Health
8 bad habits that make you age faster, according to experts

We can’t slow down time — but we can slow down its effects on us, according to experts.
The key is to make healthier choices in the areas that we can control — and that starts with breaking bad habits.
“One of the primary hallmarks of aging is accumulated cellular damage that leads to organ dysfunction and, ultimately, death,” Dr. Brett Osborn, a Florida neurologist and longevity expert with Senolytix, told Fox News Digital.
10 TIPS TO LIVE TO BE 100: ‘FAR MORE THAN WISHFUL THINKING,’ SAY LONGEVITY EXPERTS
“The key to staying healthy is minimizing cellular damage by not throwing accelerants into the fire, which is unfortunately what most Americans do.”
Doctors shared with Fox News Digital the eight most common unhealthy behaviors that speed up the aging process — and tips on how to avoid them.
The key is to make healthier choices in the areas that can be controlled — and that starts with breaking bad habits, experts say. (iStock)
1. Smoking
Smoking has been proven to shorten life expectancy.
Researchers from Action on Smoking and Health in the U.K. have reported that a 30-year-old smoker can expect to live for about 35 more years — compared to 53 years for a non-smoker.
“Smoking speeds up aging by exposing you to harmful chemicals, reducing oxygen supply, breaking down collagen and increasing oxidative stress,” Dr. Dawn Ericsson, an obstetrician/gynecologist and medical director at AgeRejuvenation in Tampa, Florida, told Fox News Digital.
SMOKING SHRINKS THE BRAIN AND DRIVES UP ALZHEIMER’S RISK, NEW STUDY FINDS
“The harmful effects of tobacco extend beyond lung health, accelerating skin aging and increasing the risk of gum disease and tooth loss.”
Smoking introduces toxins that impair skin elasticity and collagen production, which leads to wrinkles, Osborn added.

“The harmful effects of tobacco extend beyond lung health, accelerating skin aging and increasing the risk of gum disease and tooth loss,” an expert said. (iStock)
“Free radicals in smoke damage lung tissue – inducing cancer – and the walls of your blood vessels,” he told Fox News Digital.
“The incidence of heart attack, stroke and brain aneurysms is significantly higher in smokers relative to nonsmokers.”
The quickest fix is to quit smoking immediately, the experts agreed.
“The incidence of heart attack, stroke and brain aneurysms is significantly higher in smokers relative to nonsmokers.”
To increase the chance of success in quitting, Ericsson suggested setting a “quit date,” avoiding triggers and seeking support from friends, family and health care providers.
Some also get results with nicotine replacement therapy or medications like bupropion and varenicline, she said.
2. Excess sun exposure
An excess of sun exposure can lead to aging by damaging the skin’s DNA, causing wrinkles, sagging skin and dark spots, Ericsson noted.
Osborn agreed, also warning of an increased risk of skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma and melanoma, the latter of which can be fatal.

An excess of sun exposure can lead to aging by damaging the skin’s DNA, causing wrinkles, sagging skin and dark spots, a doctor said. (iStock)
“Regularly using sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing and avoiding sun exposure during peak hours can protect the skin,” Osborn advised.
CATCH SKIN CANCER WARNING SIGNS EARLY WITH REGULAR SELF-EXAMS
Other protective strategies include covering up with hats, sunglasses and protective clothing, and seeking shade during the sun’s strongest hours (between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.), according to Ericsson.
Staying hydrated and using antioxidants like vitamins C and E can also help protect the skin.
3. Poor diet
A nutrient-deficient diet has been shown to accelerate aging, experts agree.
“A diet high in processed foods, sugars and unhealthy fats can cause inflammation, damage collagen and accelerate skin aging,” Ericsson warned.
Diets high in processed foods and sugars can cause inflammation and free radical damage, Osborn added.

A nutrient-deficient diet has been shown to accelerate aging, experts agree. (iStock)
“The induced insulin-resistant or pre-diabetic state places you one step closer to the dreaded ‘metabolic syndrome’ — a gateway to diseases such as coronary artery disease, cancer and Alzheimer’s disease,” he told Fox News Digital.
To reduce aging signs, the experts recommend eating a balanced diet rich in low-glycemic index fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and anti-inflammatory fats (omega-3 and omega-9).
THESE 10 NUTRITION MISTAKES COULD BE TAKING YEARS OFF YOUR LIFE: HERE’S WHAT TO DO INSTEAD
“Antioxidants in these foods combat free radical damage, as do antioxidant supplements like vitamin C, green tea and omega-3 fatty acids,” said Osborn.
Other tips include pre-planning meals and snacks — with a focus on focusing on whole, unprocessed foods — to avoid impulsive unhealthy choices, according to Ericsson.
Cooking at home, controlling portions and staying hydrated are also good ways to improve nutrition intake, she added.
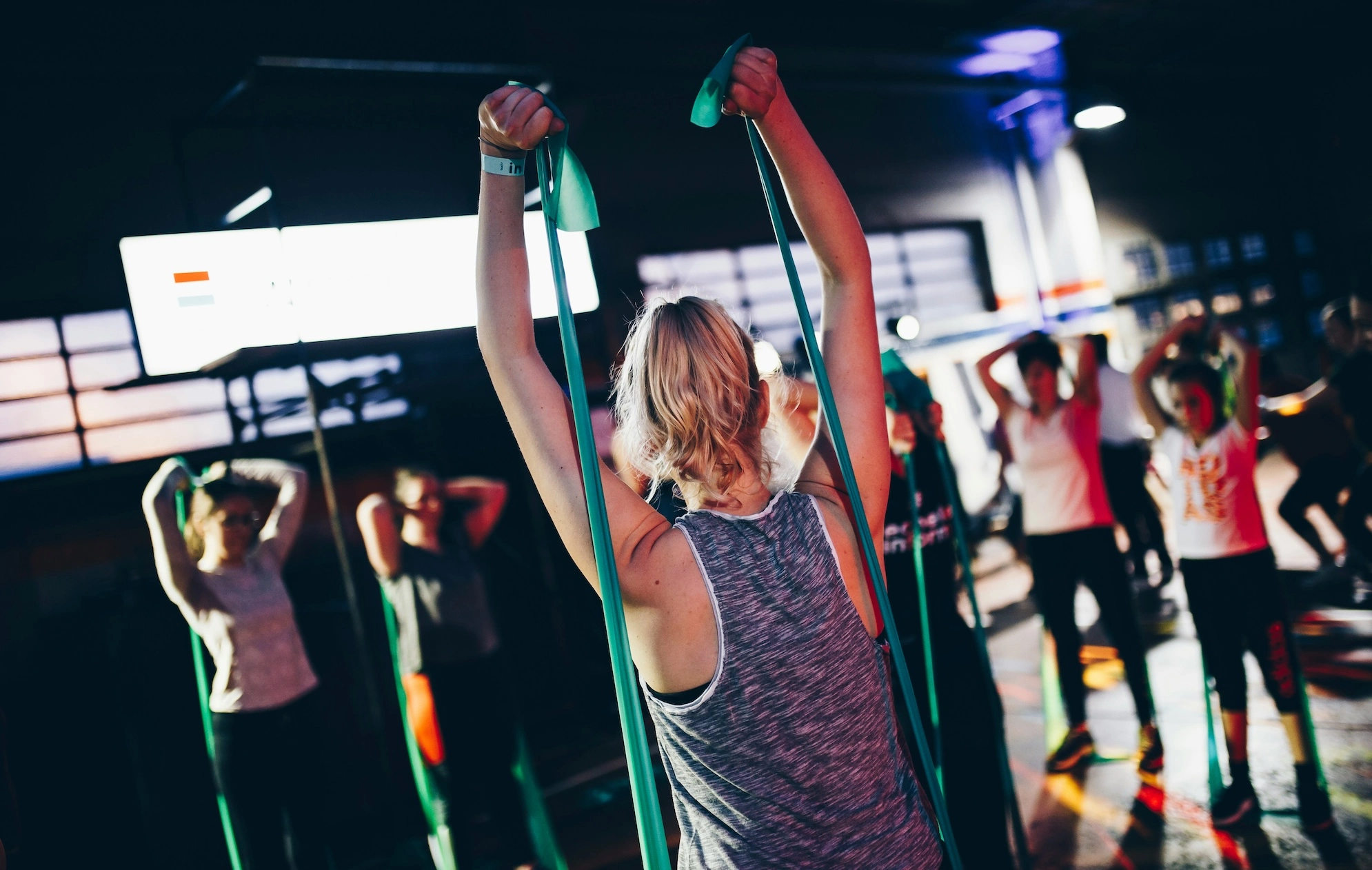
4. Lack of exercise
“Lack of exercise contributes to aging by causing muscle loss, bone density reduction, weight gain and cardiovascular issues,” Ericsson told Fox News Digital.
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining muscle mass, circulation and cognitive health as we age, she advised.
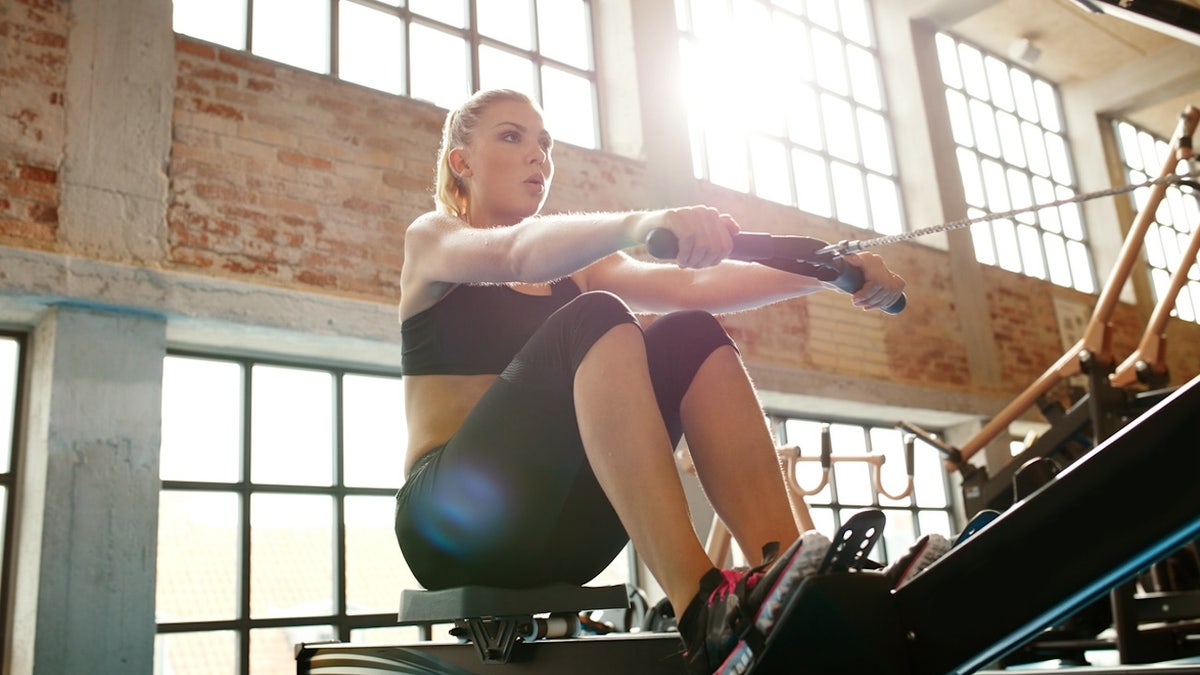

Regular physical activity, particularly strength training, is foundational to health and longevity, doctors agree. (iStock)
Osborn is also an advocate of staying active, noting that “our bodies are meant to exercise.”
“Our bodies are meant to exercise. It benefits the body and the mind.”
“Exercise turns over 100 genes associated with longevity, so don’t skip it! It benefits the body and the mind.”
Regular physical activity, particularly strength training, is foundational to your health, according to Osborn.
“This means you must lift weights and breathe hard during your workouts,” he said.
WOMEN GET MORE BENEFIT FROM EXERCISE THAN MEN, STUDY FINDS: ‘MORE TO GAIN’
On “off days,” Osborn suggests doing 45 minutes of lighter endurance training, like walking, rowing, swimming or jogging, which will improve your cardiovascular fitness while allowing you to recover from heavy bouts of strength training.
To sustain a long-term exercise routine, it’s important to find activities you consistently enjoy, set realistic goals, stay flexible and “listen to your body,” said Ericsson.
5. Excessive alcohol consumption
Alcohol dehydrates the skin and can lead to liver damage and cognitive impairment, Osborn warned.
“It also causes problems with blood sugar regulation and is intimately associated with obesity,” he said. “As alcohol is a cellular toxin, it accelerates the aging process.”
Ericsson agreed that excessive alcohol consumption accelerates aging by causing dehydration, nutrient depletion, inflammation, liver damage and collagen breakdown.
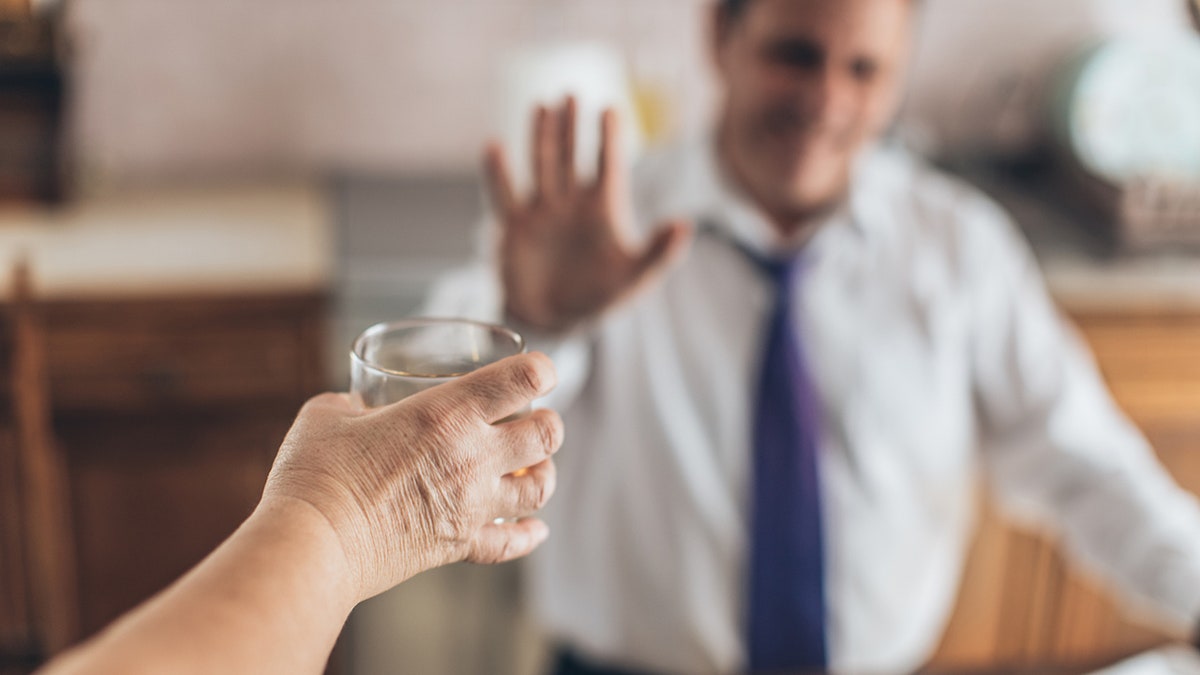

“Aim to eliminate habitual drinking within the next 6-12 months,” a longevity expert advised. “You’ll feel better and save a lot of money in the long run.” (iStock)
“Chronic drinking can dehydrate the skin, damage the liver and increase the risk of cognitive decline,” said Ericsson.
As with smoking, the fix is to eliminate alcohol consumption, experts agreed.
DRINKING A LITTLE ALCOHOL EVERY DAY WON’T HELP YOU LIVE LONGER, SAYS NEW STUDY
“I’m not saying to quit cold turkey, but aim to eliminate habitual drinking within the next six to 12 months,” Osborn advised. “You’ll feel better and save a lot of money in the long run.”
Other tips to stop drinking include avoiding triggers, staying busy with healthy activities and seeking professional help if needed, according to Ericsson.
6. Chronic stress
While some degree of stress is normal and healthy, chronic high stress levels can shorten telomeres, which are DNA protein structures that “play a central role in cell fate and aging by adjusting the cellular response to stress and growth stimulation on the basis of previous cell divisions and DNA damage,” according to the National Institutes of Health.
“Chronic stress can also exacerbate skin conditions and impact mental health, accelerating aging,” Ericsson added.
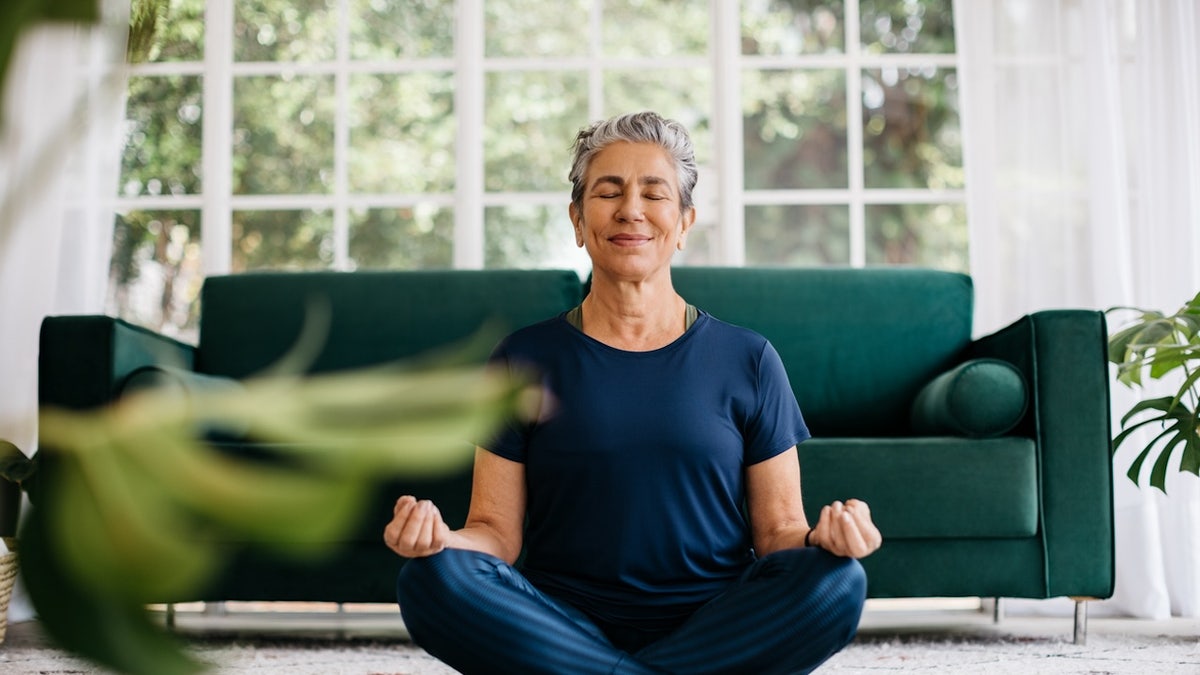

Stress management techniques like mindfulness, meditation, therapy and regular physical activity can alleviate stress, according to experts. (iStock)
Long-term stress affects the body’s ability to repair itself and can lead to premature aging, according to Osborn.
“Aging is a state of heightened inflammation — and once the body’s ability to temper inflammation via cortisol production has been exhausted, it reigns unchecked,” he said.
ALWAYS FEELING TIRED? EXPERTS SHARE 4 COMMON CAUSES OF DAYTIME FATIGUE
Stress management techniques like mindfulness, meditation, therapy and regular physical activity can alleviate stress, Osborn said.
“Strength training also reduces cortisol production (several hours post-workout) — and, by virtue, facilitates sleep, which is critical to stress reduction.”
7. Inadequate sleep
Lack of sleep accelerates aging by reducing skin health, increasing inflammation and causing hormonal imbalance, Ericsson noted.
“Inadequate sleep also hampers cell repair and affects cognitive function,” she said.
Sleep is crucial for the body’s regenerative processes, Osborn noted.
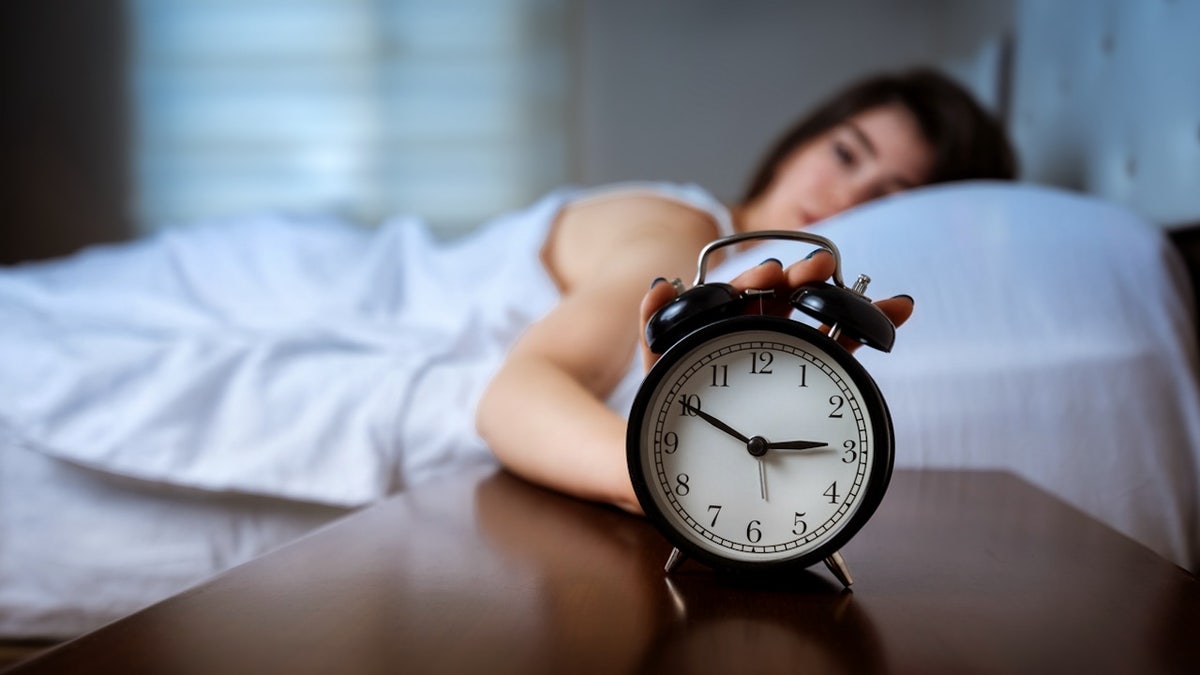

Lack of sleep accelerates aging by reducing skin health, increasing inflammation and causing hormonal imbalance, according to a doctor. (iStock)
“If you don’t sleep, you’ll have difficulty shedding that spare tire, as significant fat-burning occurs during sleep,” he said.
“You’ll also set yourself up for neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s.”
Memories are also formed during sleep, he noted.
LACK OF SLEEP COULD BE A FACTOR IN A ‘SILENT EPIDEMIC,’ EXPERTS WARN
“Sleep cannot be hacked — it is an essential part of health and well-being.”
To optimize sleep health, Osborn suggested establishing a regular schedule, creating a restful environment and avoiding stimulants before bedtime.
“Also, minimizing consumption of carbohydrates within several hours of bedtime can facilitate sleep induction,” he said.
“Sleep cannot be hacked — it is an essential part of health and well-being.”
“In a similar context, ditch the cell phone, laptop and tablet as early as possible to minimize blue light’s interference with the production of melatonin, the body’s sleep hormone.”
Manage stress and seek professional help if needed, Ericsson added.
8. Poor oral hygiene
Poor oral hygiene accelerates aging by causing gum disease, tooth loss, stained teeth and bad breath, Ericsson warned.
“Gum disease and tooth loss not only affect oral health, but also impact overall well-being, contributing to an aged appearance,” she added.
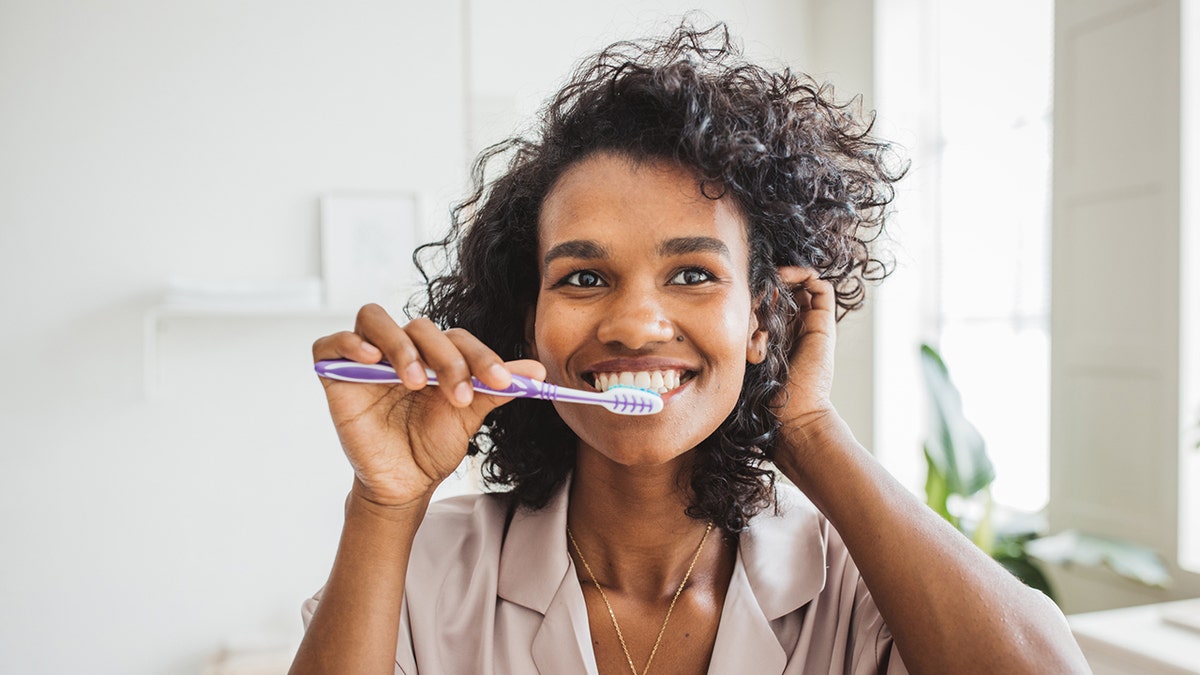

Optimal oral hygiene requires regular dental check-ups, proper brushing and flossing, and use of an antimicrobial mouthwash. (iStock)
There is also a link between heart disease risk and the incidence of coronary artery disease and gingivitis, Osborn noted.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“Inflammation is not only occurring in the mouth — it’s a systemic problem,” he said. “So, if there is a state of accelerated aging in the mouth, you better believe it’s elsewhere, let alone your entire gut.”
Optimal oral hygiene requires regular dental check-ups, proper brushing and flossing, and use of an antimicrobial mouthwash, Osborn said.
Limiting sugary and acidic foods, avoiding tobacco products, staying hydrated and chewing sugar-free gum after meals can also help with mouth health, Ericsson added.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews/health.

Health
What Happens If You Eat Eggs Every Day? Nutritionists Share the Benefits

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Ask a doctor: ‘I swallowed a bug — now what should I do?'
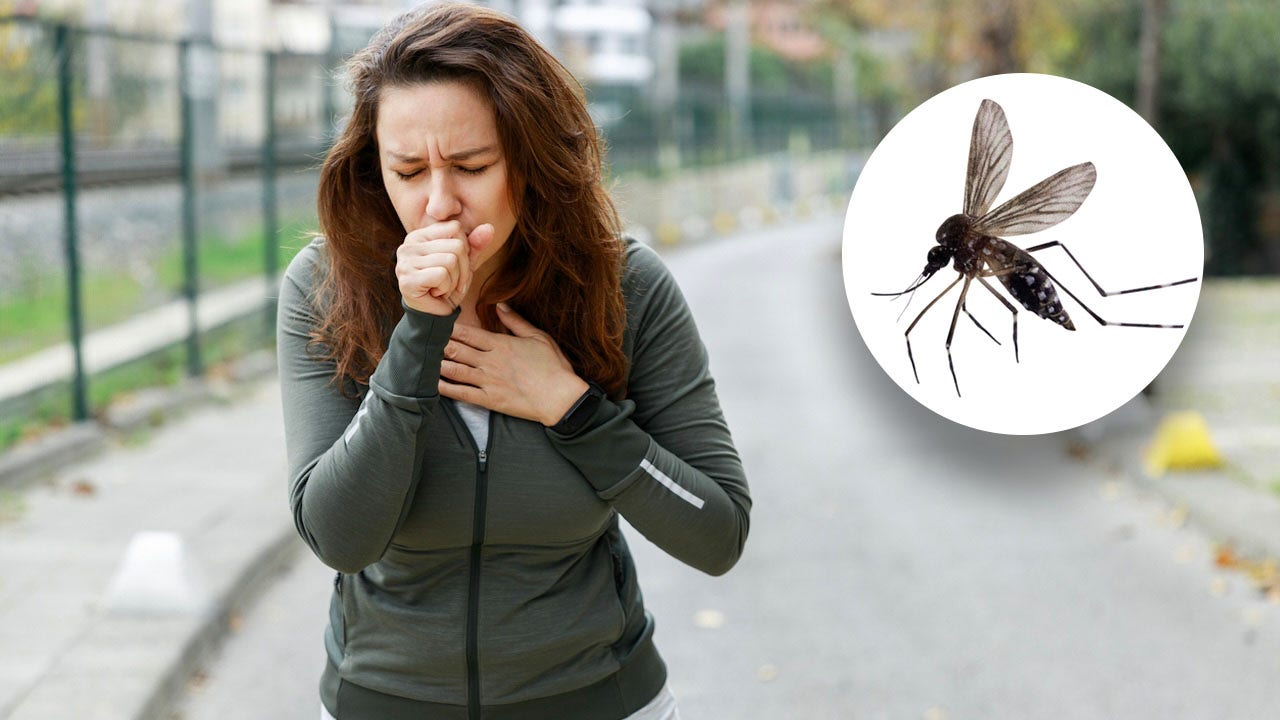

Most people have experienced that moment of discomfort when they realize a bug has wound up where it shouldn’t be — in their windpipe.
That includes Taylor Swift, who on more than one occasion has accidentally swallowed a bug while performing on stage in front of thousands of people.
It can be a startling and somewhat disgusting occurrence — but is this dangerous, or just a nuisance?
LOCAL DENGUE FEVER CASES CONFIRMED IN FLORIDA KEYS, SPREAD BY MOSQUITO BITES
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, shared with Fox News Digital the true impacts of accidentally swallowing a bug, and the best thing to do if it happens.
“Swallowing a bug can often happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” Dasgupta, who serves as chief medical advisor for Fortune Recommends, told Fox News Digital via email.
Dr. Raj Dasgupta, a quadruple board-certified physician in California, discussed the impact of accidentally swallowing a bug — and the best thing to do if it happens. (Sleepoplis)
“It can also happen if you’re talking or laughing outdoors. Sometimes it might even happen indoors if bugs are in your food or drink and you don’t realize it.”
ASK A DOCTOR: ‘HOW CAN I PREVENT SCARRING FROM BUG BITES AND POISON IVY?’
Swallowing a bug is usually not dangerous, Dasgupta noted.
“The stomach’s digestive acids usually break down the bug, and it is passed out of the body without causing harm,” he said.
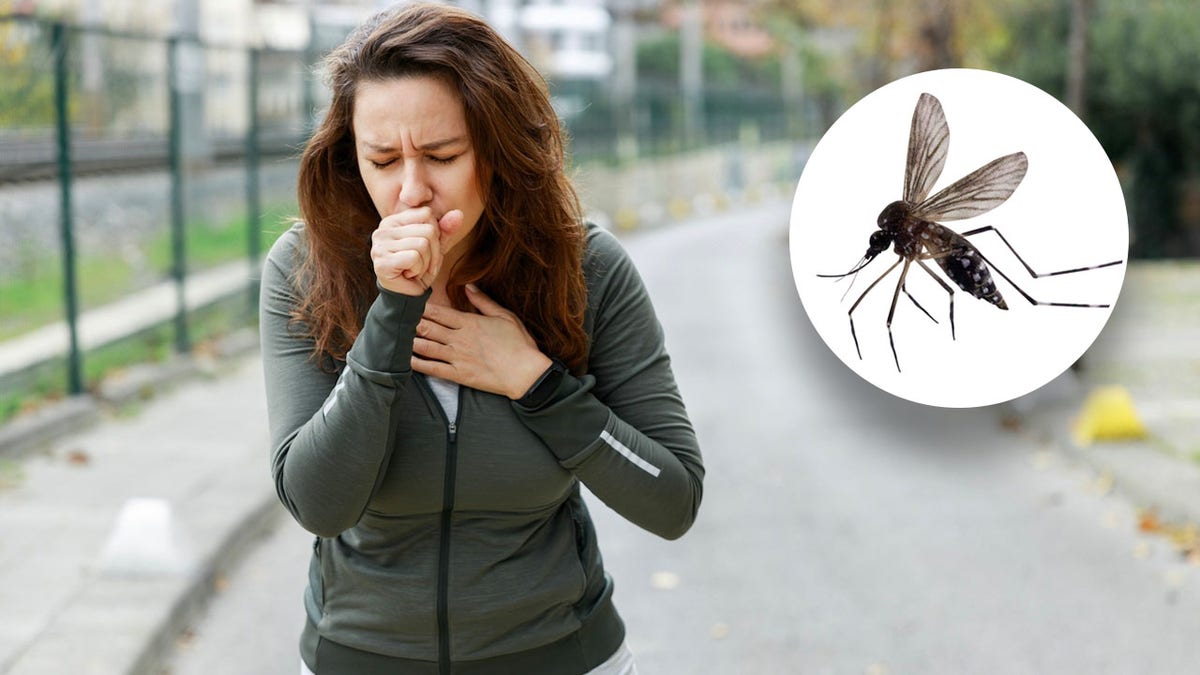

“Swallowing a bug can happen accidentally when you’re eating or drinking outside, or if a bug flies into your mouth,” the doctor told Fox News Digital. (iStock)
If the bug carries harmful bacteria or parasites, however, it could cause gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions, according to the doctor.
The type of bug can make a difference, he said.
“Bugs like beetles or ants are less of a concern, but bugs that are known to spread diseases — such as mosquitoes — might be riskier.”
If you happen to swallow a bug, drinking some water can help wash it down, Dasgupta said.
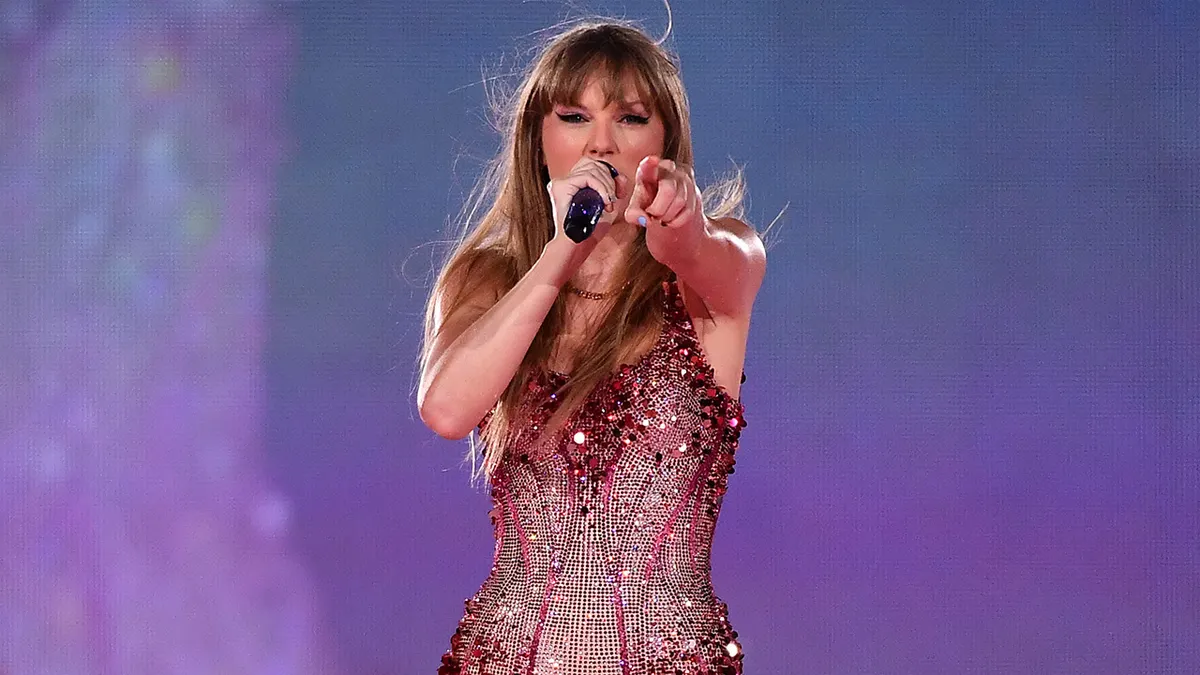

Taylor Swift has announced the accidental swallowing of bugs, mid-concert, on more than one occasion. (Marcelo Endelli/TAS23/Getty Images for TAS Rights Management)
“If you start feeling sick, like abdominal pain, vomiting or nausea, keep an eye on your symptoms,” the doctor said.
If you have severe stomach pain, ongoing vomiting, trouble breathing, or swelling, rash or itching, Dasgupta said to see a doctor.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“If you know the bug could have diseases or if you have health conditions that might complicate things, it’s a good idea to get checked out to be safe,” he added.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews/health
Some bugs — including grasshoppers, beetles, termites, mealworms and even stink bugs — are actually considered edible in certain countries, and are prepared and eaten as part of meals, according to WebMD’s website.
Health
“I’m a Dietitian, and Here’s Why an Overly Restrictive Diet Can Backfire”

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt