Health
Lupus expert debunks 7 common myths about the autoimmune disease: ‘Not a death sentence’

Fatigue, pain, swelling, rashes and hair loss are just some of the symptoms that affect people with lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks healthy tissue.
Some 1.5 million Americans are living with lupus, with about 16,000 new cases each year, according to the Lupus Foundation of America, based in Washington, D.C.
There are many myths surrounding lupus that can make it difficult for people to understand and manage the disease, according to Dr. Brooke Goldner, a board-certified medical doctor and an autoimmune professor at Cornell University.
EXPERIMENTAL LUPUS THERAPY COULD BE ‘LIFE-CHANGING’ FOR PATIENTS WITH AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE, STUDY FINDS
“It’s essential to educate yourself and others about lupus to dispel these myths and increase understanding of the disease,” Golder, who was diagnosed with lupus at the age of 16, told Fox News Digital.
For Lupus Awareness Month, Goldner shared some of the biggest misconceptions — and set the record straight on a number of issues.
Dr. Brooke Goldner, a board-certified medical doctor and an autoimmune professor at Cornell University, pictured at right, is committed to debunking lupus myths and misconceptions. (iStock/Dr. Brooke Goldner)
7 myths debunked
Myth No. 1: There is only one type of lupus
The most common type of lupus is systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but it’s not the only form of the disease.
“SLE can have a wide range of symptoms that may come and go, making it challenging to diagnose,” Goldner said.
FRIENDS RUN FOR A CURE FOR LUPUS, COMPLETING NYC MARATHON IN HONOR OF LONGTIME PAL AND LUPUS SUFFERER
Some of the common symptoms of SLE include fatigue, joint pain and stiffness, fever, hair loss, skin rashes and sensitivity to sunlight.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE), a less common form, affects only the skin.
The two least common types are neonatal lupus and drug-induced lupus, according to the Lupus Foundation of America.
Myth No. 2: Lupus is contagious
Lupus cannot be transmitted from person to person, Goldner said.
“It occurs when your immune system attacks your own tissues and organs, causing inflammation and damage,” she said.

“Lupus can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, brain and other organs,” one doctor said. (BSIP/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
“Lupus can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, brain and other organs.”
Myth No. 3: Lupus only affects women
“While lupus does affect more women than men, it can affect anyone, including children and men,” Goldner said.
Anyone can develop lupus. Yet 90% of cases affect women between the ages of 15 and 44, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Myth No. 4: Lupus is a cancer
Medicines like chemotherapy are often used in severe lupus cases, but it is not a form of cancer.
FOR AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE SUFFERERS, GINGER MAY ‘PLAY A CRITICAL ROLE’ IN CONTROLLING INFLAMMATION, STUDY FINDS
“It is an autoimmune disease, whereby the immune system begins attacking the body’s own tissues rather than just foreign invaders like viruses and bacteria,” Goldner told Fox News Digital.
“Chemotherapy is known as an immune system suppressant, which can be lifesaving when lupus is causing organ failure and aggressive immunosuppression is required.”
Myth No. 5: Lupus is caused by stress
While stress can trigger lupus symptoms, Goldner noted it is not the cause of the disease.
“The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental and hormonal factors,” she said.
Myth No. 6: Lupus is purely caused by genetics
Genetics will determine whether you have the possibility of developing lupus, but it is not a condition you are born with, according to Goldner.

Fatigue is a primary symptom of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). (iStock)
“Just like someone with the genetics to become type 2 diabetic will not develop the disease unless they have a diet and lifestyle that triggers it, the same is true for lupus,” she said.
Lupus is often triggered during times of physical and emotional stress combined with a nutrient-poor inflammatory diet, the expert added.
Myth No. 7: Lupus is a death sentence
While lupus can be a serious disease, it is “not a death sentence,” according to Goldner.
“While there is no medical cure for lupus, there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms and prevent damage to vital organs,” she said.
‘LIQUID GOLD’ COULD BRING NEW HOPE TO MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PATIENTS, STUDY SUGGESTS: ‘PROFOUND BENEFIT’
“Treatment may include medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants and corticosteroids.”
In addition to taking medications, many people with lupus can manage symptoms through healthy lifestyle interventions, according to Goldner.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy eating and stress management can help improve the quality of life for people with lupus,” the expert said.

“Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy eating and stress management can help improve the quality of life for people with lupus,” the expert said. (iStock)
As a survivor of lupus and a physician, Goldner said she has dedicated her life to bringing more awareness to the disease and helping people gain the power to manage and eliminate symptoms through nutrition and lifestyle.
“This is not to suggest that people should not use medical treatments that can be lifesaving,” she said, “but rather that they embrace taking control of all the variables they can manage, like how they eat, sleep and manage stress with self-care, so they can minimize illness and maximize recovery and remission.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.

Health
What Happens If You Eat Eggs Every Day? Nutritionists Share the Benefits

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Ask a doctor: ‘I swallowed a bug — now what should I do?'
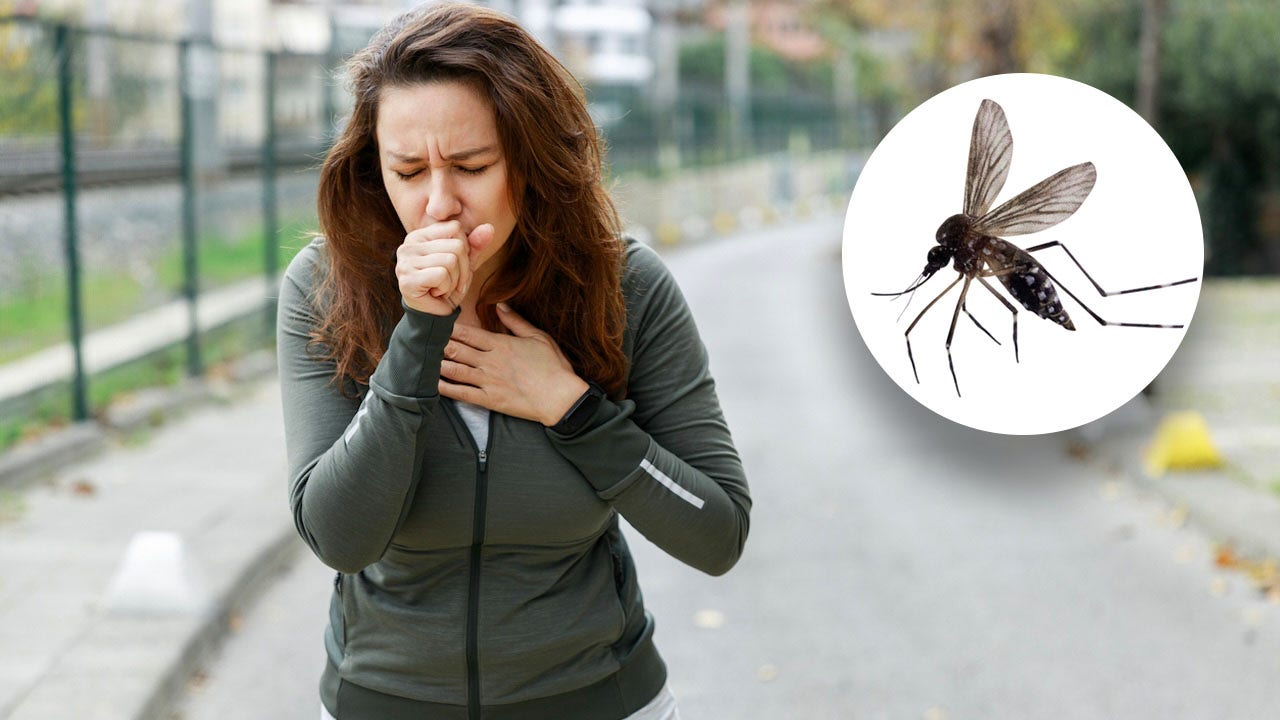

Most people have experienced that moment of discomfort when they realize a bug has wound up where it shouldn’t be — in their windpipe.
That includes Taylor Swift, who on more than one occasion has accidentally swallowed a bug while performing on stage in front of thousands of people.
It can be a startling and somewhat disgusting occurrence — but is this dangerous, or just a nuisance?
LOCAL DENGUE FEVER CASES CONFIRMED IN FLORIDA KEYS, SPREAD BY MOSQUITO BITES
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, shared with Fox News Digital the true impacts of accidentally swallowing a bug, and the best thing to do if it happens.
“Swallowing a bug can often happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” Dasgupta, who serves as chief medical advisor for Fortune Recommends, told Fox News Digital via email.
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, discussed the impact of accidentally swallowing a bug — and the best thing to do if it happens. (Sleepoplis)
“It can also happen if you’re talking or laughing outdoors. Sometimes it might even happen indoors if bugs are in your food or drink and you don’t realize it.”
ASK A DOCTOR: ‘HOW CAN I PREVENT SCARRING FROM BUG BITES AND POISON IVY?’
Swallowing a bug is usually not dangerous, Dasgupta noted.
“The stomach’s digestive acids usually break down the bug, and it is passed out of the body without causing harm,” he said.
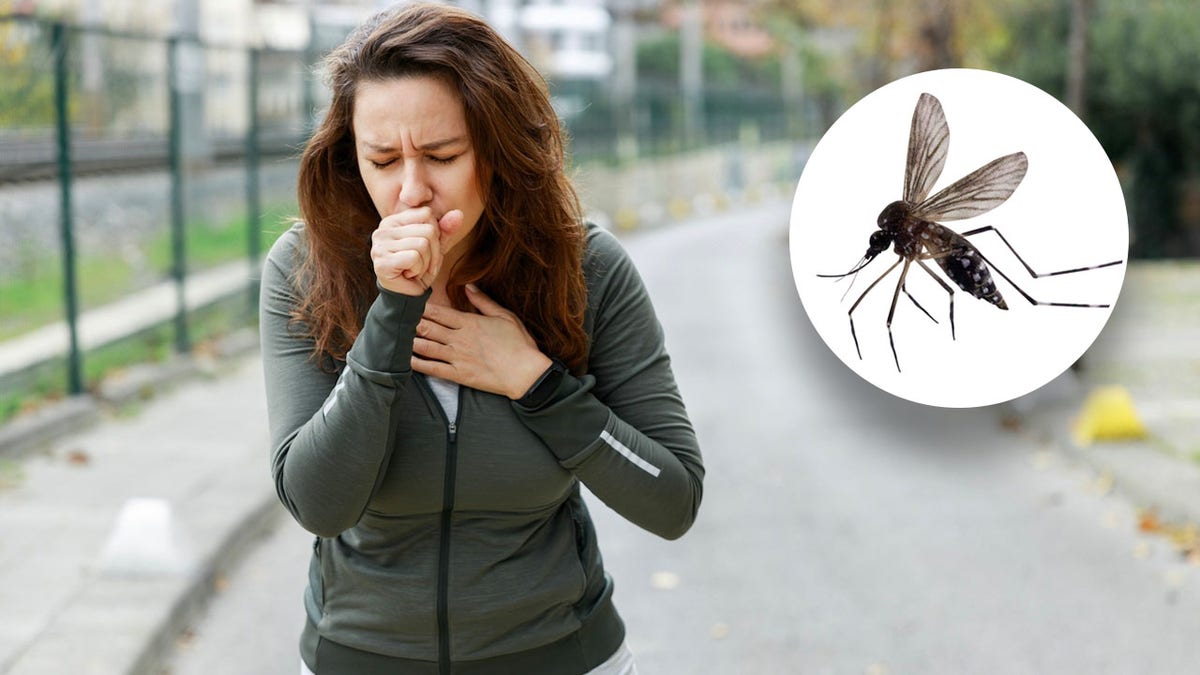

“Swallowing a bug can happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” the doctor told Fox News Digital. (iStock)
If the bug carries harmful bacteria or parasites, however, it could cause gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions, according to the doctor.
The type of bug can make a difference, he said.
“Bugs like beetles or ants are less of a concern, but bugs that are known to spread diseases — such as mosquitoes — might be riskier.”
If you happen to swallow a bug, drinking some water can help wash it down, Dasgupta said.
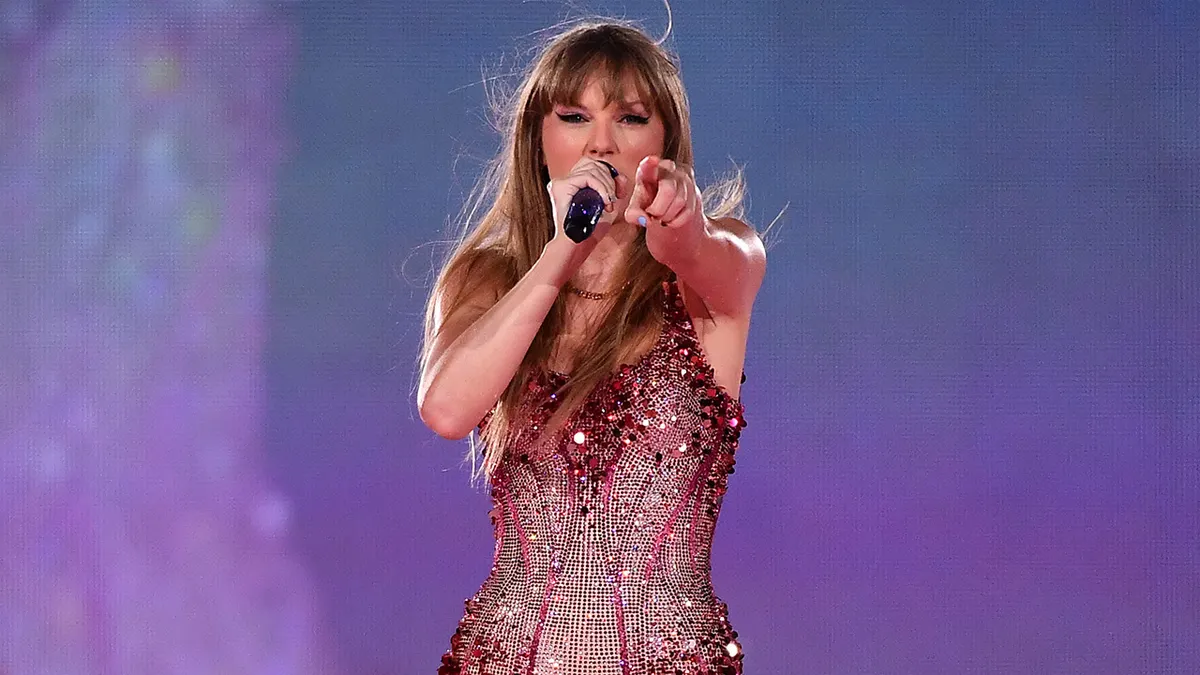

Taylor Swift has announced the accidental swallowing of bugs, mid-concert, on more than one occasion. (Marcelo Endelli/TAS23/Getty Images for TAS Rights Management)
“If you start feeling sick, like abdominal pain, vomiting or nausea, keep an eye on your symptoms,” the doctor said.
If you have severe stomach pain, ongoing vomiting, trouble breathing, or swelling, rash or itching, Dasgupta said to see a doctor.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“If you know the bug could have diseases or if you have health conditions that might complicate things, it’s a good idea to get checked out to be safe,” he added.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews/health
Some bugs — including grasshoppers, beetles, termites, mealworms and even stink bugs — are actually considered edible in certain countries, and are prepared and eaten as part of meals, according to WebMD’s website.
Health
“I’m a Dietitian, and Here’s Why an Overly Restrictive Diet Can Backfire”

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt