Health
Alan Hale Jr: 16 Facts About the Skipper from 'Gilligan's Island'

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.

Health
What Happens If You Eat Eggs Every Day? Nutritionists Share the Benefits

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Ask a doctor: ‘I swallowed a bug — now what should I do?'

Most people have experienced that moment of discomfort when they realize a bug has wound up where it shouldn’t be — in their windpipe.
That includes Taylor Swift, who on more than one occasion has accidentally swallowed a bug while performing on stage in front of thousands of people.
It can be a startling and somewhat disgusting occurrence — but is this dangerous, or just a nuisance?
LOCAL DENGUE FEVER CASES CONFIRMED IN FLORIDA KEYS, SPREAD BY MOSQUITO BITES
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, shared with Fox News Digital the true impacts of accidentally swallowing a bug, and the best thing to do if it happens.
“Swallowing a bug can often happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” Dasgupta, who serves as chief medical advisor for Fortune Recommends, told Fox News Digital via email.
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, discussed the impact of accidentally swallowing a bug — and the best thing to do if it happens. (Sleepoplis)
“It can also happen if you’re talking or laughing outdoors. Sometimes it might even happen indoors if bugs are in your food or drink and you don’t realize it.”
ASK A DOCTOR: ‘HOW CAN I PREVENT SCARRING FROM BUG BITES AND POISON IVY?’
Swallowing a bug is usually not dangerous, Dasgupta noted.
“The stomach’s digestive acids usually break down the bug, and it is passed out of the body without causing harm,” he said.

“Swallowing a bug can happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” the doctor told Fox News Digital. (iStock)
If the bug carries harmful bacteria or parasites, however, it could cause gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions, according to the doctor.
The type of bug can make a difference, he said.
“Bugs like beetles or ants are less of a concern, but bugs that are known to spread diseases — such as mosquitoes — might be riskier.”
If you happen to swallow a bug, drinking some water can help wash it down, Dasgupta said.
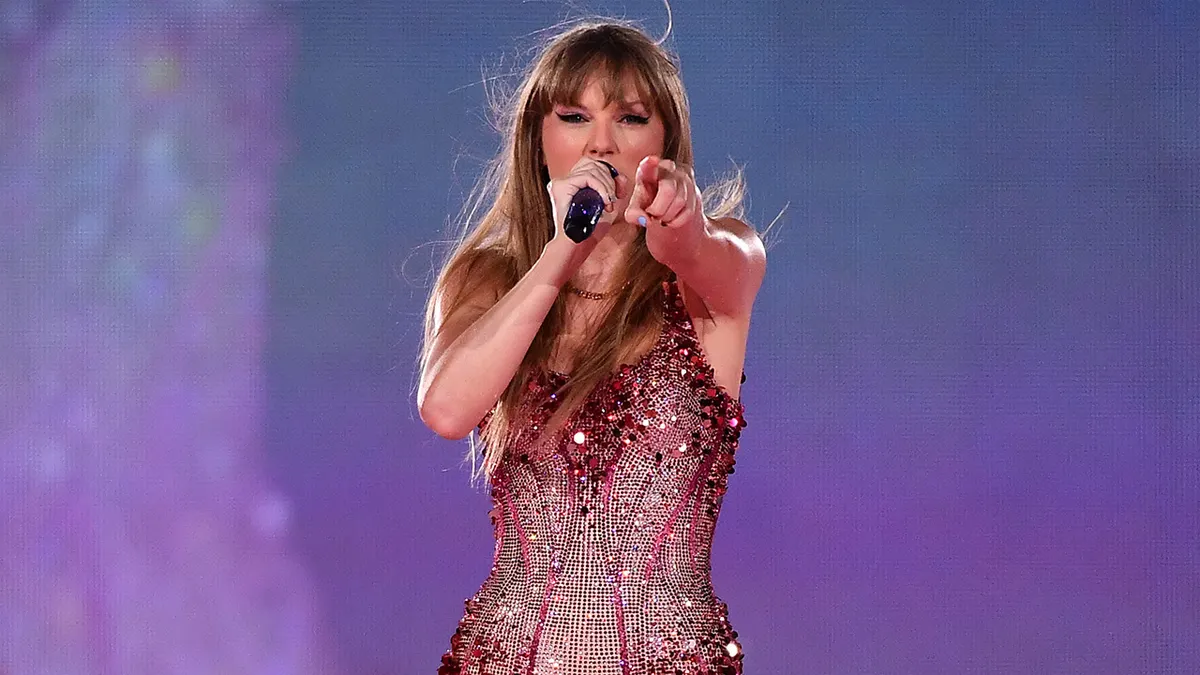

Taylor Swift has announced the accidental swallowing of bugs, mid-concert, on more than one occasion. (Marcelo Endelli/TAS23/Getty Images for TAS Rights Management)
“If you start feeling sick, like abdominal pain, vomiting or nausea, keep an eye on your symptoms,” the doctor said.
If you have severe stomach pain, ongoing vomiting, trouble breathing, or swelling, rash or itching, Dasgupta said to see a doctor.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“If you know the bug could have diseases or if you have health conditions that might complicate things, it’s a good idea to get checked out to be safe,” he added.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews/health
Some bugs — including grasshoppers, beetles, termites, mealworms and even stink bugs — are actually considered edible in certain countries, and are prepared and eaten as part of meals, according to WebMD’s website.
Health
“I’m a Dietitian, and Here’s Why an Overly Restrictive Diet Can Backfire”

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt