Health
Cancer risk rises with this little-known syndrome. Here’s how to know if you have the genetic condition

As colorectal cancer continues to spike among younger patients, doctors are warning of a little-known but widespread condition that greatly increases the risk.
Lynch syndrome is a genetic disorder that makes someone more susceptible to many different kinds of cancer.
Fox News Digital spoke with two experts about what people should know about this inherited condition.
CANCER PREVENTION IN THE ESOPHAGUS COULD BE JUST A PILL AWAY, DOCTOR SAYS: ‘TREMENDOUS BENEFIT’
Dr. Matthew Grossman, an interventional endoscopist and gastroenterologist with Atlantic Health System in New Jersey, explained the relationship between Lynch syndrome and human DNA.
“Think of DNA as a ladder,” he said. “Normally, errors in the rungs — called mismatches — are fixed by a repair system. In Lynch syndrome, this system is faulty, increasing the risk of mismatches.”
Lynch syndrome is a genetic disorder that makes someone more susceptible to many different kinds of cancer. (iStock)
Because of the mismatch repair defect, a person with Lynch syndrome is much more likely to develop abnormalities and defects in cells, which eventually lead to cancer, he said.
“Lynch syndrome is a type of germline mutation, meaning it’s inherited genetically, versus a somatic mutation, which can happen spontaneously to only a few cells,” said Grossman.
DOCTORS TOLD WOMAN SHE WAS TOO YOUNG FOR A COLONOSCOPY. THEN SHE WAS DIAGNOSED WITH STAGE 3 COLON CANCER
Dr. Ajay Bansal, a gastroenterologist at KU Medical Center at the University of Kansas, emphasized that Lynch syndrome largely flies under the radar, as 95% of patients who have the condition don’t know about it.
“They are not aware that they are at increased risk for not only colon cancer, but also uterine, ovarian, stomach, small bowel, kidney, bladder and perhaps brain cancer,” he told Fox News Digital. “So it’s very underdiagnosed.”

In healthy DNA, errors in the rungs — called mismatches — are fixed by a repair system. In Lynch syndrome, the repair system is faulty, increasing the risk of mismatches, a doctor explained. (iStock)
One of the reasons the syndrome often goes unnoticed is because it’s a “silent” condition, Bansal said. “It doesn’t cause any symptoms until you have cancer.”
The two main cancers tied to the syndrome are colon and colorectal cancer and cancer of the uterus.
“Lynch syndrome can result from four or five different mutations,” Bansal said. “Depending on the mutation, the type of cancer risk changes.”
COLORECTAL CANCER IS NOW LEADING CAUSE OF DEATH AMONG YOUNG ADULTS WITH CANCER: NEW REPORT
For example, for those who have a mutation in a gene called MLH1, the risk of getting colorectal cancer at some point in their lifetime is 80%, Bansal warned.
Among young-onset colorectal cancers, the doctor estimated that roughly 25% are a result of Lynch syndrome.
How is Lynch syndrome detected?
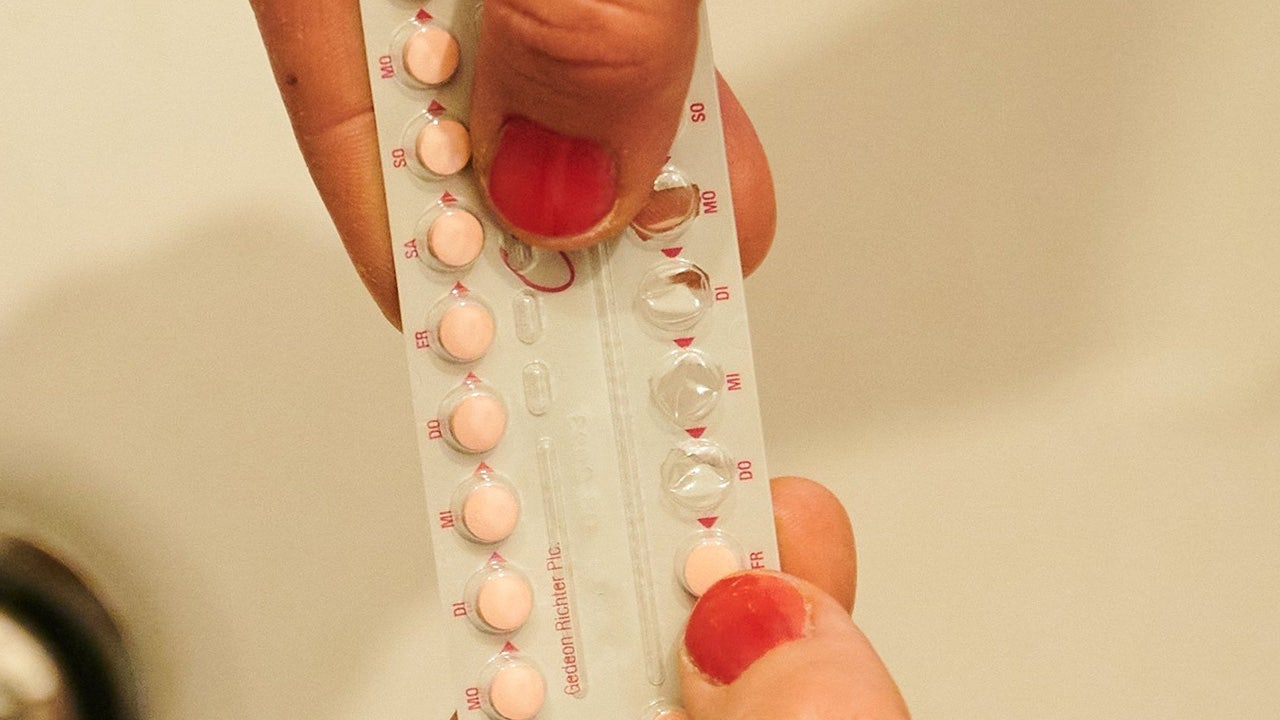
Lynch syndrome can be diagnosed by either a blood test or saliva test, Bansal said.
“If a patient has a family history of multiple colon cancers or multiple other cancers in the family, or if somebody in the family had colon cancer or uterine cancer under the age of 50, we recommend genetic testing to confirm the syndrome,” he said.
Lynch syndrome can be diagnosed through either a blood test or saliva test. (iStock)
Patients who fall into these categories are typically tested for Lynch between the ages of 18 to 25, the doctor said.
Universal genetic testing is not generally performed.
“It’s not approved for the general population, mainly because of costs and insurance concerns,” Bansal noted.
CANCER RISK COULD INCREASE WITH CONSUMPTION OF CERTAIN FOODS AND DRINKS, STUDY FINDS
Before genetic testing was available, clinicians relied on the “3,2,1 criteria” for diagnosing Lynch syndrome, according to Grossman.
“For that criteria, if patients have three or more relatives with one of the affecting cancers on the same side of the family, and this is seen in two or more generations with at least one person under age 50, that is highly diagnostic of Lynch syndrome and they should discuss the condition with a doctor,” he said.
What happens if you’re diagnosed?
There is no treatment or “cure” for Lynch syndrome, as it’s caused by a genetic mutation.
Those who test positive should closely monitor themselves for the warning signs of cancer through regular screenings — especially colonoscopies, Bansal said.

