porridge a day to share between them. Her 6-year-old daughter, Ivanka, dreamed of the poppy seed candy rolls her mom had made earlier than the battle.
“It tears you aside,” stated Ms. Beley, 33, nonetheless traumatized after her escape from the town per week in the past. “I simply sobbed, simply cried, screaming into the pillow when nobody might see.”
Shortly after Russia invaded Ukraine, it laid siege to Mariupol, utilizing the traditional warfare tactic to attempt to starve the once-bustling metropolis of 430,000 individuals into give up.
From the times when armies surrounded medieval castles in Europe to the battle of Stalingrad in World Conflict II and the squeeze placed on insurgent communities in Syria in the course of the 11-year civil battle, militaries have used sieges all through historical past whatever the catastrophic results on civilians caught within the center.
This month, Secretary of State Anthony J. Blinken accused Russia of “ravenous” cities in Ukraine. He invoked the reminiscence of the brother of President Vladimir V. Putin of Russia, Viktor, who died in infancy in the course of the German siege of Leningrad throughout World Conflict II.
“It’s shameful,” Mr. Blinken stated. “The world is saying to Russia: ‘Cease these assaults instantly. Let the meals and drugs in. Let the individuals out safely, and finish this battle of alternative towards Ukraine.’”
Students of siege warfare say the tactic serves completely different functions: to weaken enemies whereas avoiding clashes that may kill the besieging pressure’s personal troopers, or to freeze energetic fronts whereas attacking forces reposition. However the grueling nature of sieges — and the way they use starvation to show individuals’s personal our bodies towards them — give them a psychological energy distinctive amongst battle ways, in keeping with students and siege survivors.
Depriving a residential space of meals whereas bombarding it serves not solely to flush out combatants, she stated, however to speak to everybody trapped inside: “You aren’t an equal human to me. You don’t should eat, drink, have drugs and even breathe!”
After they surrounded Mariupol final month, Russian forces reduce off the town from all the things it wanted to stay, the mayor, Vadym Boychenko, stated on Ukrainian nationwide tv. Additionally they destroyed the town’s energy crops, slicing off electrical energy for residents as temperatures froze, Mr. Boychenko stated, after which the water and fuel, important for cooking and heating.
Some civilians managed to flee, making harrowing journeys by way of destroyed streets and Russian checkpoints. However about 160,000 individuals are believed to nonetheless be trapped inside the town, Mr. Boychenko stated, and greater than two dozen buses despatched days in the past to evacuate them had not been in a position to enter the town due to Russian shelling.
On Monday, the Worldwide Committee of the Crimson Cross stated it was ceasing reduction operations in Mariupol as a result of the fighters couldn’t assure the protection of assist staff.
Nearly 5,000 individuals, together with about 210 kids, have been killed there, the mayor estimated, however the figures couldn’t be confirmed due to the problem of getting data.
Russian forces are answerable for components of Mariupol, President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine informed a bunch of impartial Russian journalists on Sunday. However the heart of the town continues to carry, in keeping with Ukrainian and British navy assessments.
An aide to the mayor, Pyotr Andryuschenko, informed The New York Occasions that an estimated 3,000 Ukrainian fighters from the Azov Battalion have been defending the town towards about 14,000 Moscow-backed troopers.
When the siege started, one Mariupol resident, Kristina, stated she, her husband and two kids camped out within the entryway of their constructing, hoping it might present higher shelter and safety than their house.
Her husband, a enterprise analyst, ventured out to search out water and he or she cooked on an open fireplace. Additionally they collected rainwater and snow, boiling the water to sterilize it.
She learn fairy tales to attempt to distract the youngsters, however as soon as they obtained hungry, “the hearth was gone from their eyes,” stated Kristina, who didn’t need to use her full title for concern of retribution. “They’d no real interest in something.”
“We ate as soon as a day,” she stated. “It was principally within the morning or within the night that the youngsters cried out, saying, ‘I need to eat.’”
Her household lastly fled the town, however left behind her father and grandparents. She has struggled to maintain tabs on them as a result of the town’s cellphone networks are principally out.
Final week, she stated, they despatched a textual content that learn: “No roof, no meals and no water.”
Medical doctors who examine starvation and hunger describe a grim means of the physique mining itself to remain alive. First, it burns glucose saved within the liver, then fats, then muscle.
Whereas dehydration can name kill in lower than per week, a well-nourished grownup can survive for greater than 70 days on water alone. Youngsters, the aged and the unwell succumb extra shortly.
Different analysis has proven that hunger not solely weakens the physique however disturbs the thoughts.
Nancy Zuker, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Duke College, stated analysis performed throughout World Conflict II on 36 male conscientious objectors who ate a low calorie food plan modeled on that given to prisoners of battle confirmed that they had suffered “vital psychological penalties.”
Ongoing peace talks. Russia stated that it might sharply “cut back navy exercise” close to Kyiv and the northern metropolis of Chernihiv. The announcement was the primary signal of progress to emerge from peace talks between Ukraine and Russia in Istanbul.
Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Key Developments
She added: “They’d hunger neuroses — elevated nervousness, elevated isolation, elevated melancholy.”
That injury compounds in traumatic circumstances, like wars.
“That is hunger throughout a disaster,” she stated. “It is rather laborious to separate the profound psychological penalties from being in a state of battle from these of not having sufficient meals.”
The reminiscence of starvation haunted the conscientious objectors within the examine lengthy after that they had regained their power.
“They wanted to be surrounded by meals,” and a few remained obsessive about it, she stated. “A number of went on to develop into cooks.”
Irina Peredey, a municipal employee from Mariupol, stated that after she escaped, she was in such shock that she couldn’t eat for days.
After that, she started to crave a full meal about each hour.
“An hour passes and also you need to eat,” stated Ms. Peredey, 29. “It appears to me psychological. You consistently begin consuming — and need to eat as a lot as doable.”
At first she was confused, she stated.
“However now I see that apparently, that is how my physique is combating again.”
As Ms. Beley, the baker, fought to outlive within the basement in Mariupol, she stated, bombs shook the constructing and shells have been so frequent that ever her daughter Aida, 3, discovered to tell apart between incoming and outgoing fireplace.
The household quickly ran out of meals. One other girl gave her a jar of honey.
“That’s how we survived,” she stated. “We didn’t have meals, however we are able to’t say we didn’t eat as a result of a spoonful of honey as soon as a day is already some form of lunch.”
When her household lastly managed to flee, she felt weak, like her physique was struggling to perform. Russian troopers supplied sweet to her and her kids and at first, she refused. Then she modified her thoughts.
“Give me sweet, sugar,” she stated. “I noticed that I wanted one thing in order that I might keep myself.”
Valerie Hopkins reported from Lviv, Ukraine, Ben Hubbard from Beirut, Lebanon, and Gina Kolata from Princeton, N.J. Asmaa al-Omar and Hwaida Saad contributed reporting from Beirut.

Health
'Pendulum lifestyle' could be key to juggling daily challenges

For those who are feeling “stuck” or overwhelmed while striving for work-life balance, some experts recommend adopting a “pendulum lifestyle.”
Coined by Dr. Jeffrey Karp, Ph.D, a professor of biomedical engineering at Brigham & Women’s Hospital Harvard Medical School in Boston, the pendulum lifestyle is defined as a “concept that acknowledges life’s natural ebb and flow, and empowers you to thrive amidst the swings.”
“Rarely are we in balance … it’s just unrealistic and an anxiety-inducing expectation,” the doctor told Fox News Digital in an interview.
WHY THERE’S NO SUCH THING AS A ‘WORK-LIFE BALANCE,’ SAYS CAREER COACH AND AUTHOR
Seeing the world as a pendulum fosters a more compassionate mindset and alleviates the pressure to be perfect, Karp said.
For those who are feeling “stuck” or overwhelmed while striving for work-life balance, some experts recommend adopting a “pendulum lifestyle.” (iStock)
With this approach, people can take small steps to “swing the pendulum,” enabling them to feel more emotionally, mentally and physically “balanced” during the day, according to the expert.
This could also empower individuals who feel “stuck” when facing daily challenges, he said.
“Looking at nature, there are so many cycles, so many things that are kind of going back and forth, like night and day …. changes of seasons, and the waxing and waning of the moon,” noted Karp.
MOST PRODUCTIVE THINGS YOU CAN GET DONE EARLY IN THE MORNING BEFORE WORK, ACCORDING TO CAREER COACHES
The pendulum lifestyle involves daily “self-check-ins” where the person gauges their physical, emotional and mental energy levels, Karp said. They can then take immediate steps to move their levels in a positive direction toward the ideal balance.
“If we can visualize everything on a pendulum, we can think, ‘What’s the one step I could take today to bring the pendulum a little closer to where I want it to be?’” he said.
With this approach, people can take small steps to “swing the pendulum,” enabling them to feel more emotionally, mentally and physically “balanced” during the day. (iStock)
For example, a person who has low physical energy could visualize a pendulum with the lowest energy on one side and the highest energy on the other.
He would then do a “self-check” to identify where his energy level lies on the pendulum and what small steps could move it closer to the ideal balance point, Karp said.
“True well-being doesn’t lie in perfection or consistency, but in our ability to navigate the ebb and flow of life.”
That might mean taking a 10-minute walk, doing some jumping jacks or performing a few stretches to move the pendulum to a higher energy level position.
“This empowers the person and reminds them they are not stuck,” Karp said.

Taking a 10-minute walk, doing some jumping jacks or performing a few stretches can move the pendulum to a higher energy level position, the expert said. (iStock)
On the flip side, if it’s late at night and a person needs to wind down, she might engage in a calming exercise like meditation or listening to relaxing music as a way to swing the pendulum to a level more conducive to sleeping, the expert advised.
The pendulum lifestyle can also serve as a mood-booster, Kelp said. When someone is feeling down, watching a funny movie or practicing gratitude can help shift the pendulum.
WHAT IS ‘BRAIN ROT’? THE SCIENCE BEHIND WHAT TOO MUCH SCROLLING DOES TO OUR BRAINS
The approach could also help launch forward momentum if someone feels “stuck” in life, the expert said.
“When you start to realize that you’re not limited to being at that spot on the pendulum, but can take a step forward and be intentional, it’s just so empowering,” he said.

The daily check-in process could help individuals identify when they are feeling in less than tip-top shape and find ways to swing in a better direction, one expert said. (iStock)
Dr. Molly Sherb, an assistant professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and a licensed psychologist at Mount Sinai in New York City, commented on Karp’s concept of a pendulum lifestyle.
“When you start to realize that you’re not limited to being at that spot on the pendulum, but can take a step forward and be intentional, it’s just so empowering.”
She agreed that the daily check-in process could help individuals identify when they are feeling in less than tip-top shape and find ways to swing in a better direction.
“That might include getting better sleep or eating a healthier breakfast … to help you wake up with a better bandwidth tomorrow,” Sherb said.
Progress, not perfection
Dr. Christopher Fisher, a psychologist at Zucker Hillside Hospital Northwell Health in Queens, New York, said the pendulum lifestyle could help those who feel pressured to achieve a perfect work-life balance.
“The pendulum of life’s experiences – whether emotional, cognitive or physical – is one of the truest expressions of what it means to be human,” he told Fox News Digital.
TRUMP’S DAYLIGHT SAVING TIME PLAN AND SLEEP: WHAT YOU MUST KNOW
“True well-being doesn’t lie in perfection or consistency, but in our ability to navigate the ebb and flow of life,” he told Fox News Digital.
Sherb agreed that the essence of the pendulum lifestyle is that it’s not always possible to strike that 50-50 equal balance.

Adopt a constructive viewpoint and ask yourself what positive changes or routines can help you achieve a more optimal level on the pendulum path, one expert advised. (iStock)
“It’s about constantly tuning into yourself … and seeing which parts of your life might need you more at certain times,” she said.
“It’s not a one-size-fits-all approach, but a more tailored approach based on what you need and what people in your life need from you.”
4 steps to implementing the pendulum lifestyle
Karp shared some specific strategies for adopting the pendulum approach.
1. Perform a head-to-toe check-in each morning
Ask yourself how you are feeling emotionally, physically and mentally. What parts do not feel at a 100% level?
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
2. Make any necessary adjustments
Based on your self-check-in, consider changing your routine to accommodate your energy level or take simple steps to help move the pendulum in a positive direction, Karp suggested.
3. Be compassionate and curious
If you feel off-balance, Karp said to recognize that as part of the natural pendulum swing and to embrace it with self-compassion rather than shame and criticism.
“It’s about constantly tuning into yourself … and seeing which parts of your life might need you more at certain times.”
Adopt a constructive viewpoint and ask yourself what positive changes or routines can help you achieve a more optimal level on the pendulum path, he advised.
4. Understand your pendulum swings
It could be helpful to ask yourself specific questions, such as the following.
“What factors helped contribute to a state of feeling balanced?”
“What factors contributed to feeling off-balance?”
“What small changes can I make today to foster a sense of better balance?”
“How did I respond to feeling imbalanced and was it effective?”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
Above all, Karp said, it’s important to remember that finding balance is a “lifelong journey.”
Health
How Naomi Feil Developed a Radical Approach to Caring for Dementia Patients

Before the answers to life’s questions fit in our pocket, you used to have to turn a dial. If you were lucky, Phil Donahue would be on, ready to guide you toward enlightenment. In a stroke of deluxe good fortune, Dr. Ruth Westheimer might have stopped by to be the enlightenment. He was the search engine. She was a trusted result.
Donahue hailed from Cleveland. The windshield glasses, increasingly snowy thatch of hair, marble eyes, occasional pair of suspenders and obvious geniality said “card catalog,” “manager of the ’79 Reds,” “Stage Manager in a Chevy Motors production of ‘Our Town.’” Dr. Ruth was Donahue’s antonym, a step stool to his straight ladder. She kept her hair in a butterscotch helmet, fancied a uniform of jacket-blouse-skirt and came to our aid, via Germany, with a voice of crinkled tissue paper. Not even eight years separated them, yet so boyish was he and so seasoned was she that he read as her grandson. (She maybe reached his armpit.) Together and apart, they were public servants, American utilities.
Donahue was a journalist. His forum was the talk show, but some new strain in which the main attraction bypassed celebrities. People — every kind of them — lined up to witness other people being human, to experience Donahue’s radical conduit of edification, identification, curiosity, shock, wonder, outrage, surprise and dispute, all visible in the show’s televisual jackpot: cutaways to us, reacting, taking it all in, nodding, gasping. When a celebrity made it to the “Donahue” stage — Bill Clinton, say, La Toya Jackson, the Judds — they were expected to be human, too, to be accountable for their own humanity. From 1967 to 1996, for more than 6,000 episodes, he permitted us to be accountable to ourselves.
What Donahue knew was that we — women especially — were eager, desperate, to be understood, to learn and learn and learn. We call his job “host” when, really, the way he did it, running that microphone throughout the audience, racing up, down, around, sticking it here then here then over here, was closer to “switchboard operator.” It was “hot dog vendor at Madison Square Garden.” The man got his steps in. He let us do more of the questioning than he did — he would just edit, interpret, clarify. Egalitarianism ruled. Articulation, too. And anybody who needed the mic usually got it.
The show was about both what was on our mind and what had never once crossed it. Atheism. Naziism. Colorism. Childbirth. Prison. Rapists. AIDS. Chippendales, Chernobyl, Cher. Name a fetish, Phil Donahue tried to get to its bottom, sometimes by trying it himself. (Let us never forget the episode when he made his entrance in a long skirt, blouse and pussy bow for one of the show’s many cross-dressing studies.) Now’s the time to add that “Donahue” was a morning talk show. In Philadelphia, he arrived every weekday at 9 a.m., which meant that, in the summers, I could learn about compulsive shopping or shifting gender roles from the same kitchen TV set as my grandmother.
Sex and sexuality were the show’s prime subjects. There was so much that needed confessing, correction, corroboration, an ear lent. For that, Donahue needed an expert. Many times, the expert was Dr. Ruth, a godsend who didn’t land in this country until she was in her late 20s and didn’t land on television until she was in her 50s. Ruth Westheimer arrived to us from Germany, where she started as Karola Ruth Siegel and strapped in as her life corkscrewed, as it mocked fiction. Her family most likely perished in the Auschwitz death camps after she was whisked to the safety of a Swiss children’s home, where she was expected to clean. The twists include sniper training for one of the military outfits that would become the Israel Defense Forces, maiming by cannonball on her 20th birthday, doing research at a Planned Parenthood in Harlem, single motherhood and three husbands. She earned her doctorate from Columbia University, in education, and spent her postdoc researching human sexuality. And because her timing was perfect, she emerged at the dawn of the 1980s, an affable vector of an era’s craze for gnomic sages (Zelda Rubinstein, Linda Hunt, Yoda), masterpiece branding and the nasty.
Hers was the age of Mapplethorpe and Madonna, of Prince, Skinemax and 2 Live Crew. On her radio and television shows, in a raft of books and a Playgirl column and through her promiscuous approach to talk-show appearances, she aimed to purge sex of shame, to promote sexual literacy. Her feline accent and jolly innuendo pitched, among other stuff, the Honda Prelude, Pepsi, Sling TV and Herbal Essences. (“Hey!” she offers to a young elevator passenger. “This is where we get off.”) The instructions for Dr. Ruth’s Game of Good Sex says it can be played by up to four couples; the board is vulval and includes stops at “Yeast Infection,” “Chauvinism” and “Goose Him.”
On “Donahue,” she is direct, explicit, dispelling, humorous, clear, common-sensical, serious, vivid. A professional therapist. It was Donahue who handled the comedy. On one visit in 1987, a caller needs advice about a husband who cheats because he wants to have sex more often than she does. Dr. Ruth tells Donahue that if the caller wants to keep the marriage, and her husband wants to do it all the time, “then what she should do is to masturbate him. And it’s all right for him to masturbate himself also a few times.” The audience is hear-a-pin-drop rapt or maybe just squirmy. So Donahue reaches into his parochial-school-student war chest and pulls out the joke about the teacher who tells third-grade boys, “Don’t play with yourself, or you’ll go blind.” And Donahue raises his hand like a kid at the back of the classroom and asks, “Can I do it till I need glasses?” Westheimer giggles, maybe noticing the large pair on Donahue’s face. This was that day’s cold open.
They were children of salesmen, these two; his father was in the furniture business, hers sold what people in the garment industry call notions. They inherited a salesman’s facility for people and packaging. When a “Donahue” audience member asks Westheimer whether her own husband believes she practices what she preaches, she says this is why she never brings him anywhere. “He would tell you and Phil: ‘Do not listen to her. It’s all talk,’” which cracks the audience up.
But consider what she talked about — and consider how she said it. My favorite Dr. Ruth word was “pleasure.” From a German mouth, the word conveys what it lacks with an American tongue: sensual unfurling. She vowed to speak about sex to mass audiences using the proper terminology. Damn the euphemisms. People waited as long as a year and a half for tickets to “Donahue” so they could damn them, too. But of everything Westheimer pitched, of all the terms she precisely used, pleasure was her most cogent product, a gift she believed we could give to others, a gift she swore we owed ourselves.
I miss the talk show that Donahue reinvented. I miss the way Dr. Ruth talked about sex. It’s fitting somehow that this antidogmatic-yet-priestly Irish Catholic man would, on occasion, join forces with a carnal, lucky-to-be-alive Jew to urge the exploration of our bodies while demonstrating respect, civility, reciprocation. They believed in us, that we were all interesting, that we could be trustworthy panelists in the discourse of being alive. Trauma, triviality, tubal ligation: Let’s talk about it! Fear doesn’t seem to have occurred to them. Or if it did, it was never a deterrent. Boldly they went. — And with her encouragement, boldly we came.
Wesley Morris is a critic at large for The New York Times and a staff writer for the magazine.
Health
Eggs now qualify as ‘healthy’ food, FDA says: Here’s why

While eggs haven’t historically been considered a “health food,” the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) now classifies them as a “healthy, nutrient-dense” food, according to a new proposed rule.
The update is the result of changes in nutrition science and dietary recommendations, according to the agency.
The FDA’s “healthy” designation for food labeling purposes has been in use since the early 1990s.
‘I’M A HEART SURGEON, HERE’S WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT EGGS, YOUR HEART AND YOUR HEALTH’
“Healthy diets are made up of a variety of food groups and nutrients, and the ‘healthy’ claim can help consumers identify those foods that are the foundation of healthy dietary patterns,” the agency stated in its guidance.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration now classifies eggs as a “healthy, nutrient-dense” food, according to a new proposed rule. (iStock)
“On behalf of America’s egg farmers, we are thrilled to see the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announce that eggs meet the updated definition of ‘healthy,’” said Emily Metz, president and CEO of the American Egg Board, in a statement sent to Fox News Digital.
“This is an important milestone for eggs, bringing current nutrition science and federal dietary guidance into alignment, and affirming eggs’ role in supporting the health of American families, with nutritional benefits for everyone.”
5 EGG MYTHS DISPELLED BY AN EXPERT, PLUS TIPS FOR EVERY EGG LOVER
Metz referred to eggs as a “nutritional powerhouse,” noting that they contain eight essential nutrients that support health at every age.
“Eggs are particularly known for being one of the highest quality proteins available, playing a vital role in muscle health and overall wellness,” she added.
“This is a significant milestone, as eggs are an affordable source of high-quality protein and a rich source of nutrients.”
Tanya Freirich, a registered dietitian nutritionist in Charlotte, North Carolina, who practices as The Lupus Dietitian, noted that eggs are a “fantastic source” of protein, choline, B vitamins and selenium, as well as a “fair source” of vitamin D, vitamin E, calcium and zinc.
“While in the past, many people were told to avoid eggs due to their cholesterol content, in more recent years, research has shown that dietary cholesterol intake does not increase your blood levels of cholesterol as much as previously understood,” she told Fox News Digital.
“Eggs, especially pasture-raised or omega 3-enriched, are particularly nutritious.”

The president and CEO of the American Egg Board referred to eggs as a “nutritional powerhouse,” noting that they contain eight essential nutrients that support health at every age. (iStock)
While eggs are a “superior” replacement for sugary cereals or a doughnut, Freirich cautioned that, like other foods, they should be consumed in moderation.
“[The FDA’s announcement] doesn’t mean we should all consume multiple eggs every day,” she said. “Current studies and recommendations support consuming up to one egg a day.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
New Jersey-based registered dietitian Erin Palinski-Wade also said she was “very happy” to hear the FDA’s recognition of eggs as a healthy food.

While eggs are a “superior” replacement for sugary cereals or a doughnut, one dietitian cautioned that, like other foods, they should be consumed in moderation. (iStock)
“This is a significant milestone, as eggs are an affordable source of high-quality protein and a rich source of nutrients such as choline, vitamin D and essential fatty acids that many of us fall short on in our diets,” she told Fox News Digital.
The dietitian said she hopes that the designation will dispel the “outdated concerns” about eggs and dietary cholesterol.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“This will go a long way in helping consumers make informed choices about their dietary protein sources and support eggs as part of a nutritious diet.”
Fox News Digital reached out to the FDA for comment.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCanadian premier threatens to cut off energy imports to US if Trump imposes tariff on country
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25782636/247422_ChatGPT_anniversary_CVirginia.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25782636/247422_ChatGPT_anniversary_CVirginia.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoInside the launch — and future — of ChatGPT
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25789444/1258459915.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25789444/1258459915.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoOpenAI cofounder Ilya Sutskever says the way AI is built is about to change
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoU.S. Supreme Court will decide if oil industry may sue to block California's zero-emissions goal
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25546252/STK169_Mark_Zuckerburg_CVIRGINIA_D.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25546252/STK169_Mark_Zuckerburg_CVIRGINIA_D.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta asks the US government to block OpenAI’s switch to a for-profit
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoConservative group debuts major ad buy in key senators' states as 'soft appeal' for Hegseth, Gabbard, Patel
-
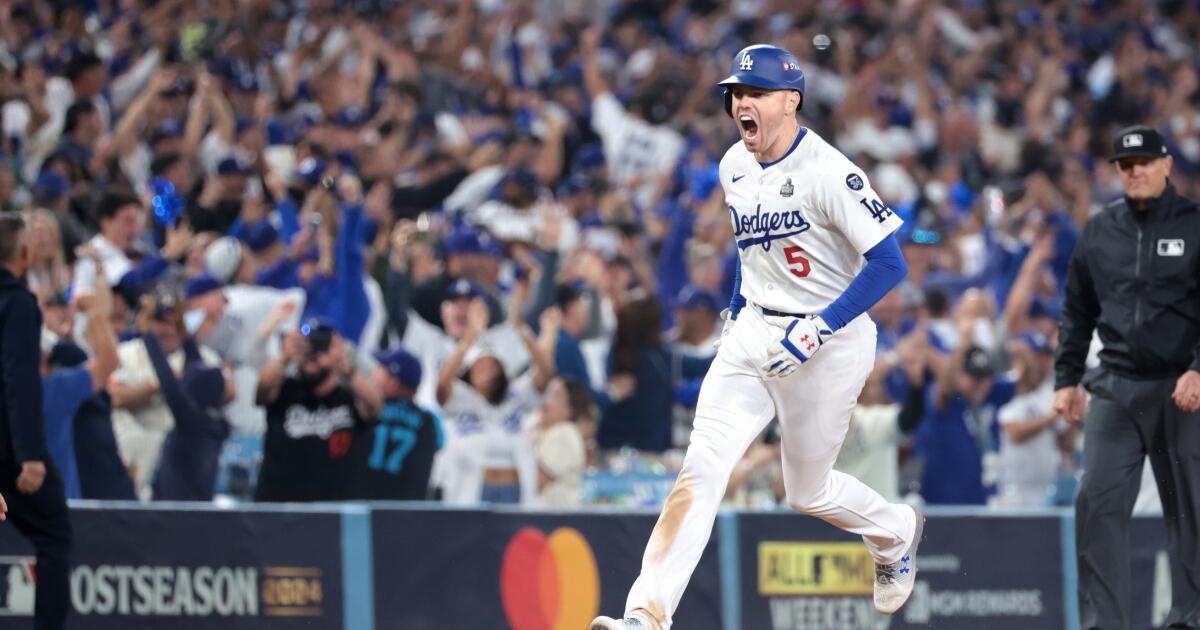

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoFreddie Freeman's World Series walk-off grand slam baseball sells at auction for $1.56 million
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23951353/STK043_VRG_Illo_N_Barclay_3_Meta.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23951353/STK043_VRG_Illo_N_Barclay_3_Meta.jpg) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoMeta’s Instagram boss: who posted something matters more in the AI age