Patients should talk to their primary care doctors about their family history, a doctor advised. (iStock)
In the general population, among people without Lynch syndrome, it is recommended to start colonoscopies at the age of 45.
In patients with Lynch syndrome — especially those with more aggressive phenotypes and genotypes — Bansal recommended starting colonoscopies at the age of 25 and repeating them every one to two years.
“The idea here would be to monitor closely so we can prevent colon cancer by removing polyps or catching it at an early stage when we can treat it,” he said.
CANCER SCREENINGS: HERE ARE 5 TYPES AND CRITICAL INFORMATION TO KNOW ABOUT EACH
Bansal, who specializes in studying vaccines for cancer prevention, is currently running a clinical trial for a new cancer vaccine. The participants are all people with Lynch syndrome.
“We felt that we had to do something to change the natural history of cancer in this high-risk population,” he told Fox News Digital.
In the trial, researchers are testing a combination of three vaccines that were initially created by a scientist at the National Cancer Institute.

“If a patient has a family history of multiple colon cancers or multiple other cancers in the family, or if somebody in the family had colon cancer or uterine cancer under the age of 50, we recommend genetic testing to confirm the syndrome,” a doctor said. (iStock)
“These vaccines attack those cells in the colorectal area that express abnormal proteins, and then it can train the immune cells to get rid of those cells in the colon — and perhaps in other organs such as the stomach, small bowel, pancreas and uterus — before they turn into cancer or polyps.”
The first two safety phases of the trial have already been completed.
Next, the researchers will perform randomized controlled trials to gauge the effectiveness of the vaccines in keeping cancer at bay.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
If the trial is successful, Bansal said he envisions the vaccine extending to other types of cancers.
Bansal’s main advice to patients is to talk to their primary care doctors about their family history.
The two main cancers tied to the syndrome are colon and colorectal cancer and cancer of the uterus. (iStock)
“In medical care, everybody’s so busy that we don’t discuss family history enough,” he said. “Patients should ask their doctor about their family history of cancers and the possibility of genetic testing, which has become much cheaper than ever before.”
Grossman agreed that it’s important to be aware of the risks associated with the genetic condition.
“Knowing you have Lynch syndrome allows for more frequent colonoscopies and additional cancer screenings that will help save lives,” he said.
“This is a great example of how our increased knowledge of genetics has improved our clinical care.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.

Health
What Happens If You Eat Eggs Every Day? Nutritionists Share the Benefits

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Ask a doctor: ‘I swallowed a bug — now what should I do?'

Most people have experienced that moment of discomfort when they realize a bug has wound up where it shouldn’t be — in their windpipe.
That includes Taylor Swift, who on more than one occasion has accidentally swallowed a bug while performing on stage in front of thousands of people.
It can be a startling and somewhat disgusting occurrence — but is this dangerous, or just a nuisance?
LOCAL DENGUE FEVER CASES CONFIRMED IN FLORIDA KEYS, SPREAD BY MOSQUITO BITES
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, shared with Fox News Digital the true impacts of accidentally swallowing a bug, and the best thing to do if it happens.
“Swallowing a bug can often happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” Dasgupta, who serves as chief medical advisor for Fortune Recommends, told Fox News Digital via email.
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, discussed the impact of accidentally swallowing a bug — and the best thing to do if it happens. (Sleepoplis)
“It can also happen if you’re talking or laughing outdoors. Sometimes it might even happen indoors if bugs are in your food or drink and you don’t realize it.”
ASK A DOCTOR: ‘HOW CAN I PREVENT SCARRING FROM BUG BITES AND POISON IVY?’
Swallowing a bug is usually not dangerous, Dasgupta noted.
“The stomach’s digestive acids usually break down the bug, and it is passed out of the body without causing harm,” he said.

“Swallowing a bug can happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” the doctor told Fox News Digital. (iStock)
If the bug carries harmful bacteria or parasites, however, it could cause gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions, according to the doctor.
The type of bug can make a difference, he said.
“Bugs like beetles or ants are less of a concern, but bugs that are known to spread diseases — such as mosquitoes — might be riskier.”
If you happen to swallow a bug, drinking some water can help wash it down, Dasgupta said.
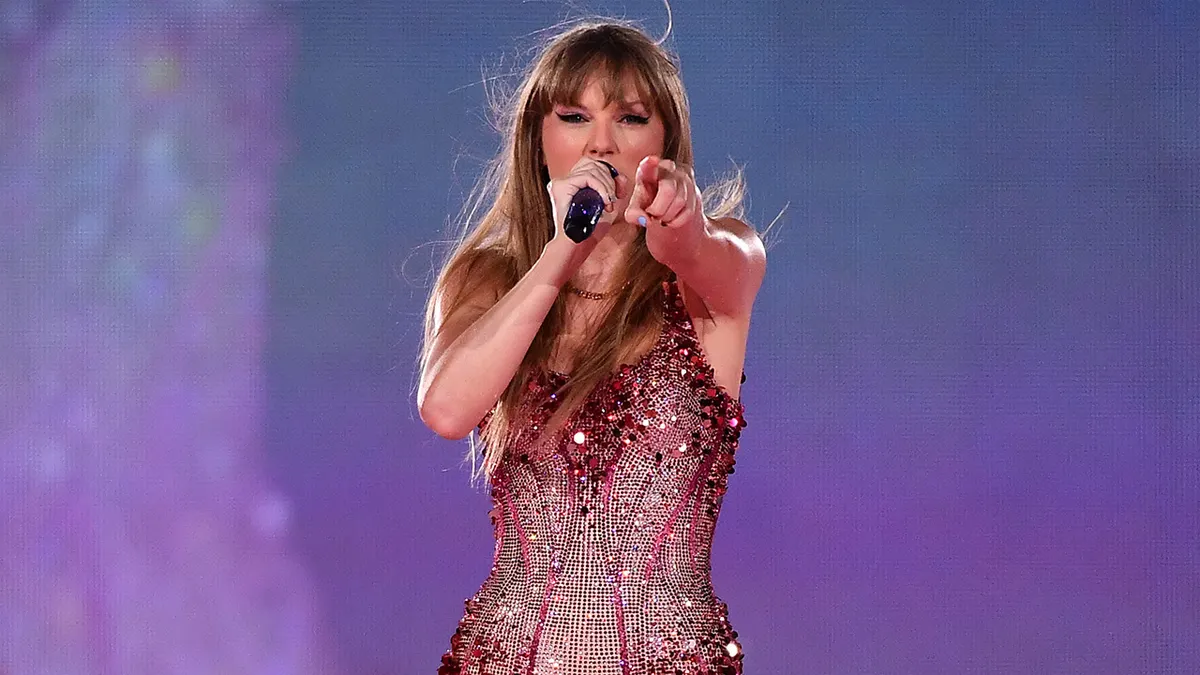

Taylor Swift has announced the accidental swallowing of bugs, mid-concert, on more than one occasion. (Marcelo Endelli/TAS23/Getty Images for TAS Rights Management)
“If you start feeling sick, like abdominal pain, vomiting or nausea, keep an eye on your symptoms,” the doctor said.
If you have severe stomach pain, ongoing vomiting, trouble breathing, or swelling, rash or itching, Dasgupta said to see a doctor.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“If you know the bug could have diseases or if you have health conditions that might complicate things, it’s a good idea to get checked out to be safe,” he added.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews/health
Some bugs — including grasshoppers, beetles, termites, mealworms and even stink bugs — are actually considered edible in certain countries, and are prepared and eaten as part of meals, according to WebMD’s website.
Health
“I’m a Dietitian, and Here’s Why an Overly Restrictive Diet Can Backfire”

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt